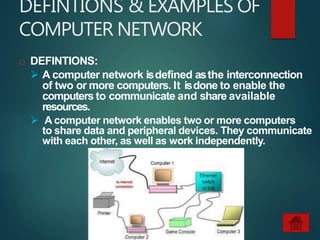
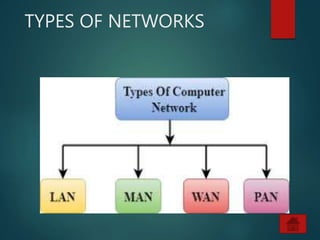
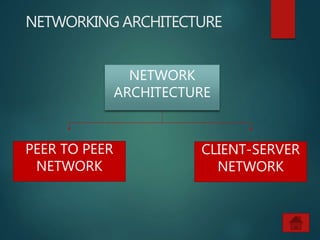
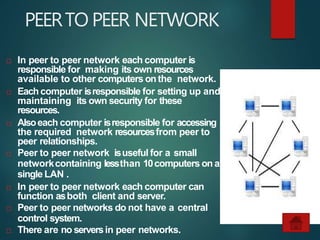
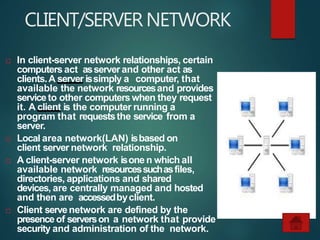
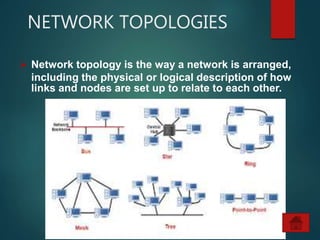
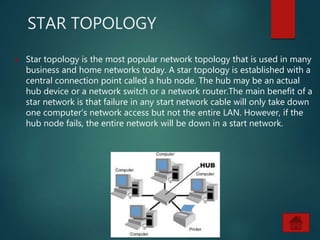
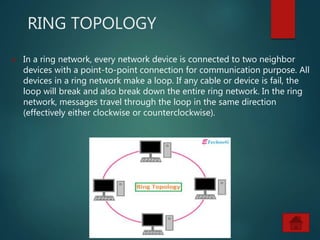
The document provides an overview of basic networking concepts, including definitions, advantages, components, types of networks, network architecture, topologies, and security. It explains that a computer network allows for resource sharing and communication among interconnected computers and describes various network types such as LAN, WAN, and PAN. Additionally, it covers different network topologies including star, ring, bus, and mesh, along with network security principles to protect against unauthorized access.