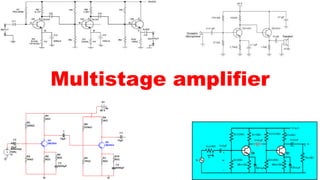
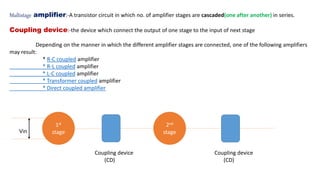
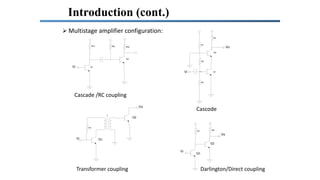
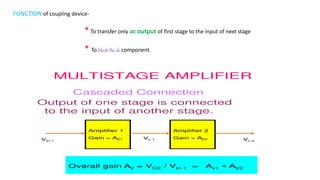
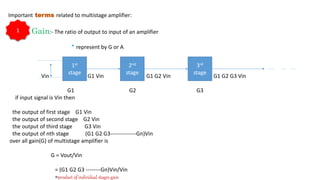
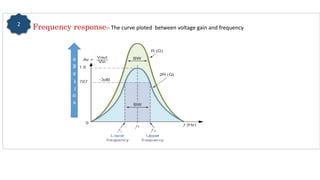
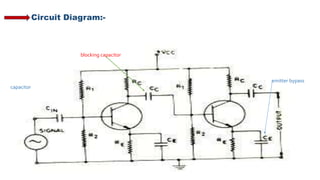
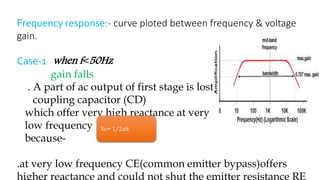
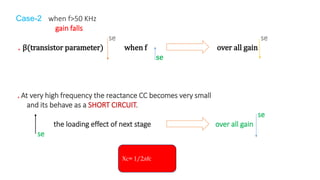
The document describes a multistage transistor amplifier. It defines a multistage amplifier as having multiple amplifier stages connected in series using coupling devices. It discusses different types of coupling devices like RC, RL, LC and transformer coupling. It explains the working of a typical multistage amplifier including how the gain is calculated as the product of individual stage gains. It describes how the frequency response varies with lower gains at very low and very high frequencies. Advantages include low cost and good frequency response. Disadvantages include increased noise over time and poor impedance matching. Multistage amplifiers are widely used as voltage amplifiers in audio applications.