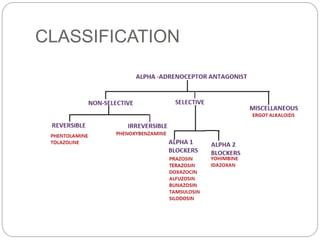
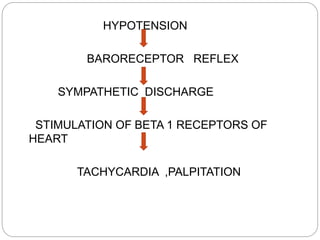
This document discusses different types of alpha adrenergic blockers, including their classification, mechanisms of action, effects, uses, and examples. It covers reversible nonselective alpha blockers like phentolamine and tolazoline, irreversible nonselective blockers like phenoxybenzamine, and reversible selective alpha-1 blockers like prazosin. These drugs cause vasodilation and reduce blood pressure by blocking alpha receptors. They are used to treat conditions like hypertension, Raynaud's disease, prostate issues, and pheochromocytoma. The document also briefly mentions alpha-2 blockers, ergot alkaloids, and other miscellaneous agents that have alpha blocking properties.