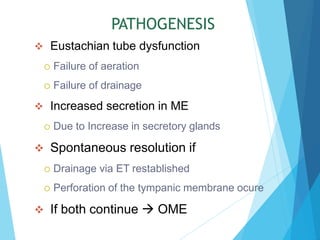
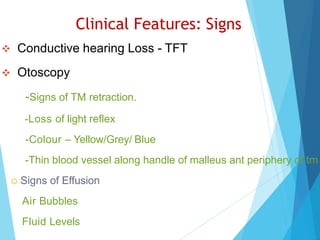
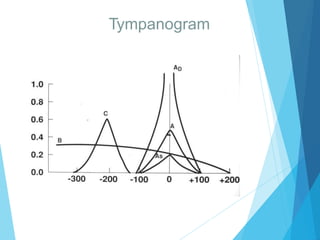
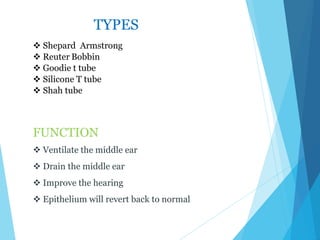
This document discusses serous otitis media (SOM), also known as glue ear. SOM is a chronic accumulation of non-purulent fluid in the middle ear cavity behind an intact eardrum. It most commonly affects young children and can cause conductive hearing loss. The causes include Eustachian tube dysfunction from infections, allergies, or obstructions. Treatment involves medical management with decongestants, antihistamines, or antibiotics. Surgical interventions like myringotomy with ventilation tube insertion may be used to drain fluid and improve hearing if medical therapy fails. Complications can include persistent ear infections, perforation of the eardrum, or retraction pockets in severe cases.