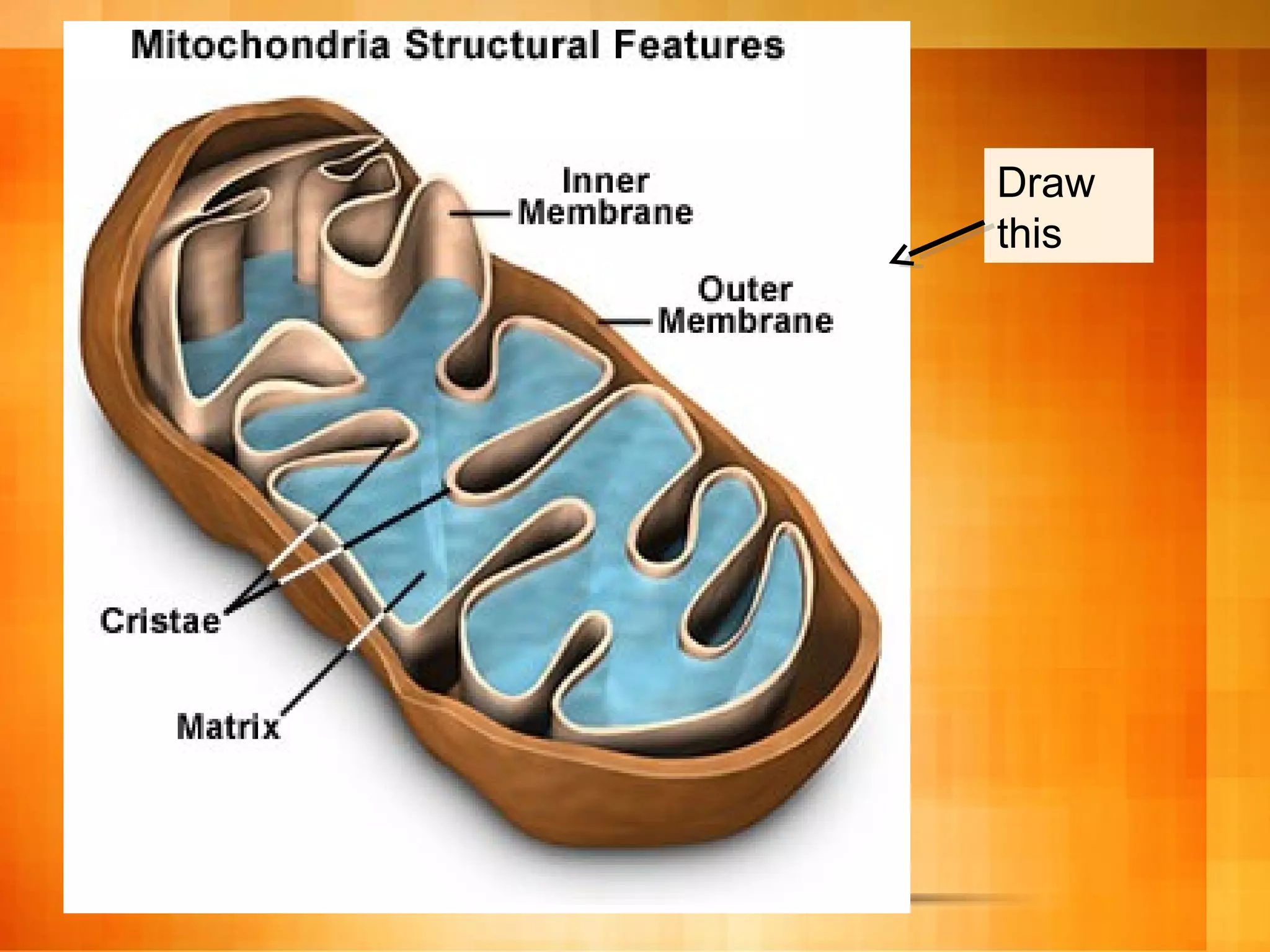
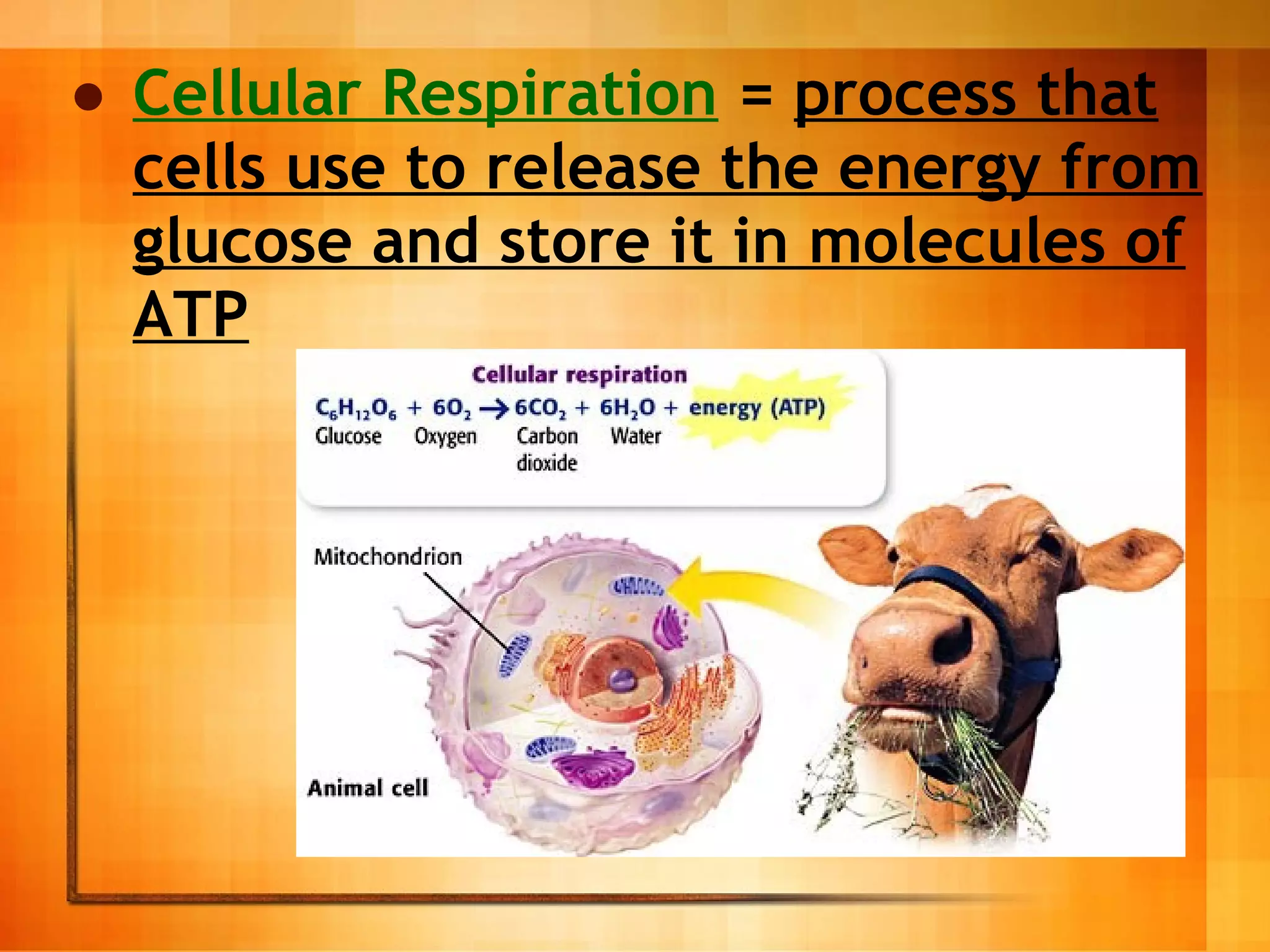
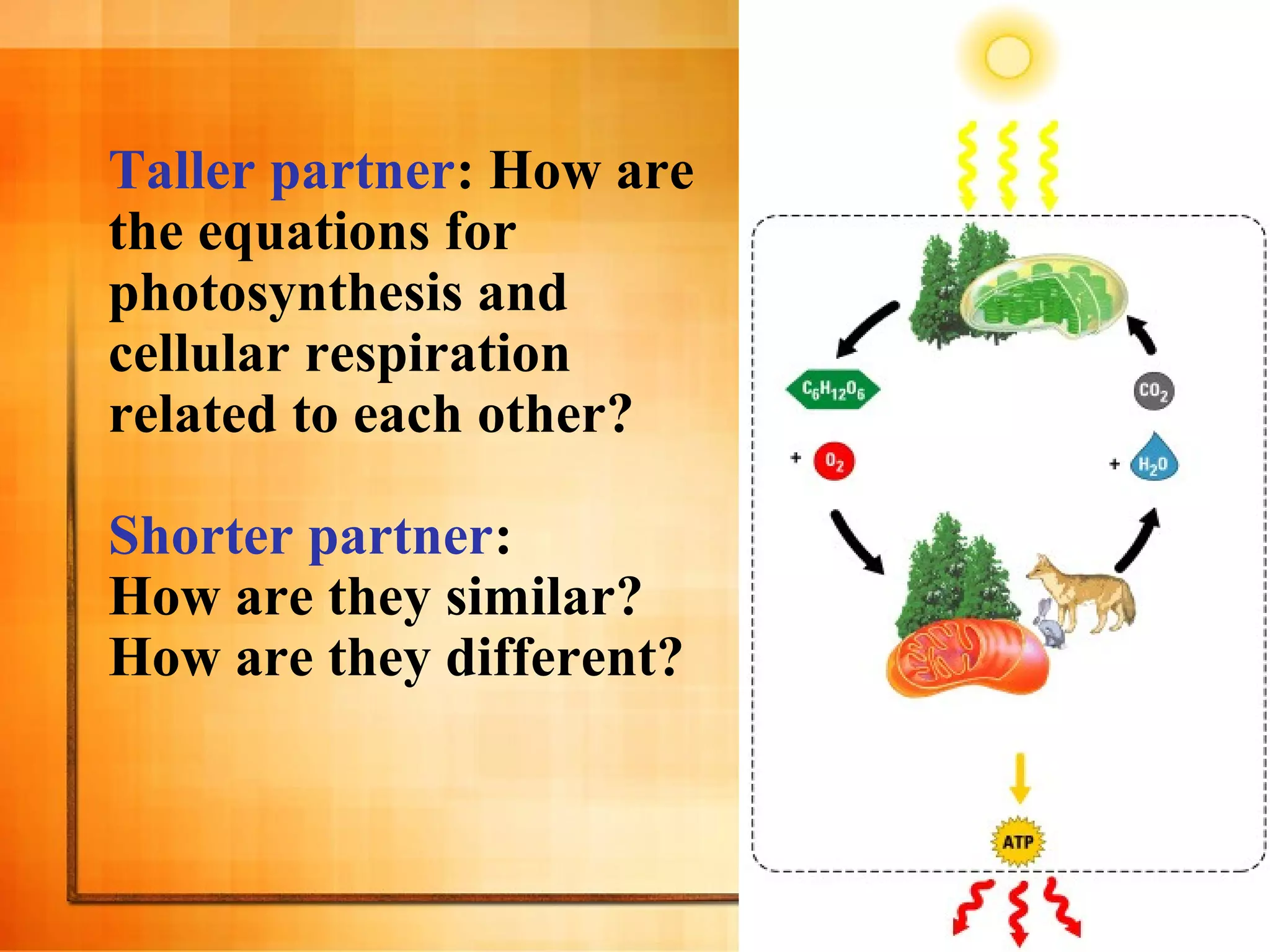
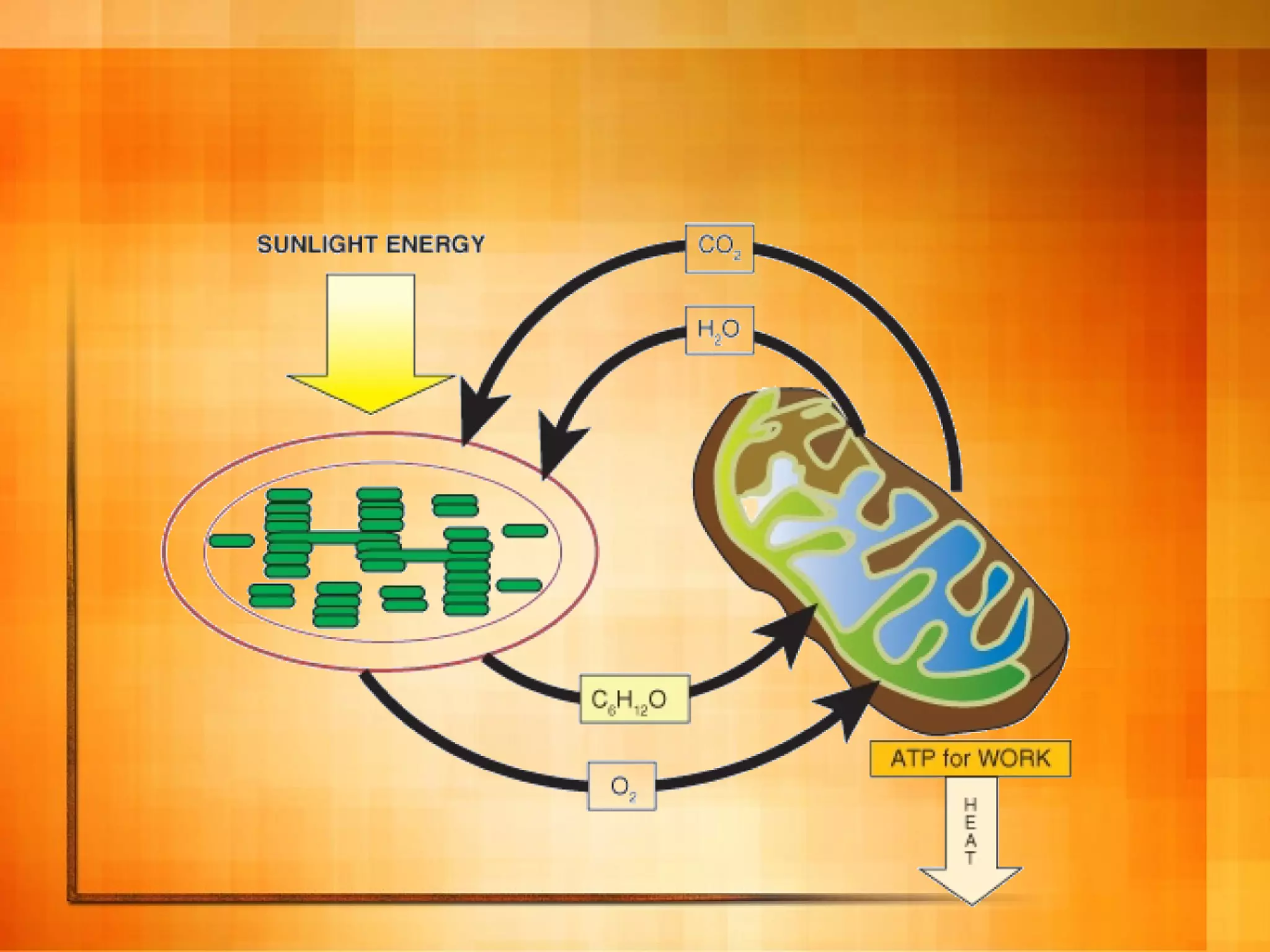
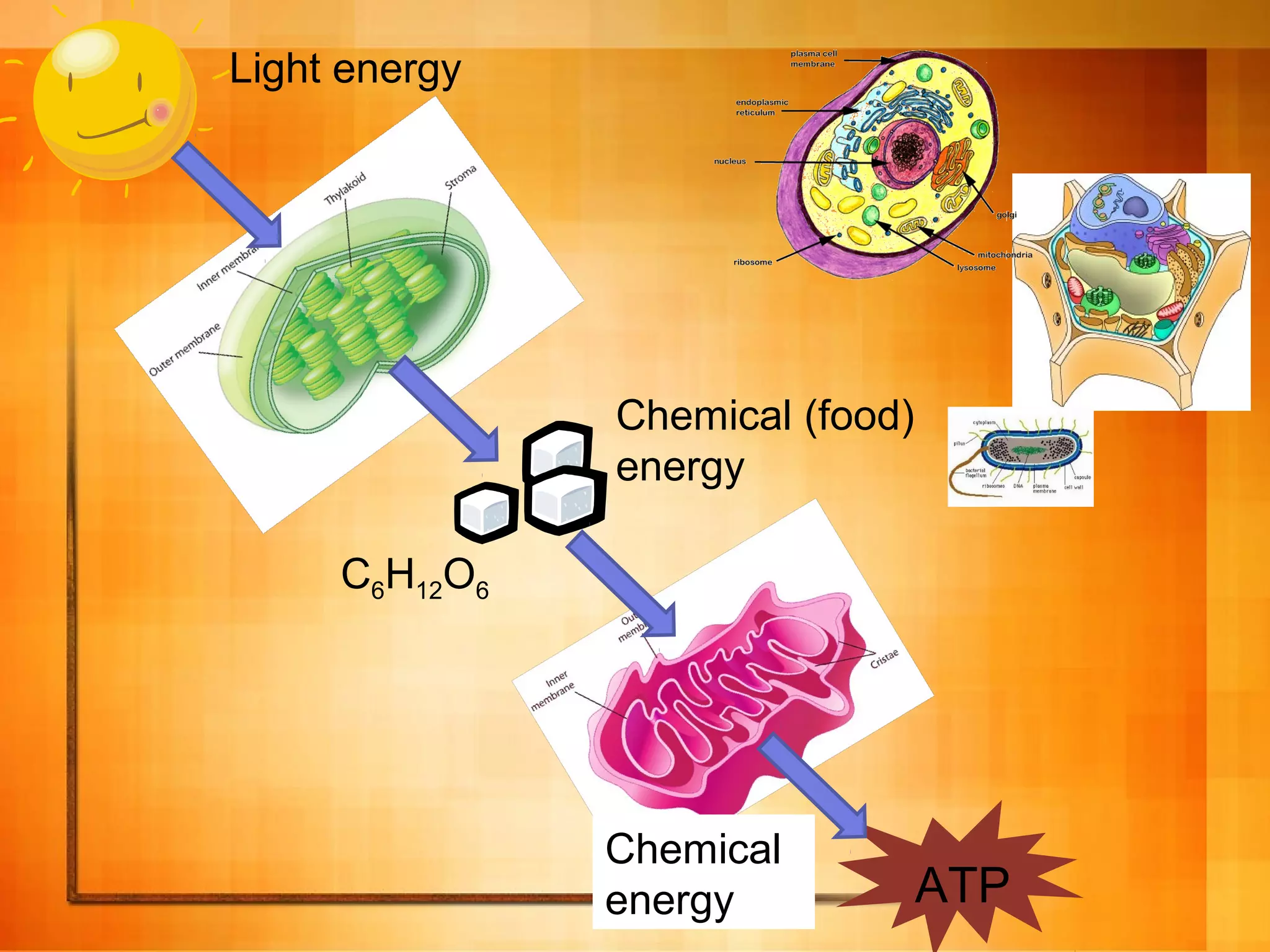
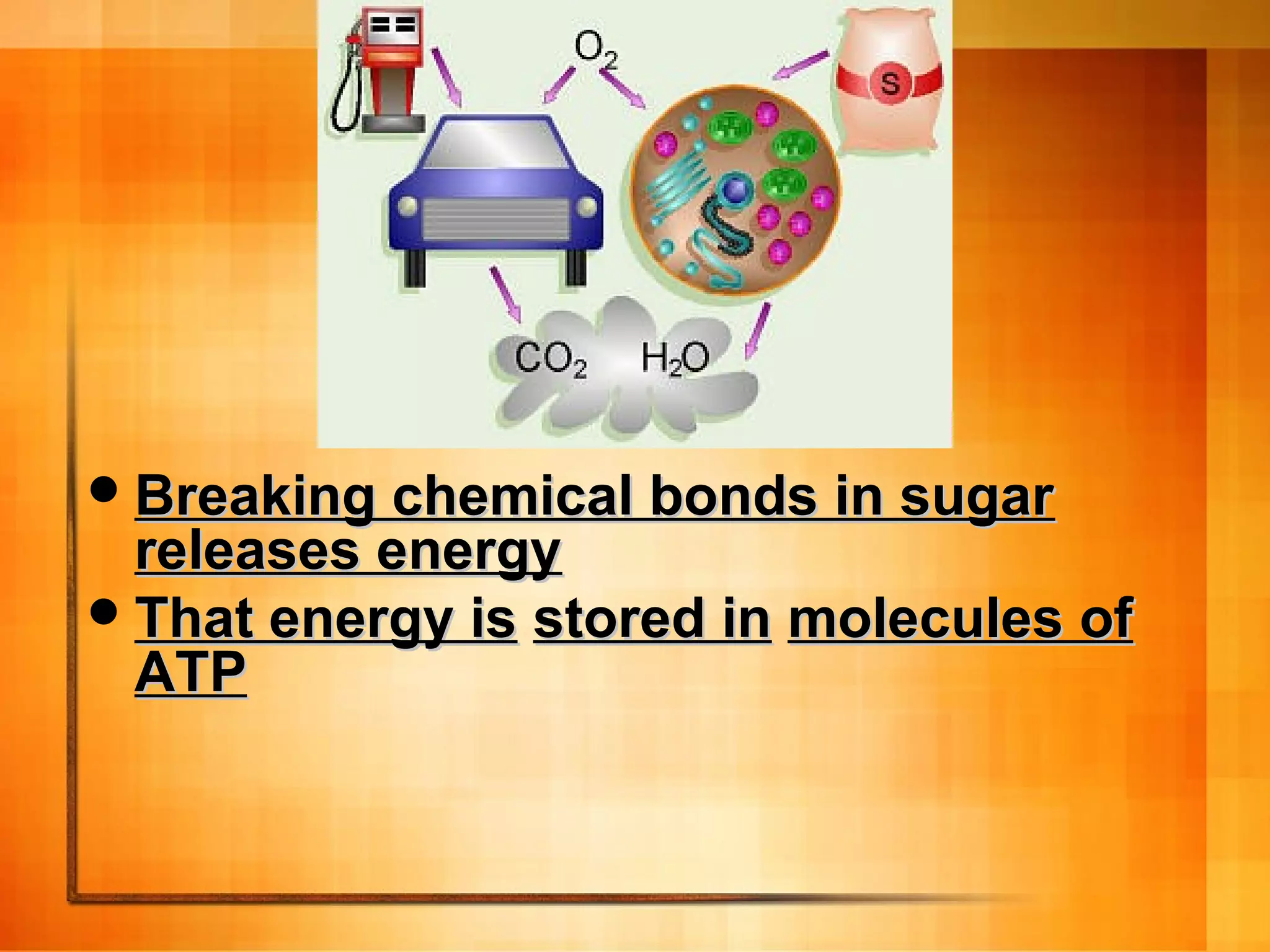
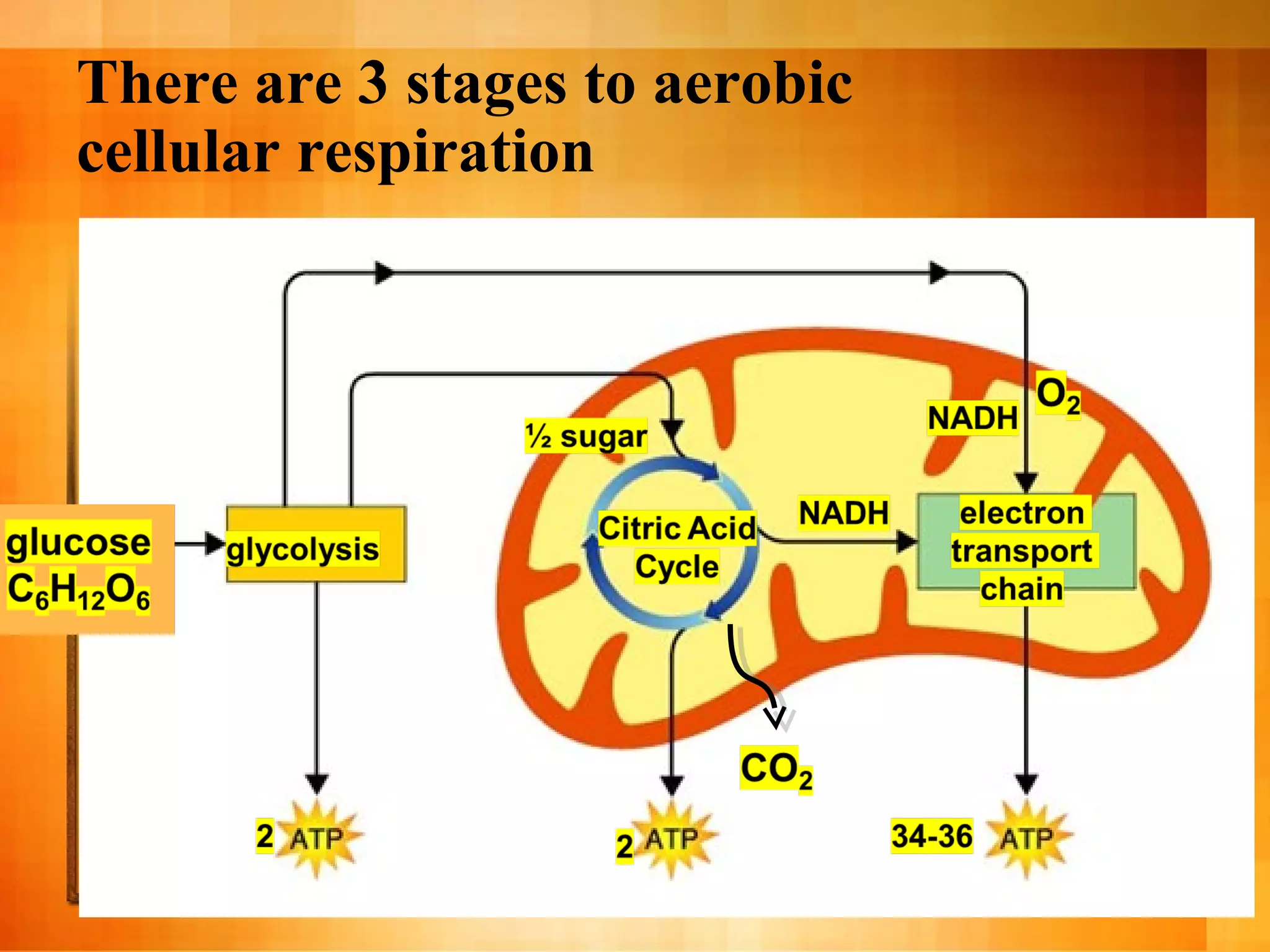
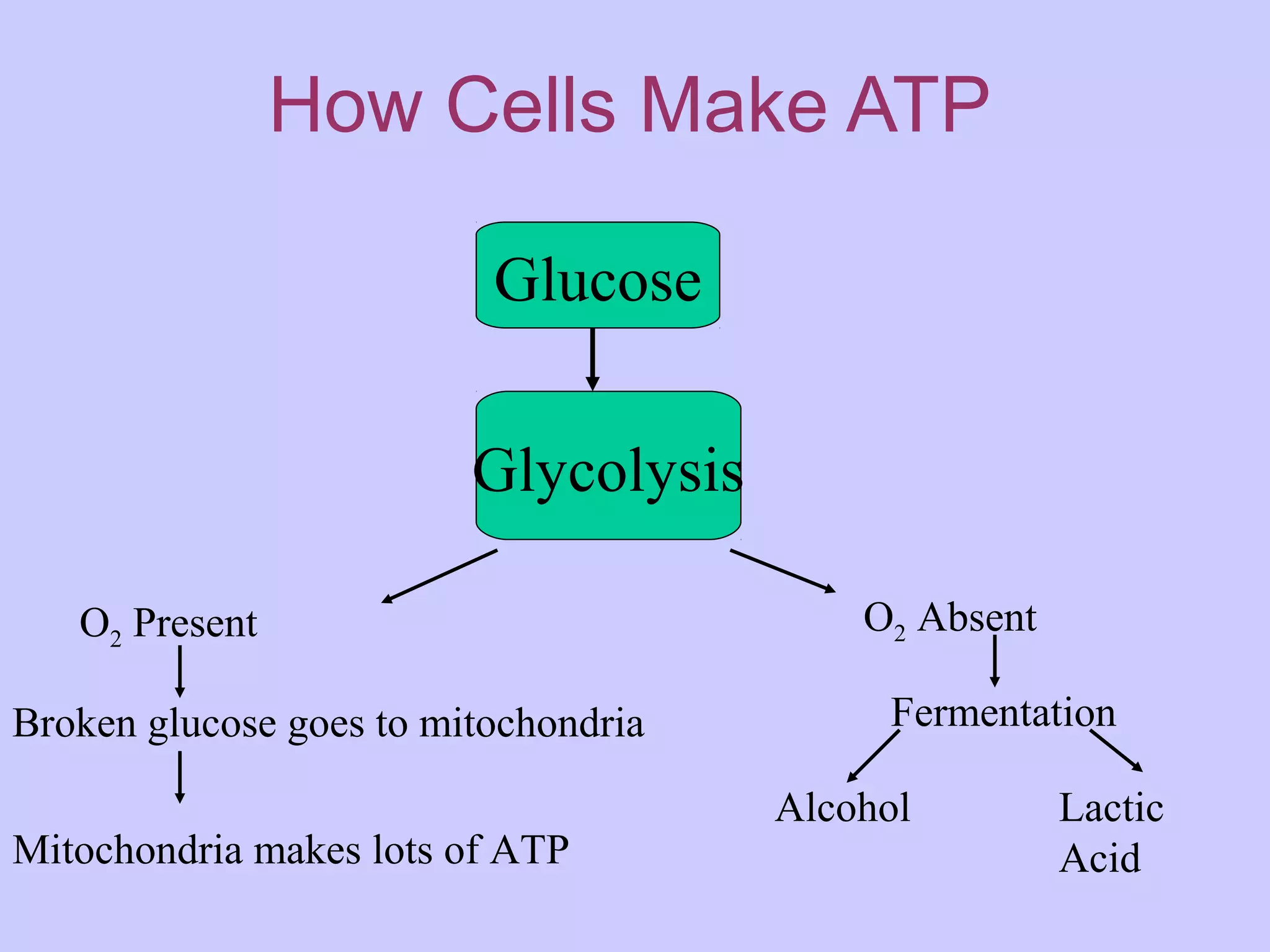
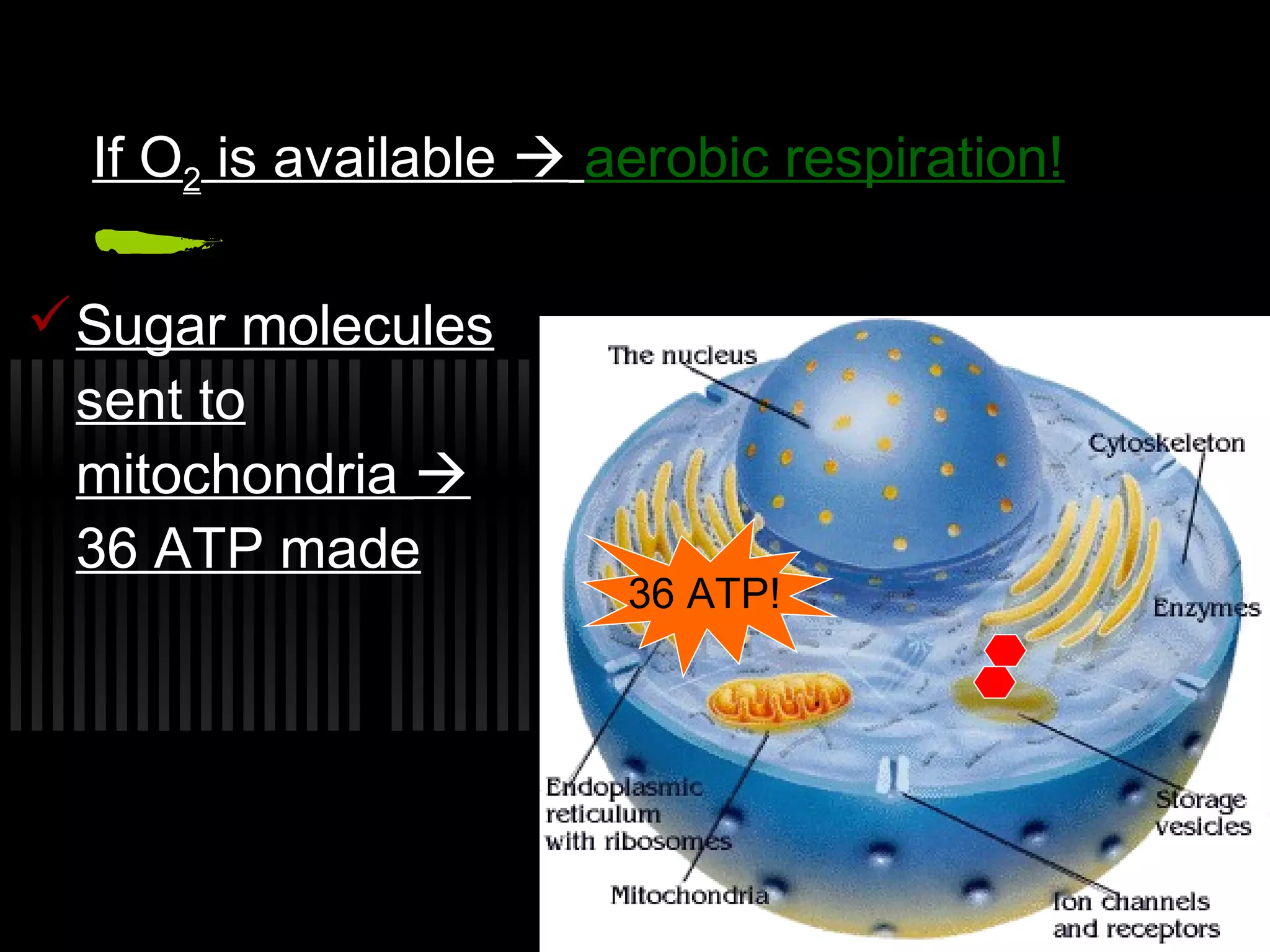
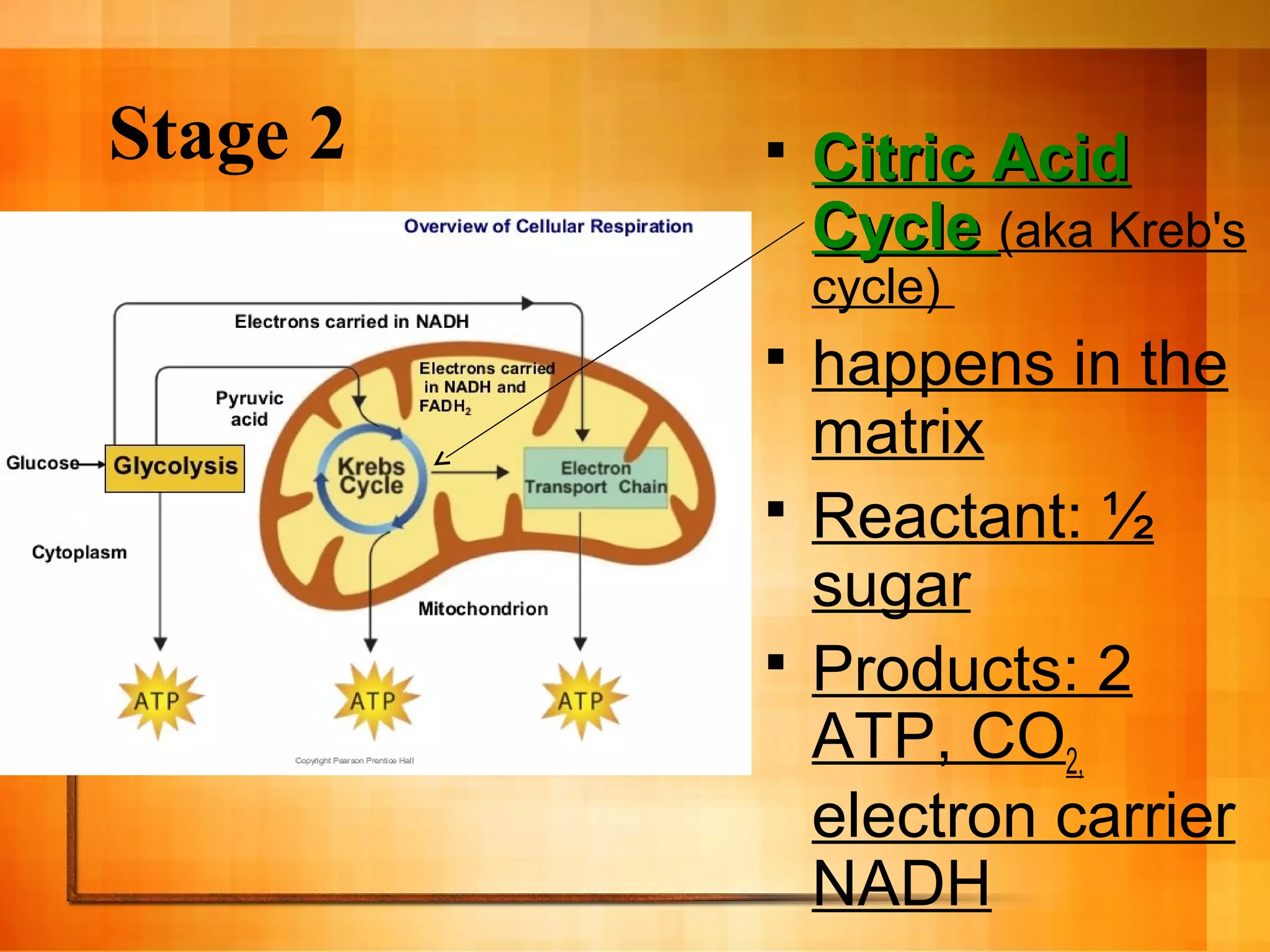
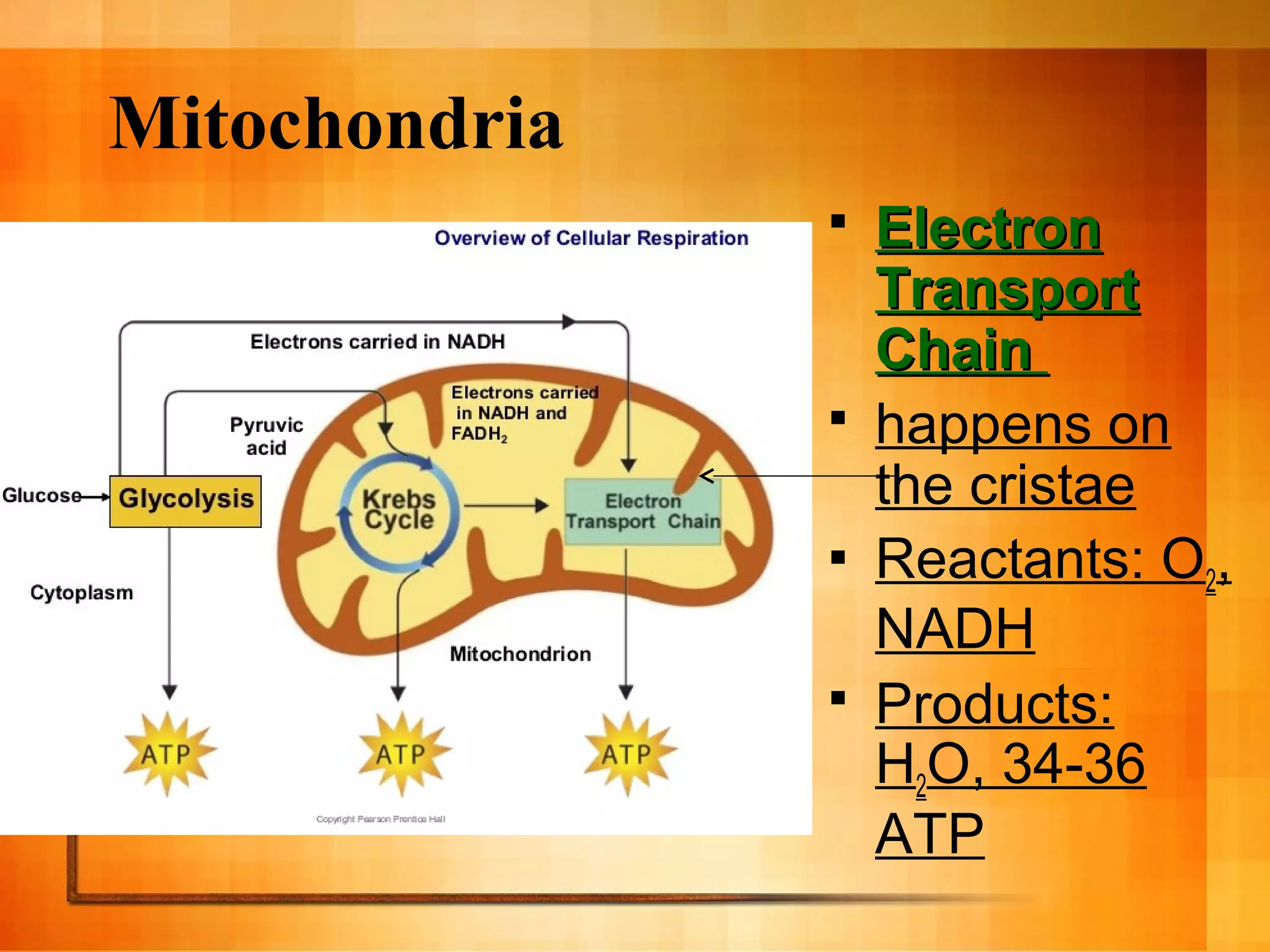
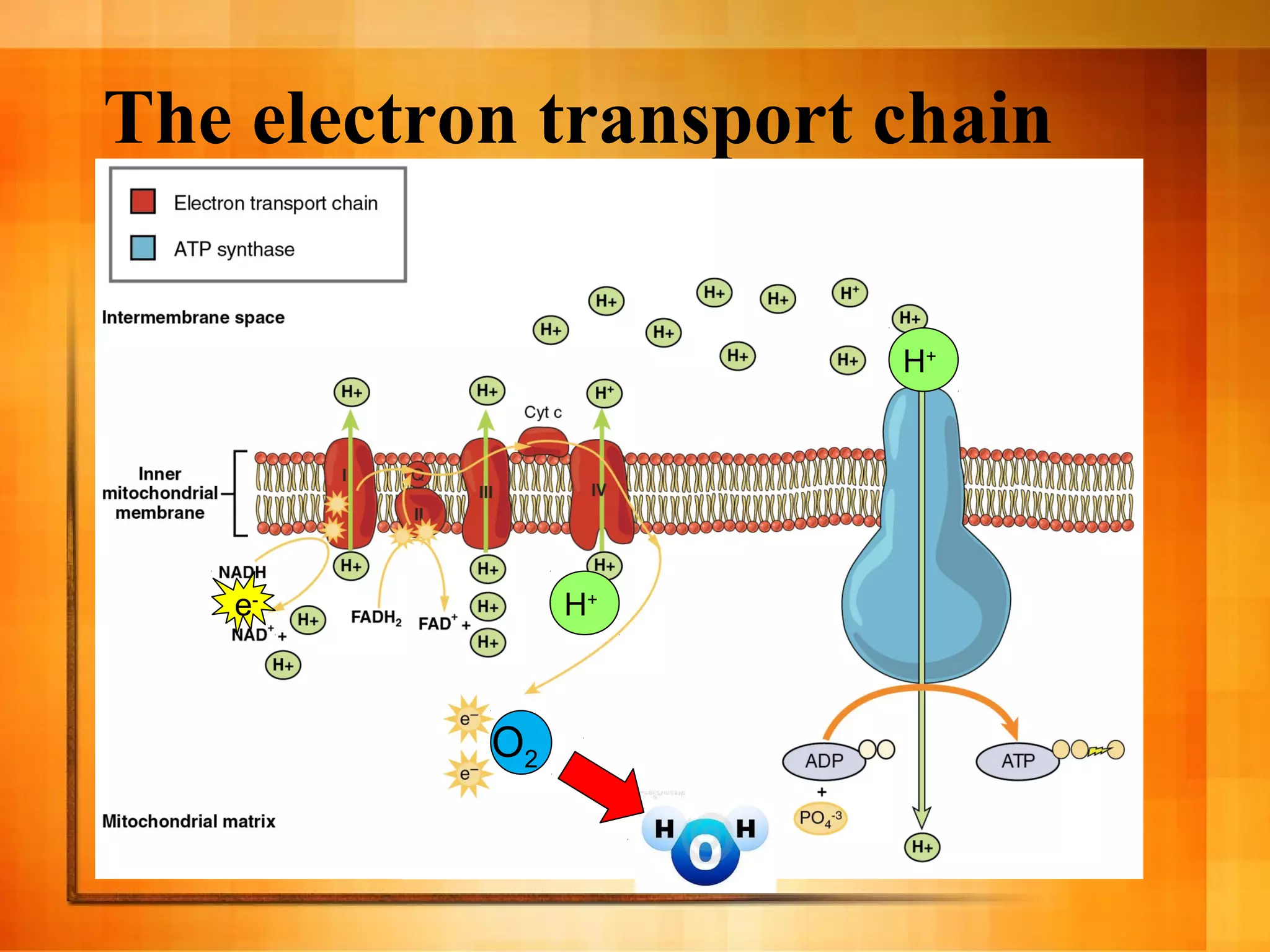
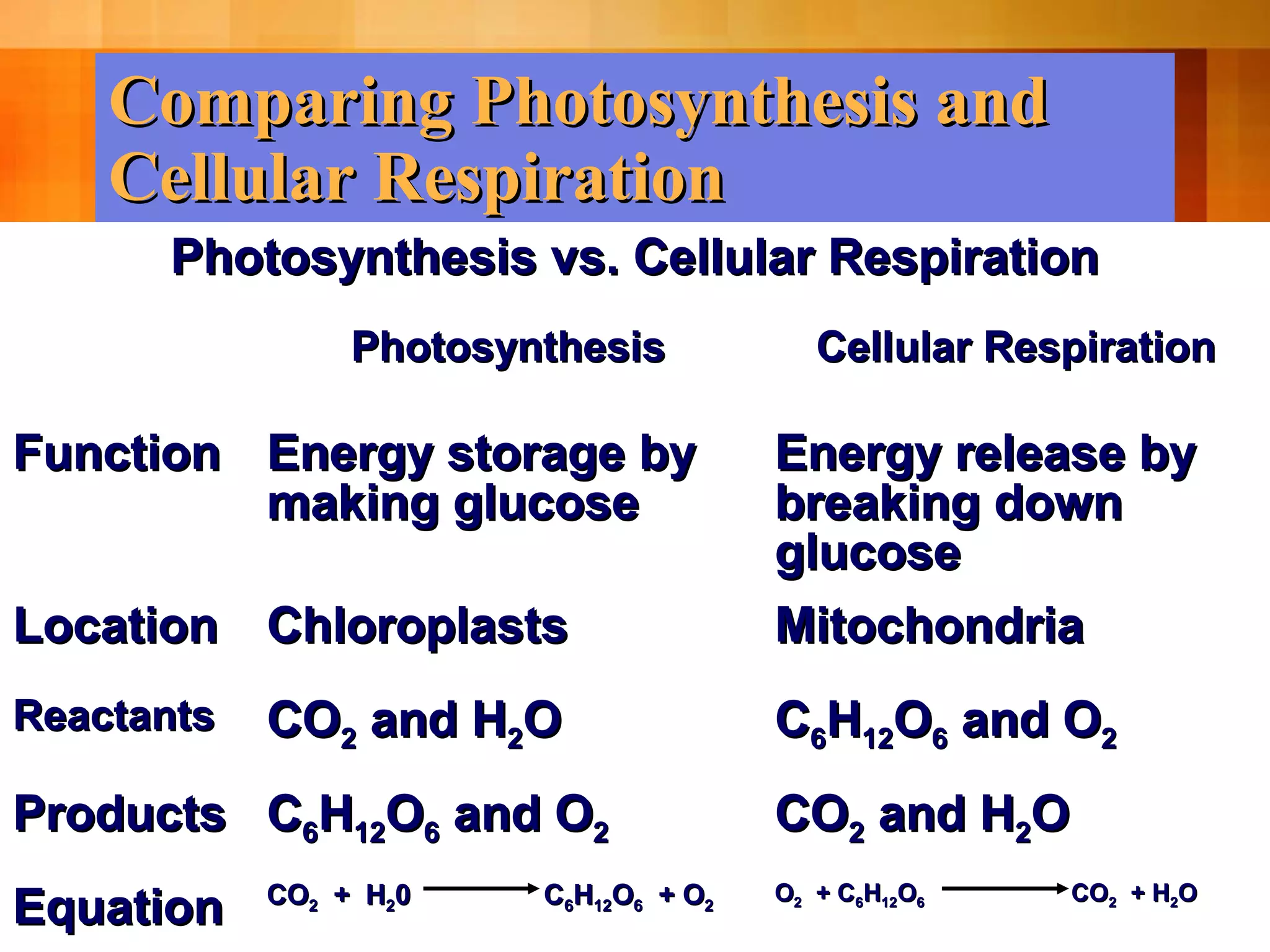
Cellular respiration is the process cells use to release energy stored in glucose and store it in ATP. It occurs in three main stages:
1. Glycolysis breaks glucose into pyruvate, producing 2 ATP.
2. The citric acid cycle in the mitochondria further breaks down pyruvate, producing more ATP, CO2, and electron carriers.
3. The electron transport chain uses oxygen to generate most of the cell's ATP through oxidative phosphorylation as electrons are passed through protein complexes, producing up to 36 ATP per glucose molecule.