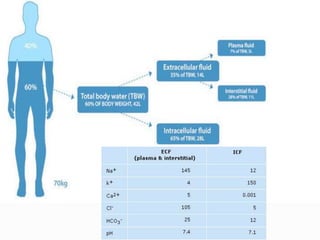
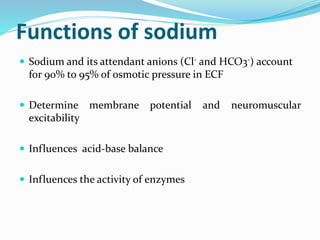
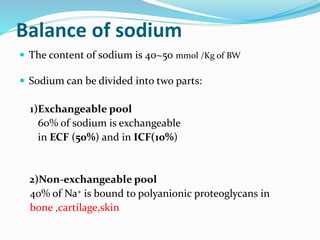
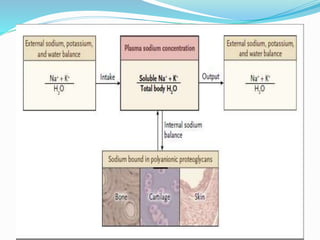
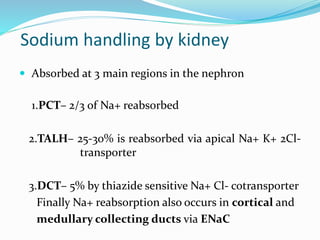
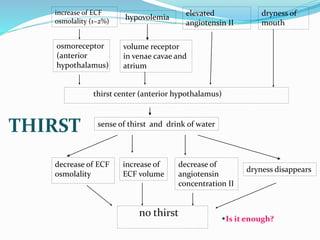
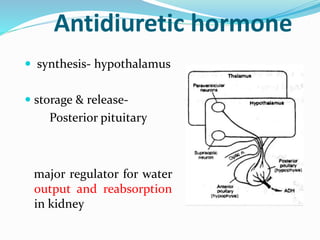
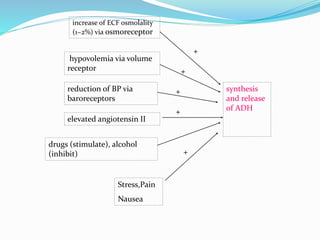
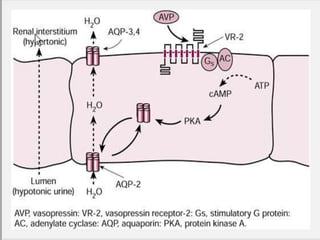
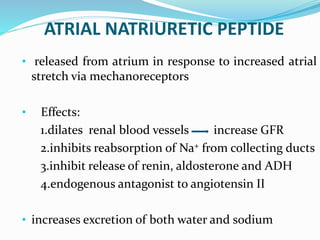
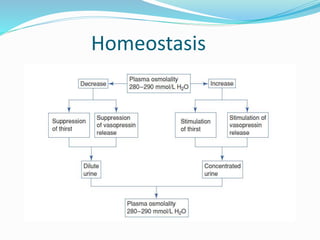
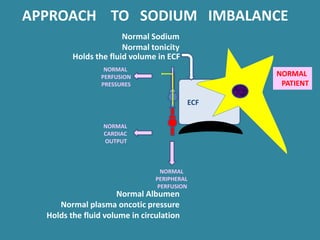
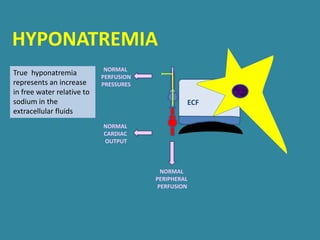
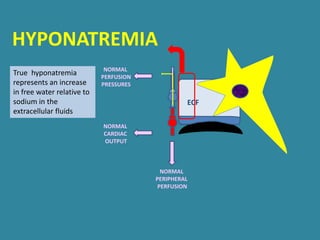
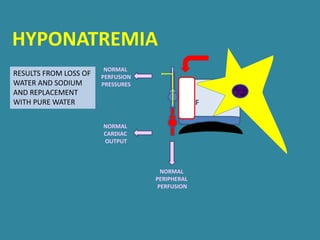
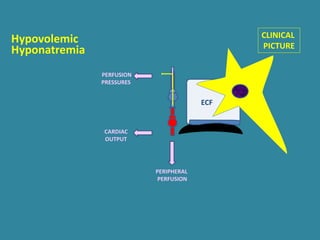
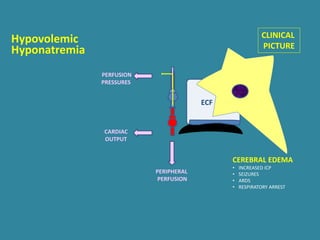
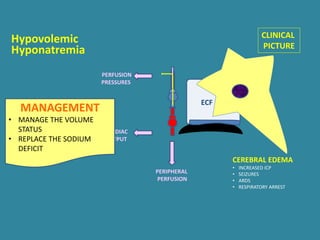
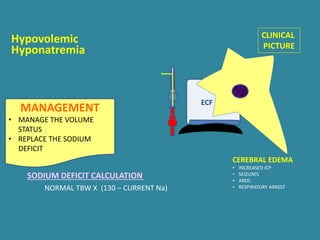
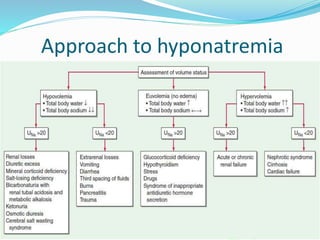
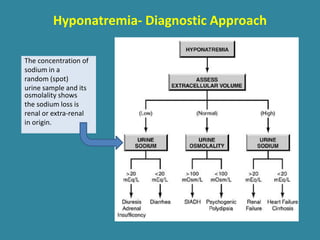
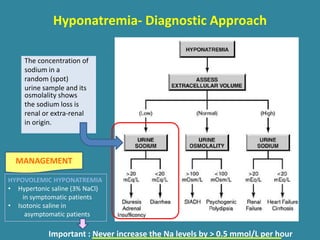
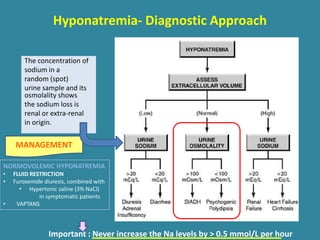
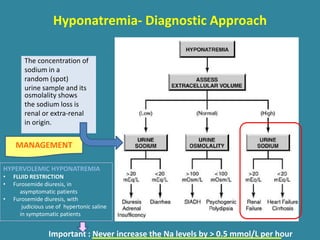
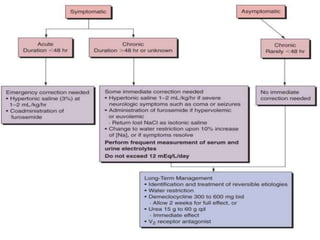
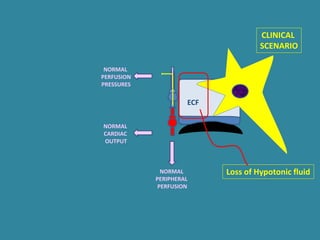
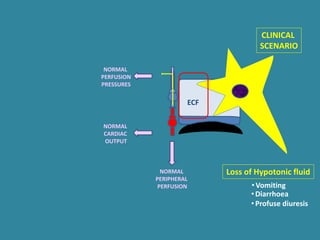
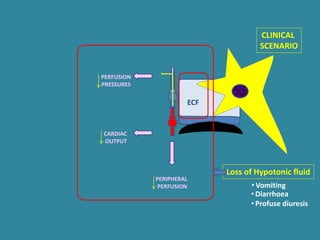
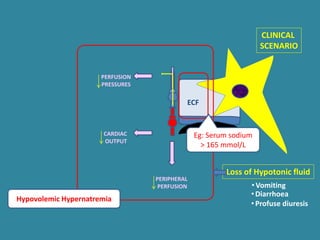
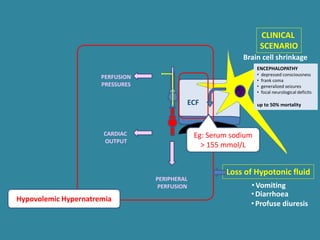
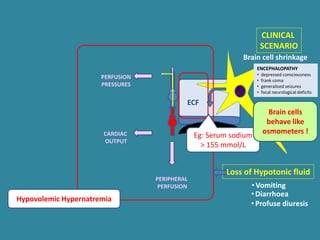
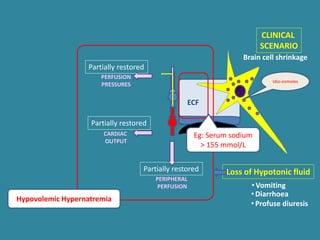
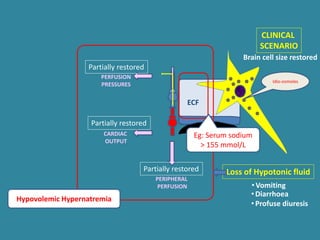
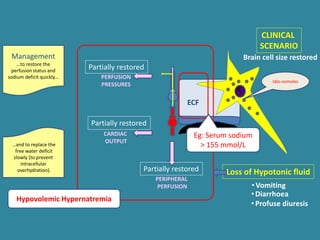
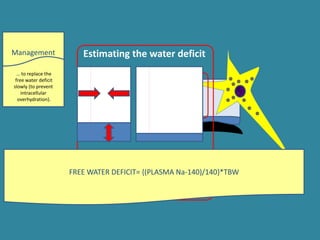
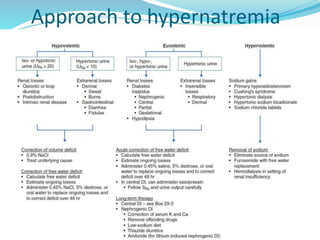
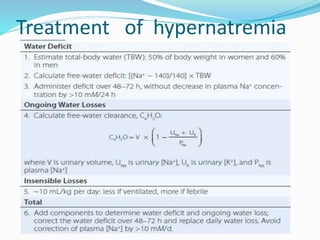
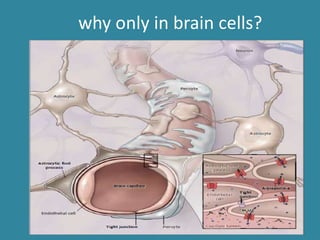
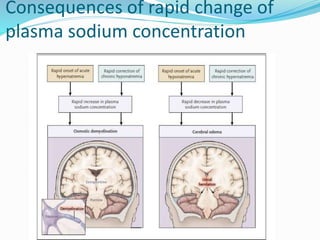
This document discusses sodium metabolism and disorders of sodium balance. It begins by outlining the normal functions of sodium in the body, including determining membrane potential and acid-base balance. It then describes normal sodium metabolism, handling, and regulation by factors like the kidneys, aldosterone, and antidiuretic hormone. The document also summarizes approaches to diagnosing and managing sodium imbalances like hyponatremia and hypernatremia. It stresses the importance of first assessing a patient's volume status and correcting deficits or excesses slowly to avoid complications in conditions like cerebral edema or encephalopathy.