Chlamydia trachomatis
- 3. CHLAMYDIAL CONJUCTIVITIS This is a type of conjunctivitis caused by chlamydia. Chlamydia is neither a bacteria nor a virus but it shares the properties of both the organisms. The group comprises of: psittacosis. Lymphogranuloma venereum trachomatis
- 4. Life cycle of chlamydia
- 5. Ocular infections caused by chlamydia Trachoma conjunctivitis. Lymphogranuloma conjunctivitis. Psittacosis is associated with animals
- 6. TRACHOMA This is one of the leading cause of preventable blindness in the world caused by chlamydia trachomatis. it’s a chronic keratoconjunctivitis, primarily affecting the superficial epithelium of conjunctiva and cornea simultaneously. Its characterised by a mixed follicular and papillary response of conjunctival tissue
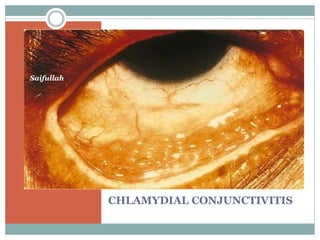
- 7. trachoma
- 9. Aetiology Its caused by a bedsonian organism, the chlamydia trachomatis belonging to PLT group. It’s an epitheliotropic organism and produces intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies called HP BODIES(halbersteadter prowazek bodies) Serotypes: there are only 11 serotypes A-K but I does not exists and Ba does exists.
- 11. Predisposing factors Age Sex Race Climate Socioeconomic status Environmental factors source of infection Discharge from the eye of infected person, In endemic area.
- 12. Modes of infection Direct spread Vector transmission Material transfer Clinical features These are described based on two phases Viz; - phase of active trachoma - Phase of cicatricial trachoma
- 13. Phase of active trachoma Symptoms: In the absence of secondary infection -mild foreign body sensation -occasionally lacrimation -slight stickiness of the lid -scanty mucoid discharge. in the presence of secondary bacterial infection -acute mucoprulent discharge.
- 14. Signs of active trachoma Conjunctival signs -congestion of upper tarsal and forniceal conjunctiva. -conjunctival follicles -papillary hyperplasia Corneal signs -superficial keratitis -Herbert follicles -progressive pannus -corneal ulcer
- 15. Phase of cicatricial trachoma Conjunctival signs -conjunctival scarring -concretions( of gland of henle) -other conjunctival sequelae including *concretions *pseudocyst *xerosis *symblepharon
- 16. Artl’s line
- 18. Corneal sign *regressive pannus *Herbert pits *corneal opacity *other corneal sequelae (blinding sequelae) -corneal ectasia -corneal xerosis -total corneal pannus
- 20. Lid signs. *sequelae in the lids may be. -trichiasis -entropion -tylosis -ptosis -madarosis -ankyloblepharon lacrimal apparatus sequelae *chronic dacryocystitis *chronic dacryoadenitis
- 21. WHO grading of trachoma
- 22. Complications of trachoma The only complication of trachoma eye infection is corneal ulcer which may occur due to rubbing by concretions or trichiasis with superimposed bacterial infection. DIAGNOSIS Diagnosis can be done based on its clinical signs and clinical grading should be done as per W.H.O grading into TF,TI,TS,TT or CO.
- 23. Laboratory diagnosis Conjunctival cytology Detection of inclusion body ELISA PCR Isolation of chlamydia Serotypes of TRIC agents using micro immunofluorescence.
- 24. Differential diagnosis Trachoma with follicular hypertrophy this has to be differentiated from acute adenoviral follicular conjunctivitis. (epidemic keratoconjunctivitis) as follows: *distribution of follicles *associated signs *lab diagnosis Trachoma with predominant papillary hypertrophy This has to be differentiated from palpebral form of spring catarrh as follows:
- 25. - Papillae are large in size and usually associated with cobble-stone arrangement in spring catarrh. -PH of tears is usually alkaline -discharge is ropy -conjunctival cytology should be well done. -pannus and follicles are present in both. Treatment of trachoma SAFE treatment strategy
- 26. ADULT INCLUSION CONJUNCTIVITIS This is a type of acute follicular conjunctivitis associated with mucoprulent discharge. It usually affects sexually active young adults. Its also called swimming pool conjunctivitis. Aetiology - serotype D to K of chlamydia trachomatis are assoc. with inclusion conjunctivitis. - Primary source in male is urethritis and cervicitis in female - Contaminated finger, water or swimming pool.
- 27. Clinical features Symptoms *ocular discomfort, foreign body sensation. *mild photophobia *mucoprulent discharge. Signs *conjunctival hyperemia *acute follicular hypertrophy *superficial keratitis *preauricular lymphadenopathy
- 28. treatment Topical tetracycline 1% eye ointment 4/day x 6weeks Systemic drugs are: - Azithromycin 1gm s.d - tetracycline 250mg 4/day x3to 4 weeks - Erythromycin as in above - Doxycycline 200mg/week x 3 weeks. Prophylaxis *personal hygiene *regular chlorination of water *treatment of sexual partner.
- 29. THANK YOU