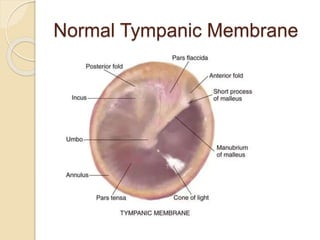
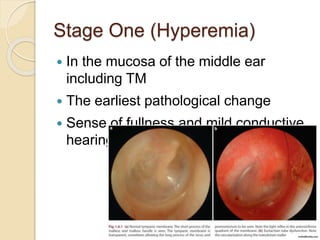
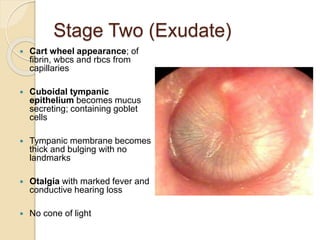
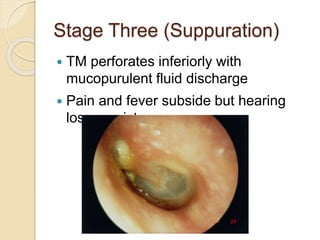
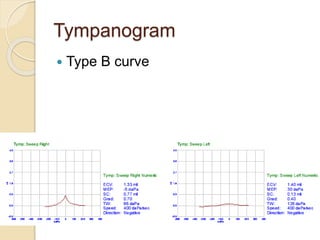
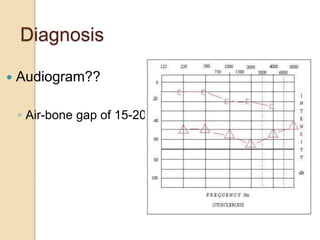
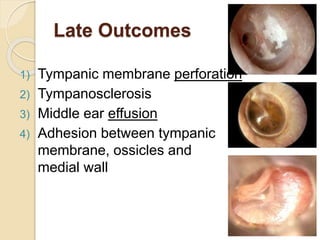
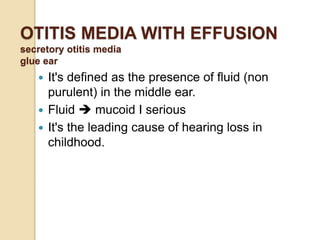
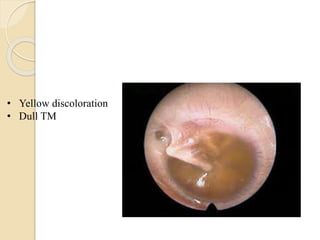
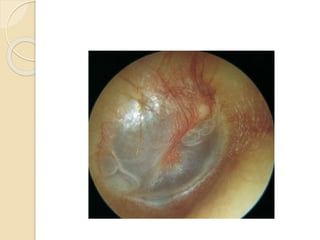
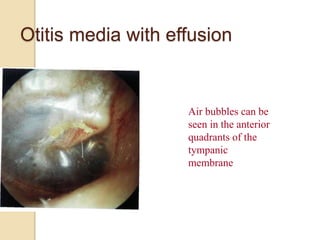
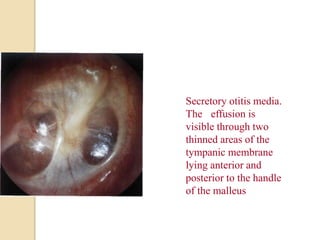
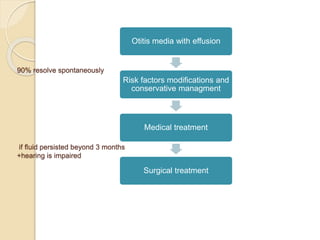
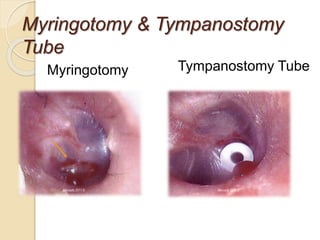
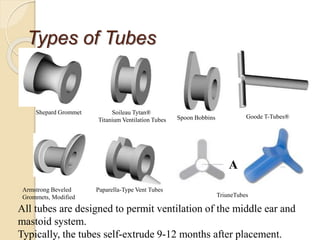
Acute otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear that typically occurs in young children between the ages of 3-7. It is usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection spreading from the nose and throat to the middle ear space. Symptoms include fever, ear pain, and hearing loss. It progresses through four stages from hyperemia to resolution. Diagnosis is made based on symptoms and examination of the eardrum. Treatment involves antibiotics which are most effective in the early stages. Otitis media with effusion involves non-purulent fluid in the middle ear causing hearing loss. It may develop after acute otitis media or due to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Treatment includes conservative measures, antibiotics