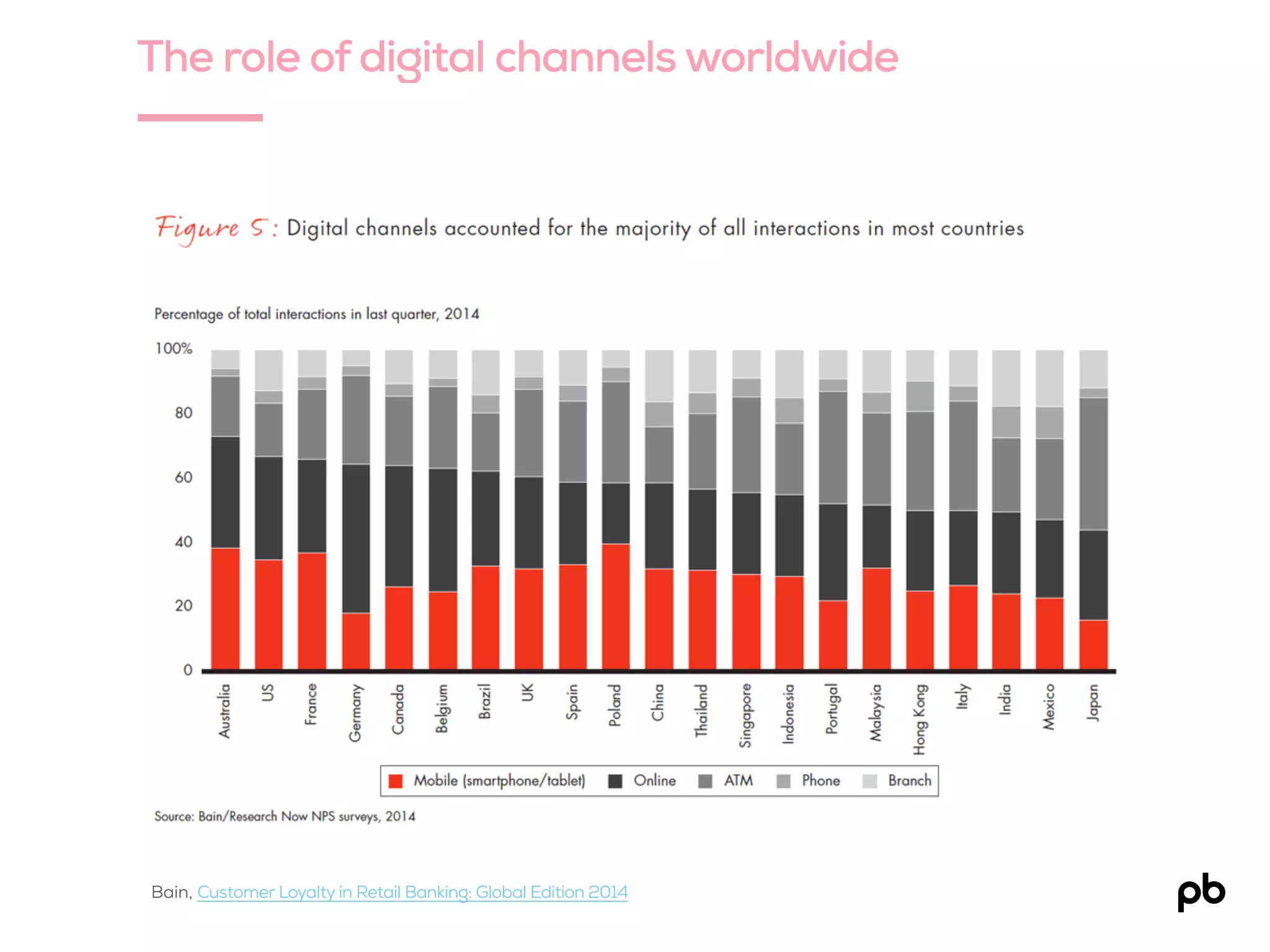
Pieter Baert's keynote on design thinking emphasizes its importance in the financial industry, highlighting a user-centered approach to problem solving that involves empathy and creativity. Key aspects of design thinking include being hands-on, iterative, and applicable to 'wicked' problems where both the problem and solution are unclear. The process, which involves empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing, aims to innovate and improve customer experience amidst challenges faced by financial institutions.