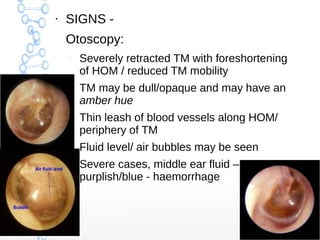
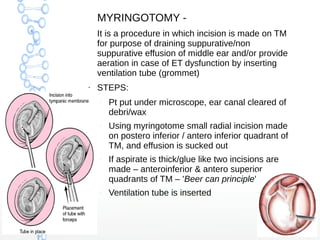
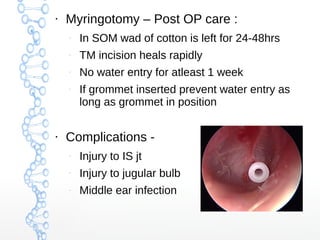
Secretory otitis media (SOM), also known as serous otitis media or glue ear, is a non-purulent inflammation of the middle ear caused by an accumulation of fluid. It most commonly affects school-aged children between 3-8 years old. The pathogenesis involves malfunction of the Eustachian tube, which fails to ventilate and drain the middle ear, as well as increased secretory activity of the middle ear mucosa. Symptoms include hearing loss, delayed speech development, and mild ear aches. Treatment involves medical management with decongestants and antibiotics or surgical procedures like myringotomy with ventilation tube insertion to drain the fluid. Complications can include atelectasis, oss