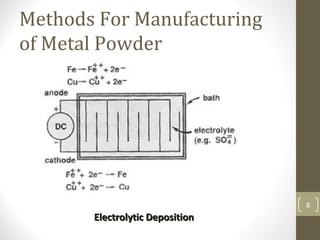
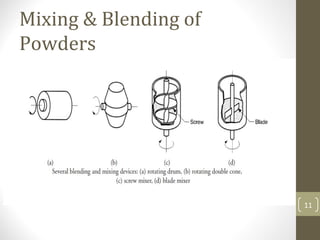
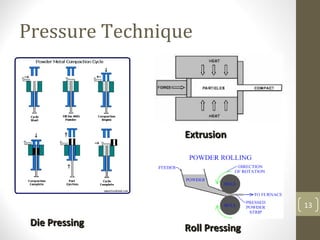
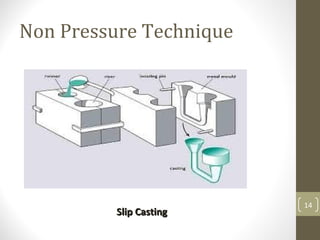
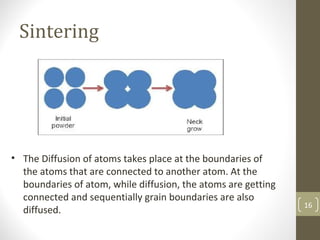
The document outlines the basic processes of powder metallurgy, which include powder manufacture, mixing, compacting, and sintering. It describes various methods for producing metal powder such as mechanical processes, atomization, electrochemical deposition, and reduction techniques. The final steps involve compacting the powder into a 'green compact' and sintering it to achieve the desired strength and properties.