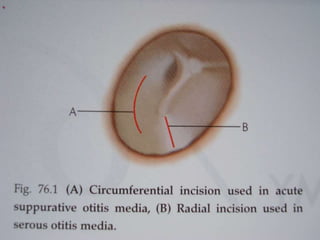
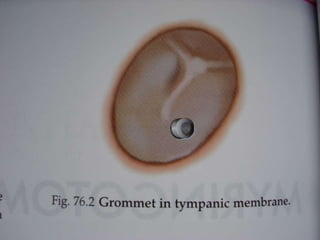
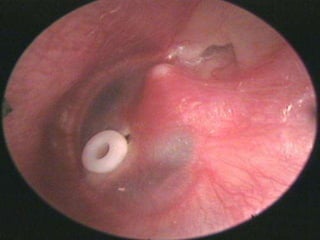
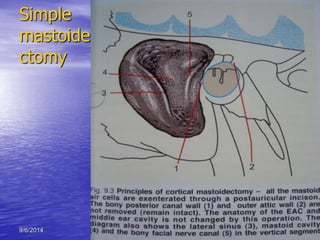
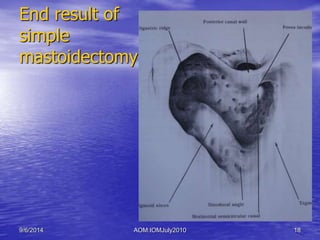
Acute otitis media (AOM) is an inflammation of the middle ear cleft mucosa that is classified as either acute (lasting up to 3 weeks), subacute (3 weeks to 3 months), or chronic (over 3 months). AOM is commonly caused by viruses that lead to upper respiratory tract infections in children ages 3 to 7. It is characterized by symptoms like earache, fever, and hearing loss. Diagnosis involves examining the red and bulging tympanic membrane. Treatment primarily involves antibiotics, analgesics, and ear drops if perforation is present. Surgery is rarely needed and includes procedures like myringotomy or mastoidectomy for complications or treatment failures.