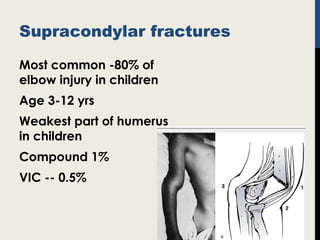
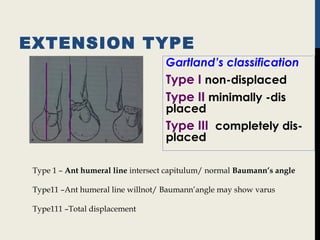
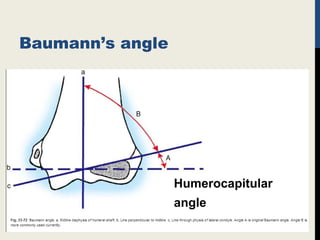
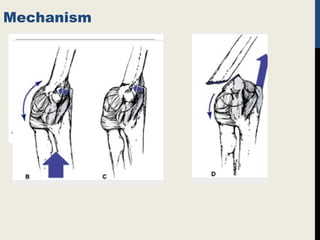
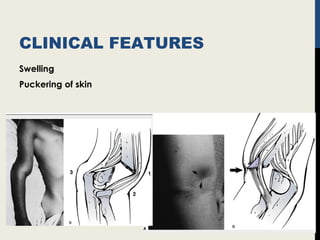
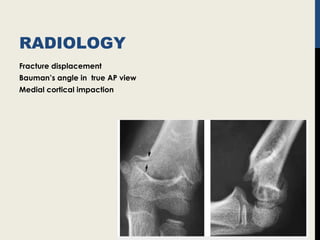
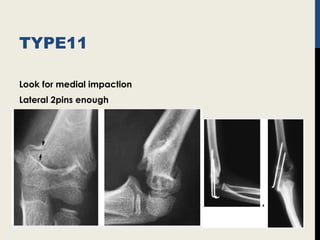
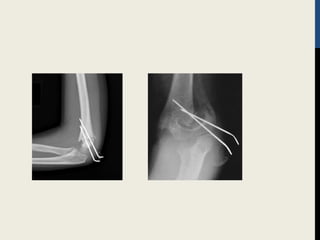
Supracondylar fractures of the humerus are the most common elbow injuries in children aged 3-12 years. They occur just above the elbow joint where the humerus is weakest. Extension-type fractures account for 95% of cases. Treatment depends on the degree of displacement classified using Gartland's system. Non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures are treated with splinting while displaced fractures may require closed or open reduction with pinning. Complications can include nerve palsies, vascular injuries, compartment syndrome and malunion leading to cubitus varus deformity sometimes requiring corrective osteotomy.



![Pin configuration
[lateral]
Parallel pins
Crossed pins
Medial pin transcapitular
Instability – 3rd
pin
Newton’s study
AO recommendation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17supracondylar-161002110237/85/supra-condylar-fracture-humerus-13-320.jpg)




![VASCULAR INJURY
Brachial artery injury / vascular
insufficiency
Assess by color, warmth, capillary refill
Angiogram ? NO
Need emergency reduction and pinning
Pulse is absent 12-15% but vascular repair is needed only in
1-2% [Rockwood and Green]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17supracondylar-161002110237/85/supra-condylar-fracture-humerus-19-320.jpg)




![AETIOLOGY
Malunion on s.c.fx coronal angulation aggravated
by malrotation and hyper extension --- static deformity
Growth disturbance 20% of growth
[5yr old 1 yr growth is 2mm]
Avascular necrosis of trochlea rare cause
CMR &LA POP Cubitus varus --50% of cases.
CMR and closed pinning -- 6.6%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17supracondylar-161002110237/85/supra-condylar-fracture-humerus-24-320.jpg)










