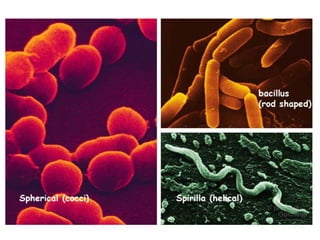
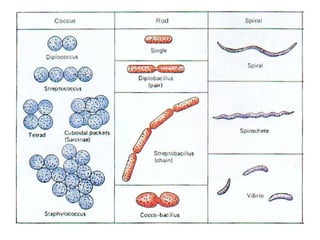
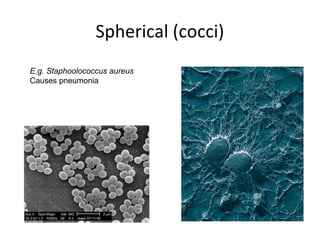
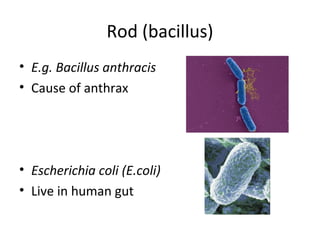
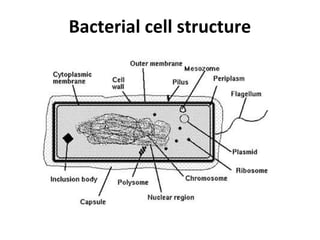
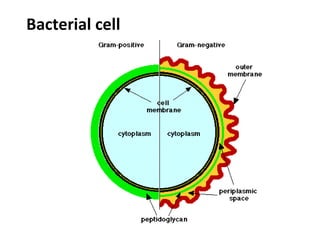
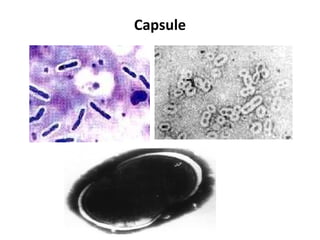
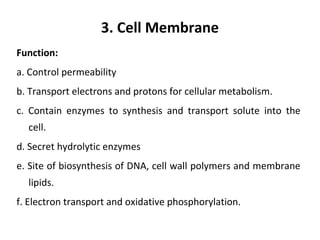
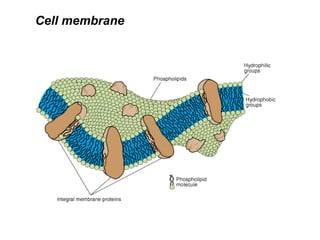
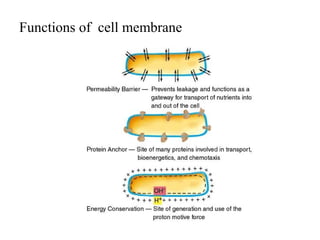
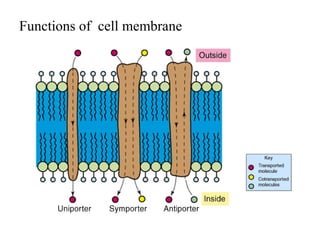
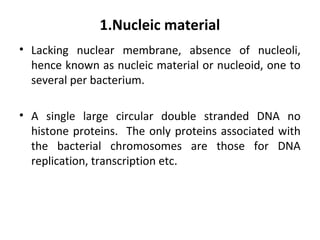
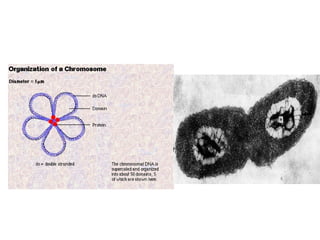
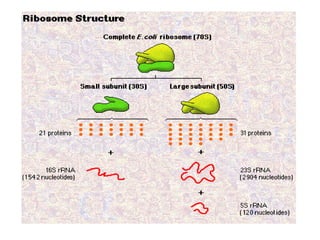
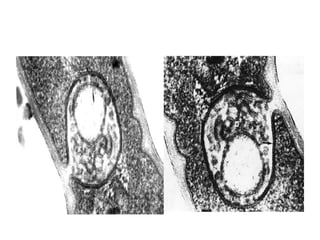
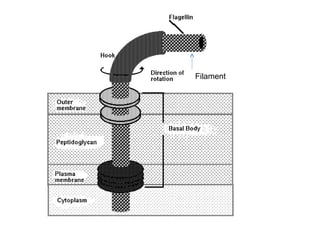
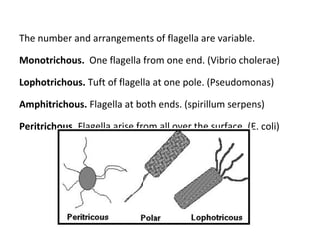
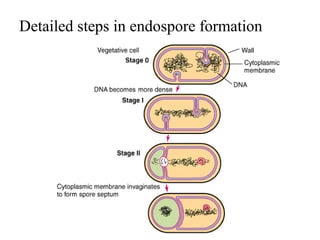
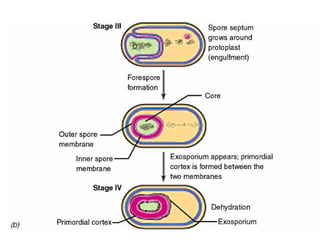
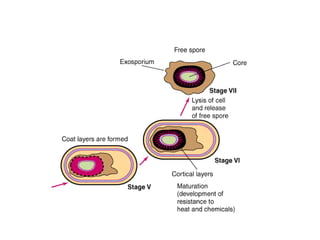
Bacteria are classified according to their shape into three main categories: spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacillus), and spiral (spirillum). Their cell structure includes a capsule, cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm containing nuclear material and ribosomes, and sometimes appendages like flagella or pili. Some bacteria form dormant endospores to survive harsh conditions, which have a highly resistant structure including a core, cortex, coat, and sometimes exosporium.