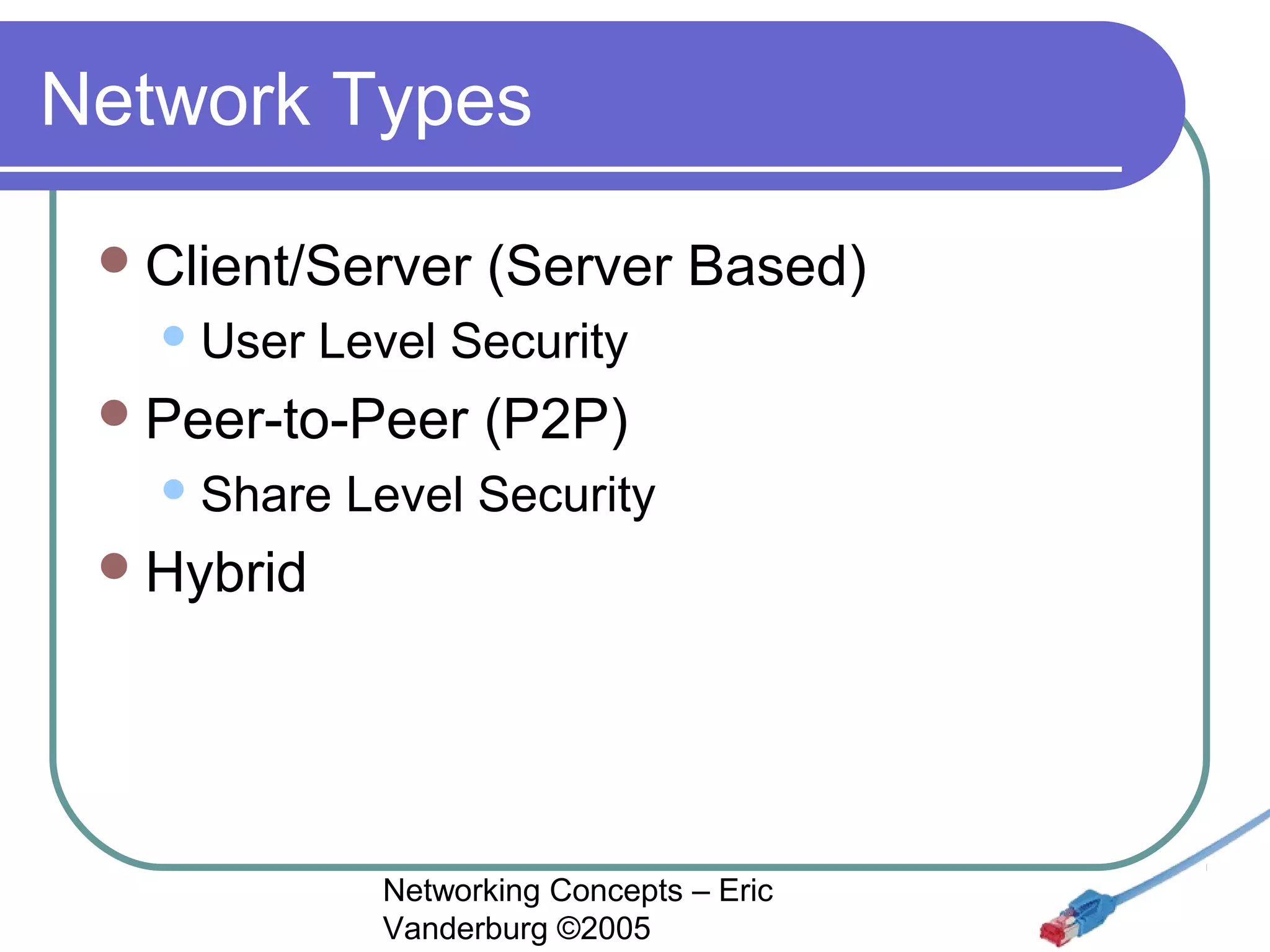
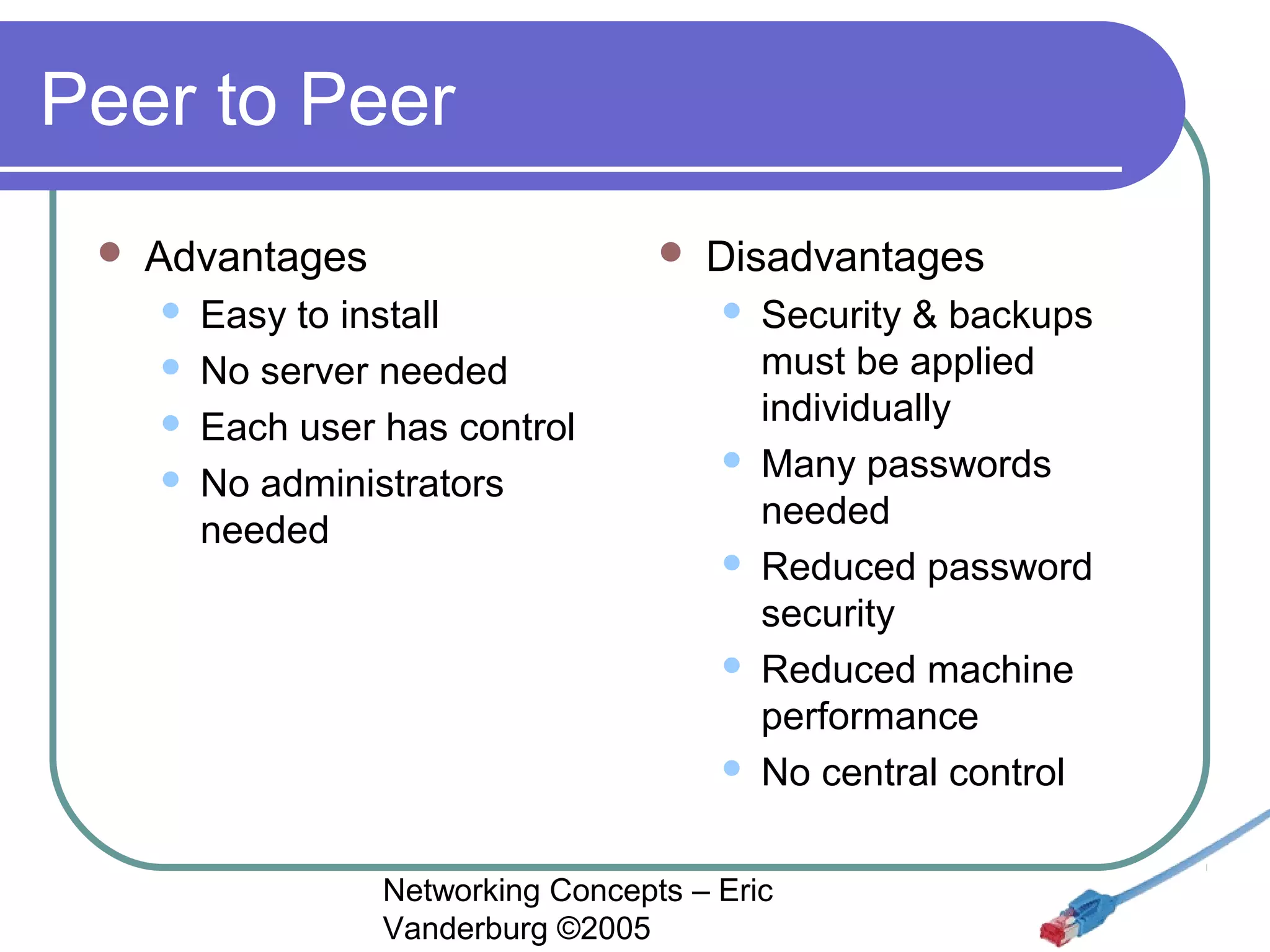
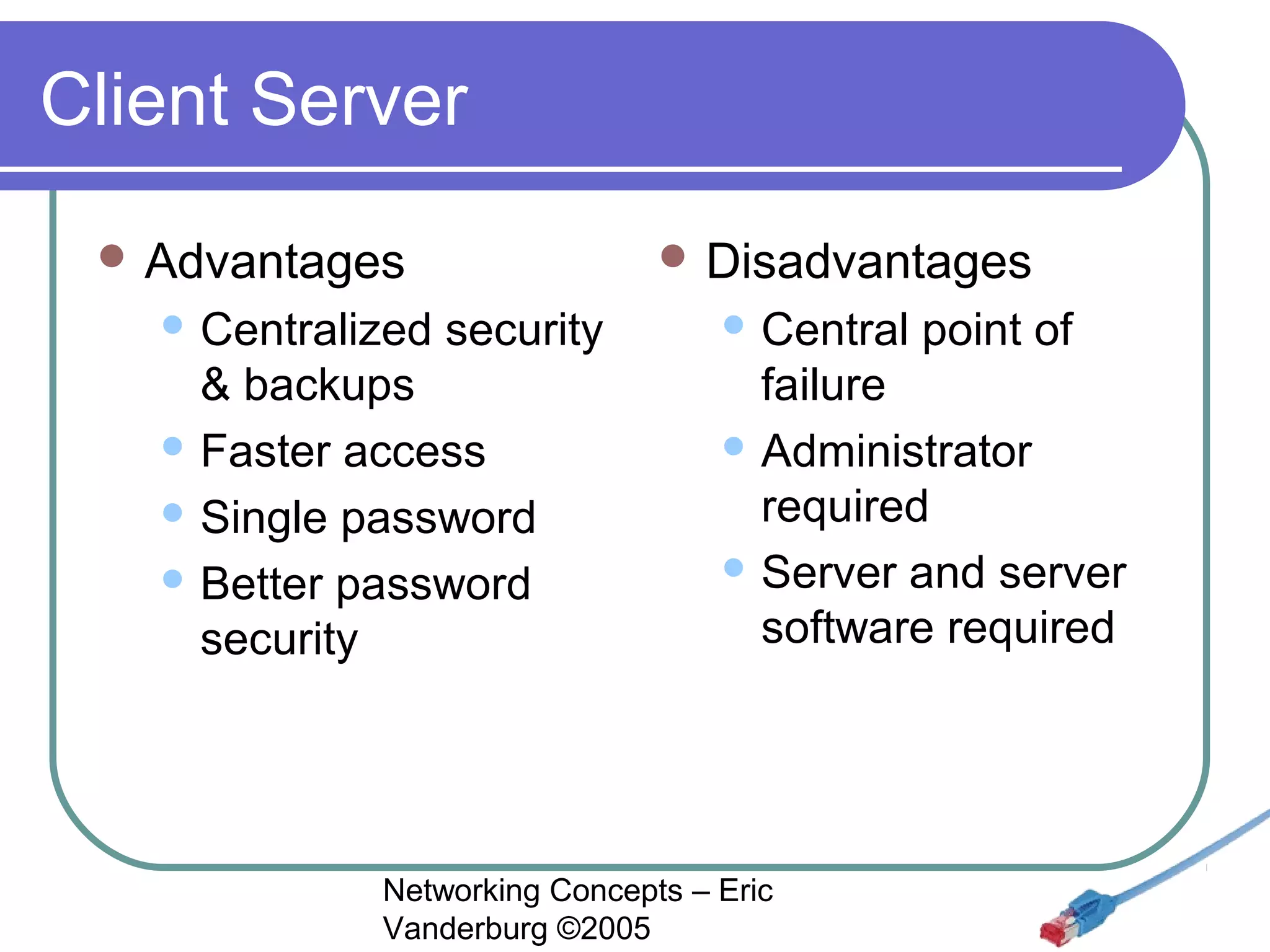
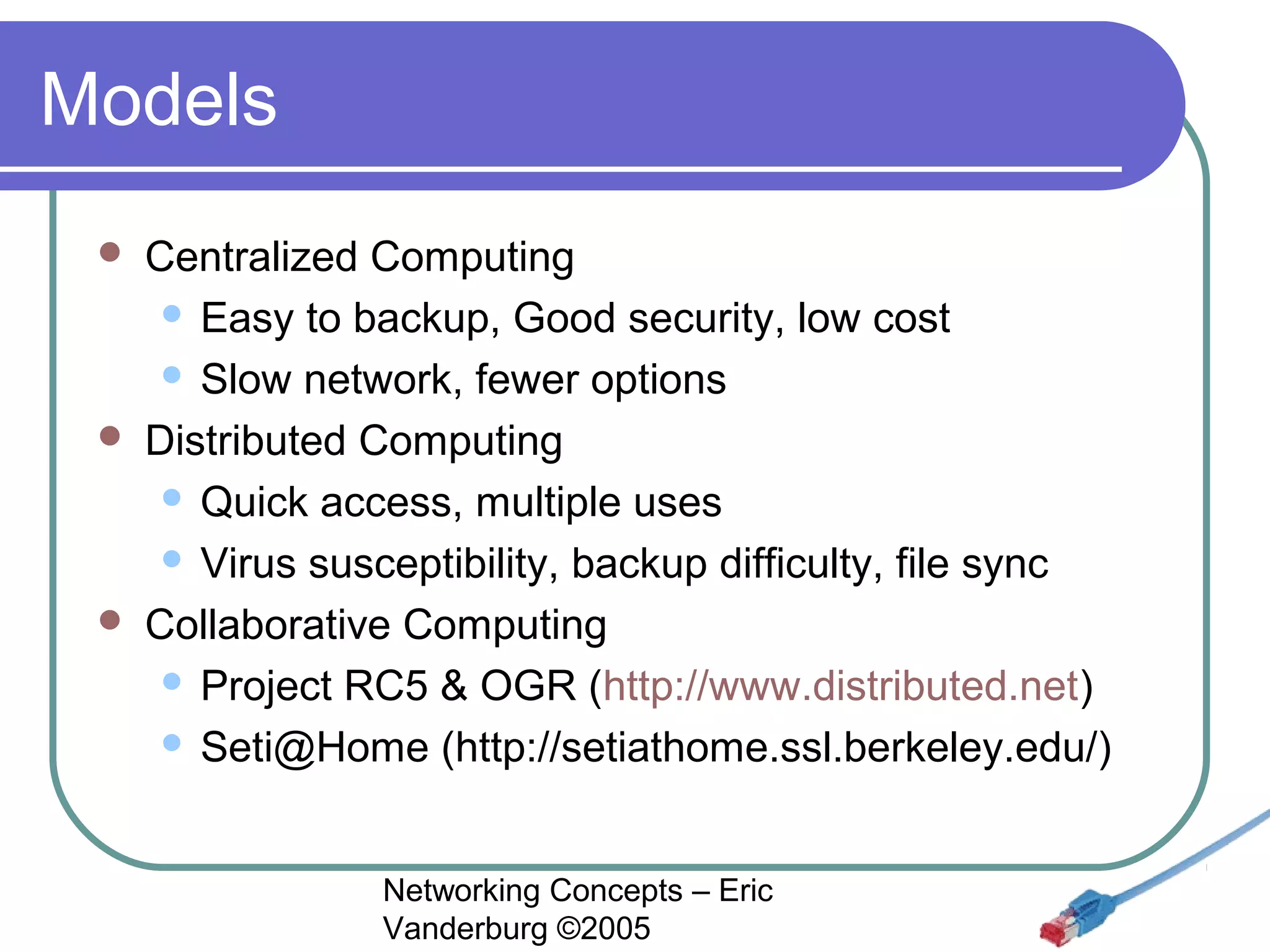
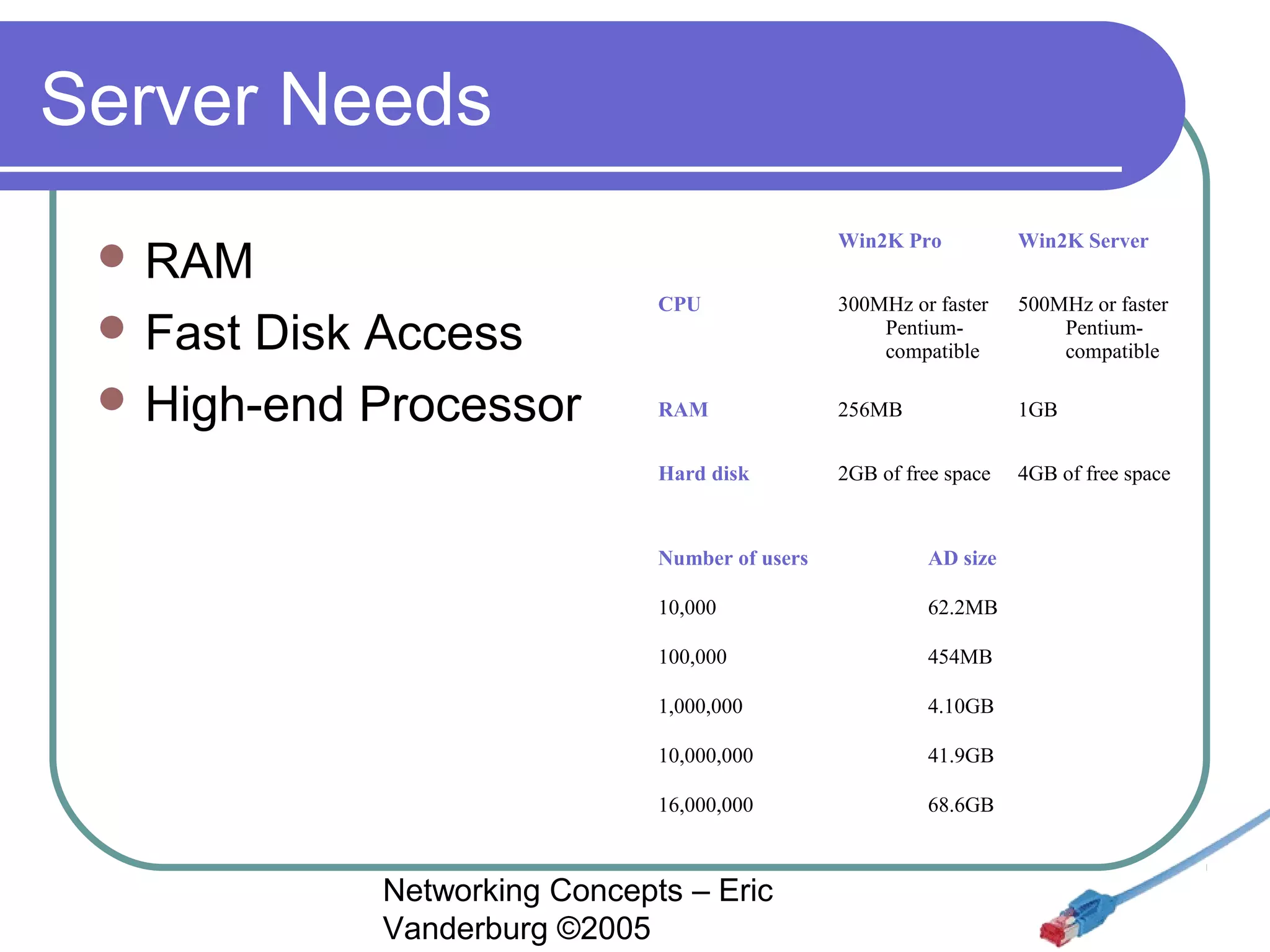
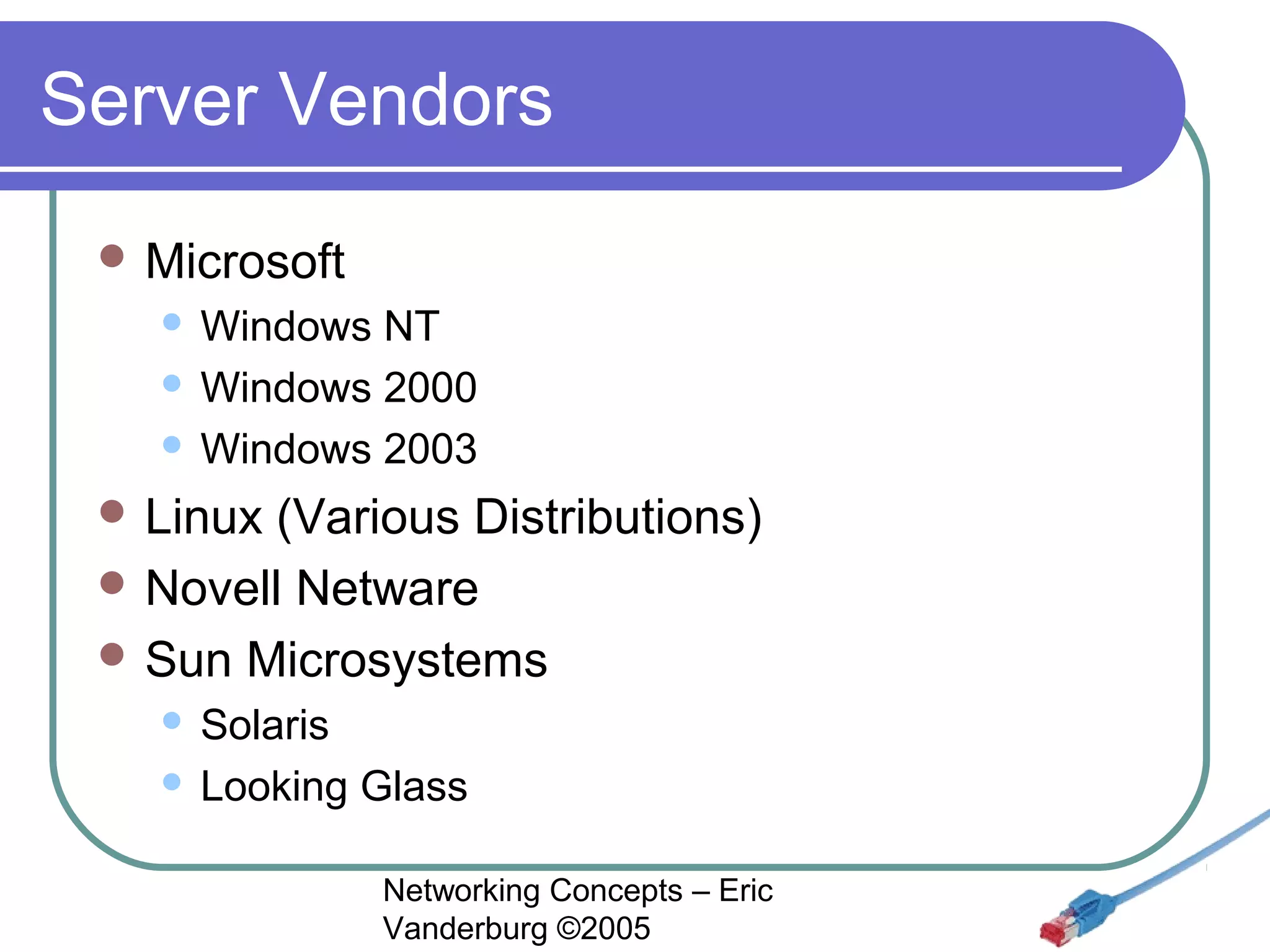
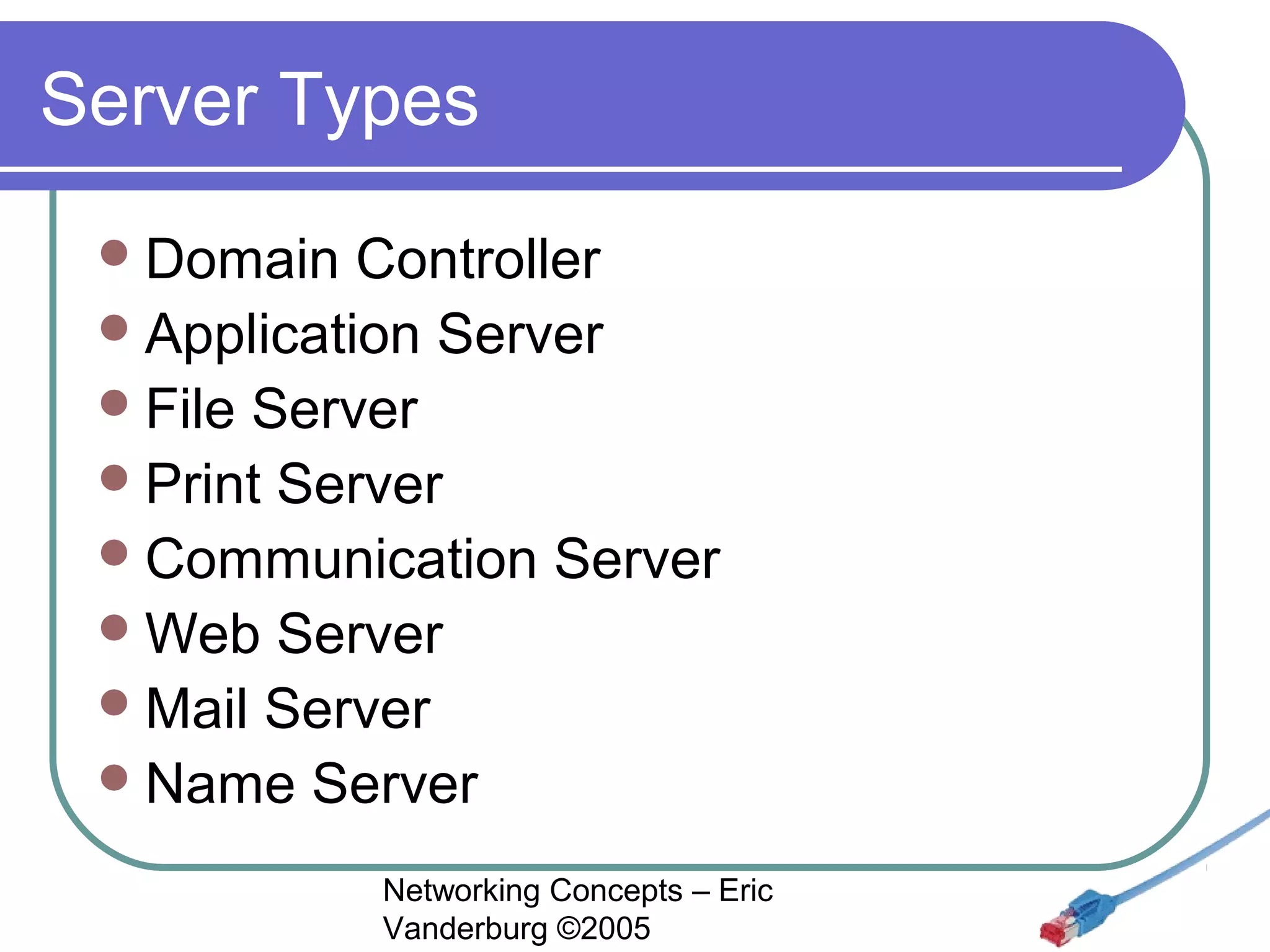
This document provides an introduction and overview of key networking concepts. It discusses the instructor's background and certifications. Some key points covered include how networks can reduce redundancy, enhance capabilities, share resources, and allow communication. Important acronyms like LAN, WAN, MAN, and NIC are defined. The document also summarizes network basics, types including client/server and peer-to-peer, advantages and disadvantages of each, and different server needs, vendors, and types.