Embed presentation
Downloaded 154 times



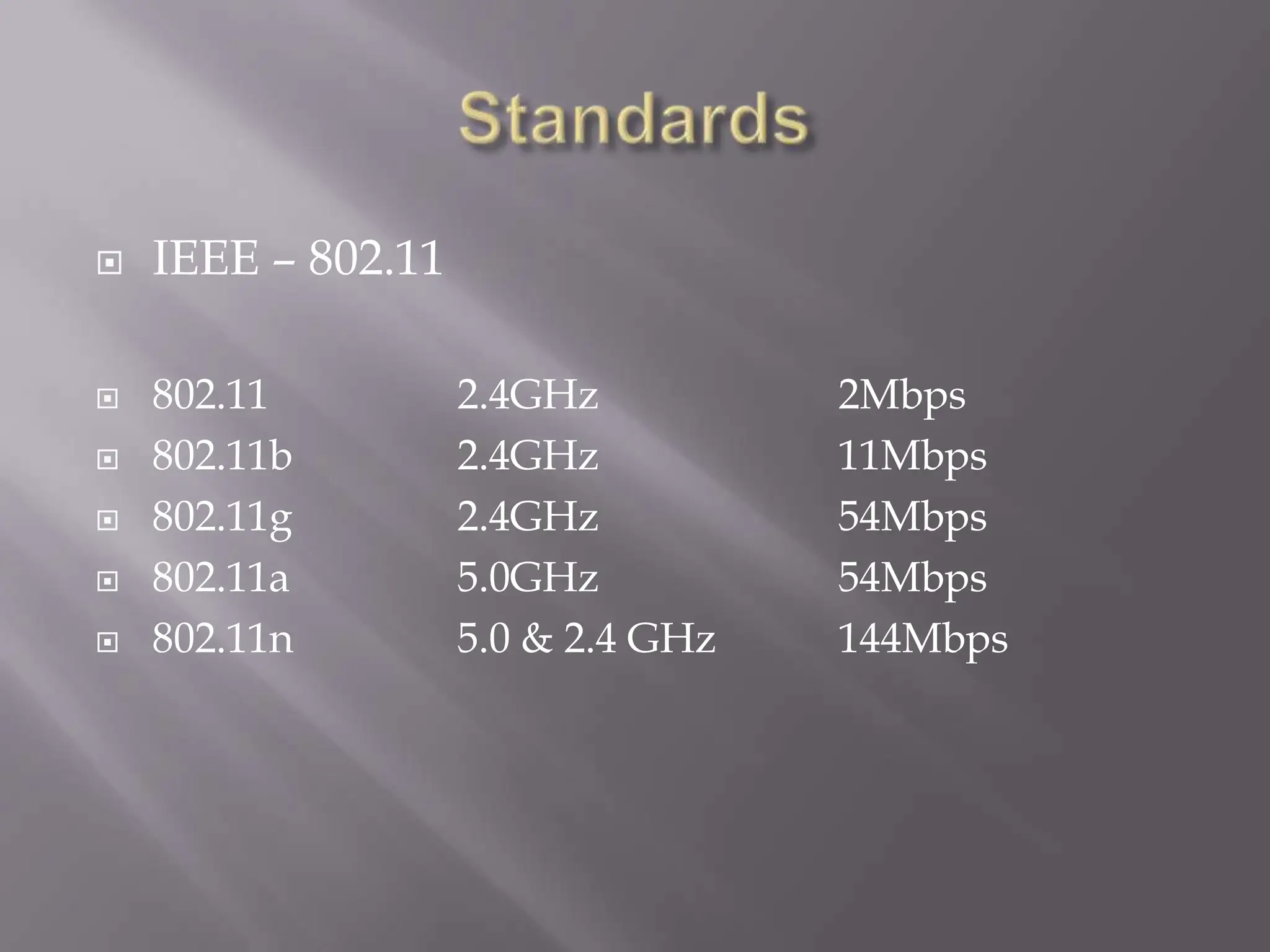

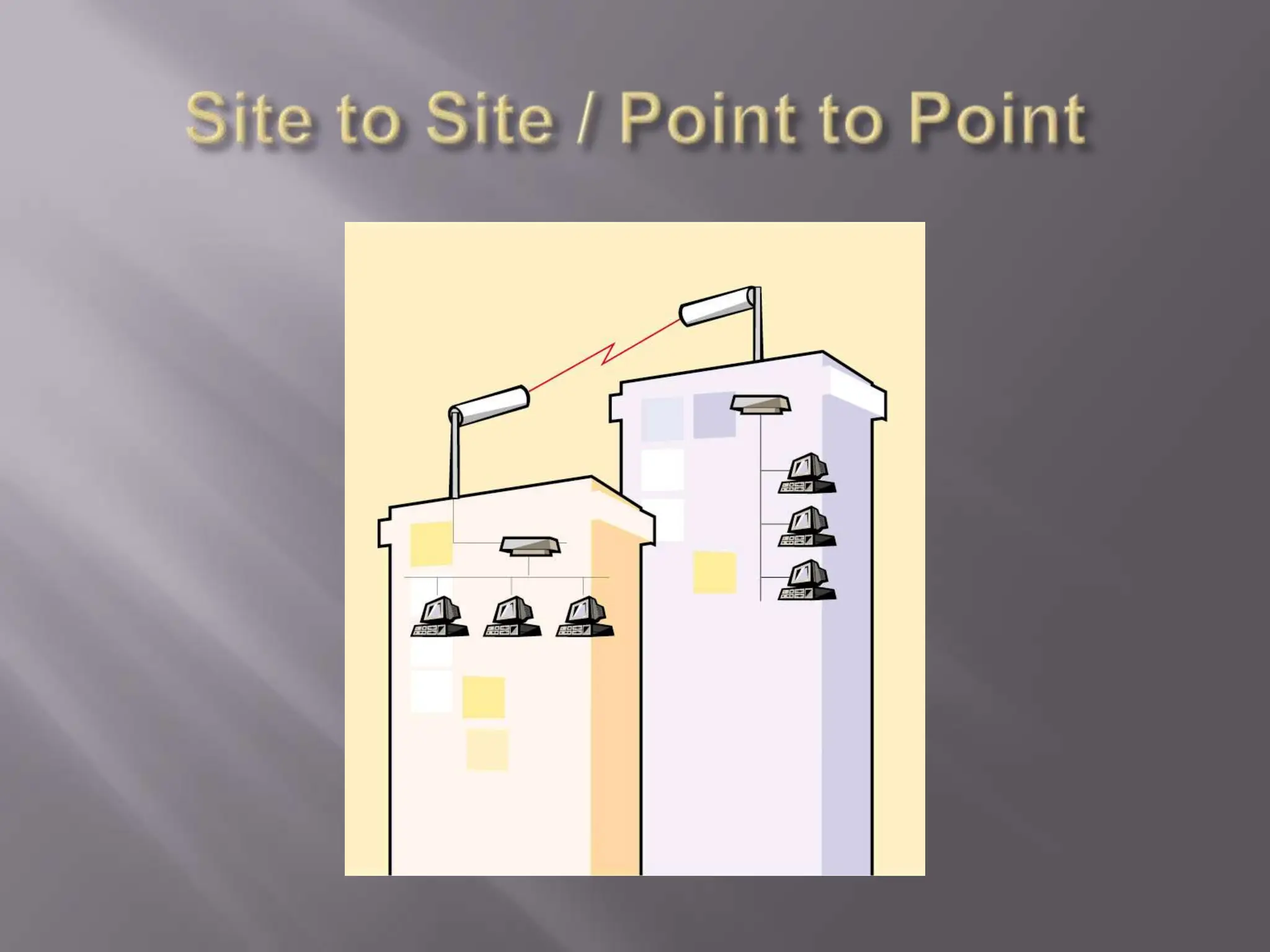
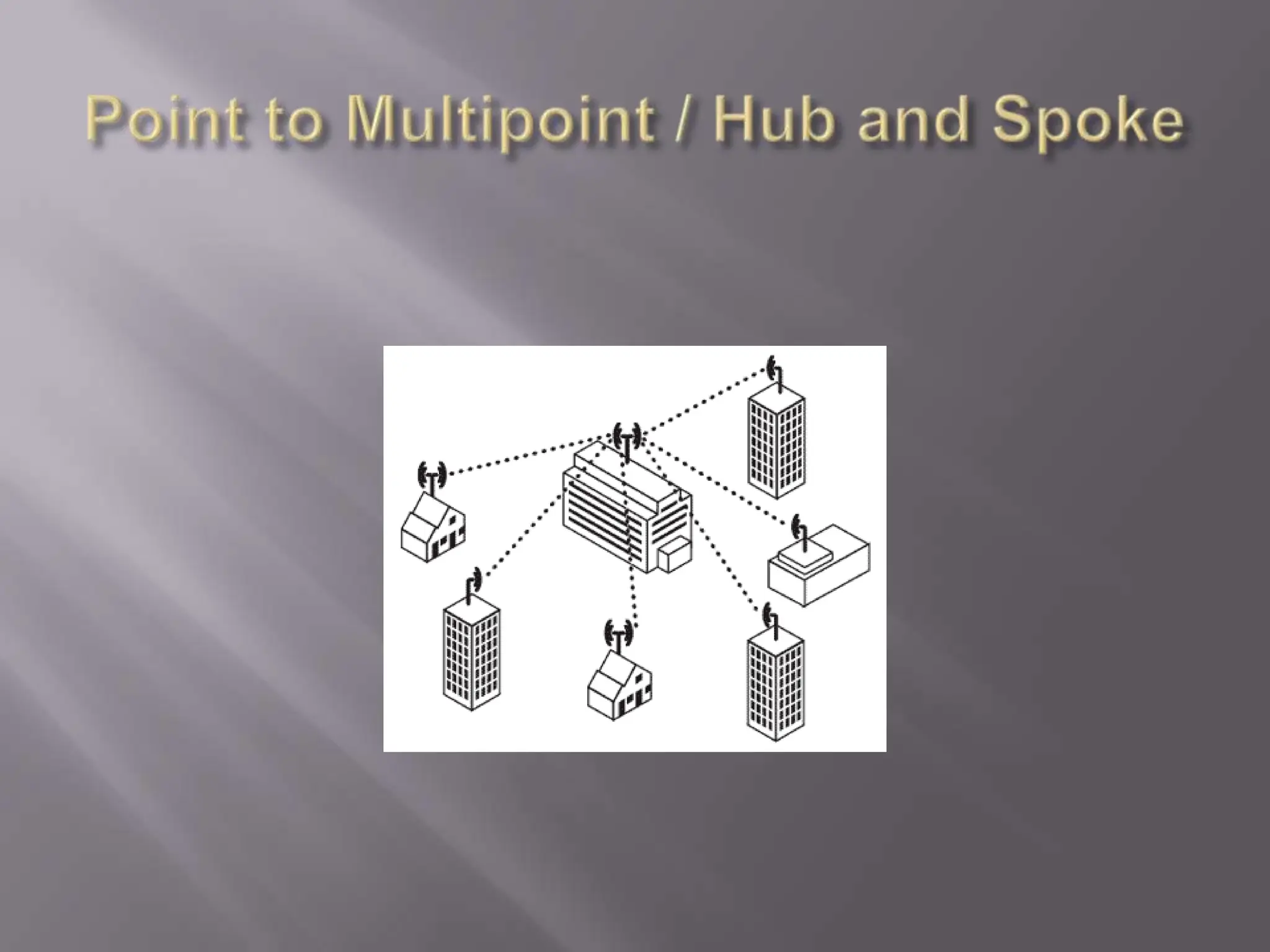


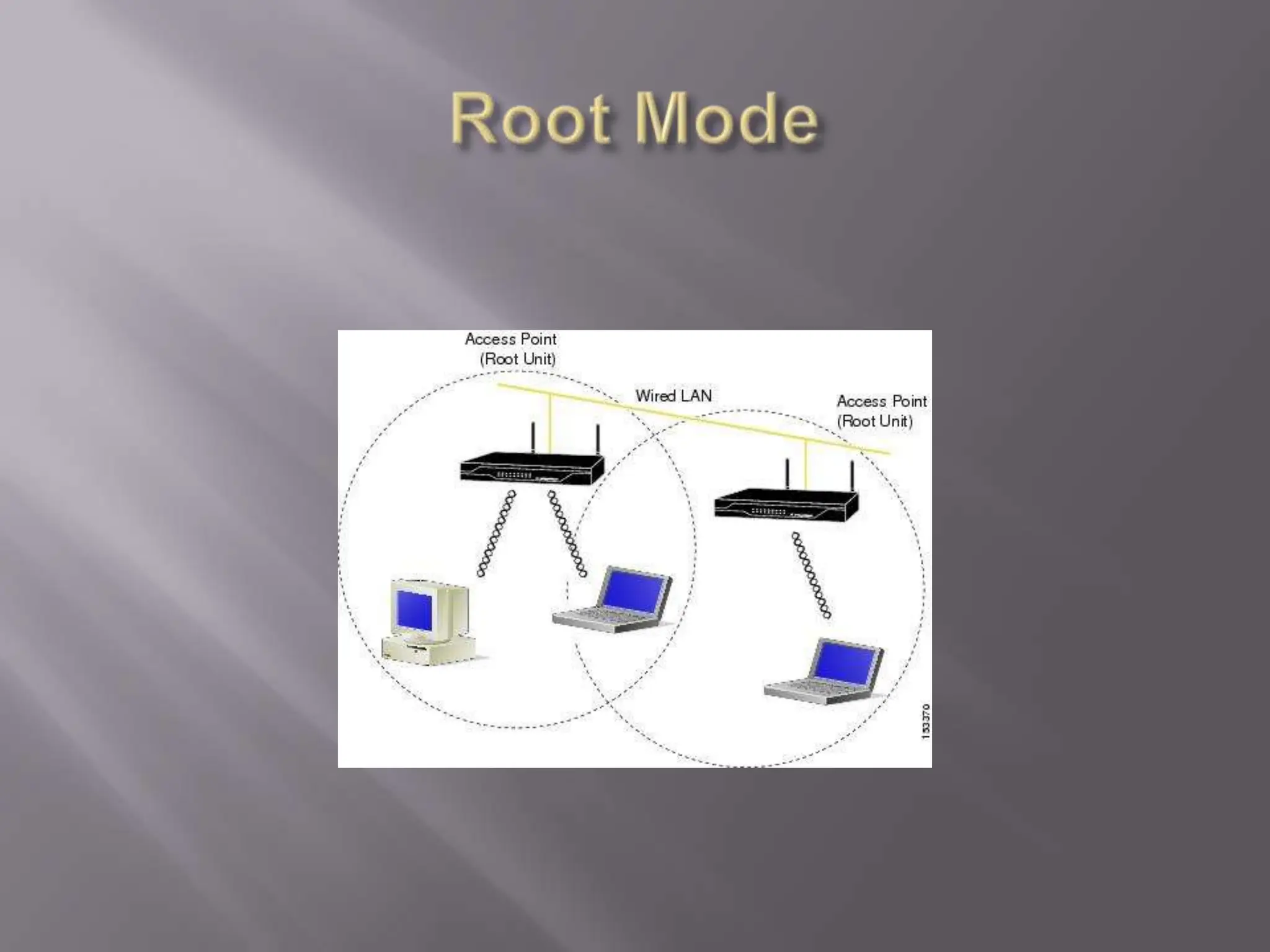
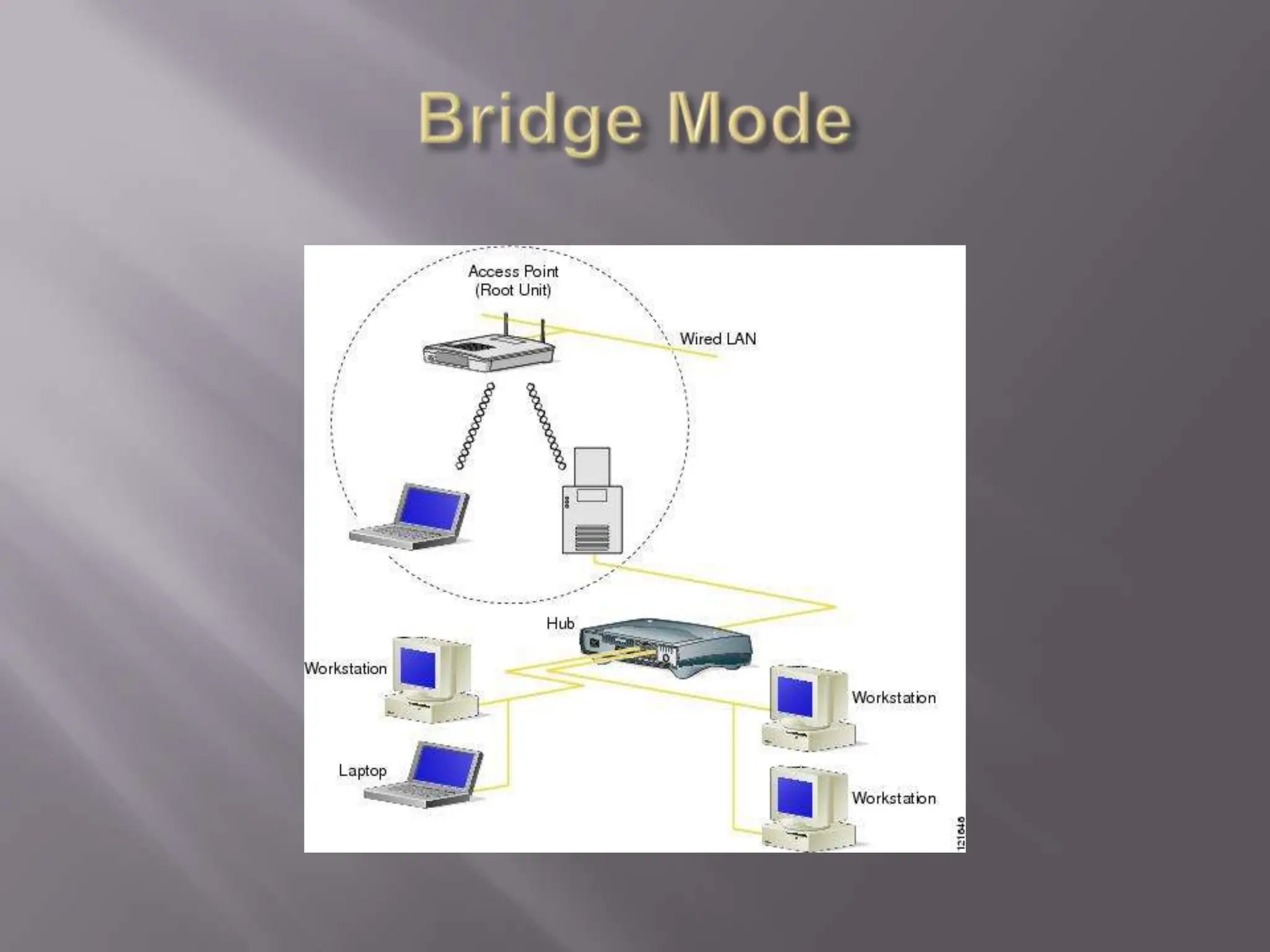
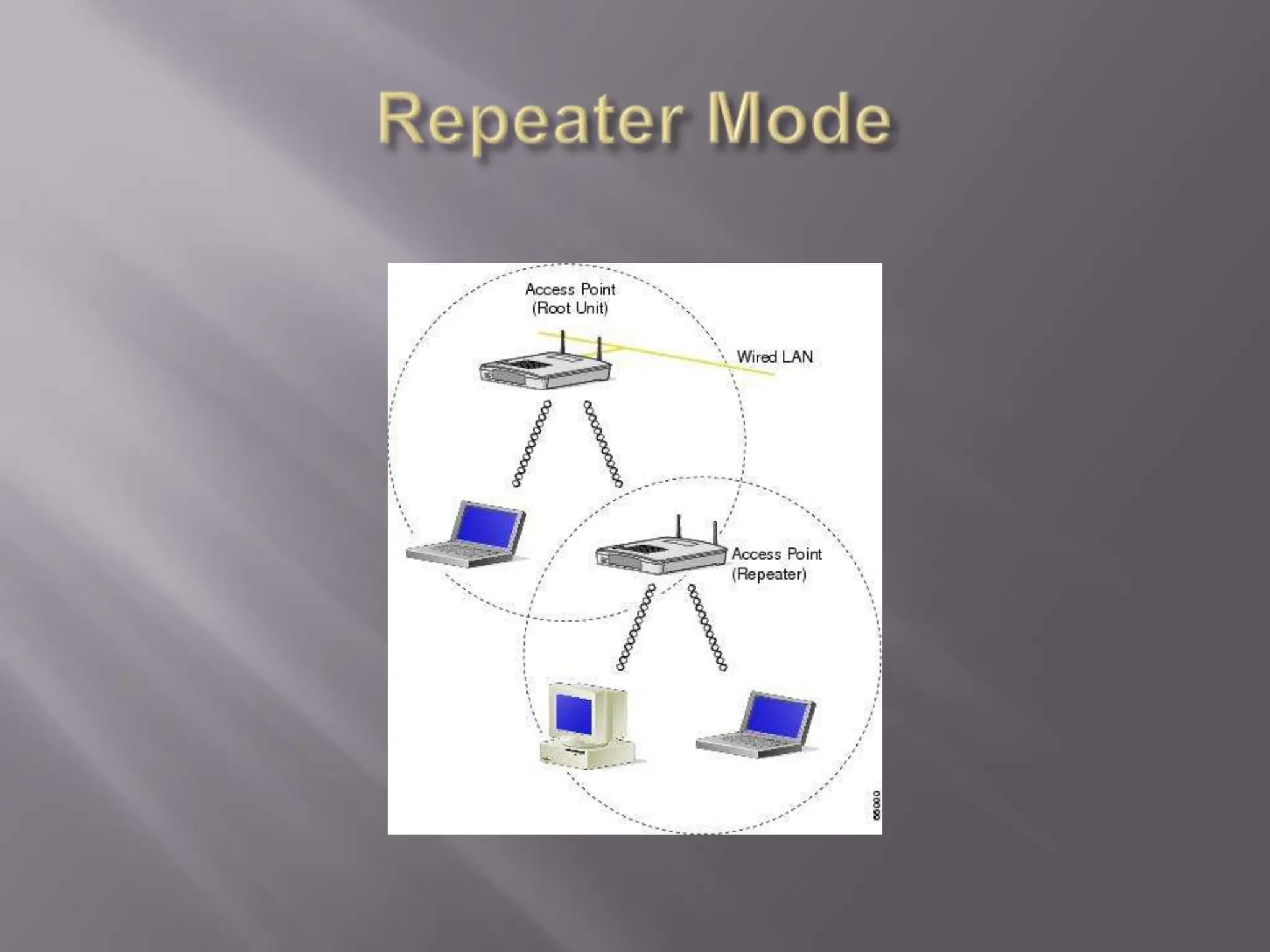



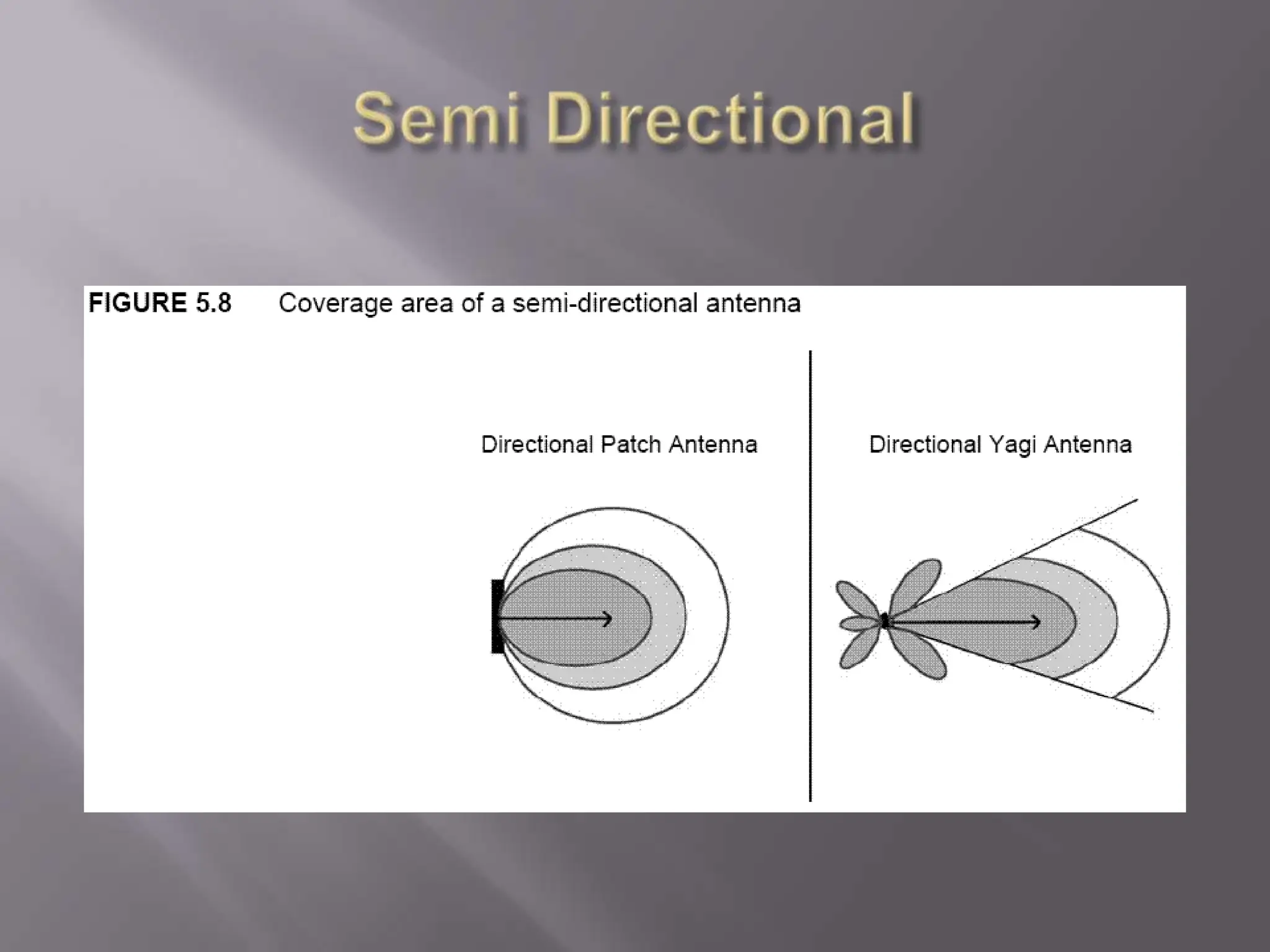








The document discusses wireless networking, highlighting key governing bodies such as the FCC and IEEE, while outlining the benefits and drawbacks of wireless technology. It details various standards and architectures, including IEEE 802.11 specifications and types of devices like access points and antennas. The security protocols for wireless networks, such as WEP and WPA, are also addressed, emphasizing their importance in securing connections.






















