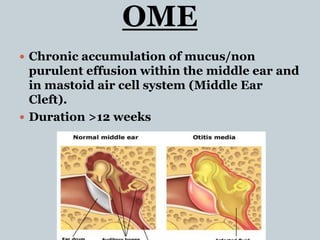
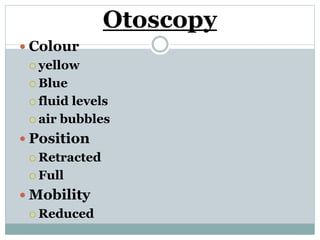
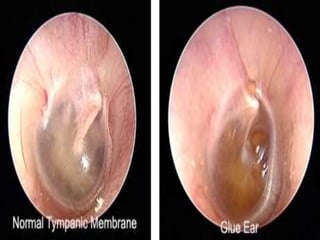
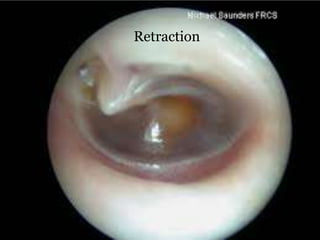
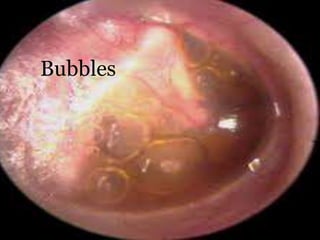
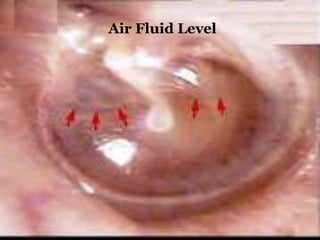
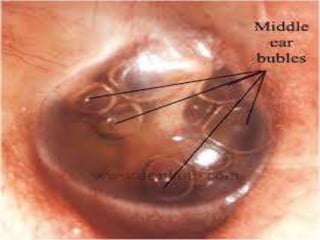
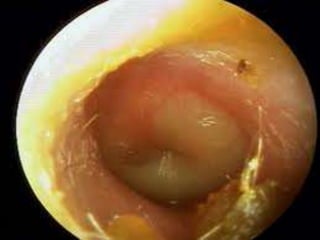
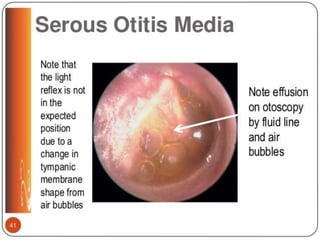
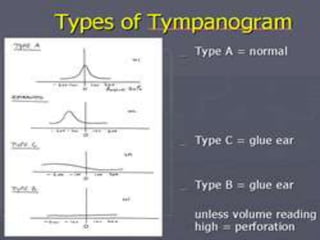
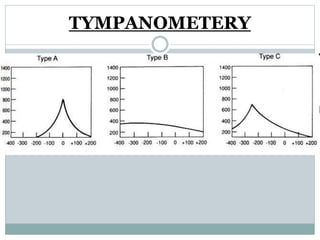
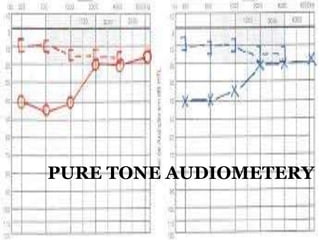
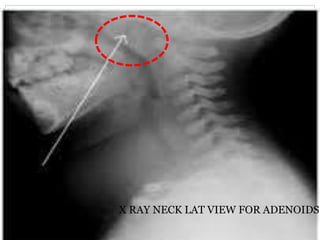
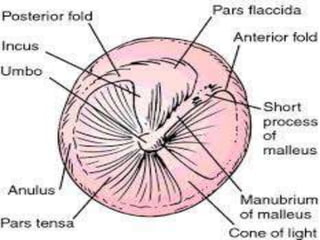
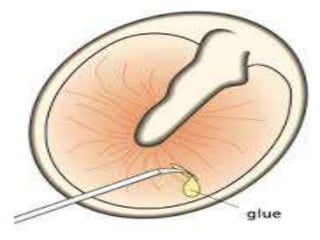
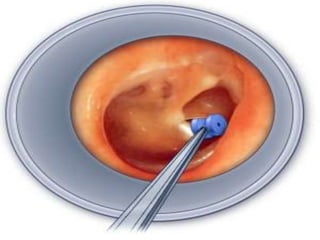
This document provides information about otitis media with effusion (OME), also known as glue ear. It defines OME as a chronic accumulation of mucus or non-purulent effusion in the middle ear cavity lasting more than 12 weeks. The document discusses the etiology, symptoms, examination findings, and treatment options for OME. Treatment may involve watchful waiting, medical management using decongestants or mucolytics, or surgical insertion of ventilation tubes to drain the middle ear.