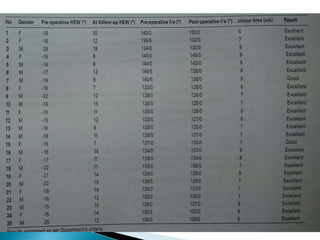
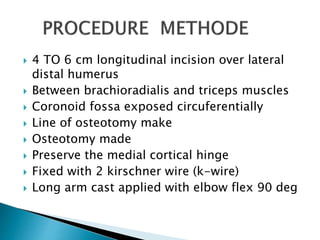
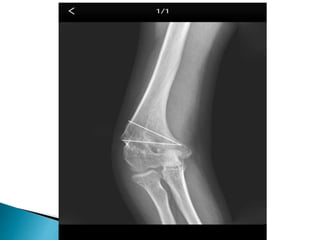
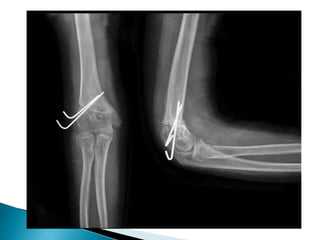
Dr. Sandeep Tripathi presented a new technique for correcting cubitus varus, or gunstock deformity of the elbow, using a lateral closing wedge isosceles triangular osteotomy. The technique was performed on 25 patients aged 6-12 with cubitus varus secondary to malunion of a supracondylar fracture. A lateral incision was made, the osteotomy performed, and fixed with K-wires. Most patients had excellent results with a mean carrying angle of 11.7 degrees. Complications included minor infection and scarring, with one revision for displacement. The author concluded the technique is practical, effective, and reliable for correcting cubitus varus.