This document discusses the different types of communication in organizations, including:
1) Formal and informal communication channels. Formal communication follows the chain of command while informal "grapevine" communication occurs between individuals.
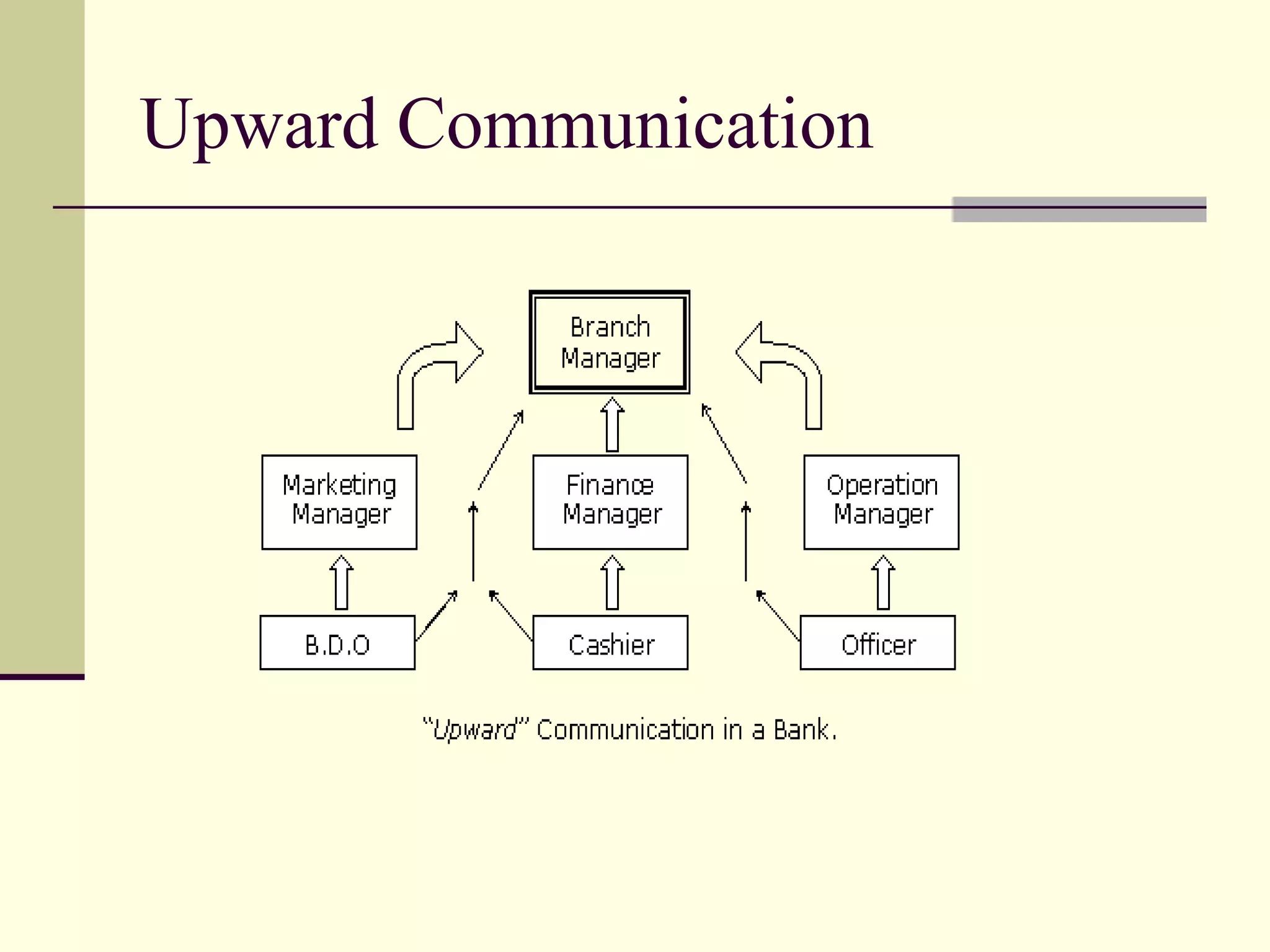
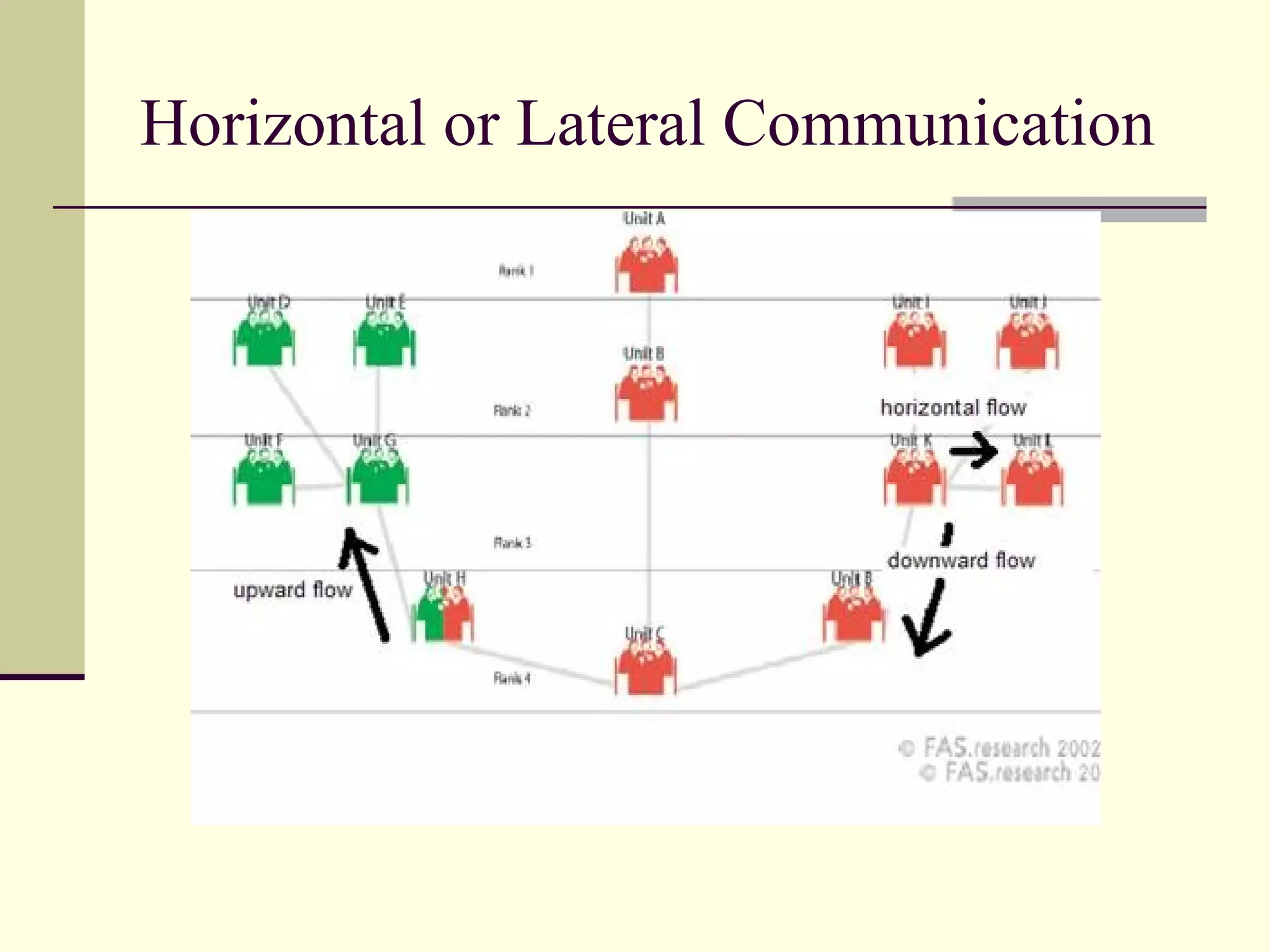
2) The direction of communication flow, including downward from superiors to subordinates, upward from subordinates to superiors, horizontal between peers, and diagonal across functions.
3) The methods of communicating, either orally, in writing, or through gestures. Both formal and informal communication channels have their advantages and disadvantages for information sharing in organizations.