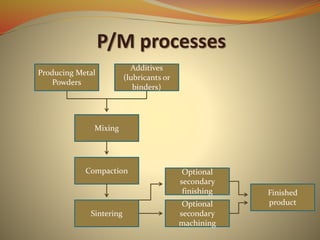
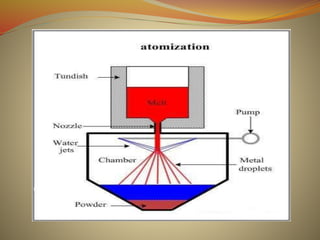
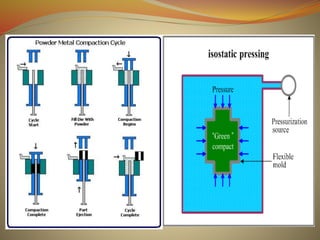
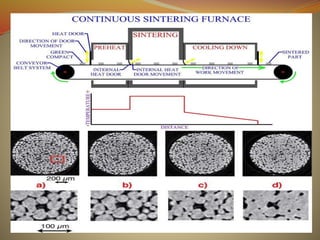
Powder metallurgy is a process that involves producing metal powders, mixing them with additives, compacting them into a desired shape, and then sintering the compact to fuse the particles together. Metal powders are commonly produced via atomization, which involves breaking liquid metal into fine droplets. The powders are then mixed with lubricants or binders before being compacted under high pressure. The compacted "green" part is then sintered at a temperature below melting to bond the particles and increase strength without melting. Final products may require additional machining. Powder metallurgy allows for complex shapes and compositions with reduced machining compared to other metalworking methods.