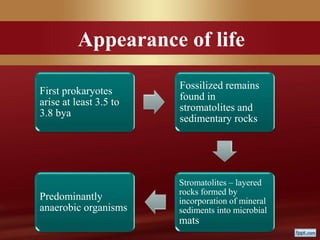
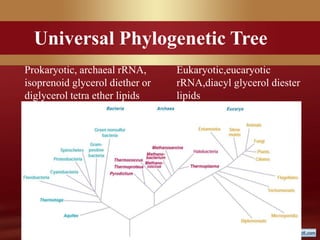
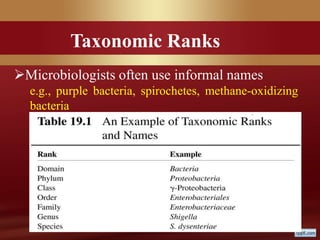
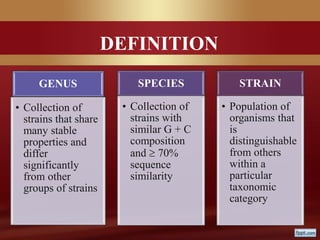
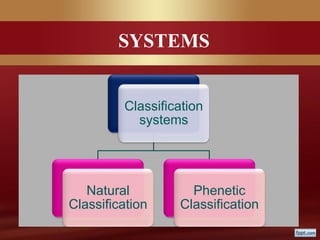
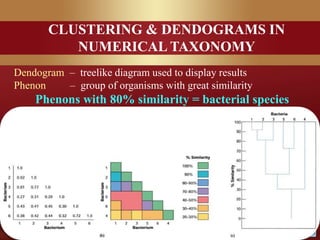
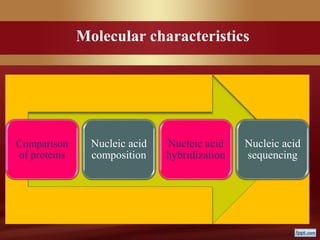
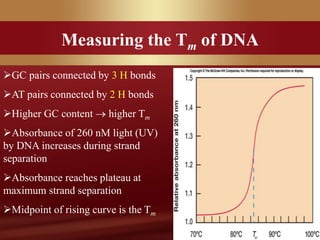
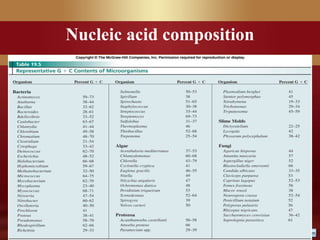
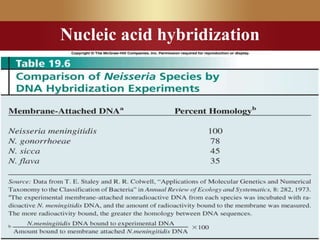
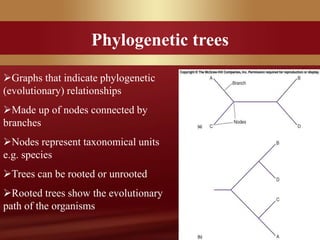
This document provides an overview of microbial taxonomy. It discusses the key components of taxonomy including classification, nomenclature, and identification. Classification involves arranging organisms into meaningful groups. Nomenclature assigns names to these taxonomic groups. Identification determines which taxon a new isolate belongs to. The document also covers evolutionary relationships between prokaryotes and eukaryotes as well as classical and molecular characteristics used in taxonomy.