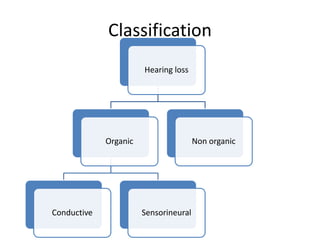
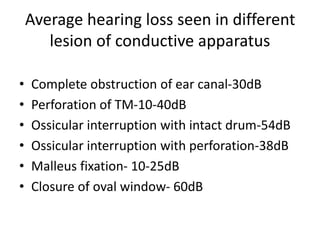
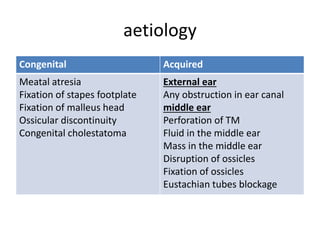
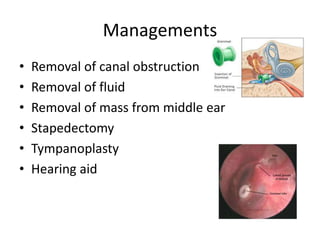
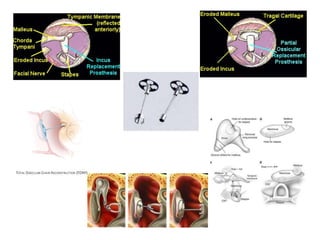
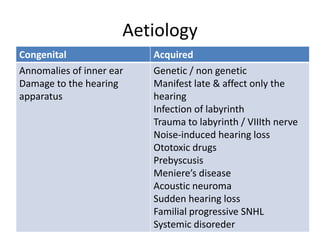
Hearing loss can be classified as conductive, sensorineural, or mixed. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not properly conducted from the outer ear to the inner ear. Common causes include earwax buildup, fluid in the middle ear, or problems with the ossicles. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. Common causes include noise exposure, certain medications, aging, and genetic factors. Treatment depends on the type and cause of hearing loss but may include surgery, hearing aids, or treating any underlying medical conditions. Hearing loss can significantly impact quality of life but early diagnosis and management can help address the condition.