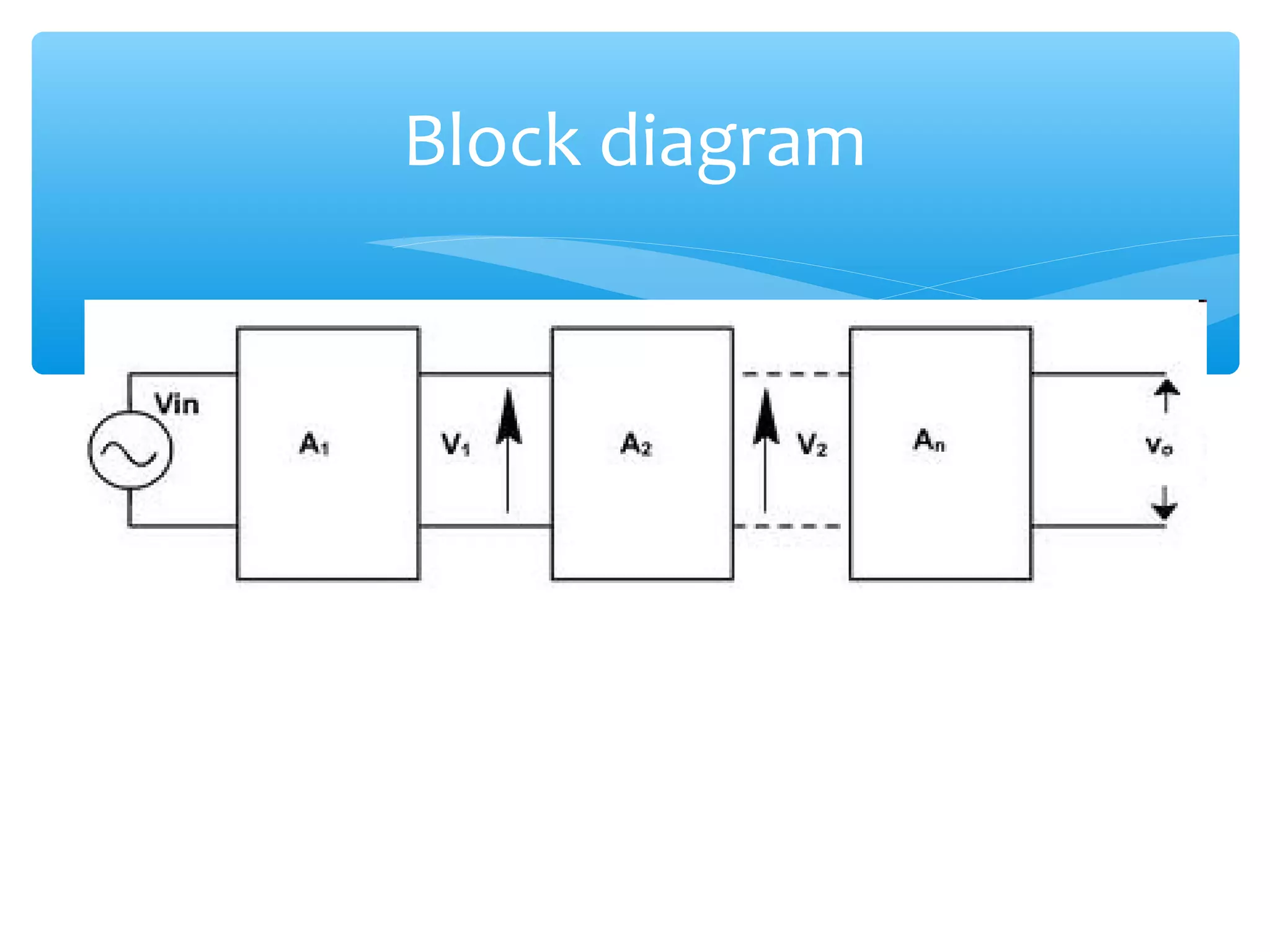
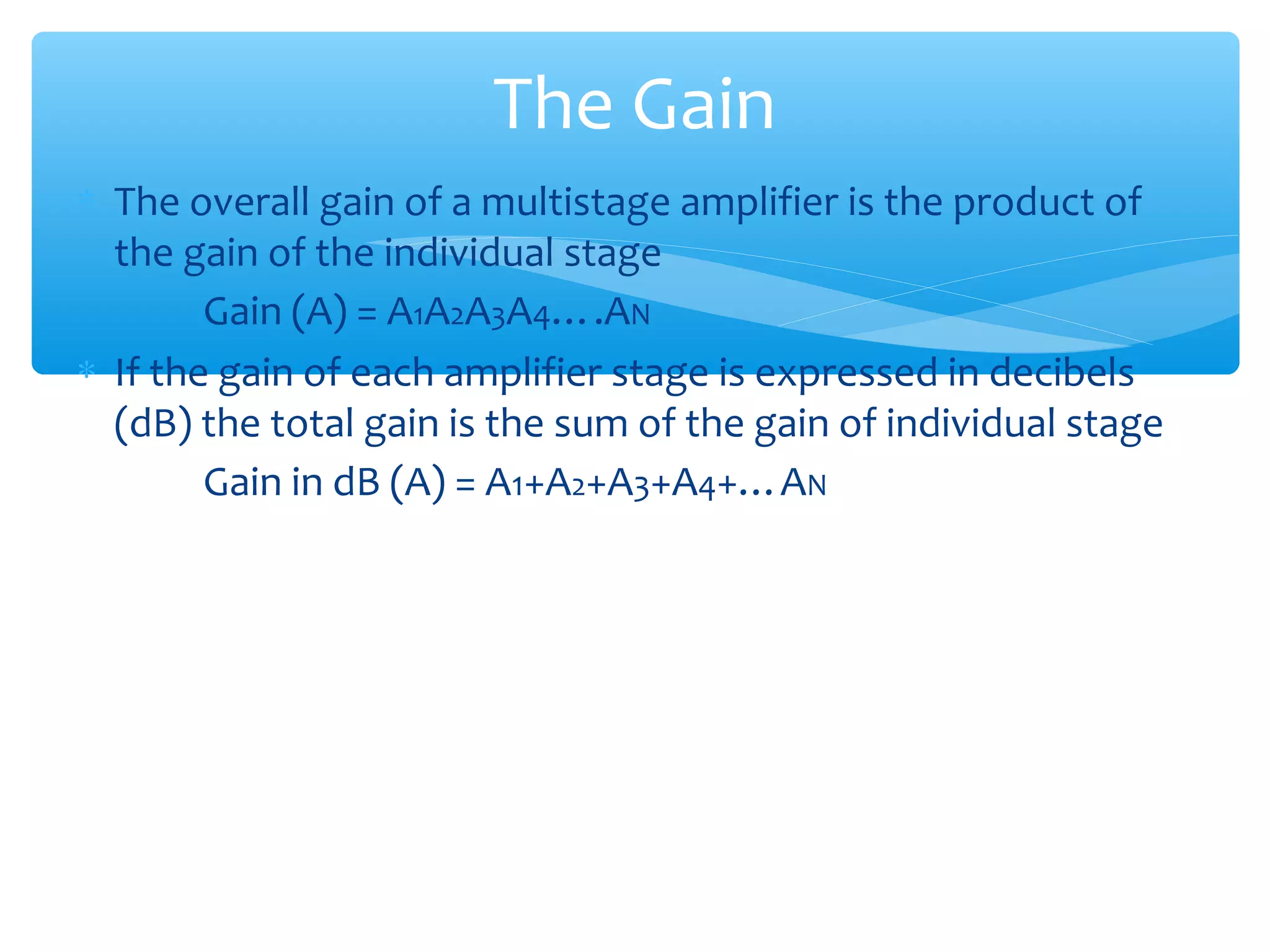
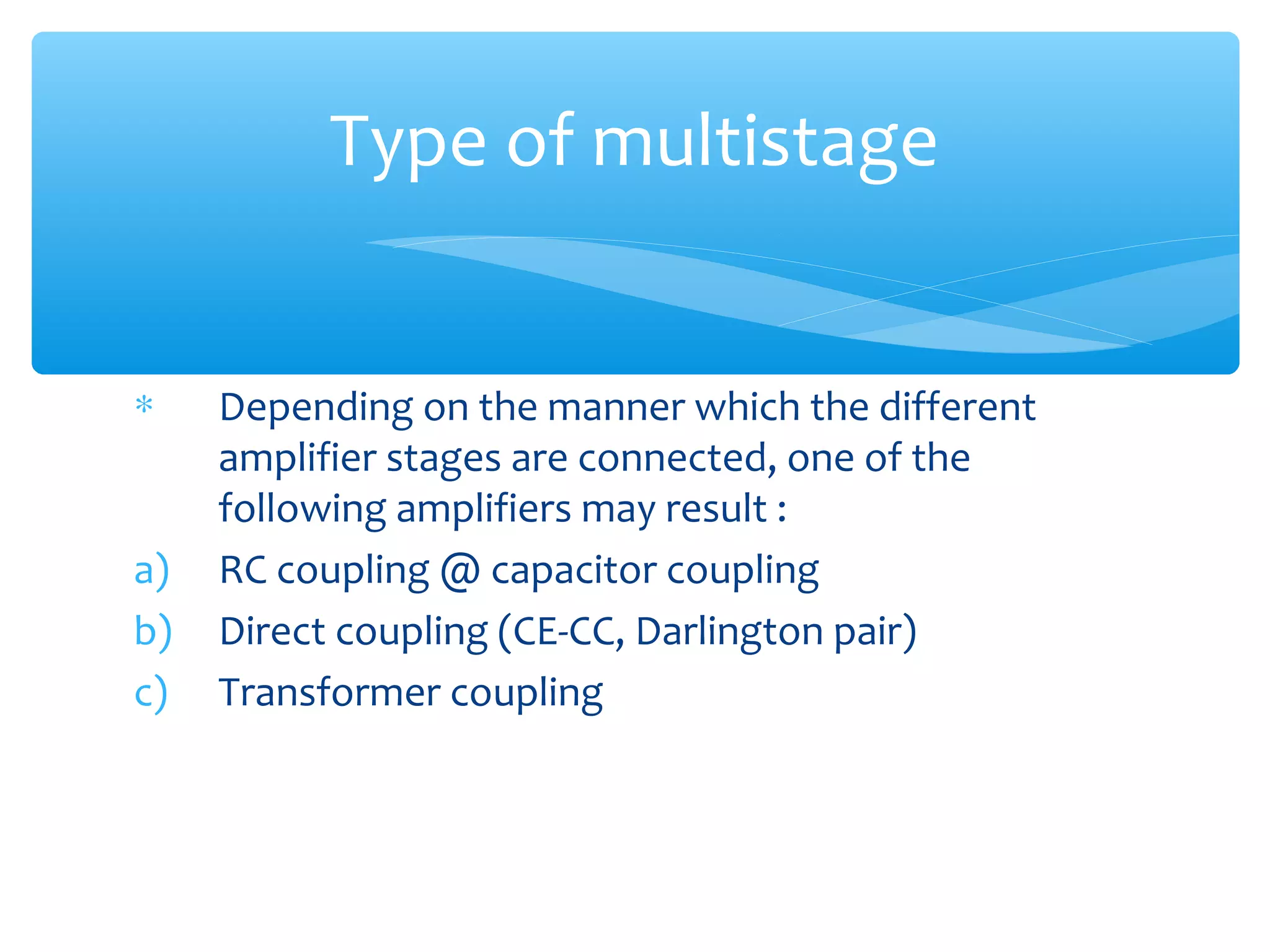
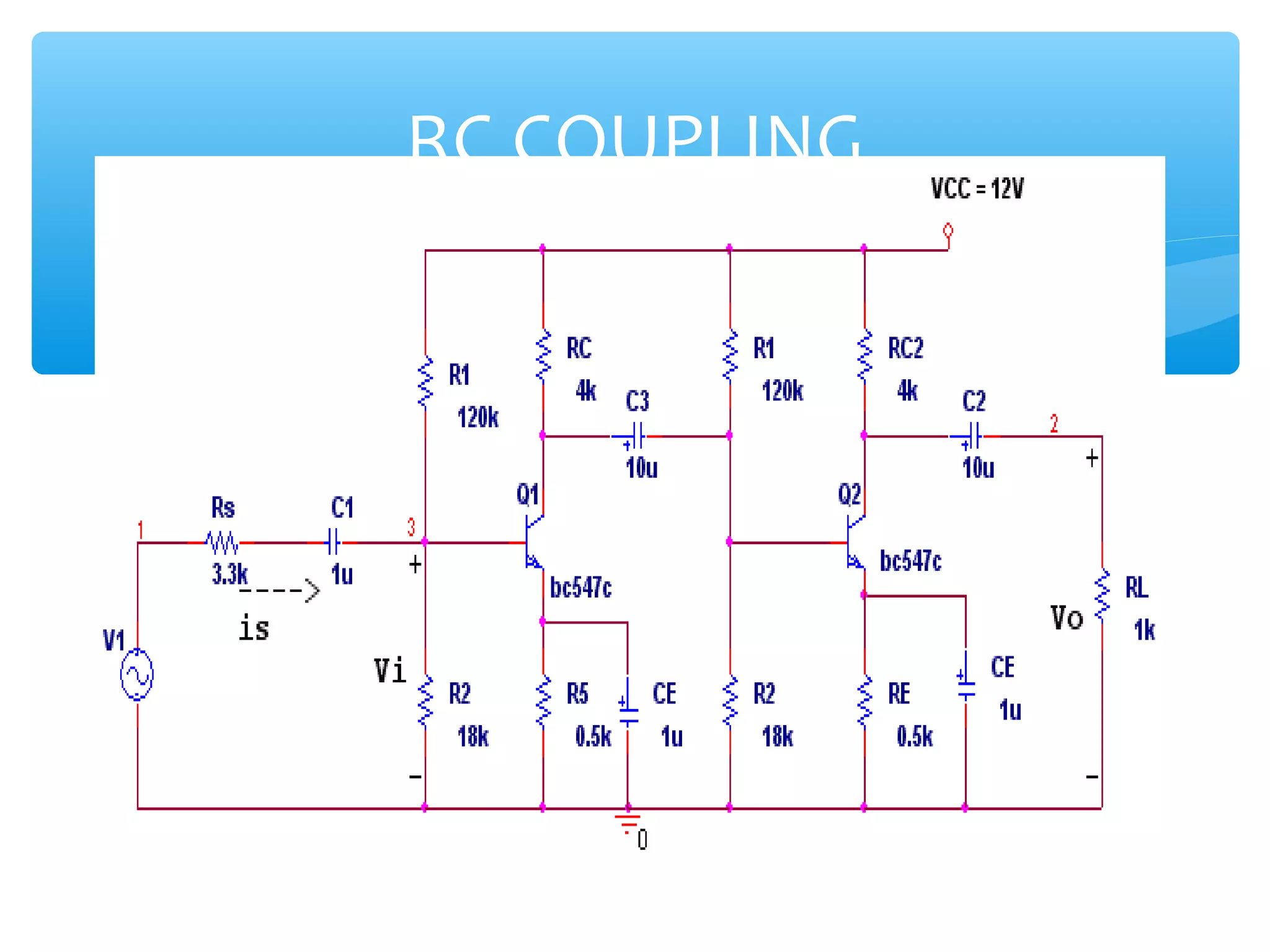
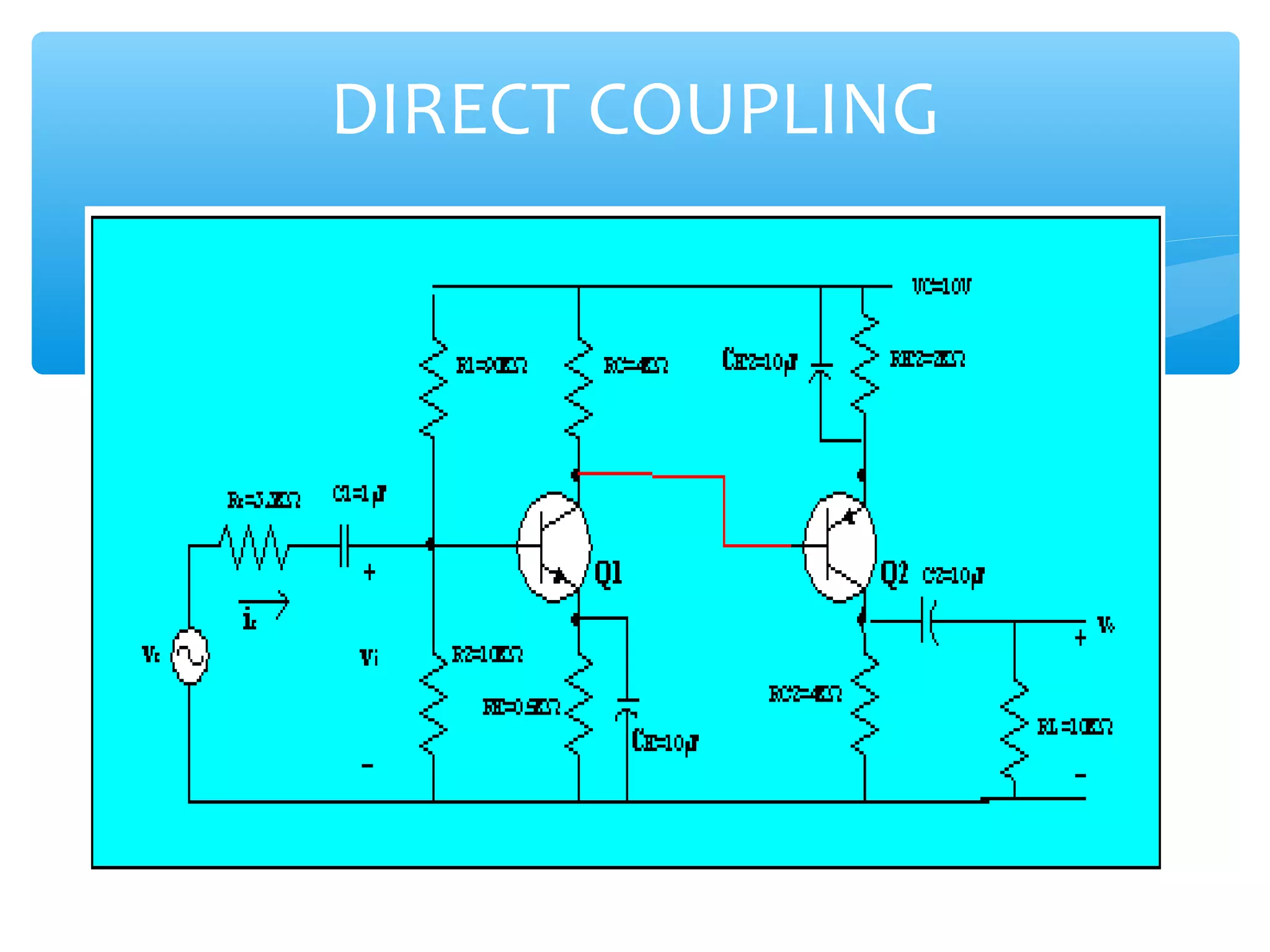
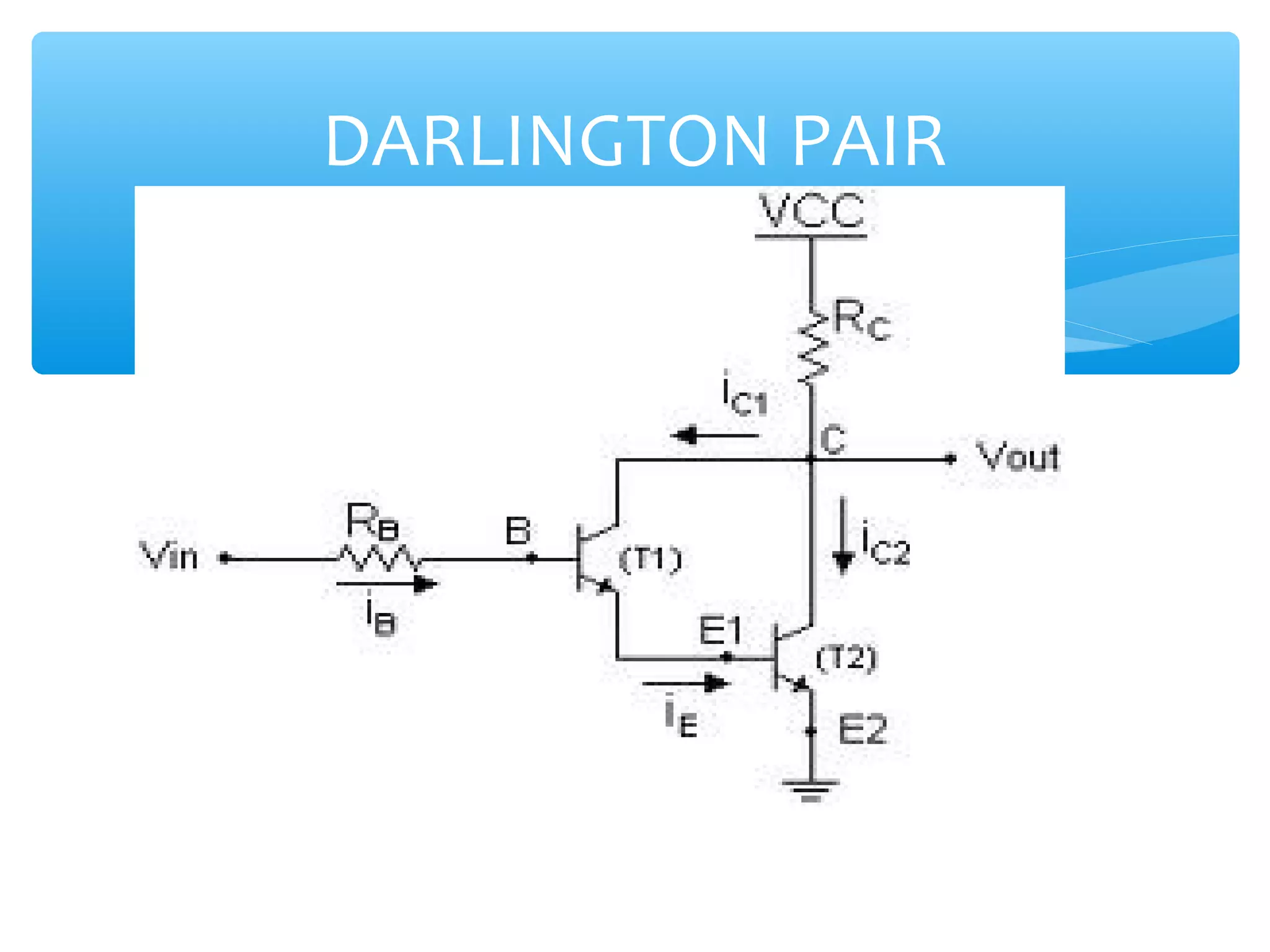
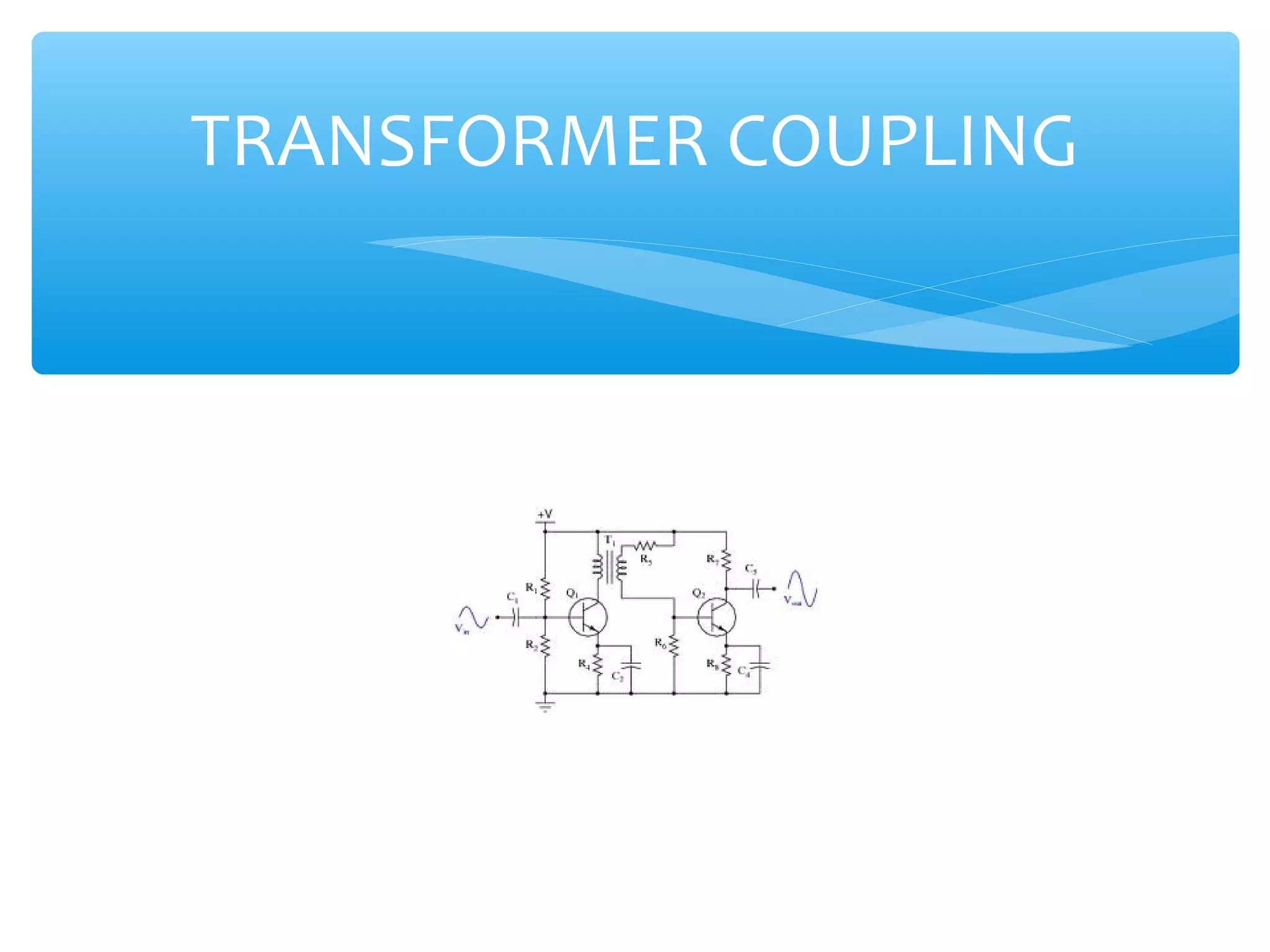
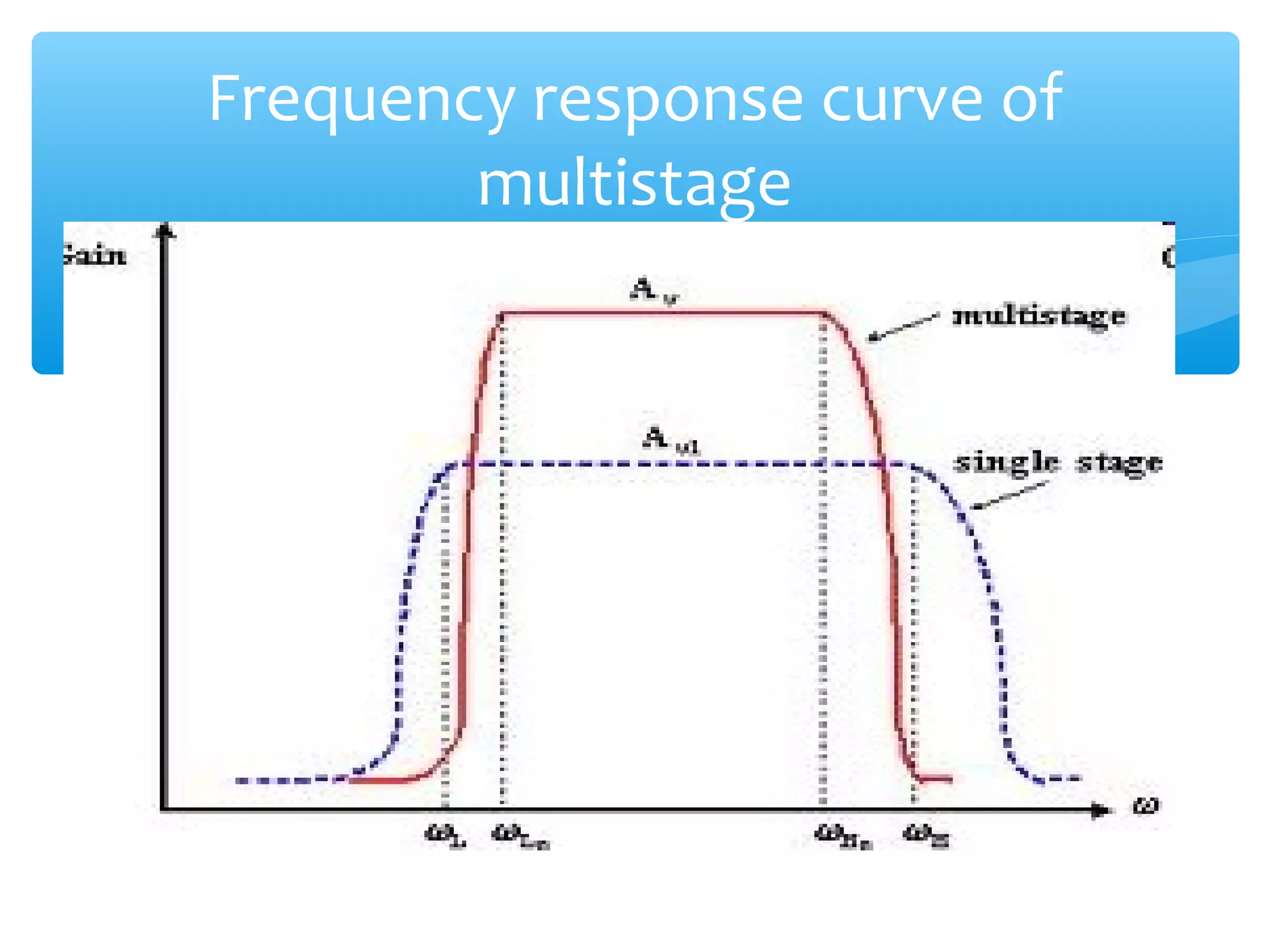
Chapter 4 of the document covers multistage amplifiers, which enhance gain and modify characteristics using configurations like cascode and cascade connections, as well as different coupling methods such as RC, direct, and transformer coupling. Each method has distinct advantages and disadvantages, influencing frequency response and biasing. The overall gain of a multistage amplifier is determined by the product or sum of the gains of individual stages, depending on whether decibels or linear values are used.