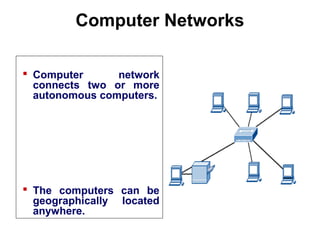
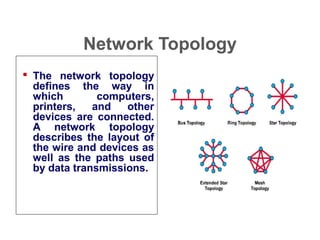
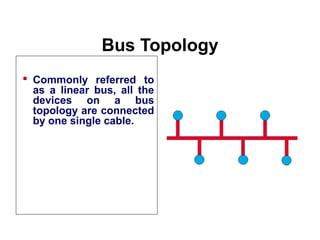
This document provides an overview of information networks presented by Dr. Kamal Gulati. It covers topics such as networked enterprises, business uses of the internet, intranets and extranets, and distributed/cloud computing. It then details 30 topics related to computer networks including networking terminology, models, classifications, topologies, components, media, and applications. The document concludes with profiles of Dr. Kamal Gulati which outlines his academic and professional experience working in computer science and information technology fields.

























![Dr. Kamal Gulati
Associate Professor |
University Quality Support Head |
Mentoring Programme Coordinator
[Ph. D., M.Sc. (Computer Science), M.C.A., M.B.A]
Professional Certifications:
•Certified Microsoft Innovative Educator
•Data Science 101 Certification from Big Data University
•R Language 101 Certification from Big Data University
•SQL Certification from SOLOLEARN.com
•Certified IBM Big Data 101 from Big Data University
•R Program & Python Certified from DataCamp
•Wiley Certified Big Data Analyst [WCBDA]
•Certification on DBMS from IIT Mumbai
•Certified Cisco Certified Network Associate [CCNA]
•Certified Microsoft Certified Professional [MCP]
•Certified Brainbench in Computer Fundamentals, Microsoft Access, MySQL 5.7 Administration &
Microsoft Project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationnetworks-171208050509/85/Information-Networks-Covered-all-the-Important-Topics-47-320.jpg)




