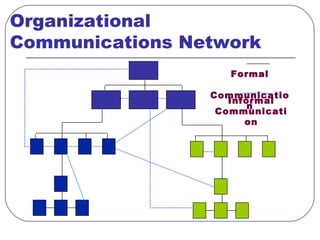
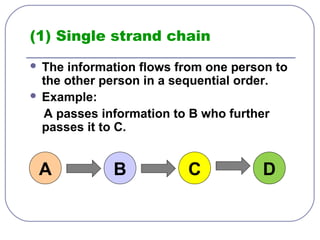
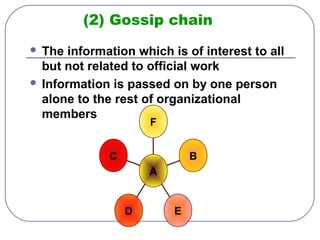
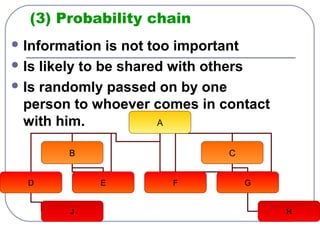
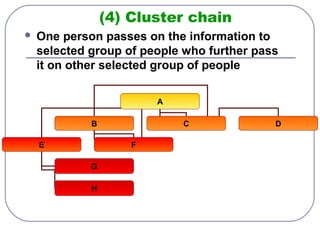
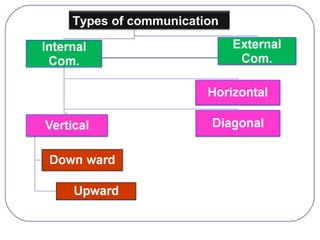
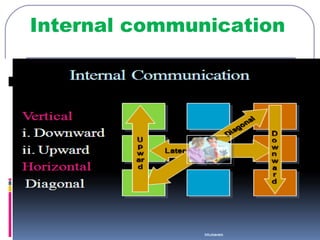
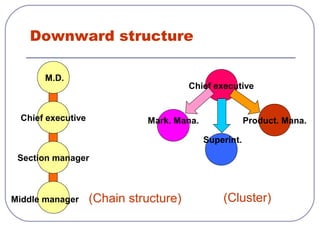
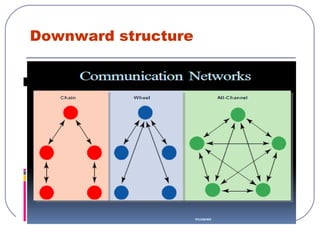
This document discusses formal and informal channels of communication within organizations. It defines formal communication as controlled, top-down communication through official reports and records. Informal communication refers to unofficial grapevine networks that spread information between employees. While formal channels ensure effective information flow, they can be slow and expensive. Informal channels are faster but information may be inaccurate. The document also examines downward, upward, horizontal, and diagonal types of internal communication within an organizational structure.