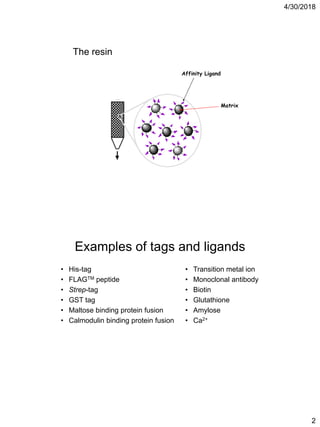
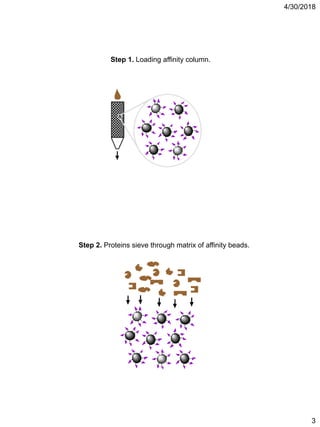
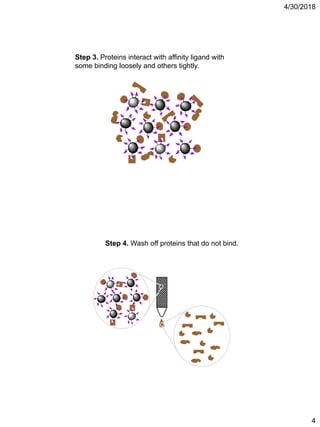
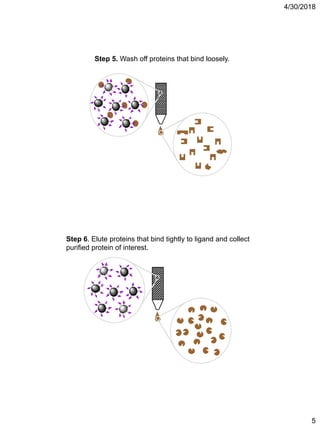
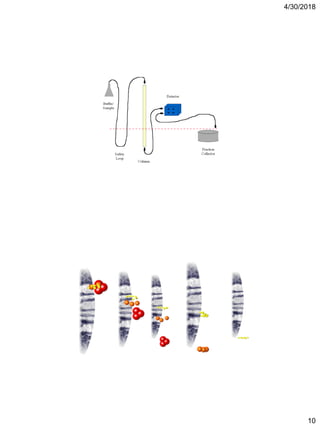
Affinity chromatography is a technique that uses the specific binding properties of a molecule to purify it from a mixed sample. The process involves passing a sample over a column containing beads with affinity ligands attached. Proteins in the sample either bind tightly, bind loosely, or do not bind to the ligands on the beads. Multiple wash steps are used to remove non-binding and loosely binding proteins, leaving only the tightly bound protein of interest, which can then be eluted and collected in a purified form.