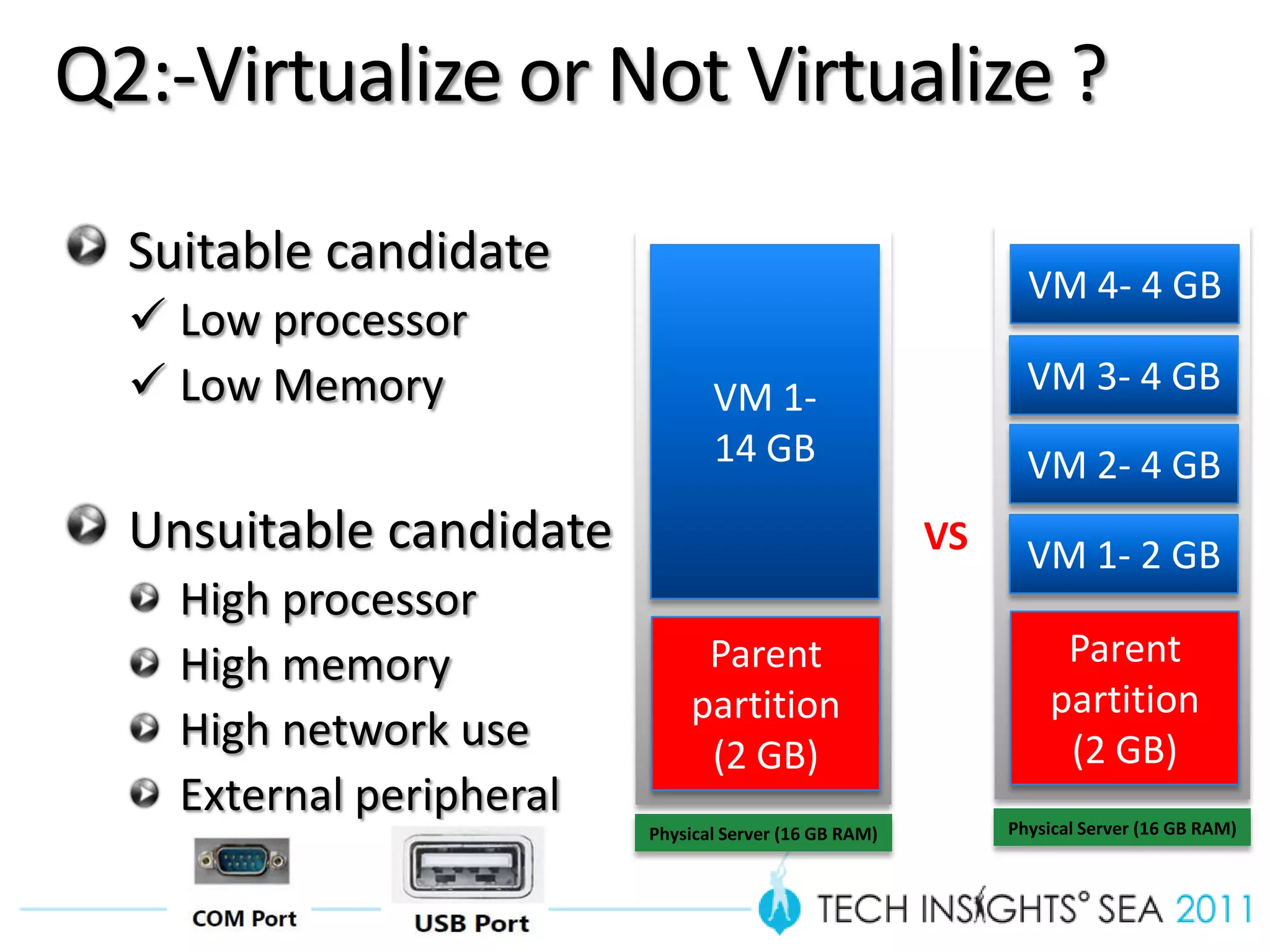
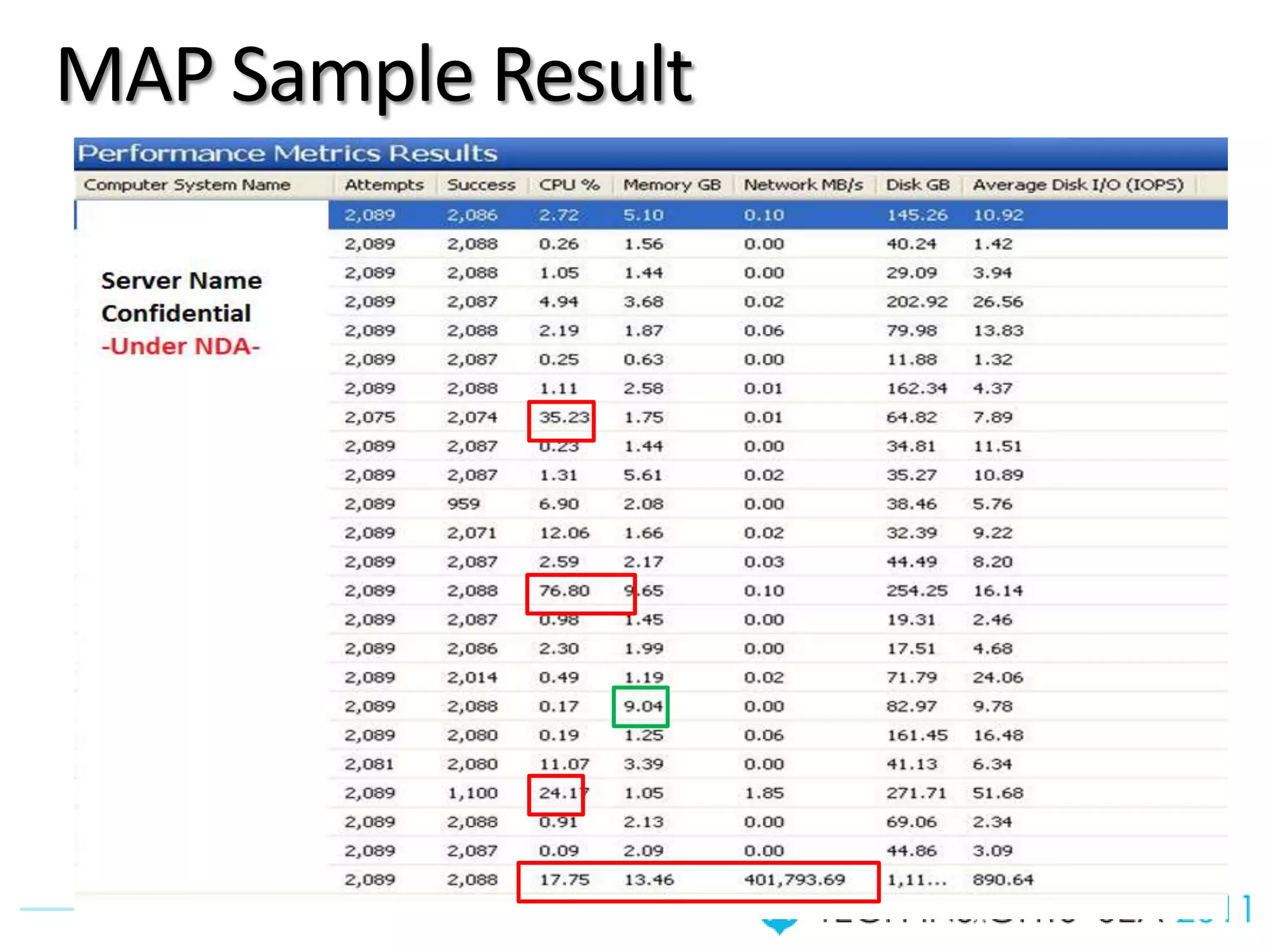
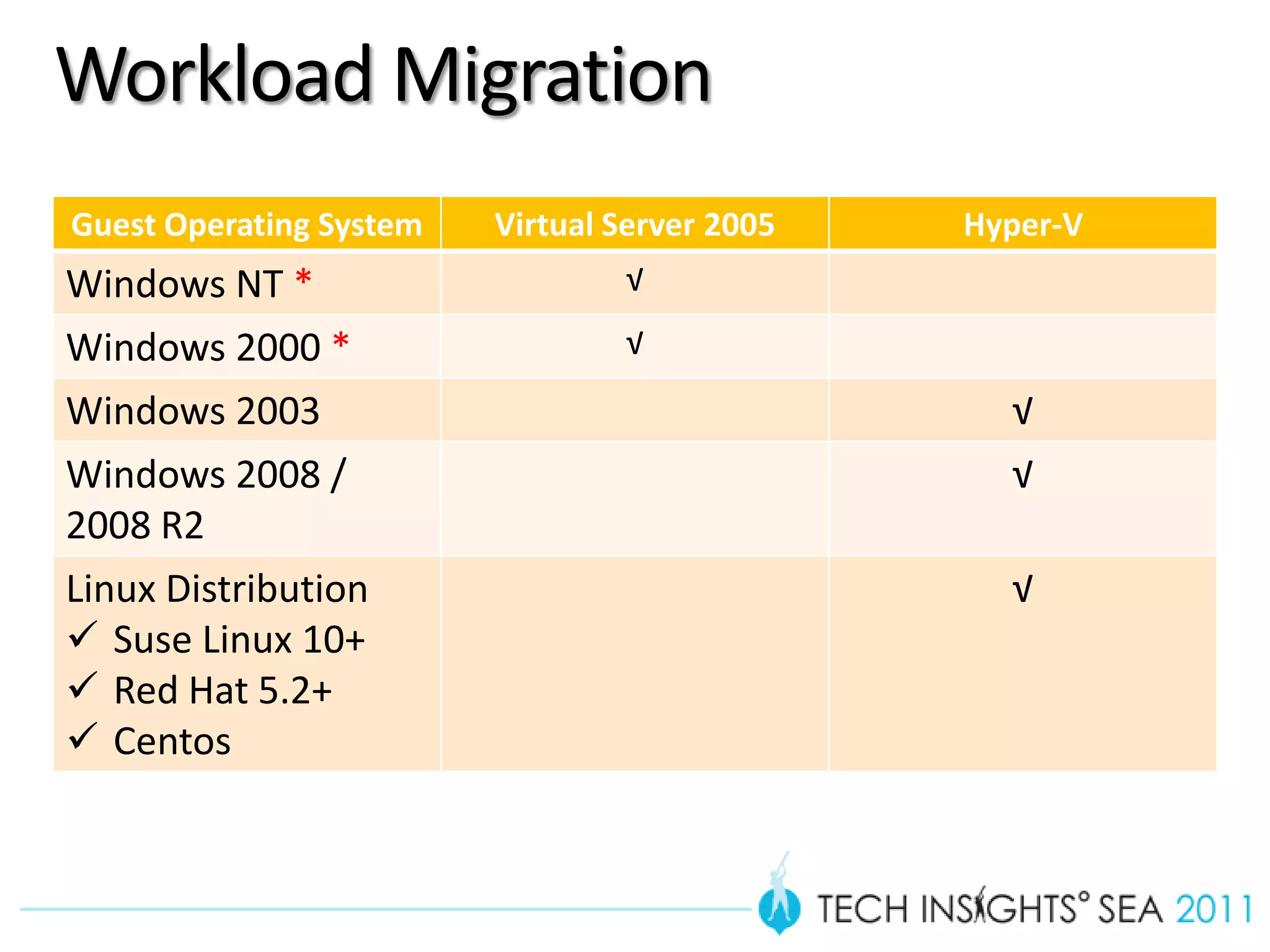
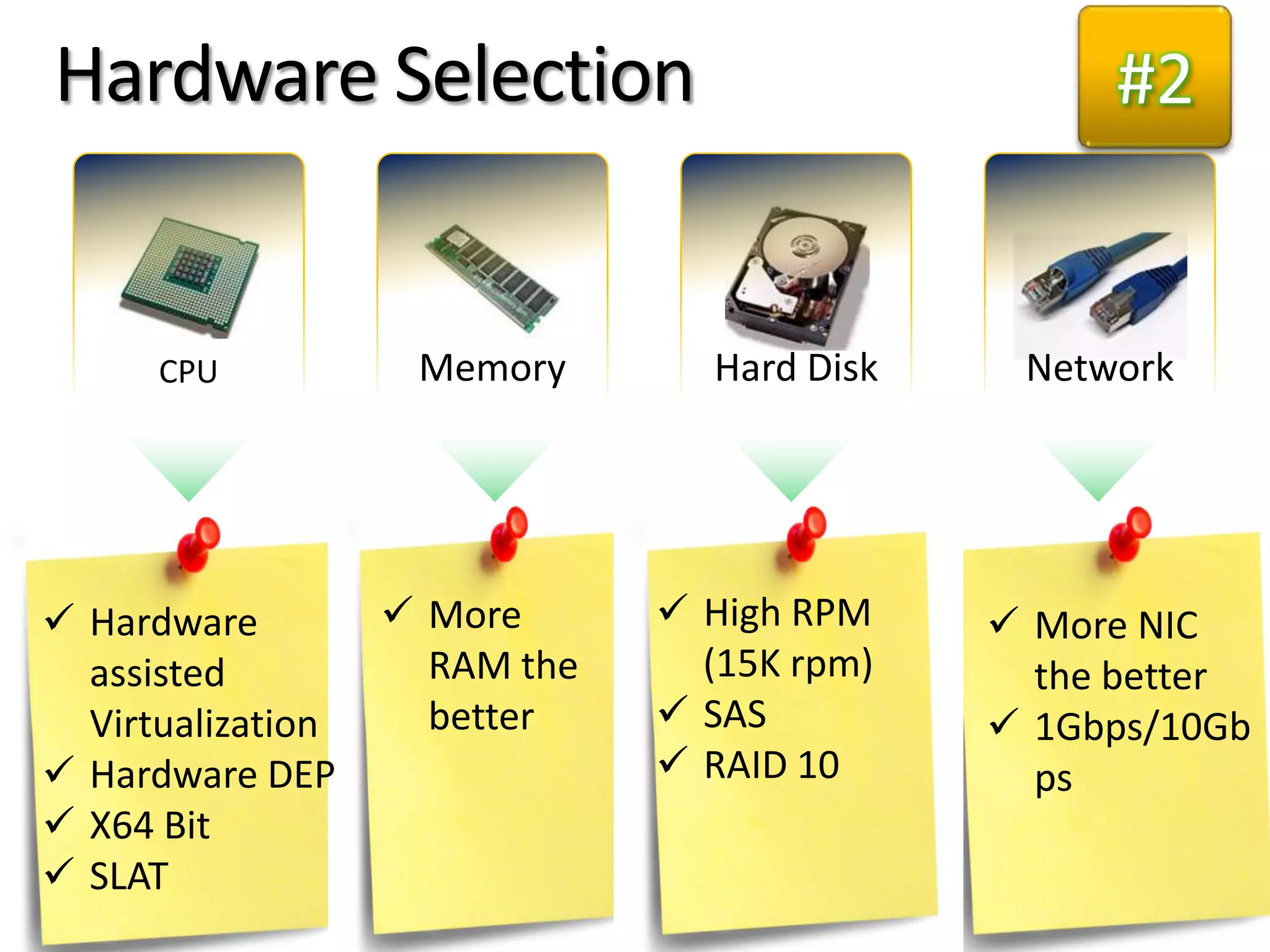
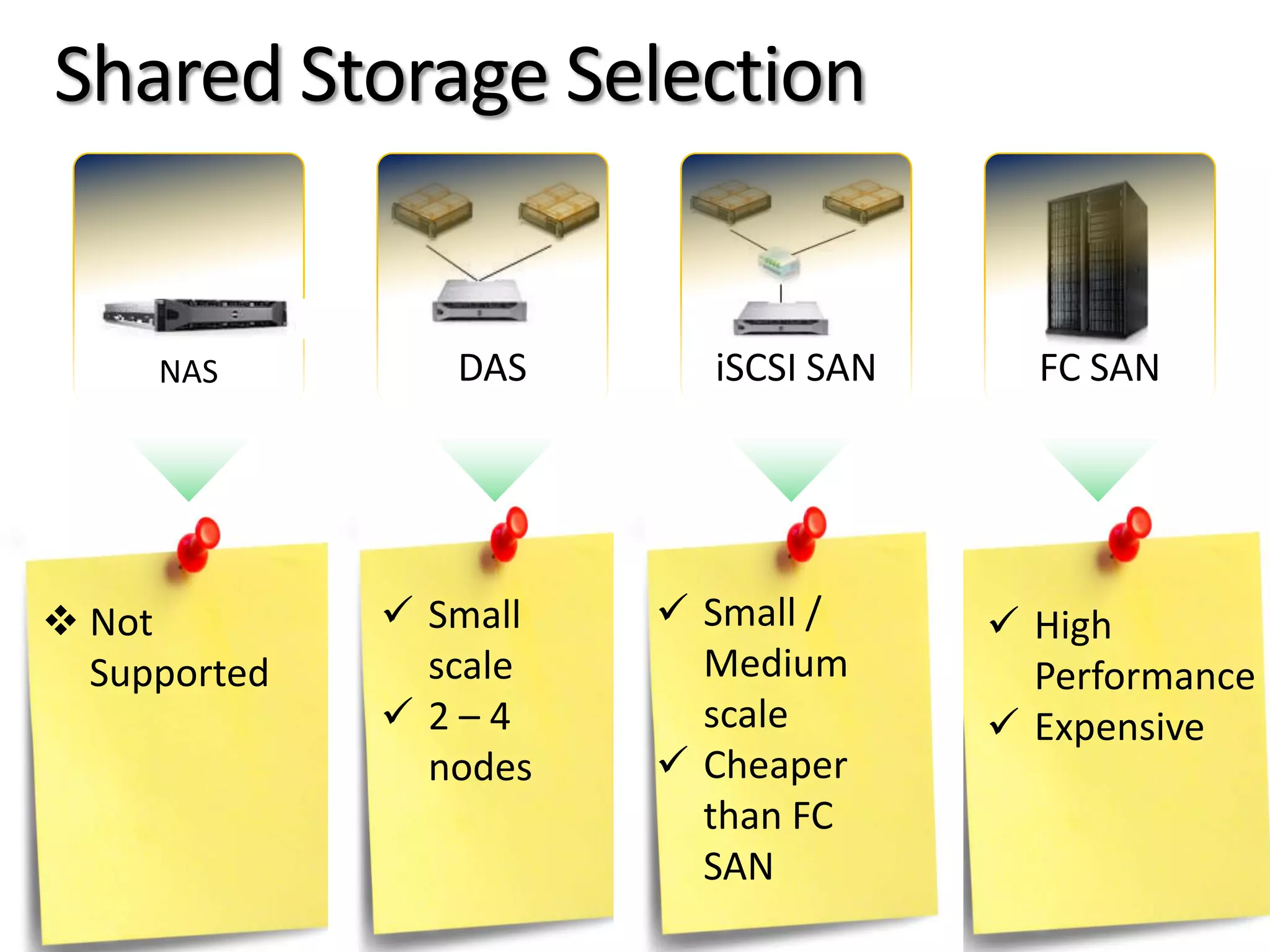
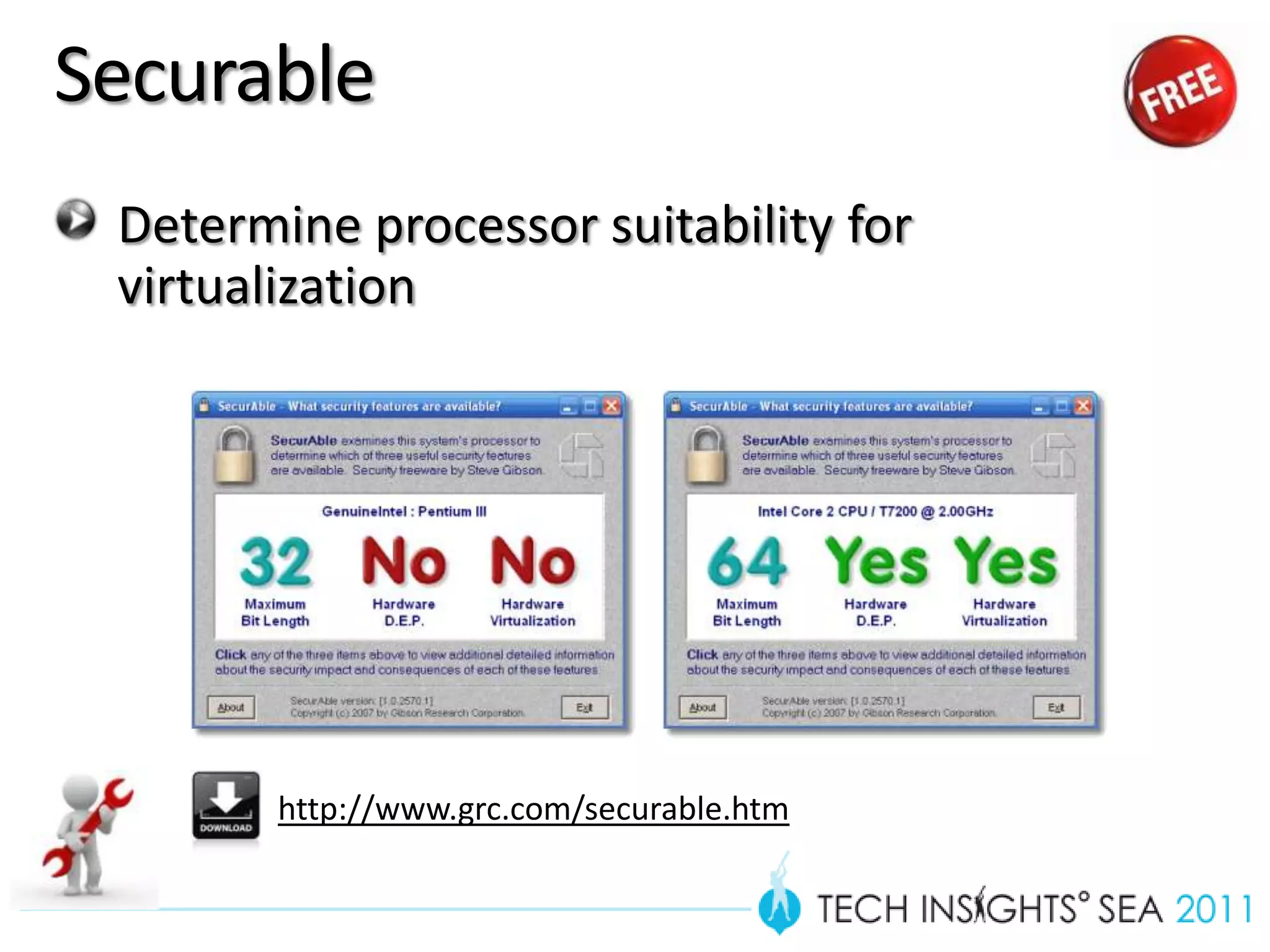
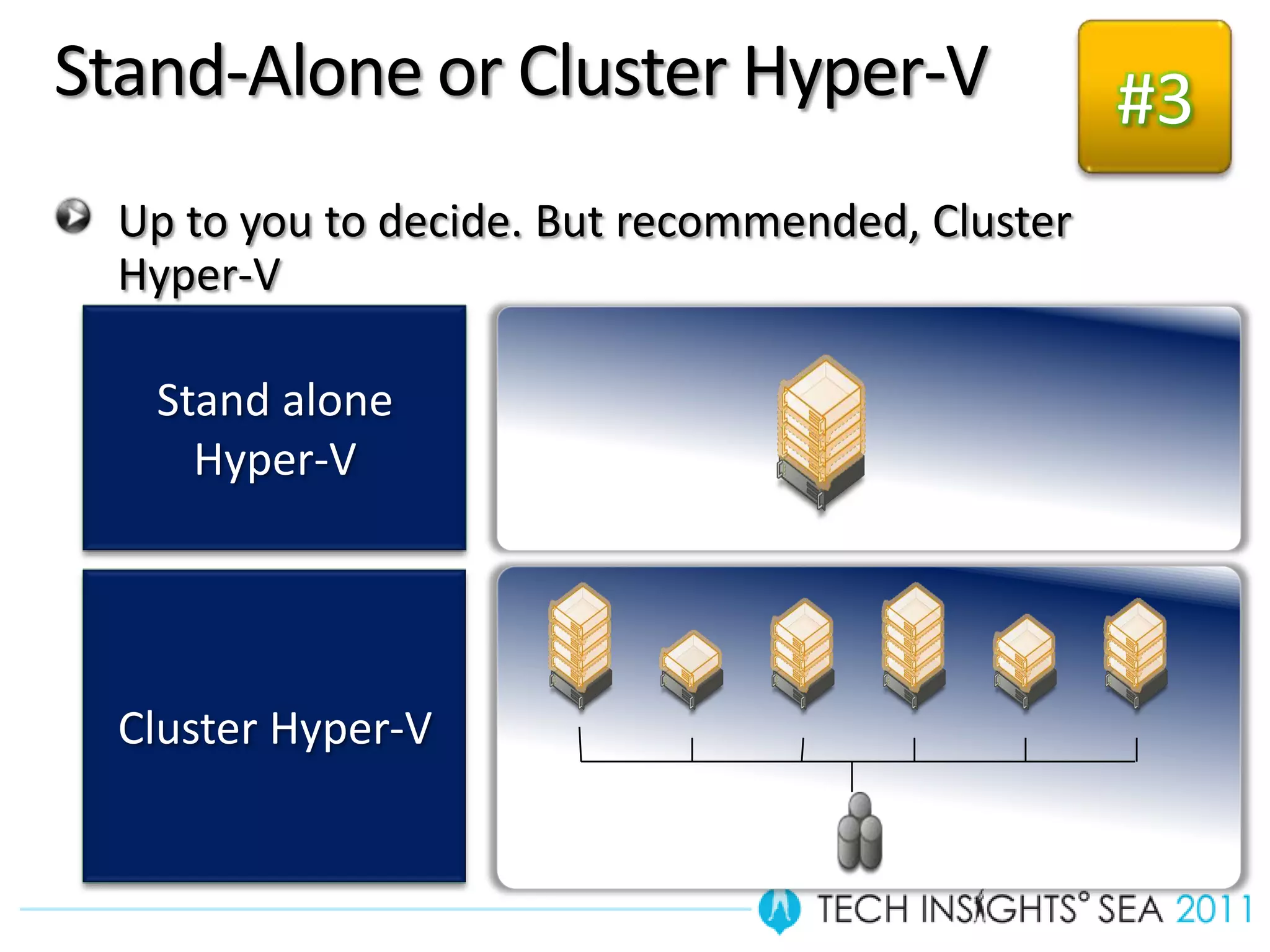
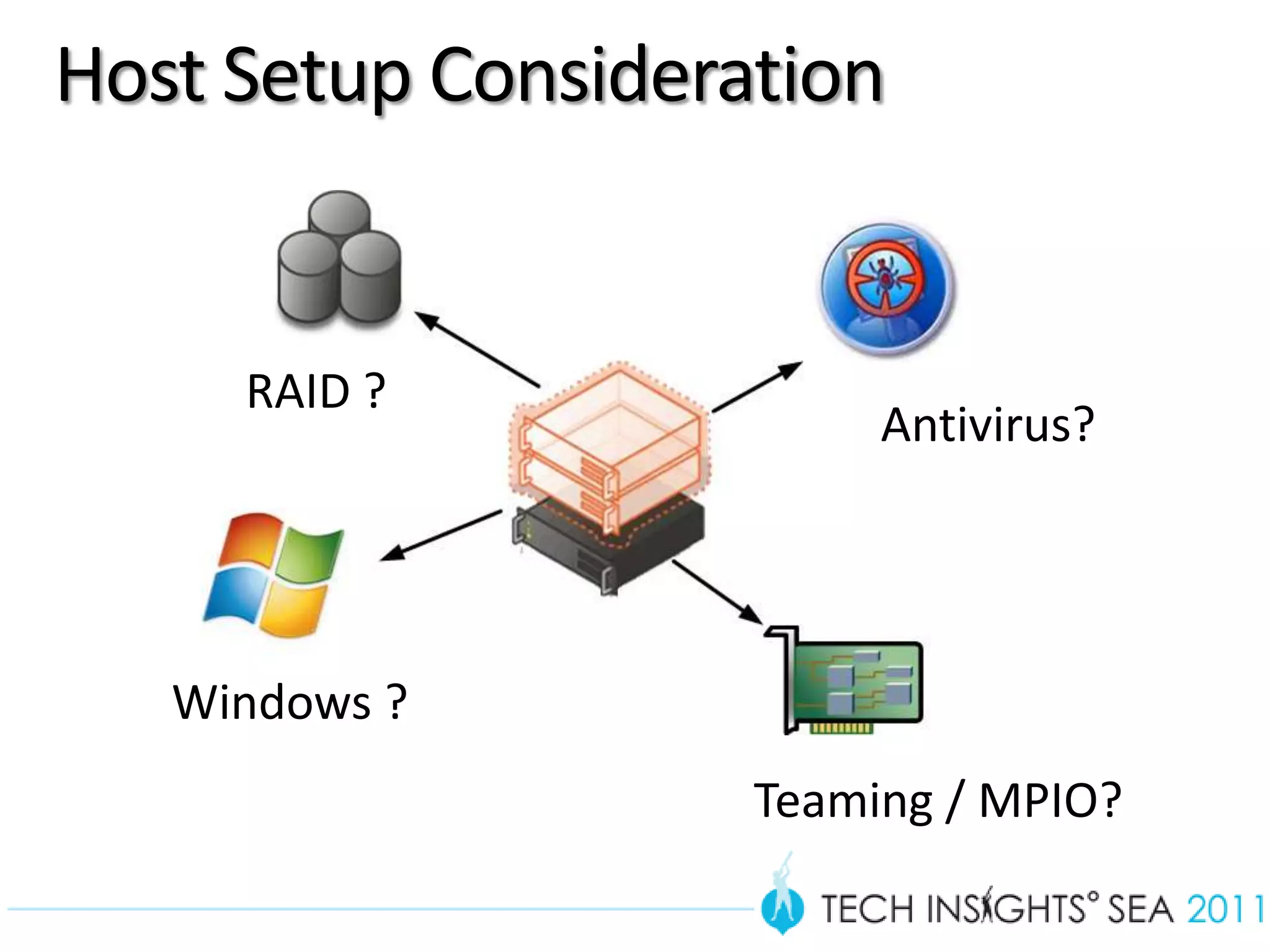
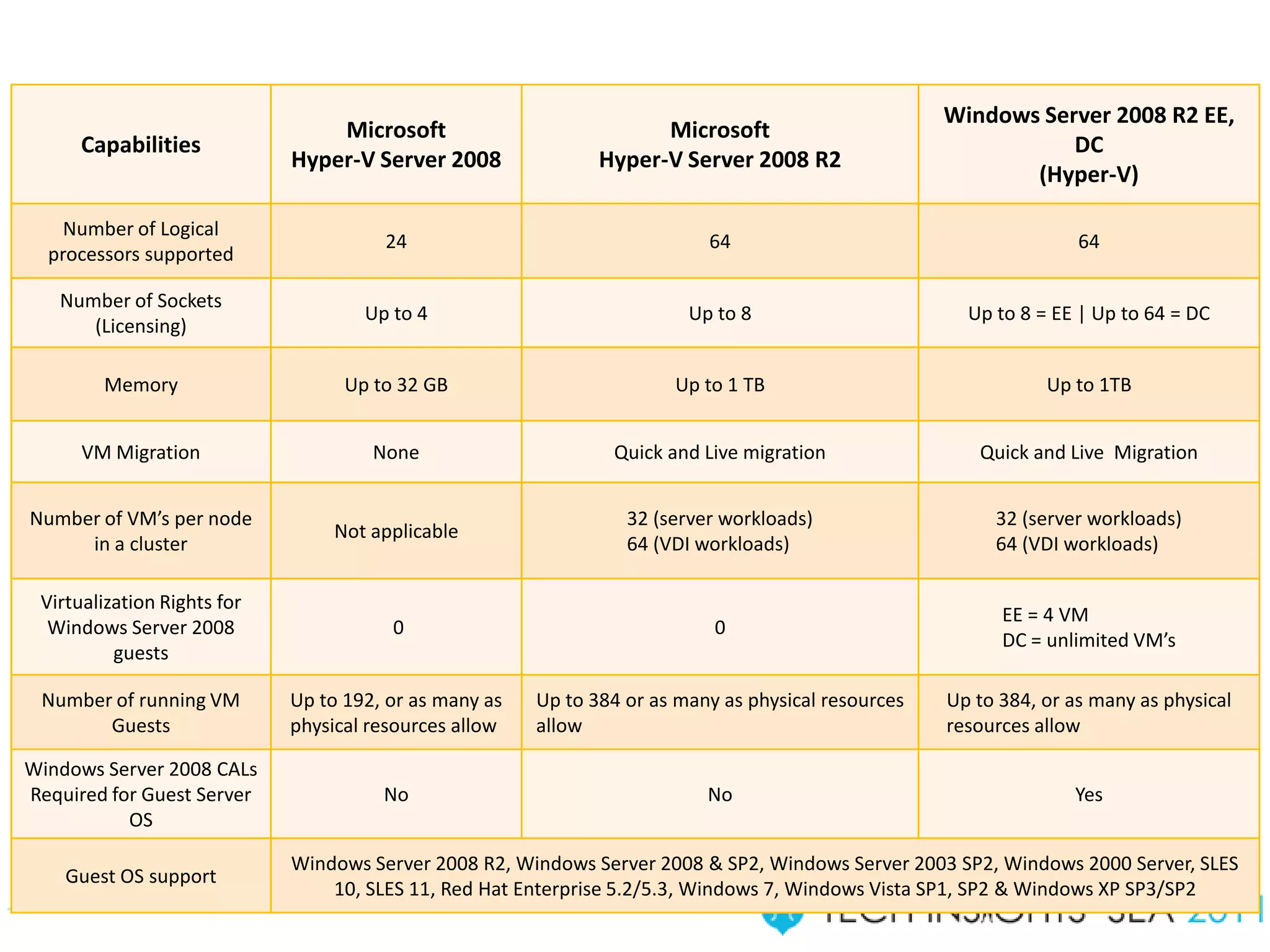
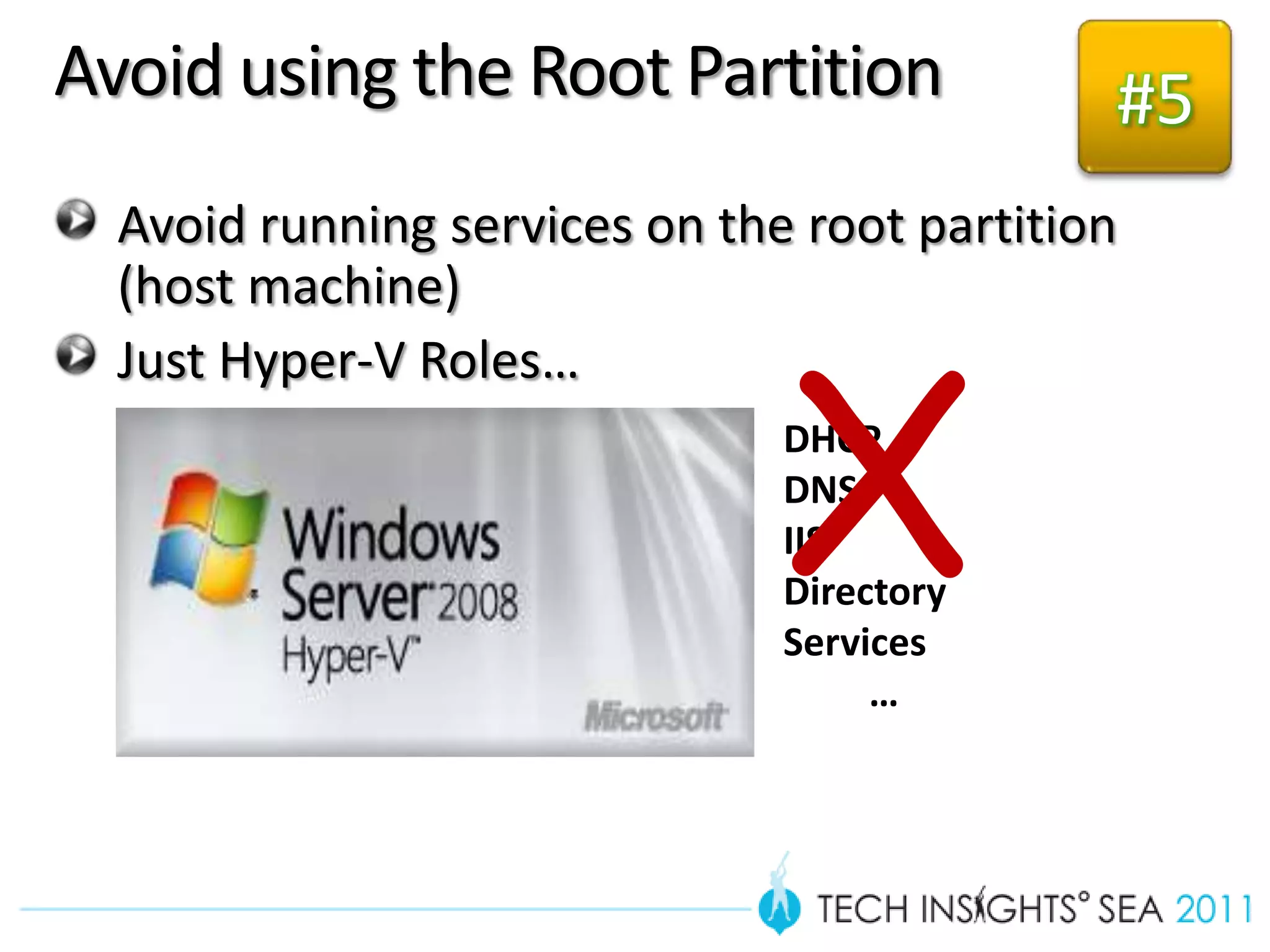
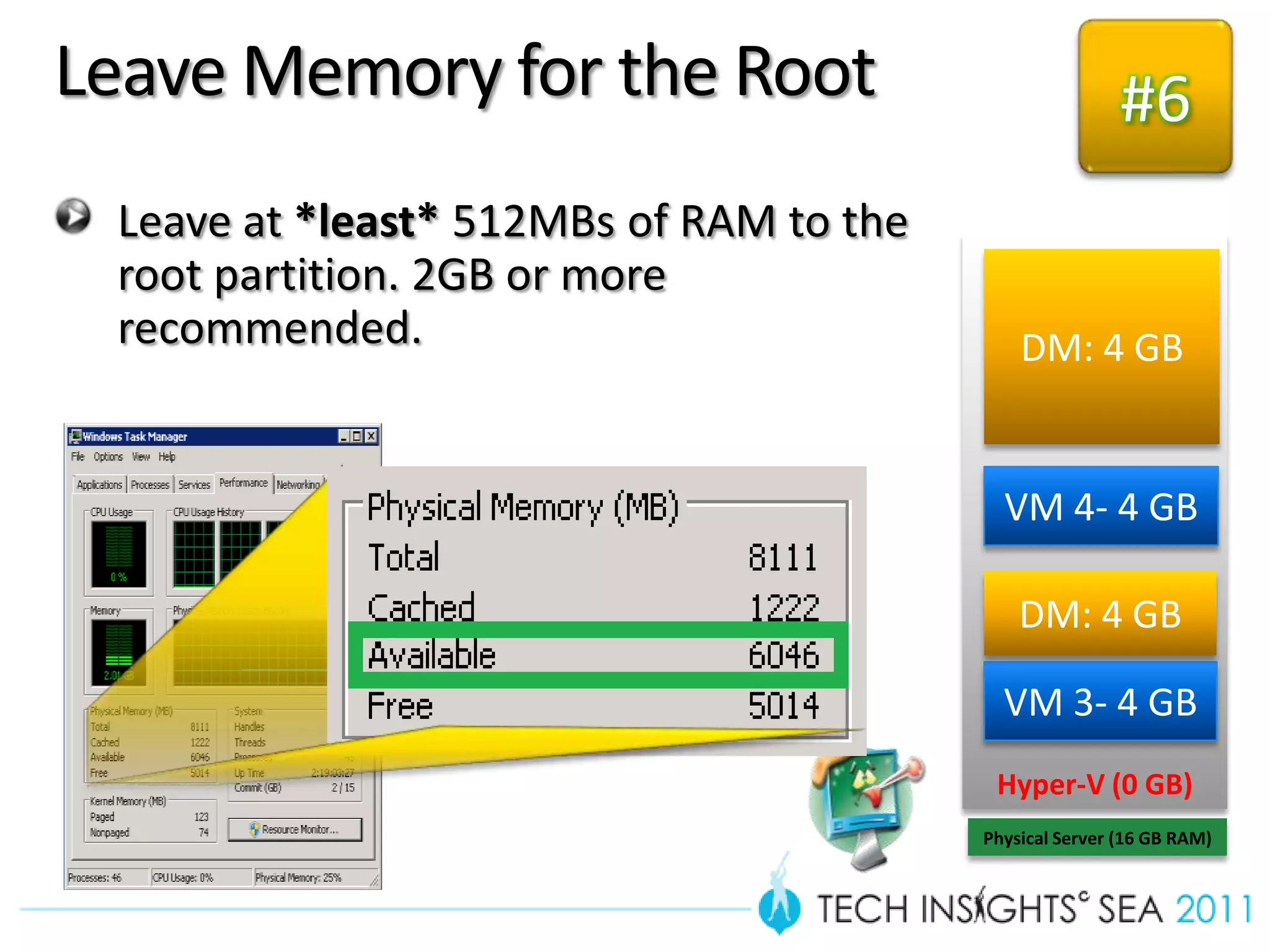
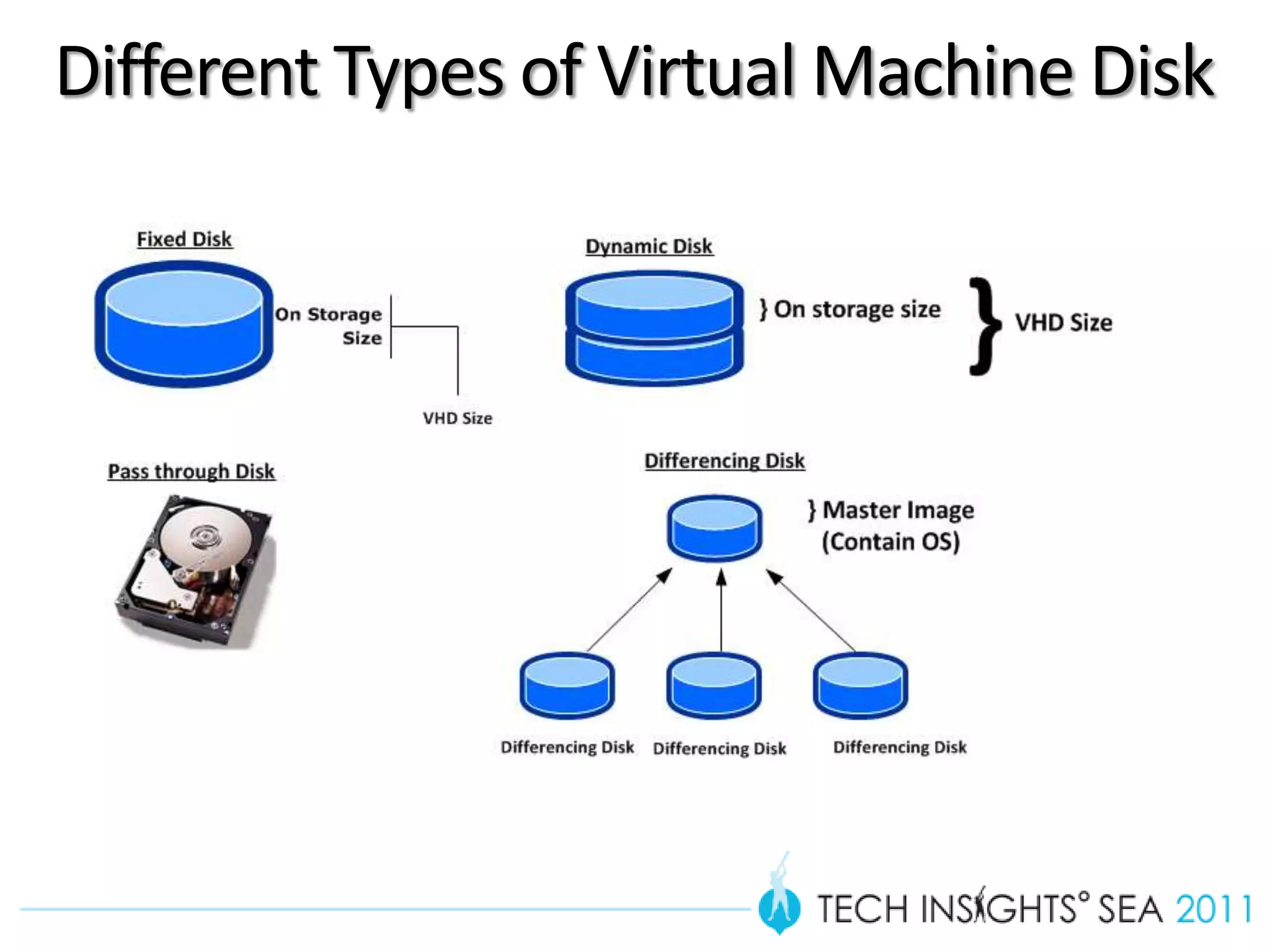
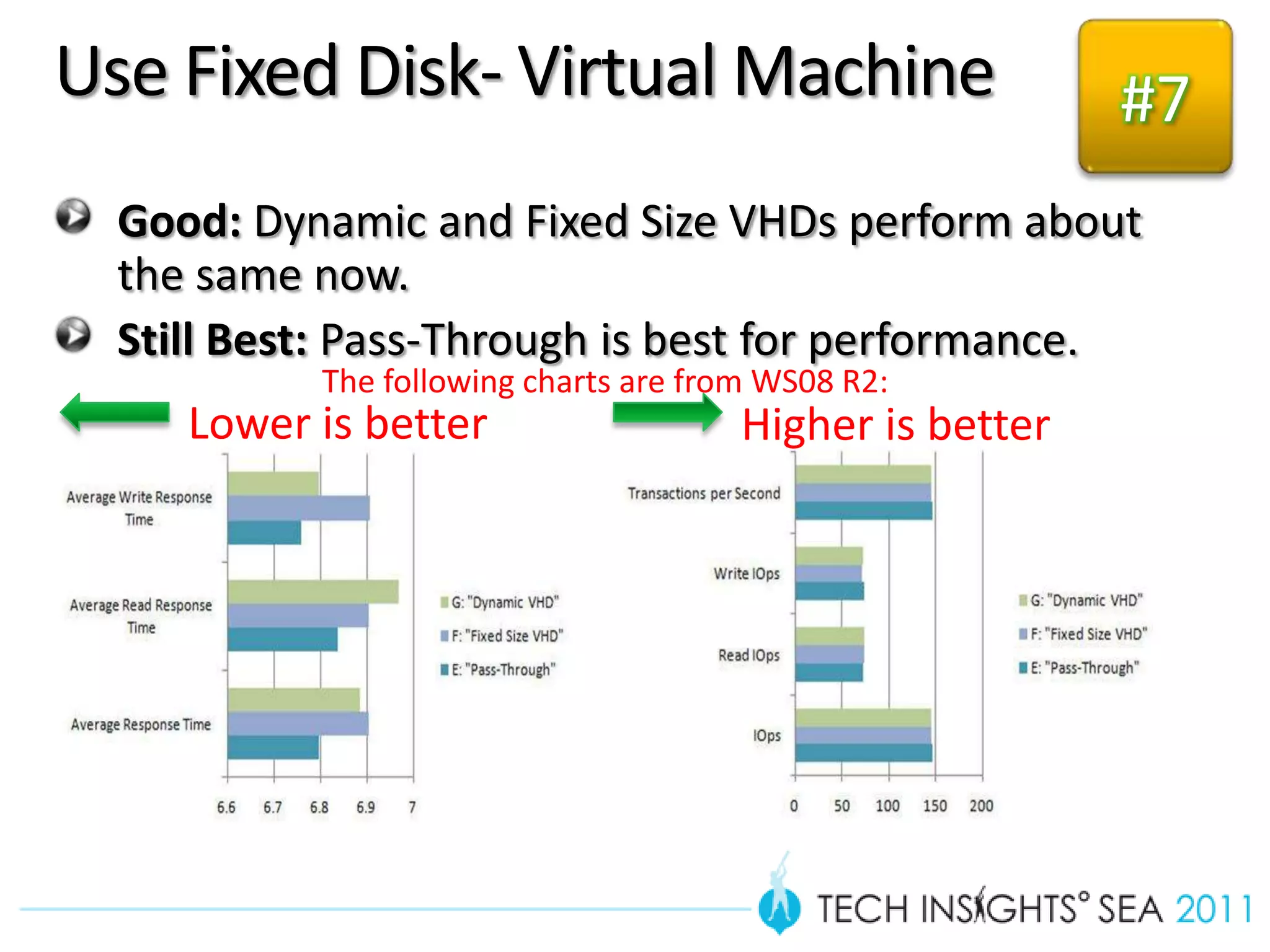
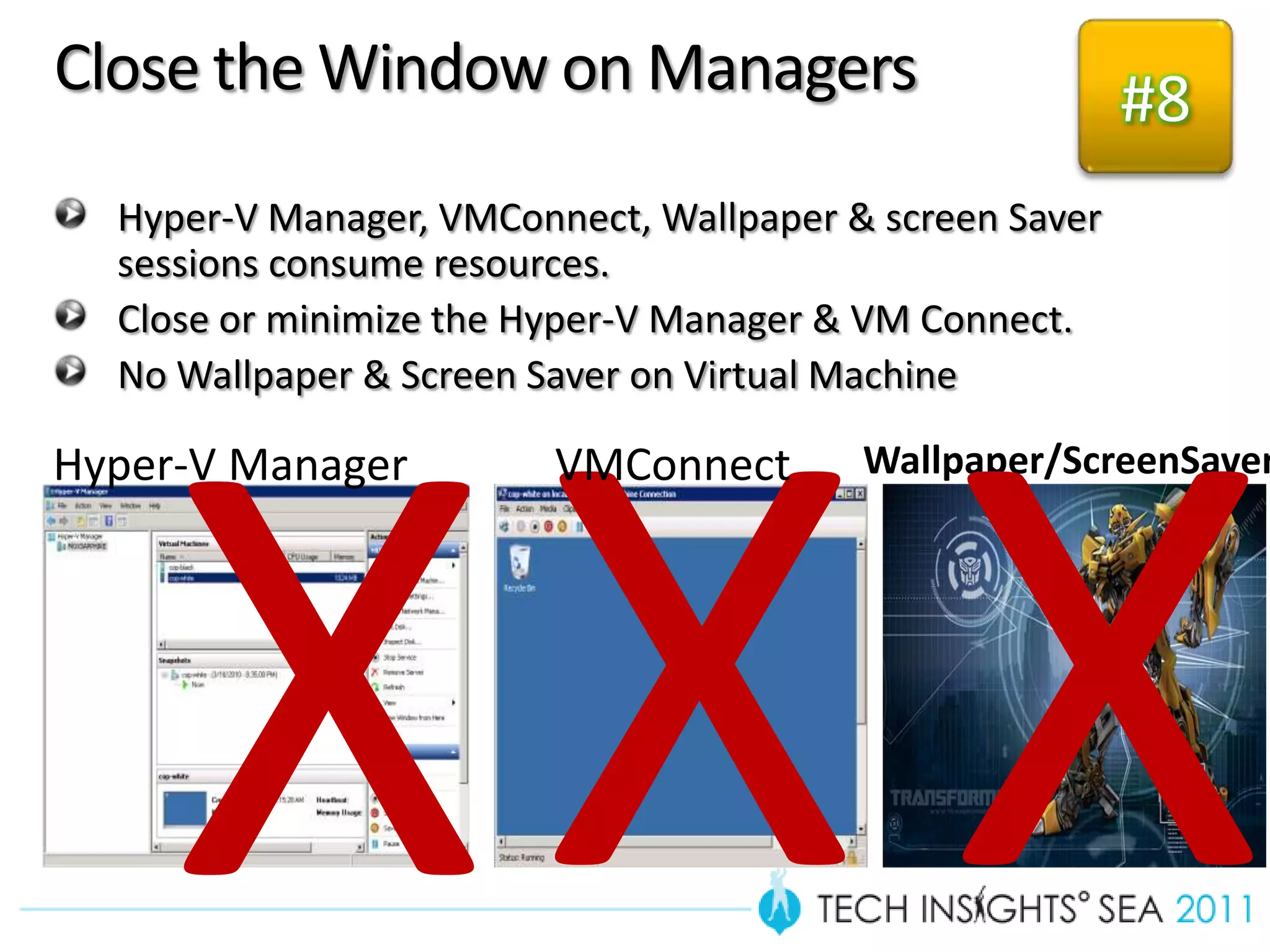
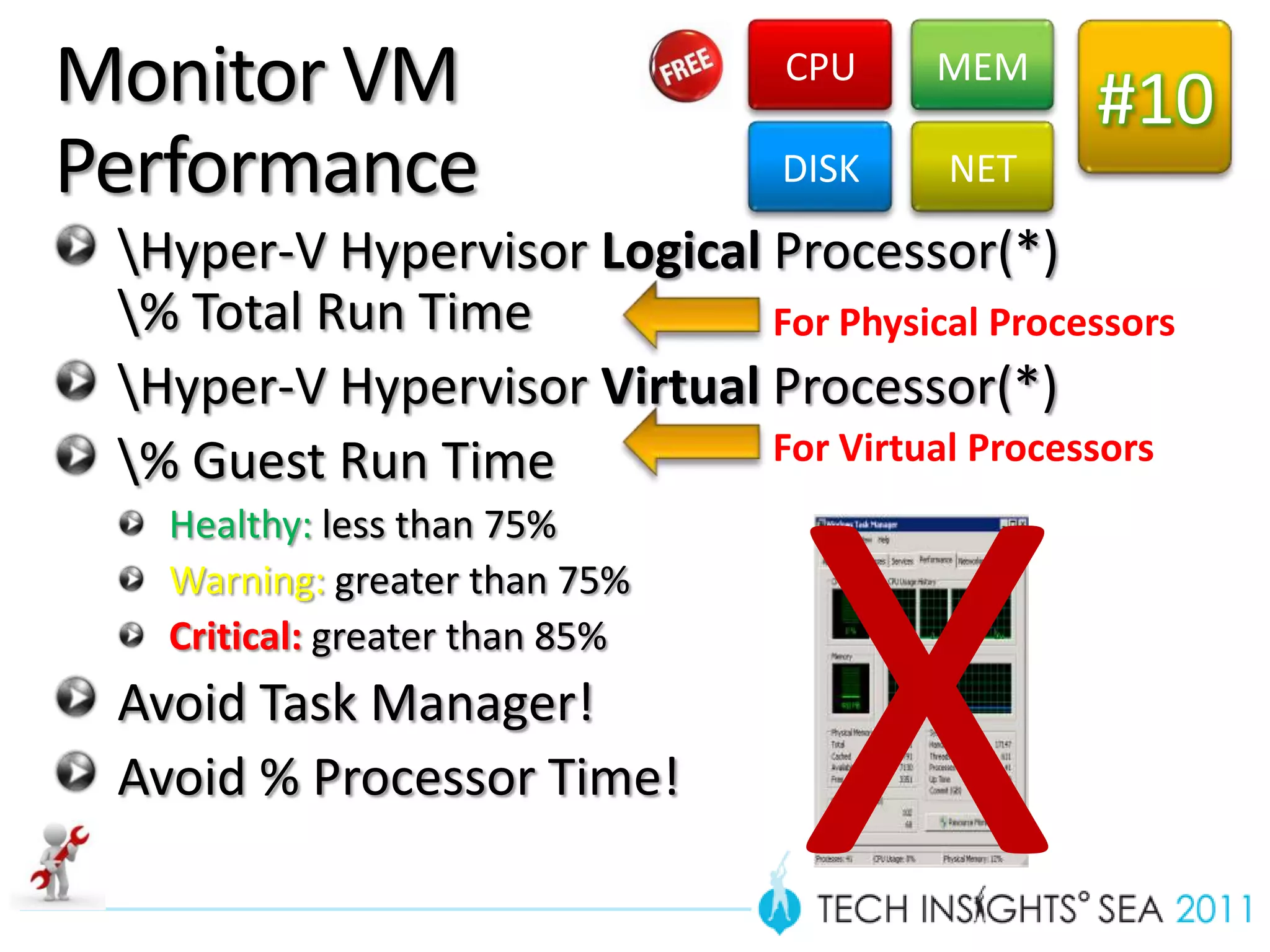
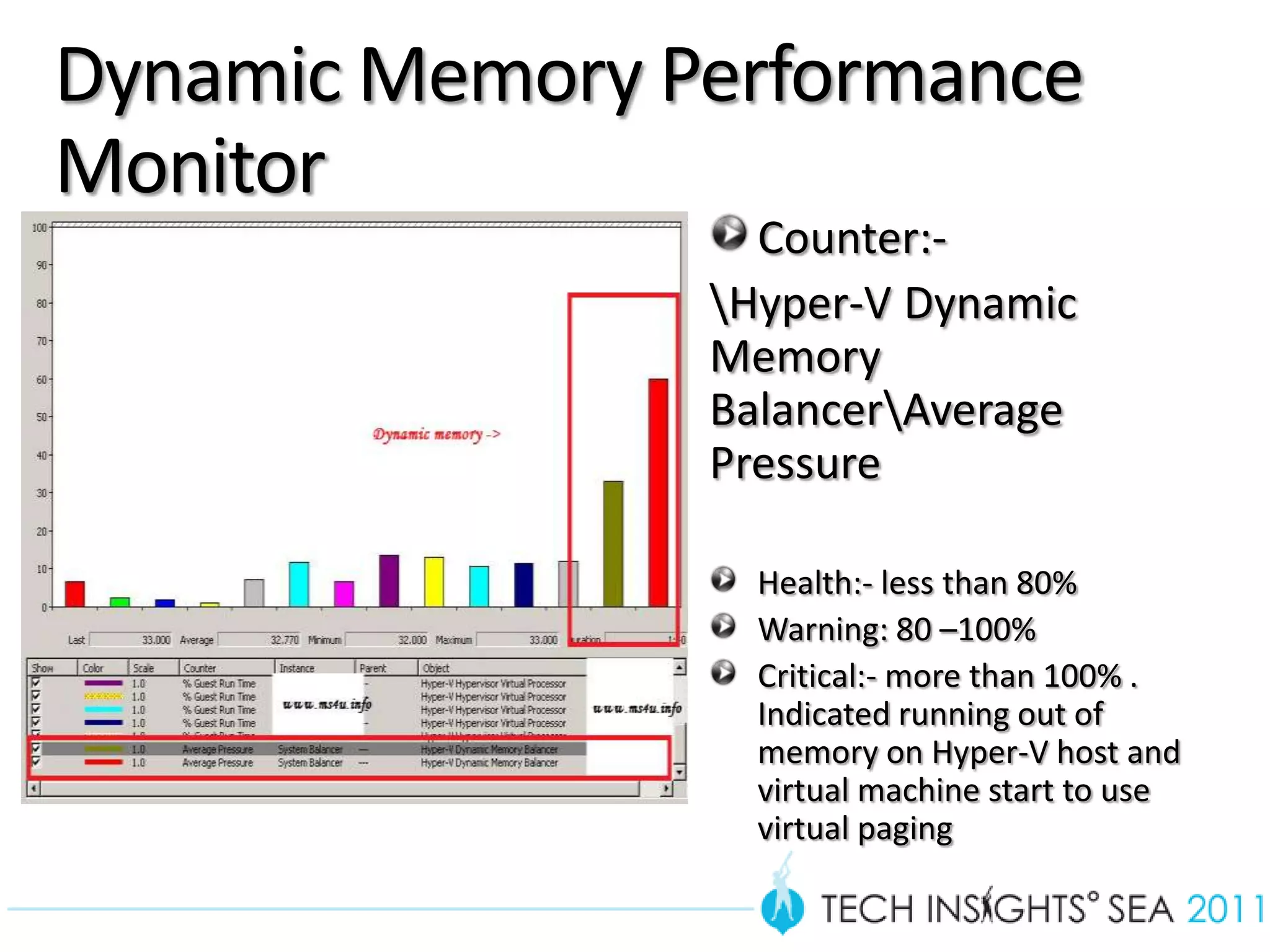
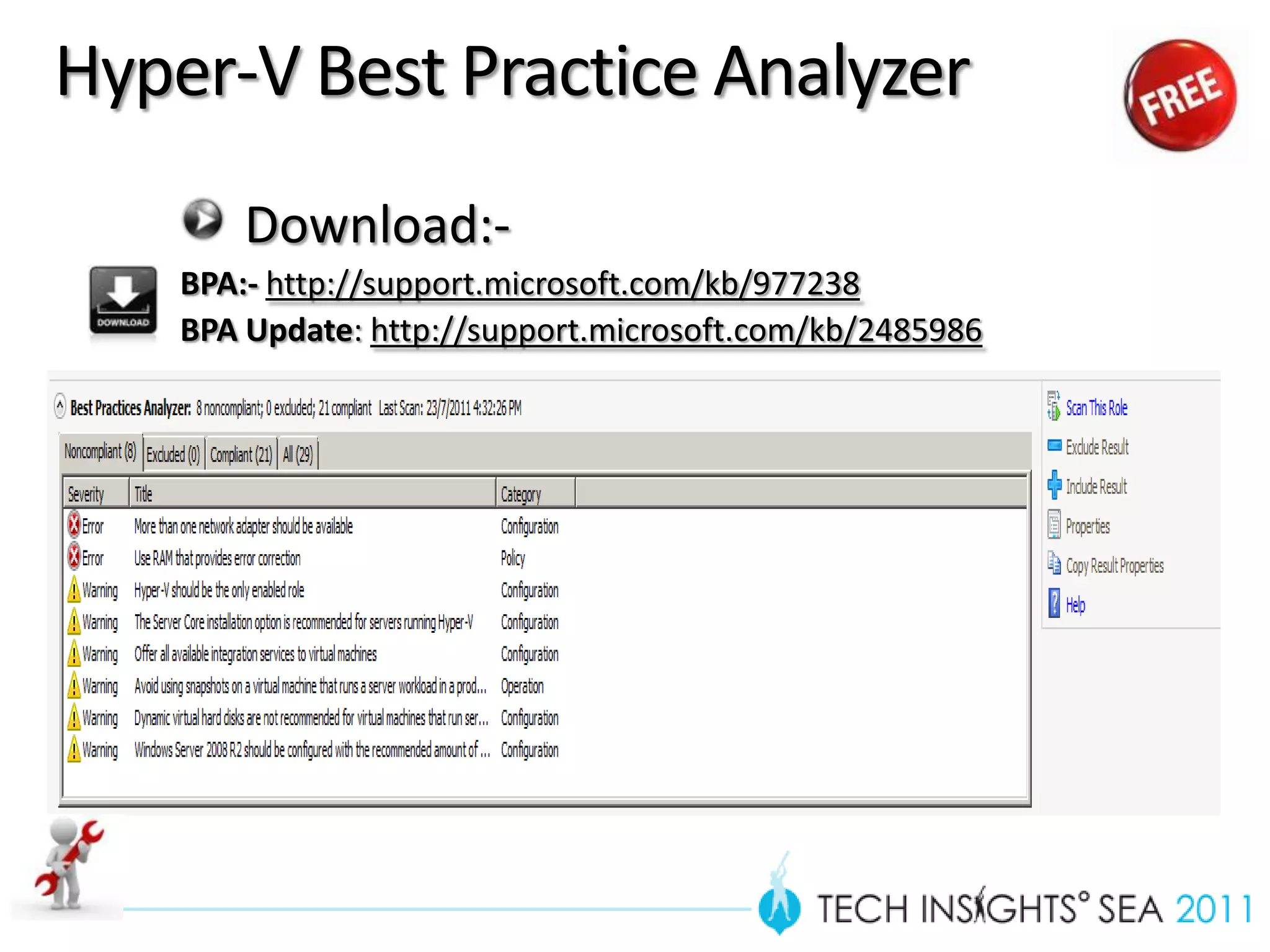
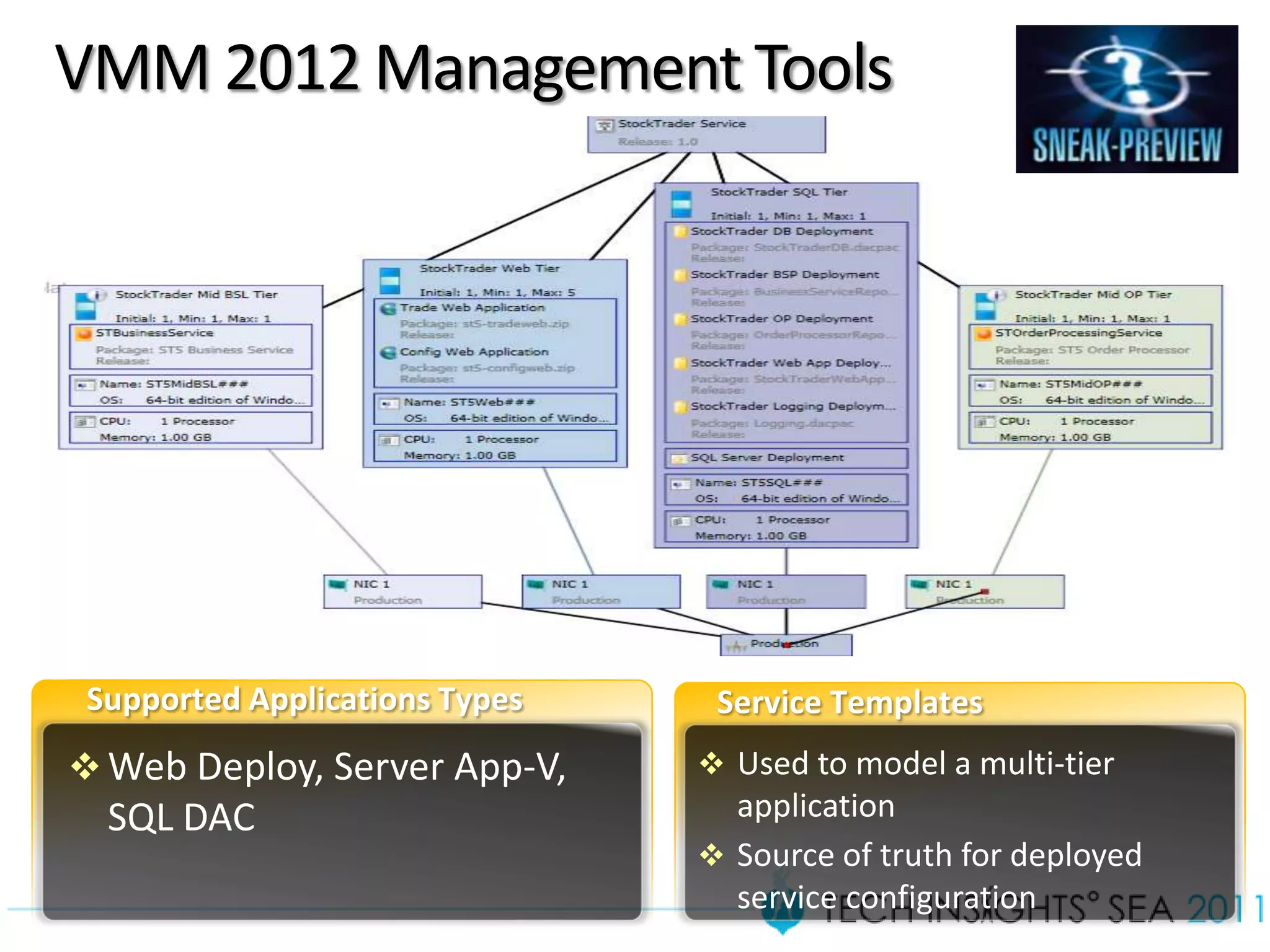
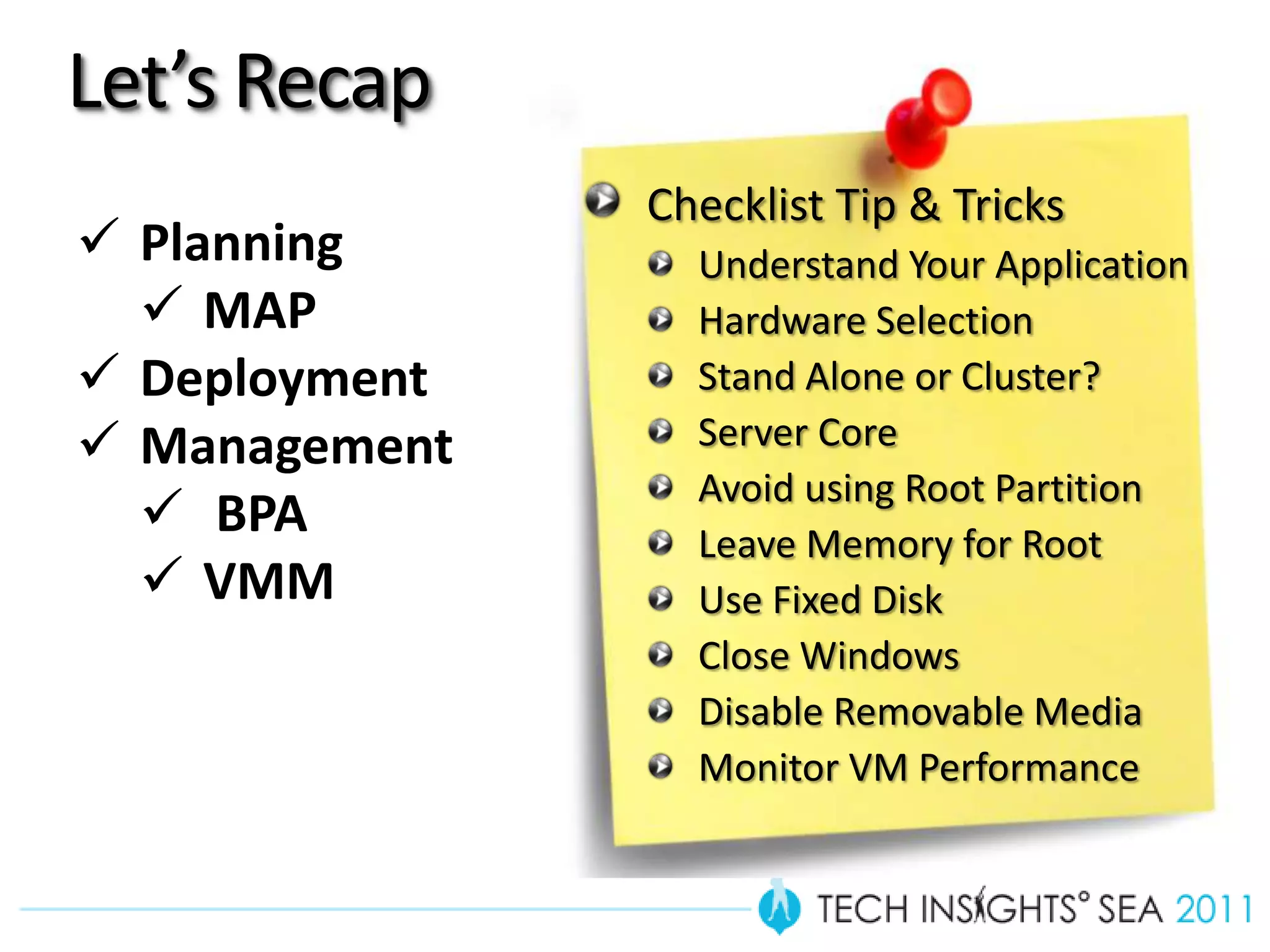
- The document provides virtualization best practices for planning, deployment, and management of virtual machines. It includes 10 tips and tricks such as understanding applications before virtualizing, selecting proper hardware, deciding between stand-alone or clustered Hyper-V, using Server Core to reduce attacks, and monitoring VM performance. The document also recommends some free tools for analyzing virtualization configurations.