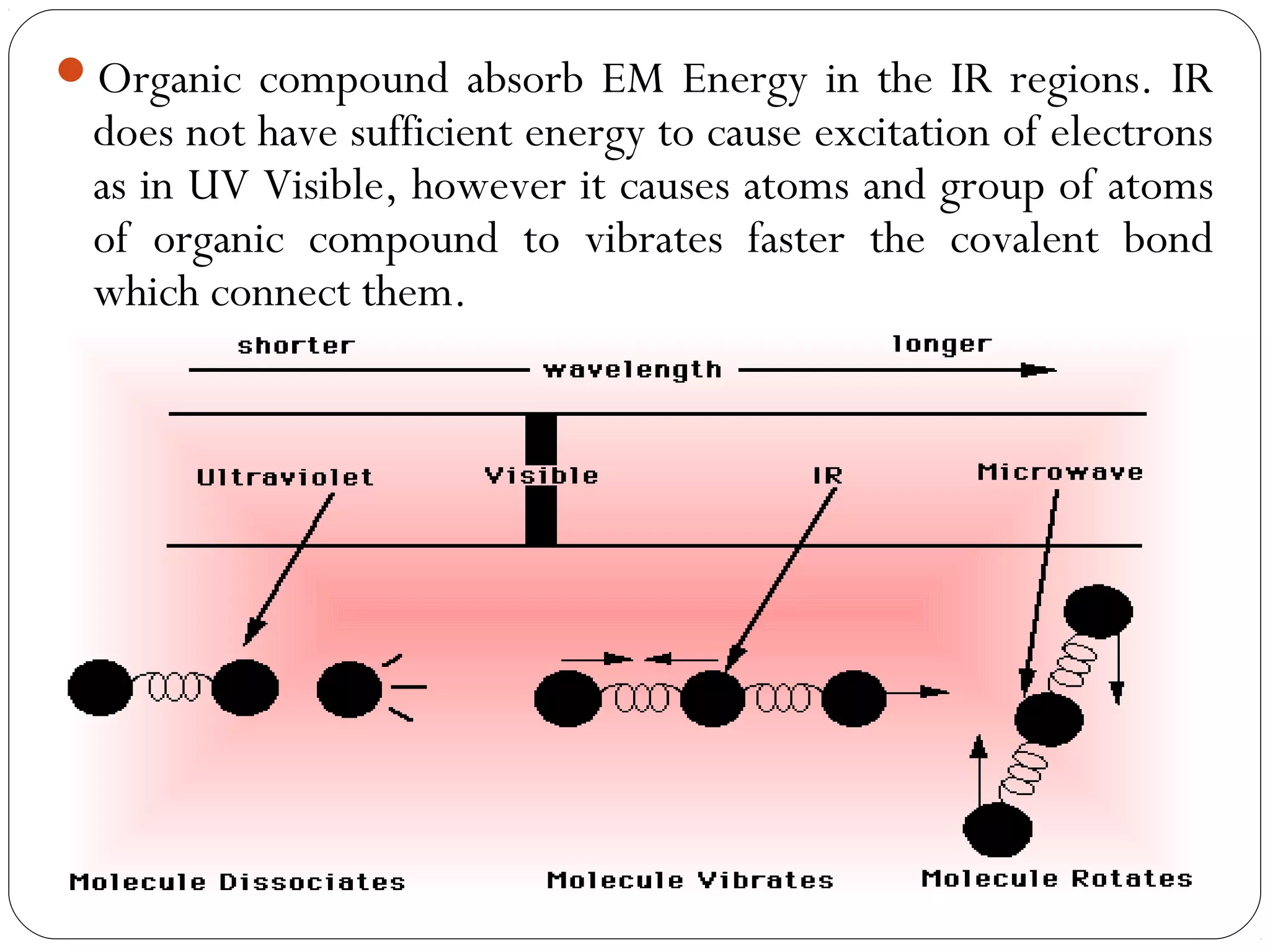
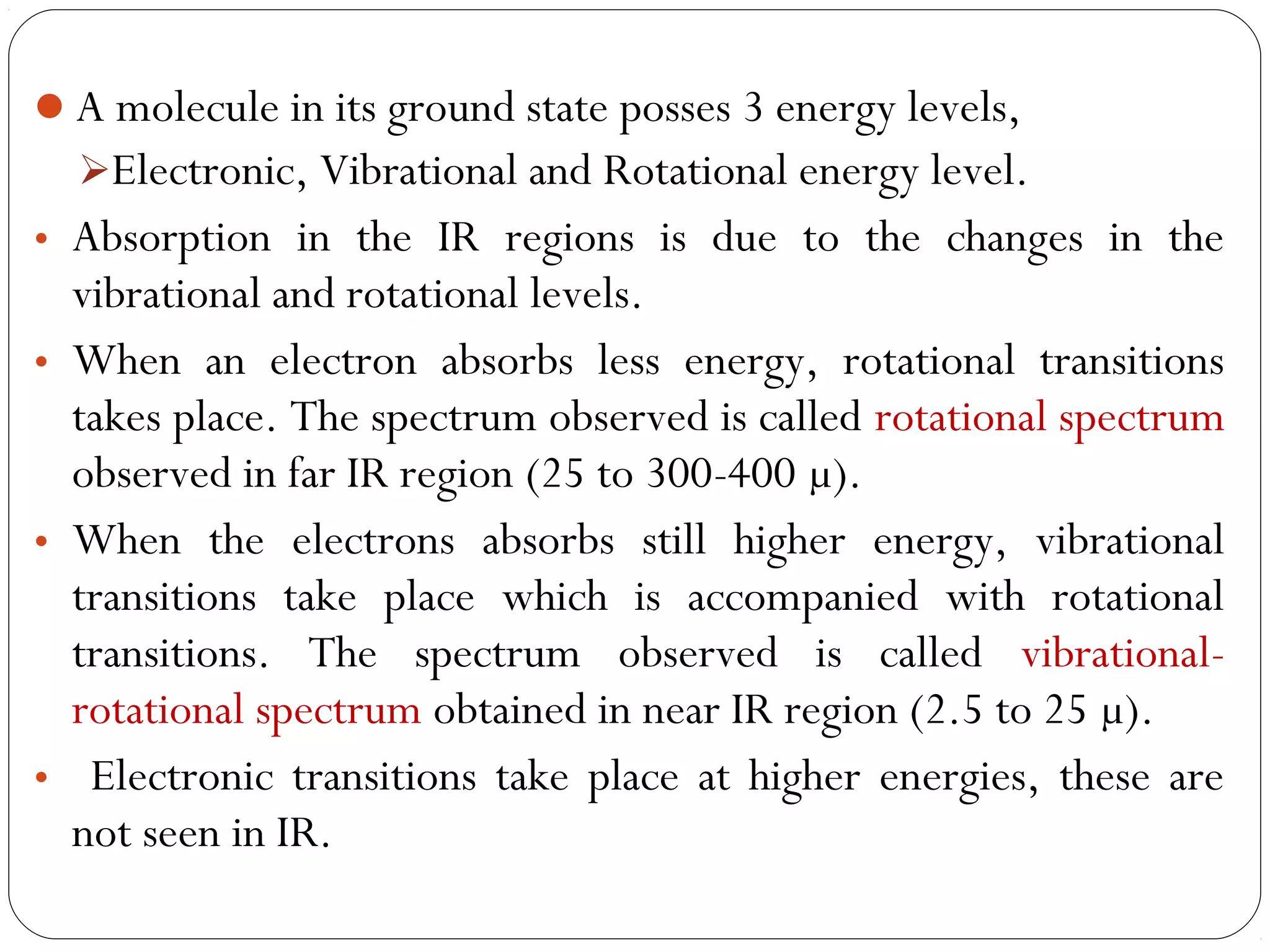
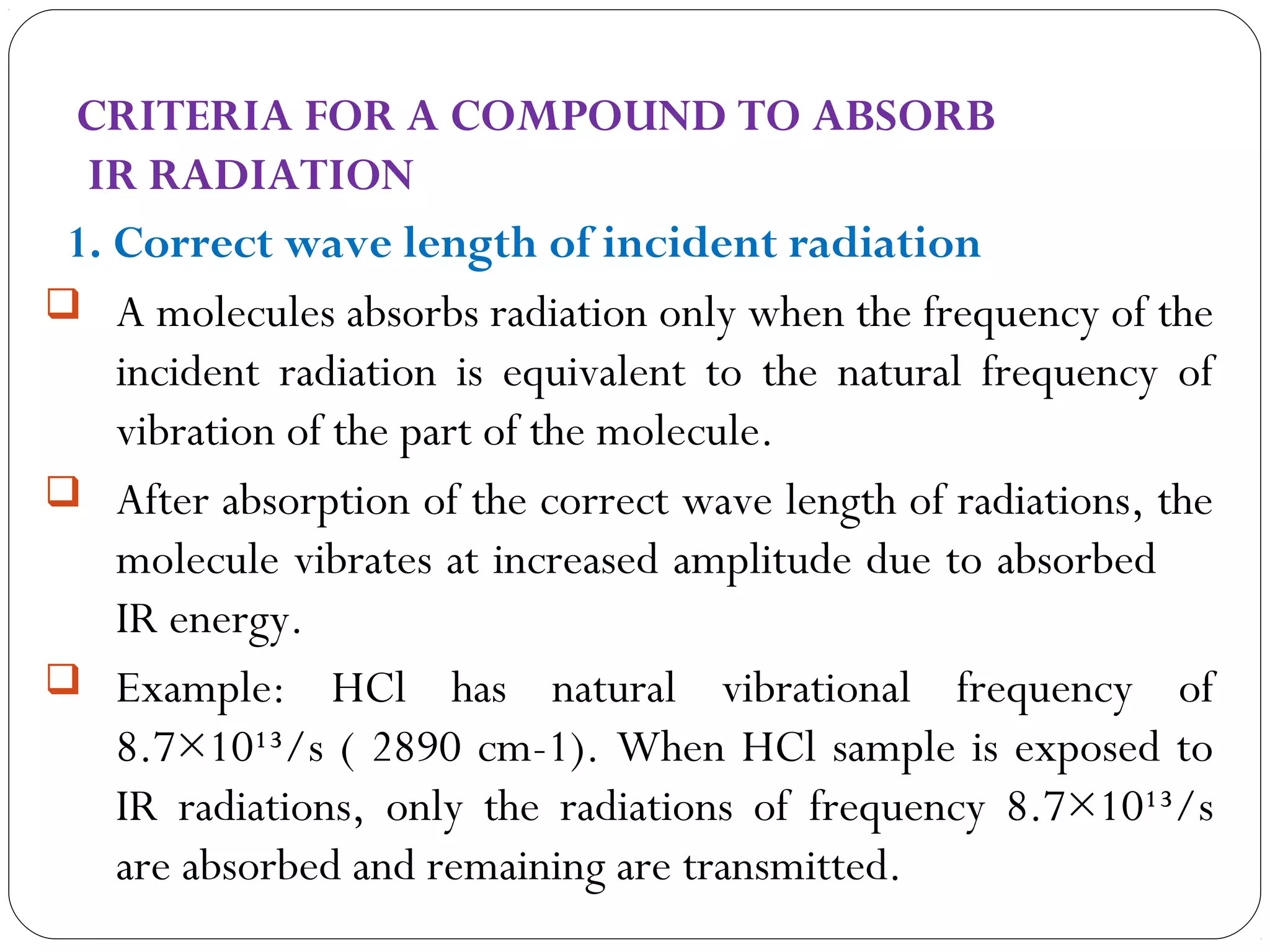
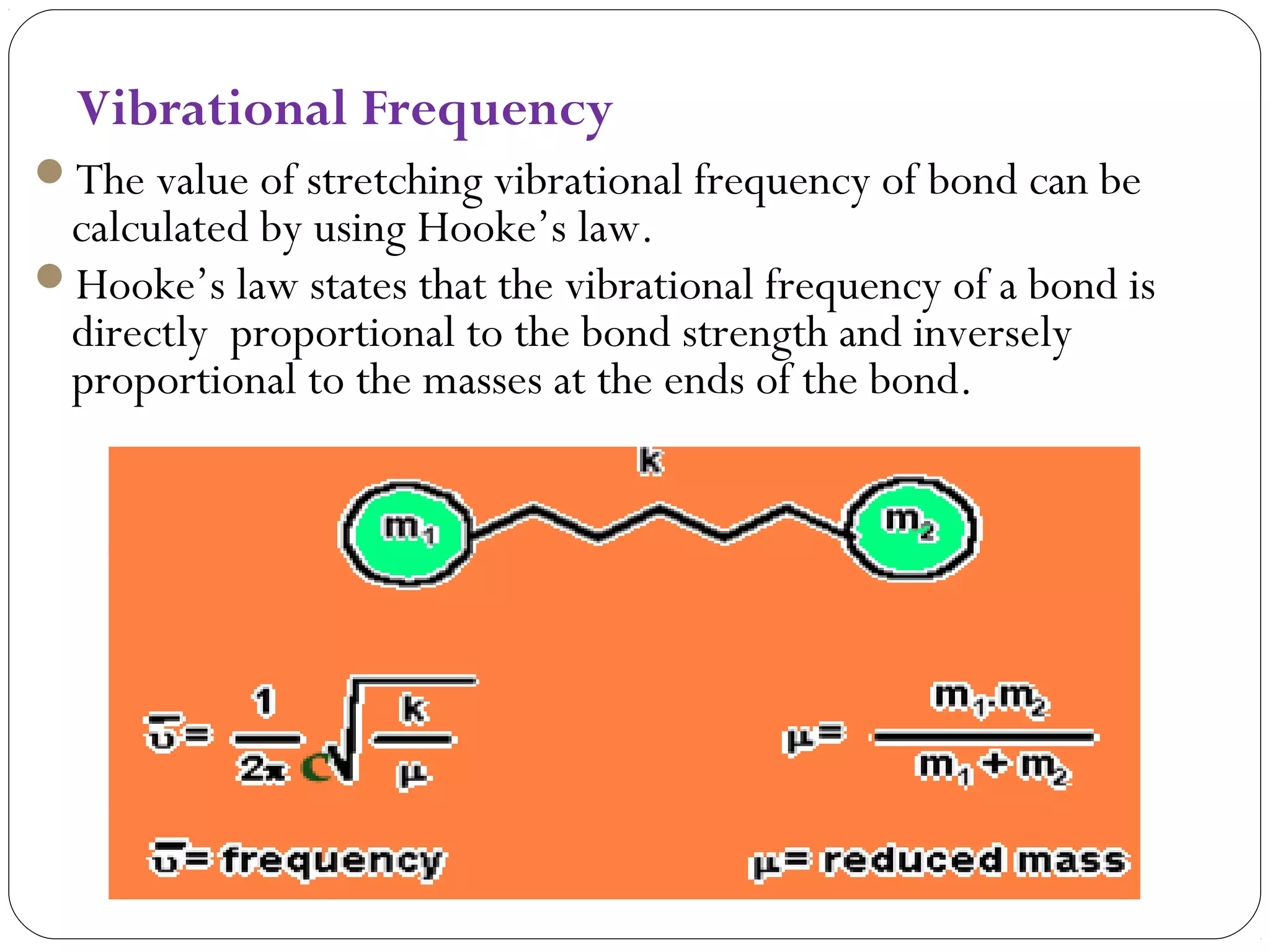
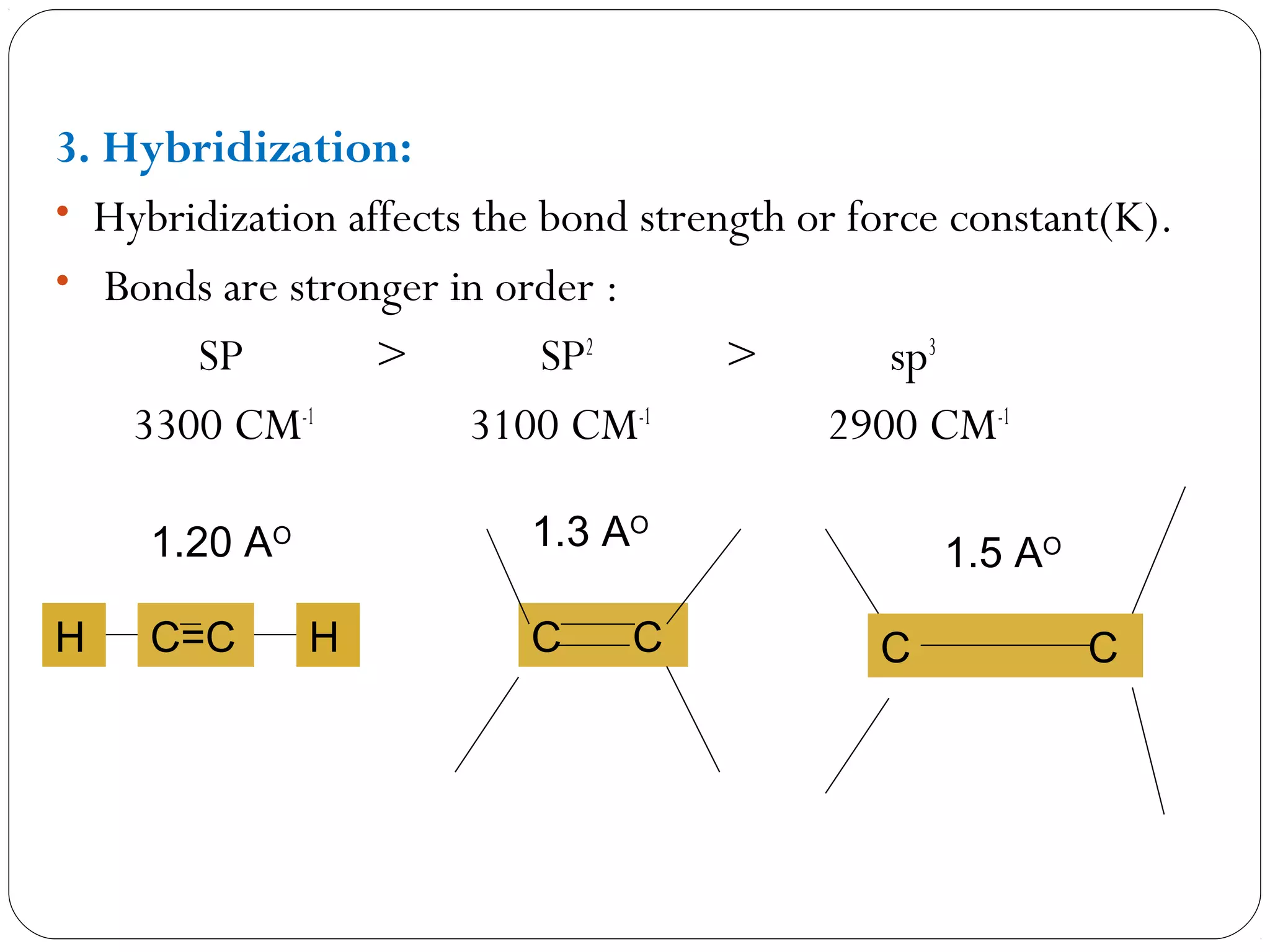
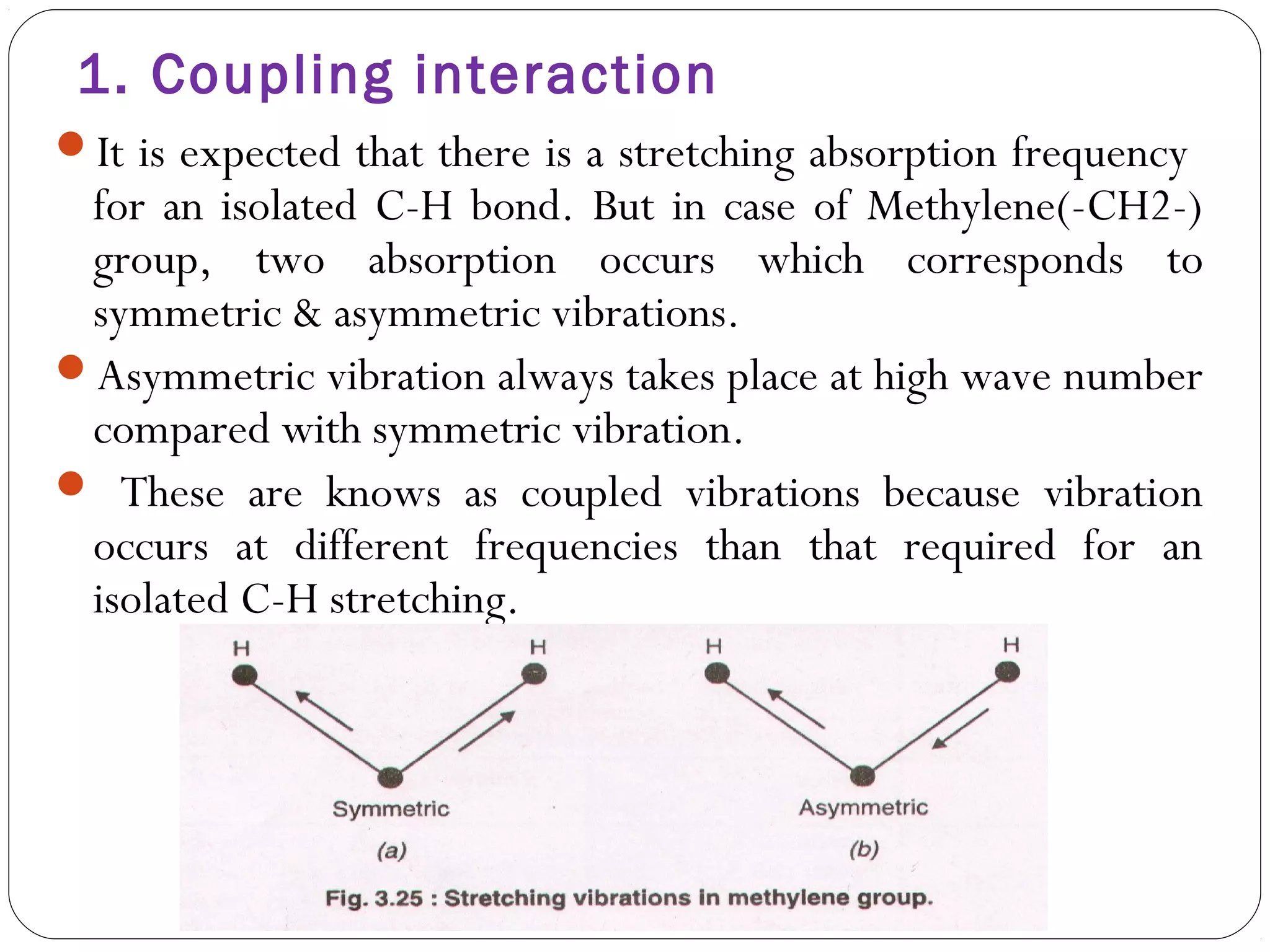
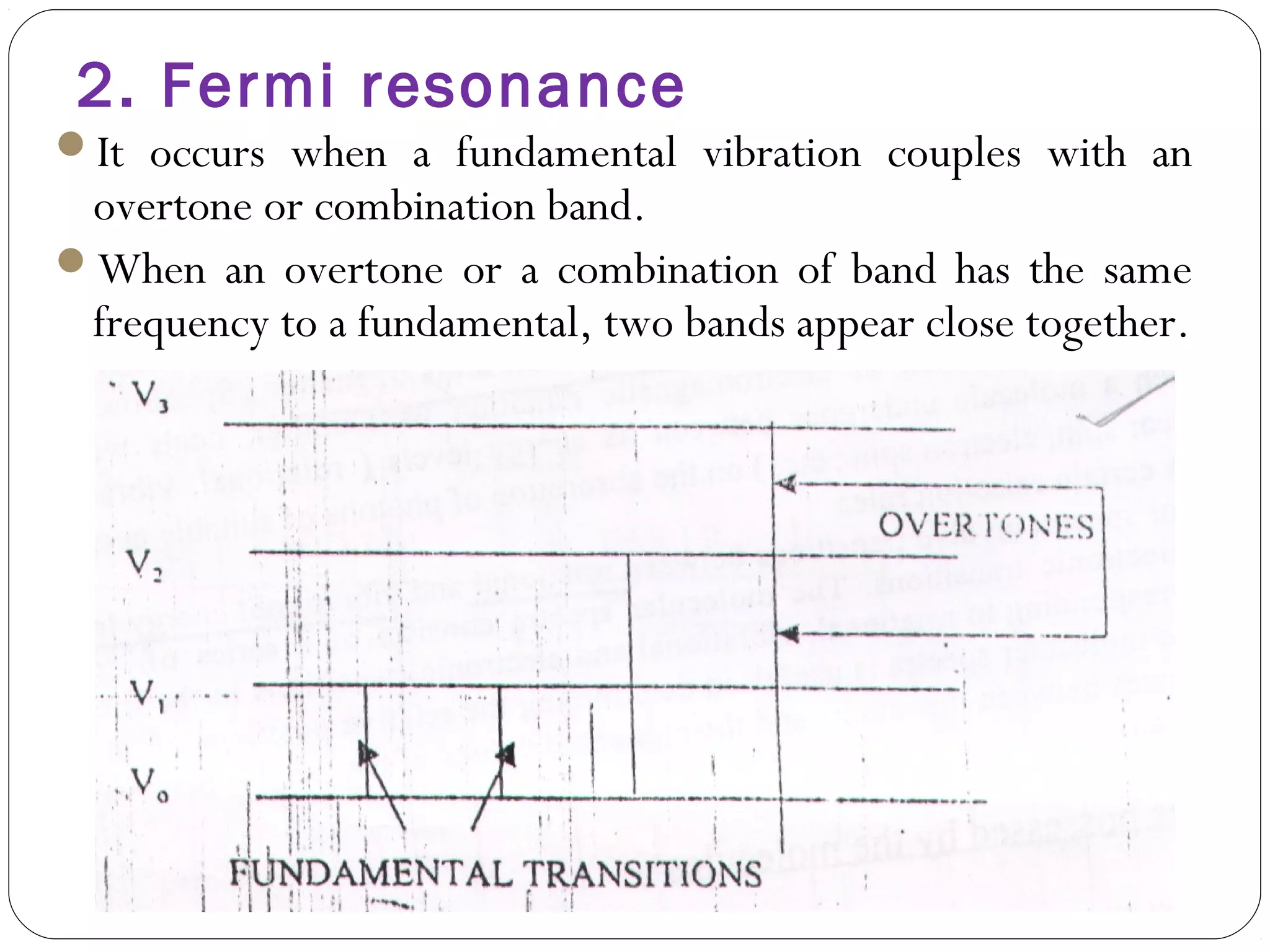
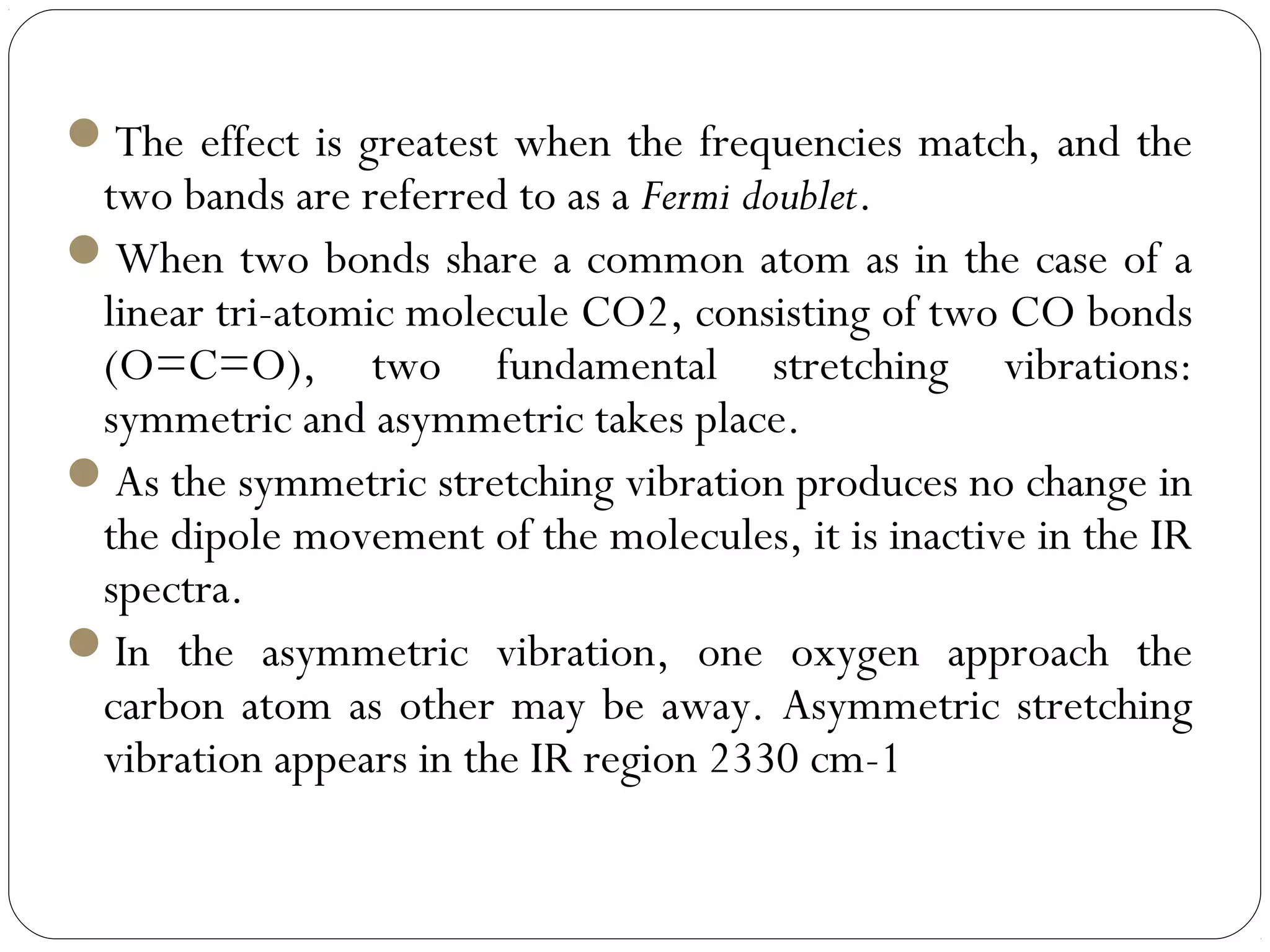
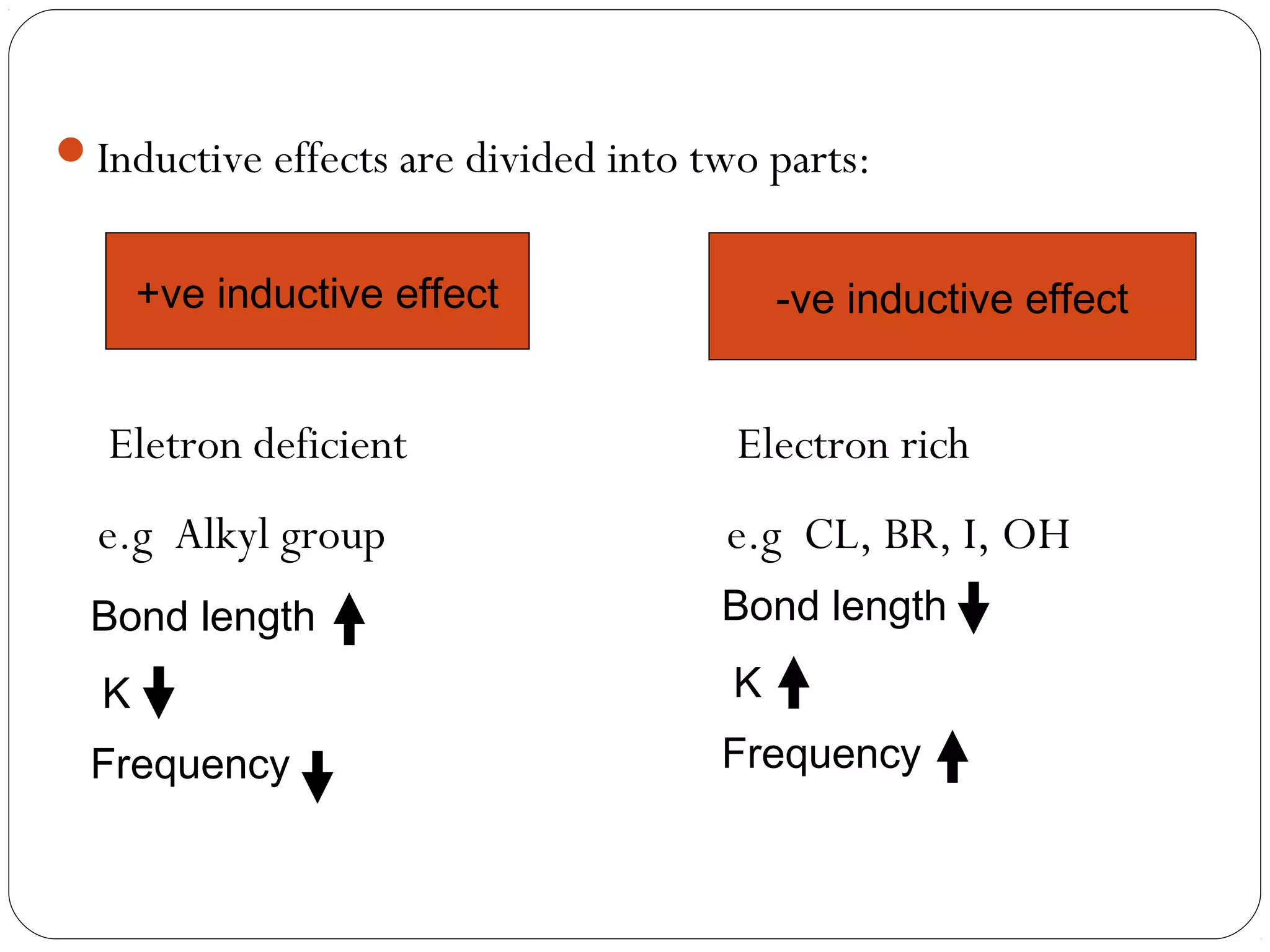
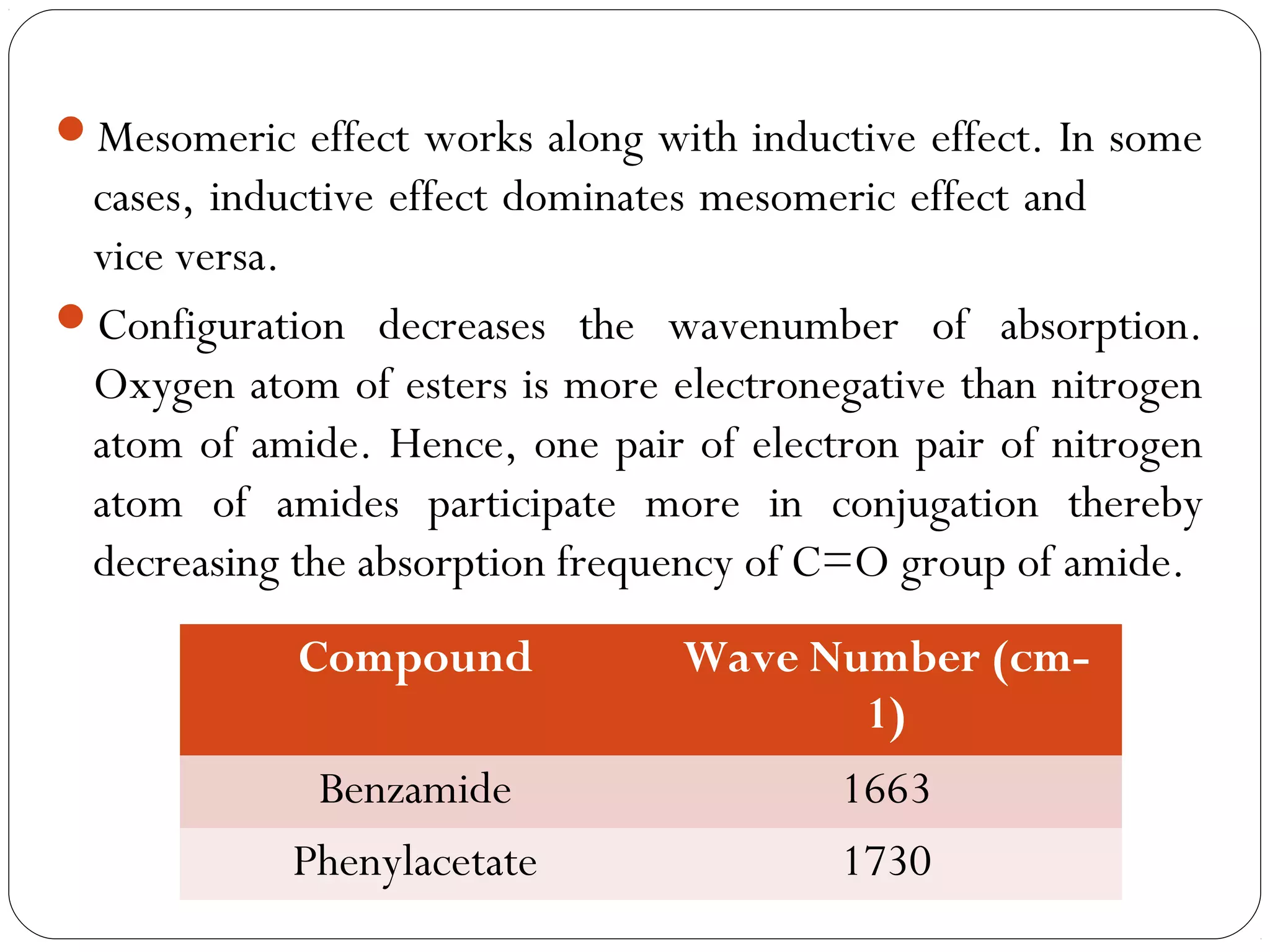
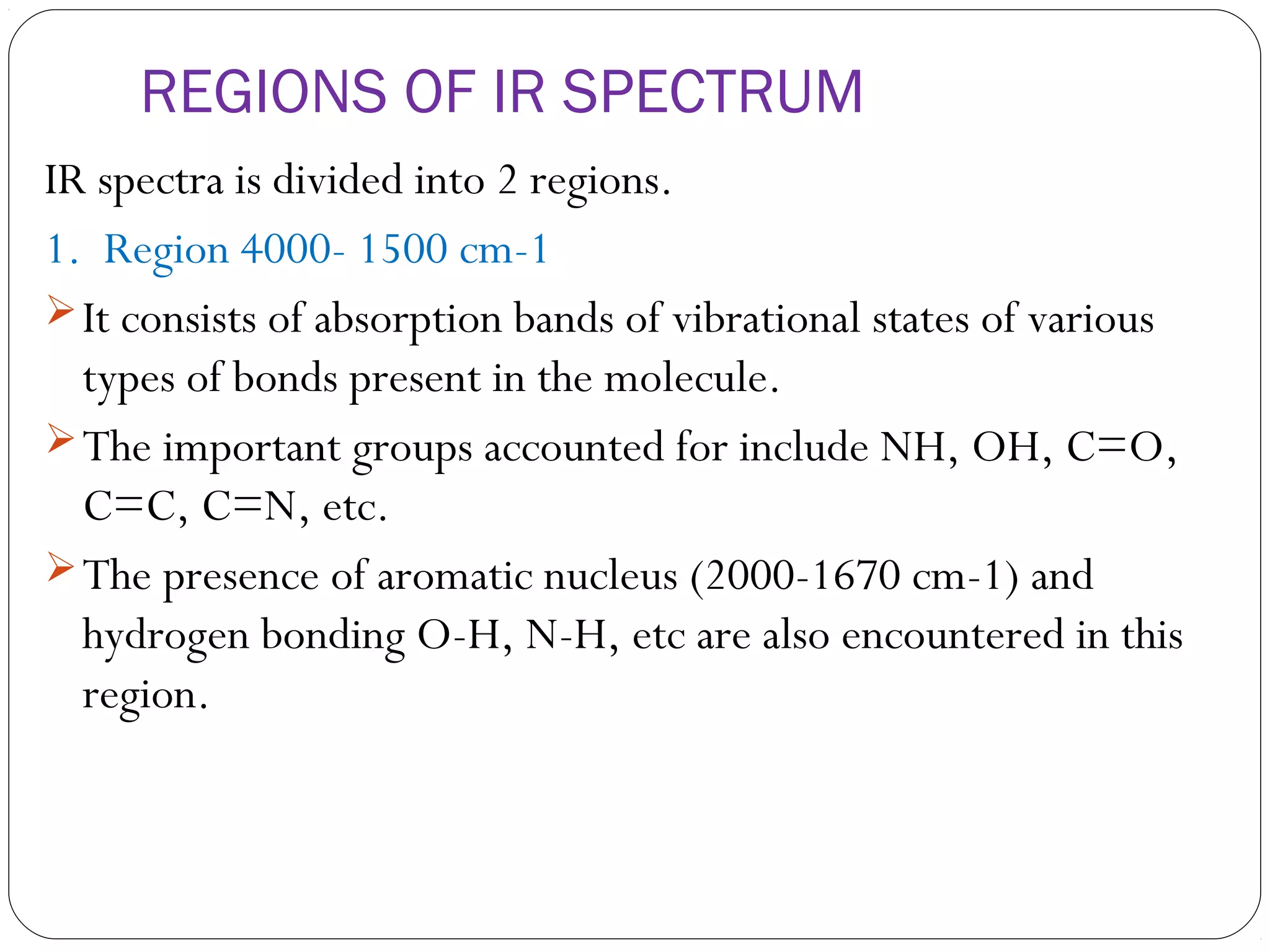
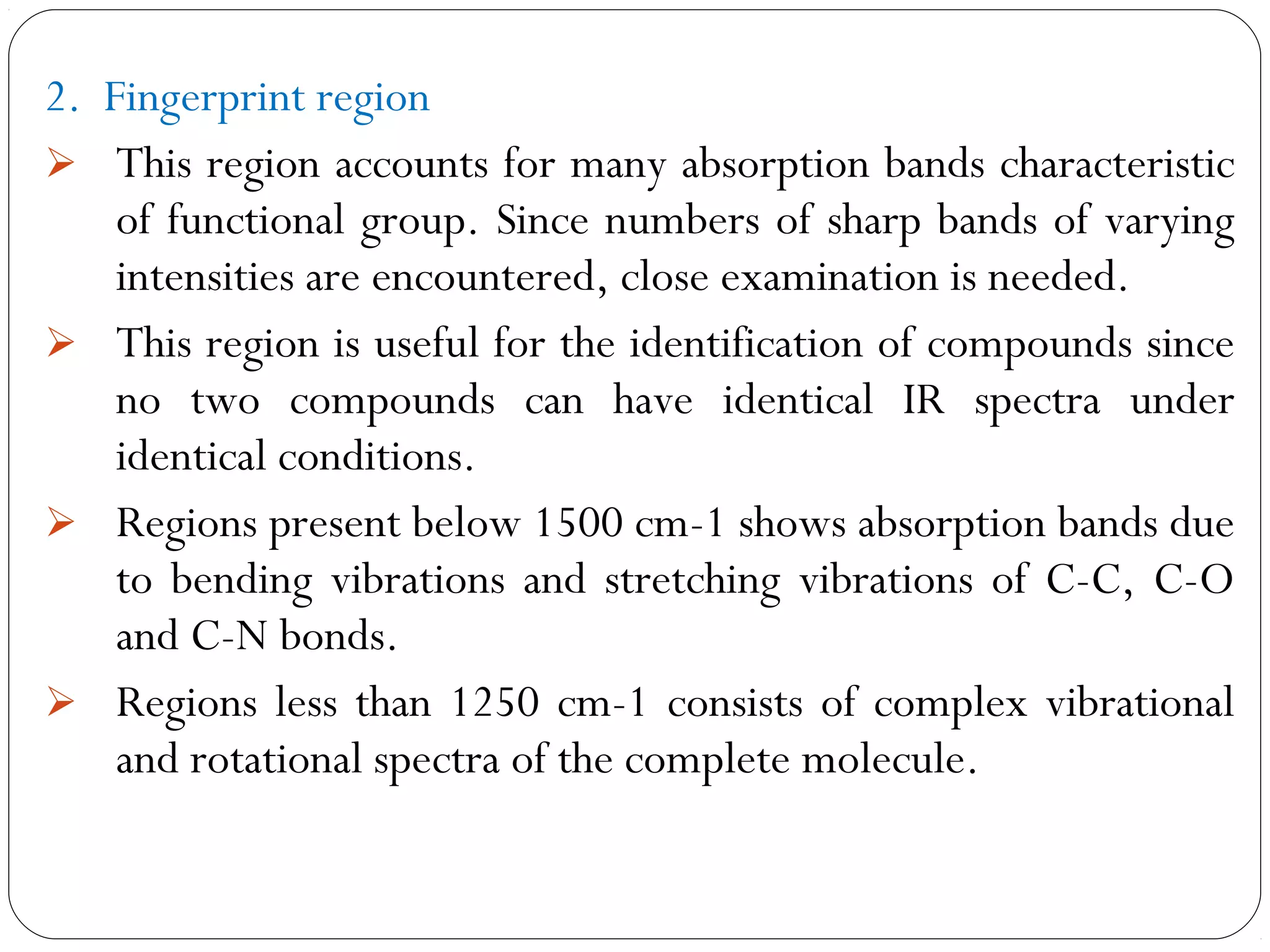
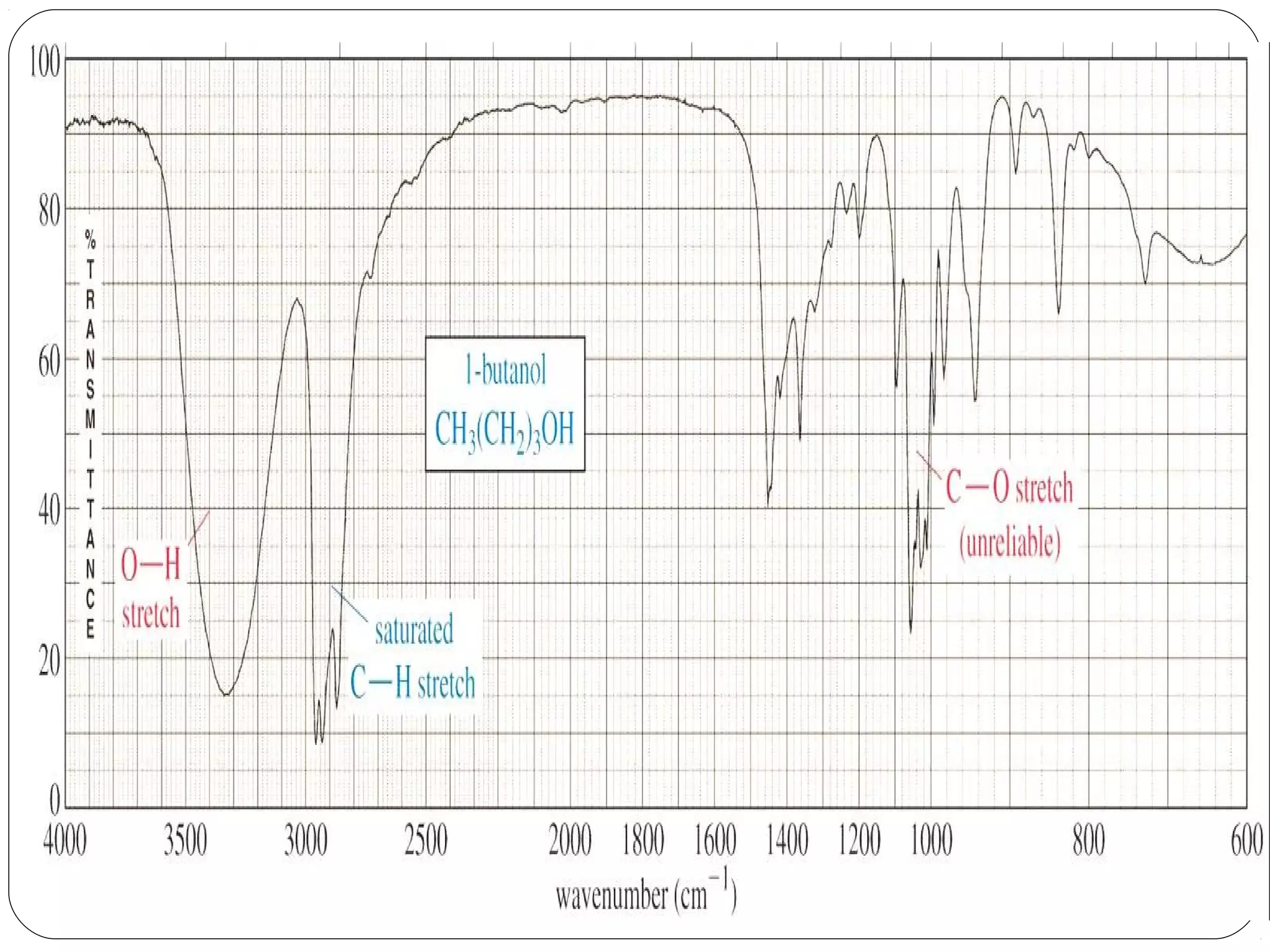
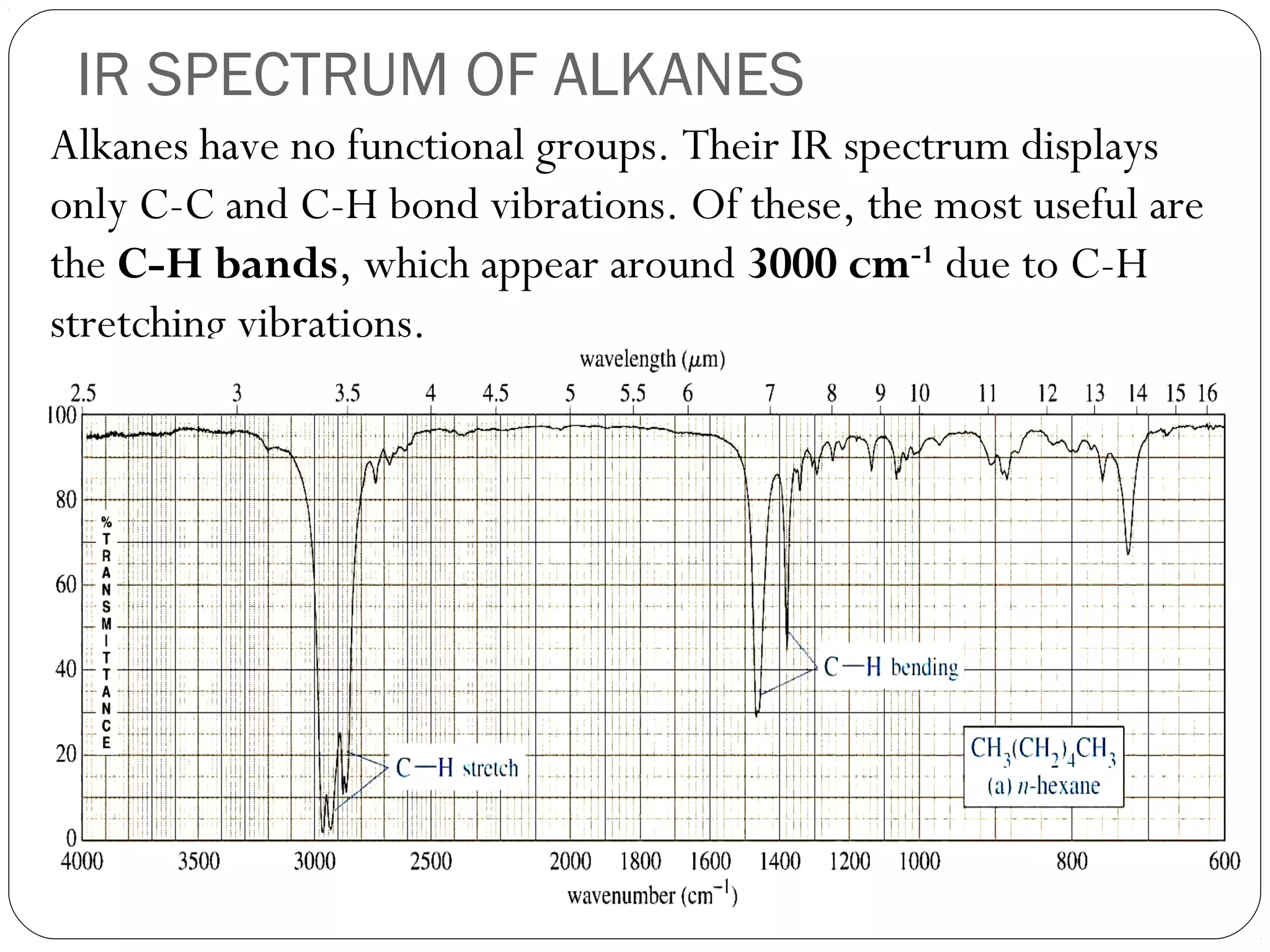
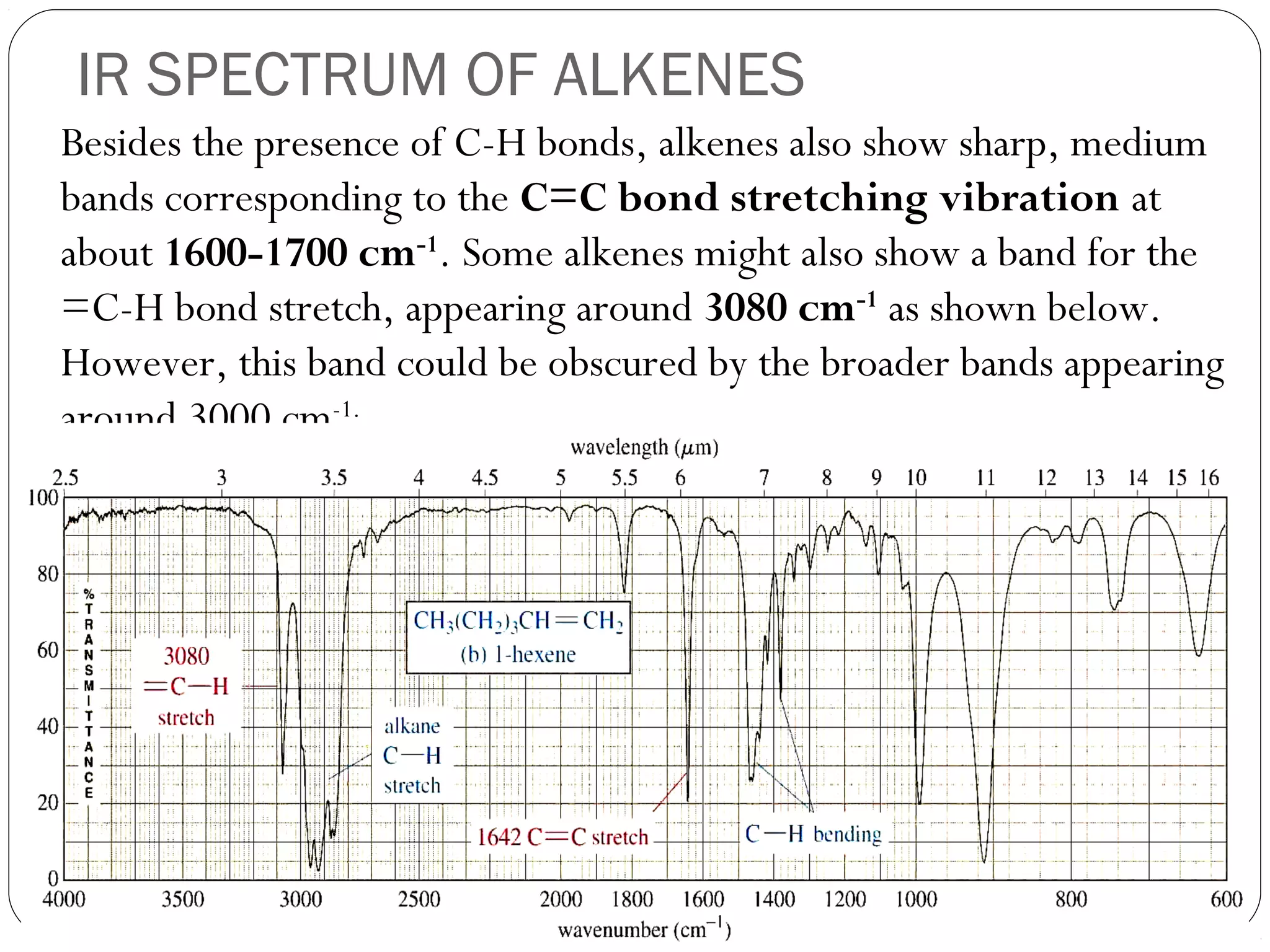
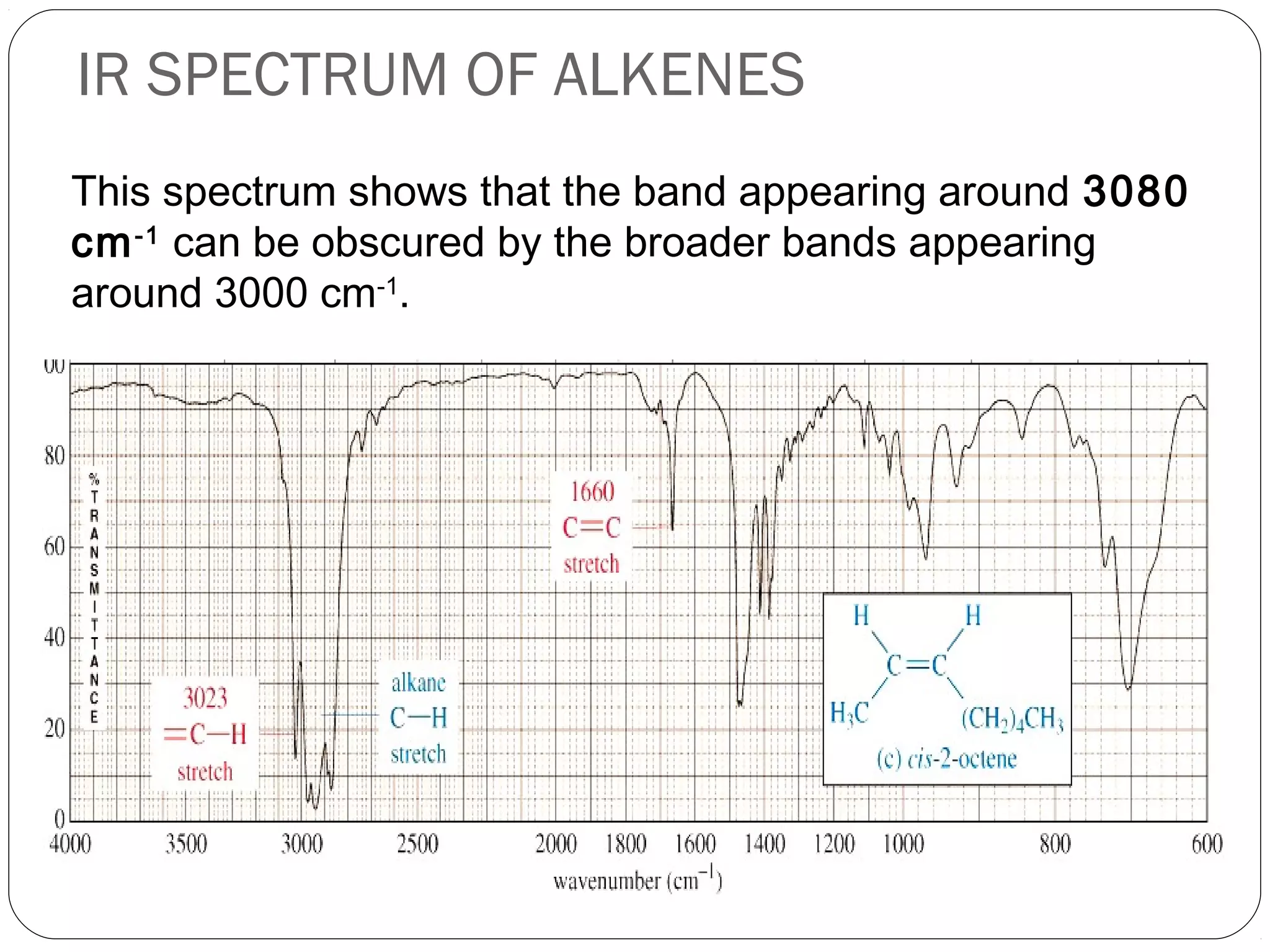
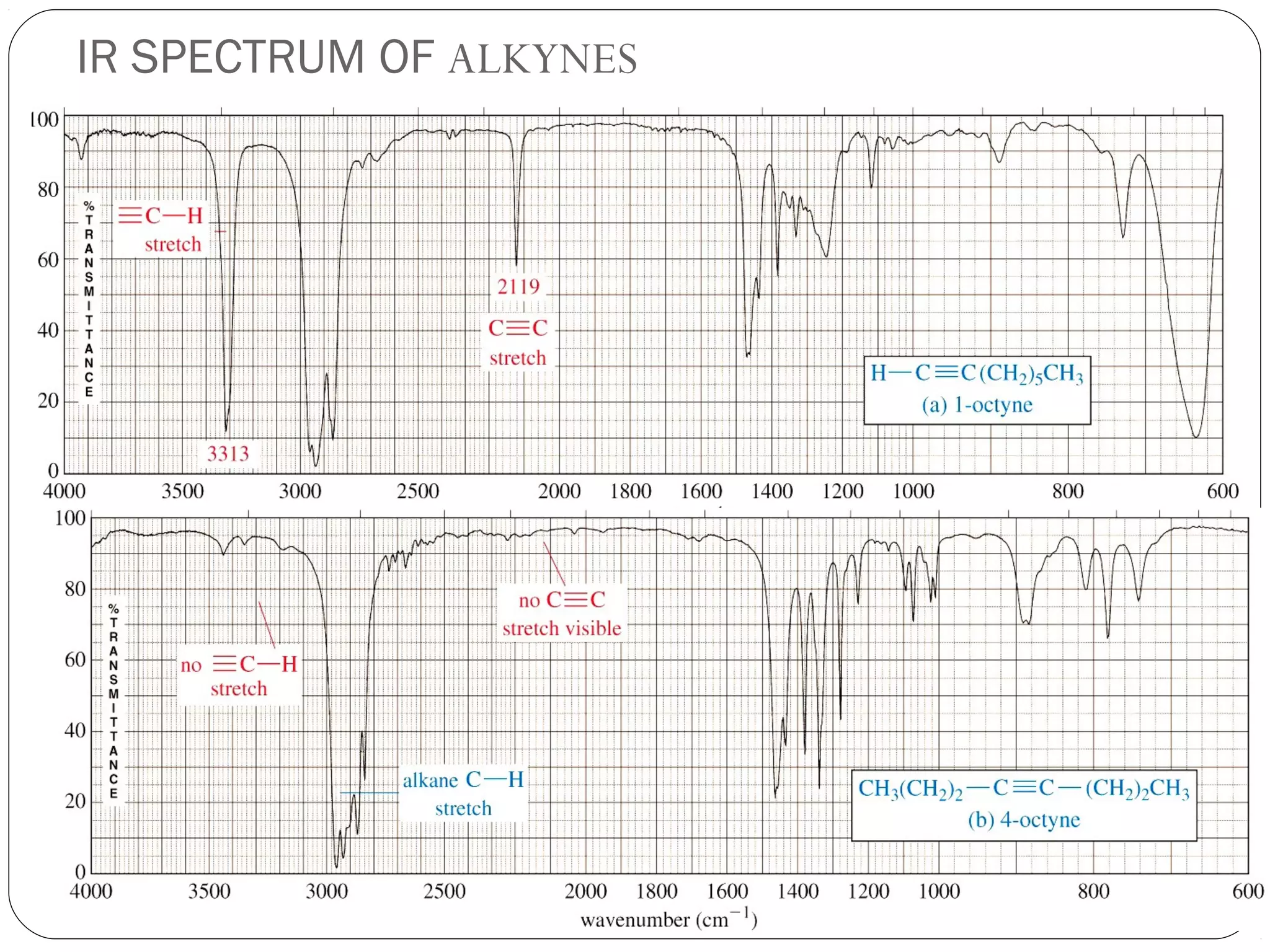
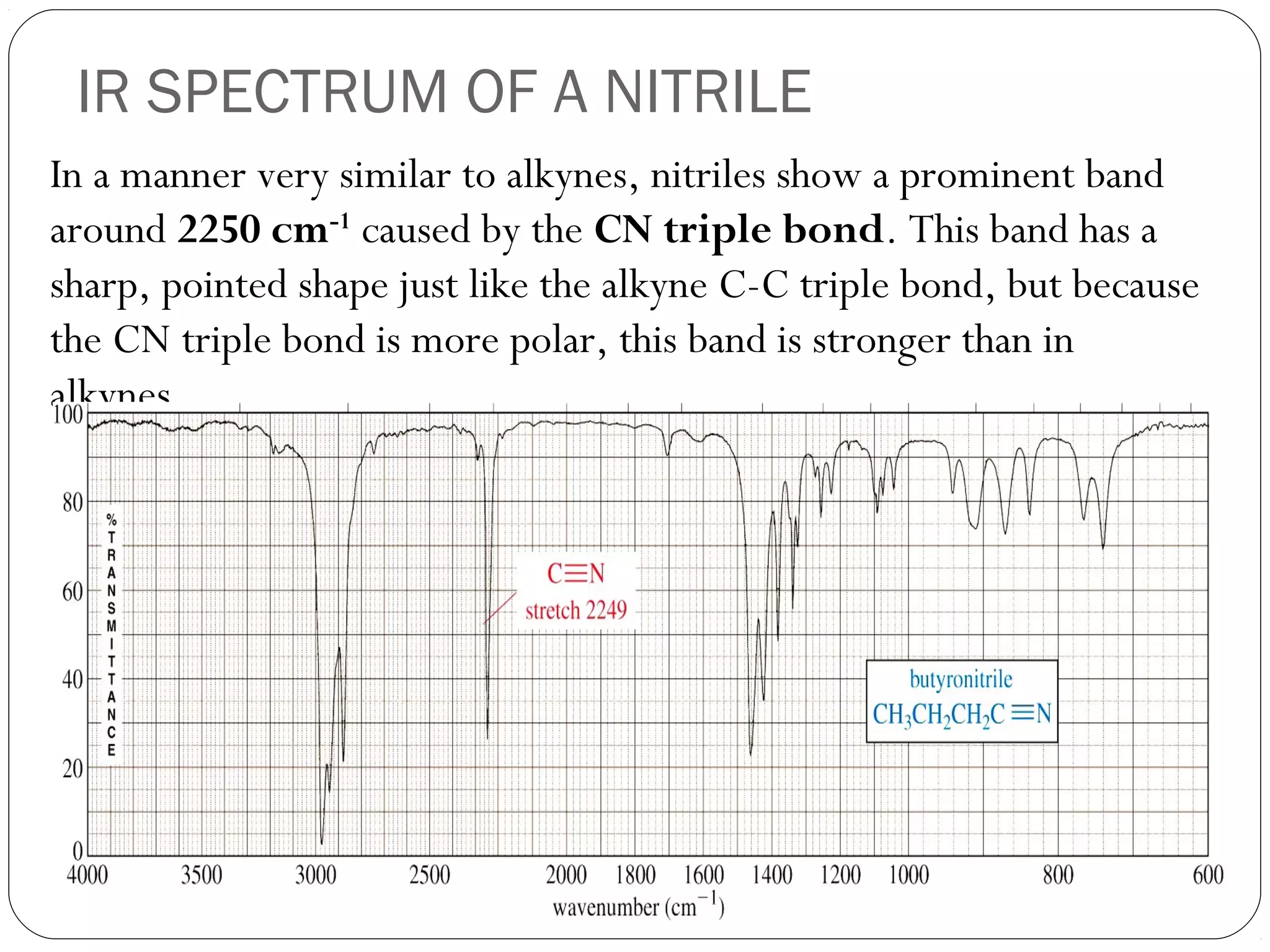
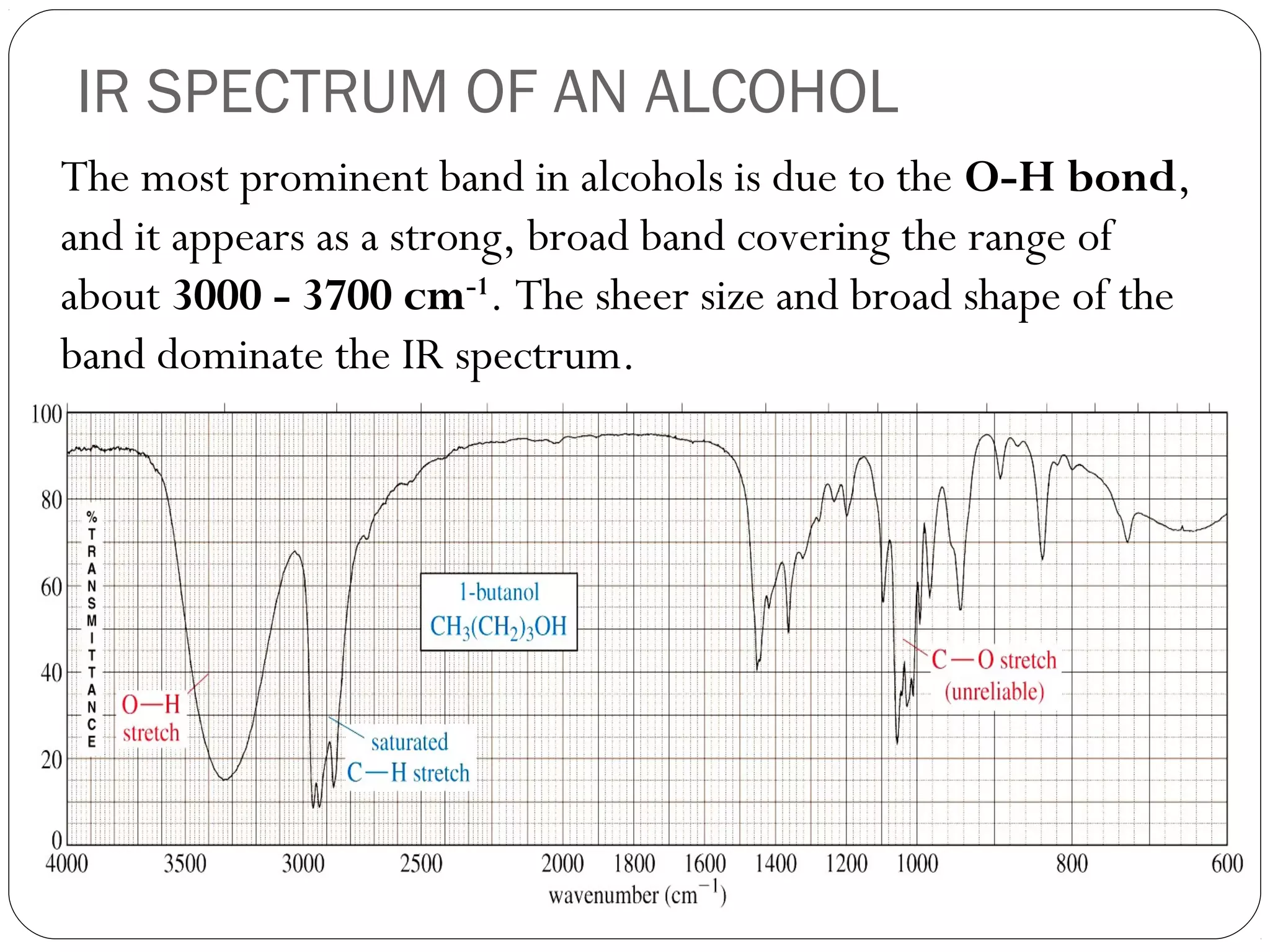
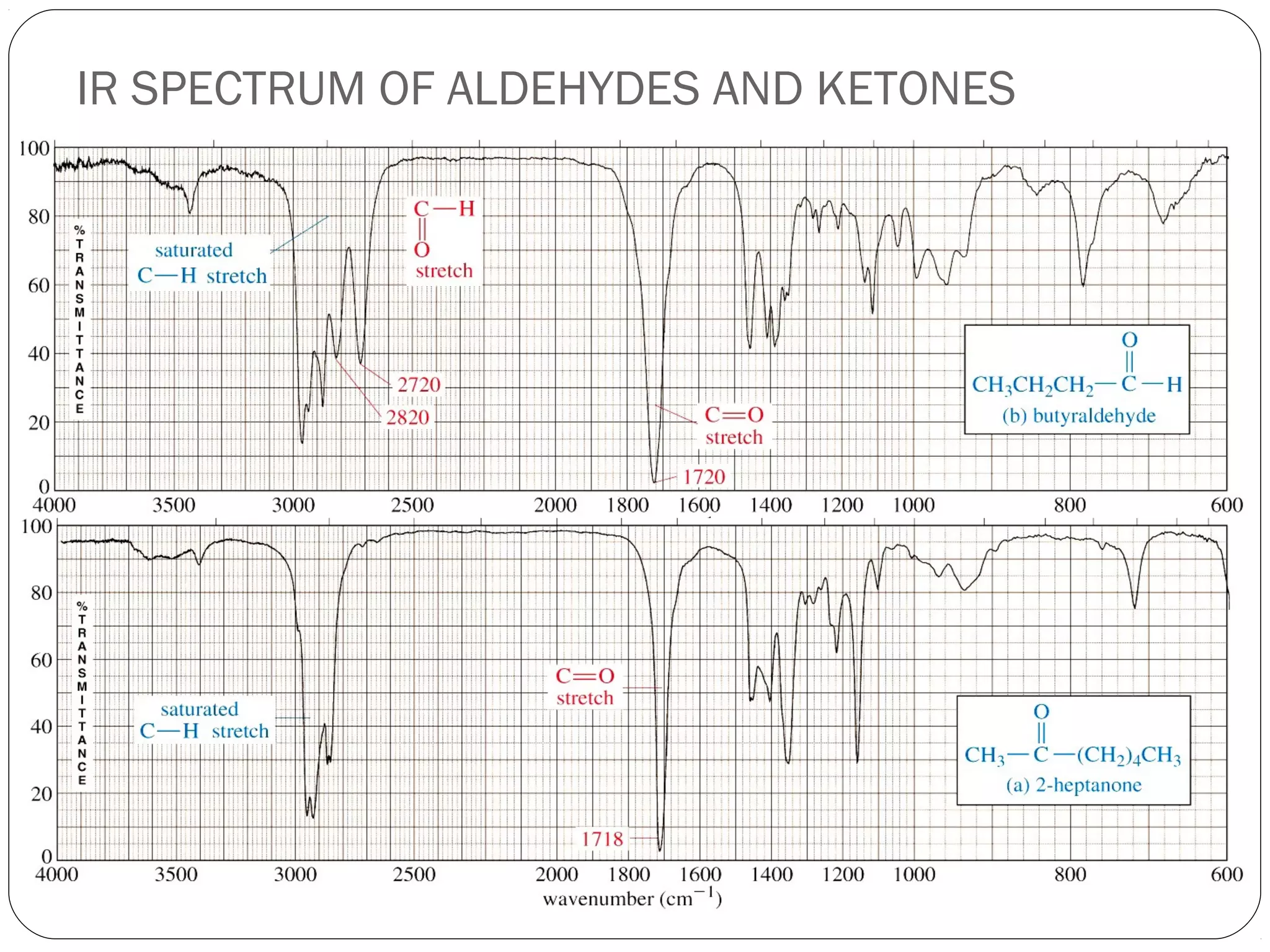
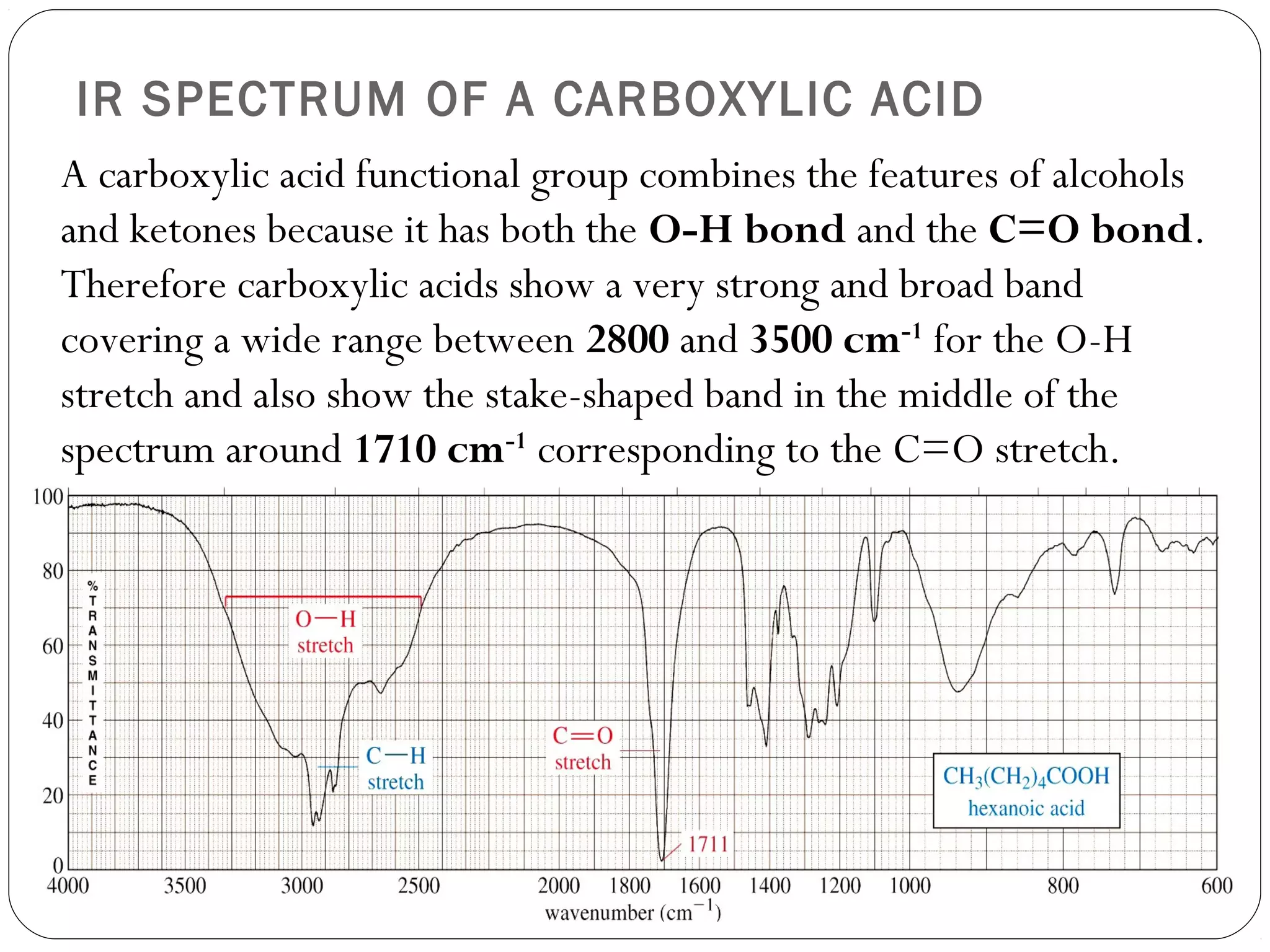
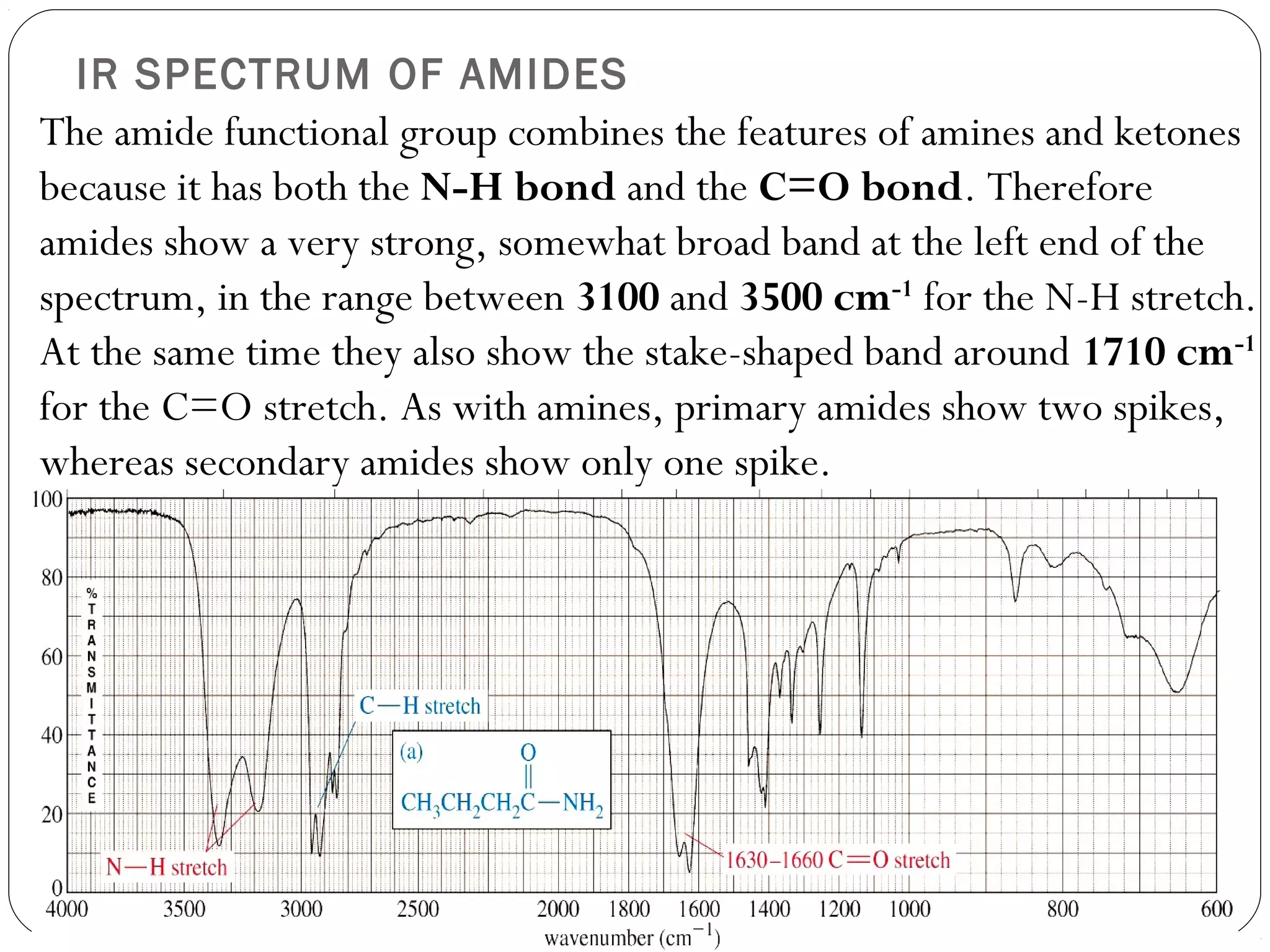
The document summarizes infrared (IR) spectroscopy, including its principle, instrumentation, applications, and interpretation of spectra. IR spectroscopy works by detecting the vibrational and rotational absorption frequencies of molecules when exposed to IR radiation. The spectrum produced provides information on molecular structure and bonding. Key regions of the IR spectrum correspond to common functional groups like C=O, N-H, and O-H. Analysis of peak positions and relative intensities allows identification of compounds and detection of impurities.


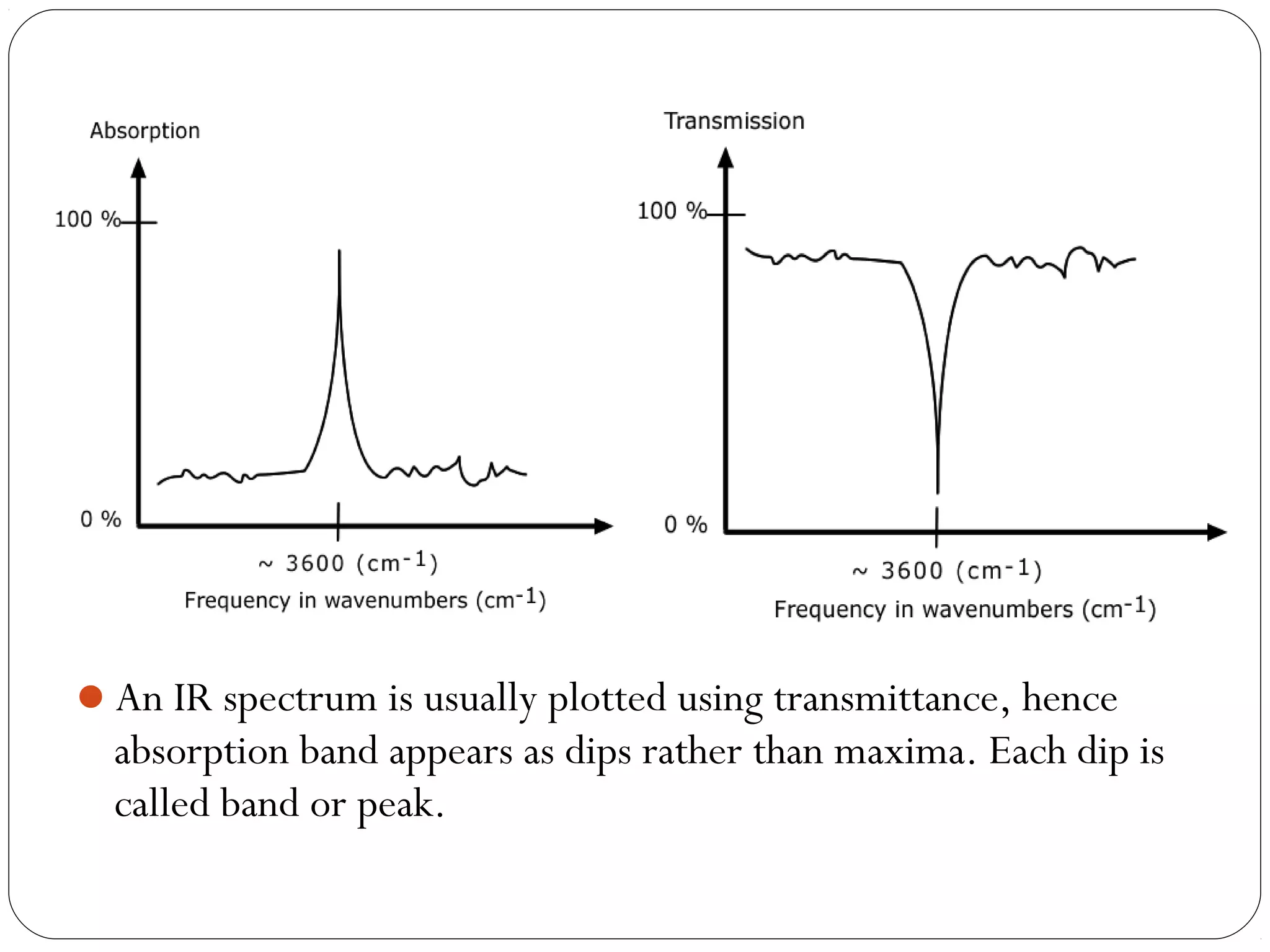
![ IR spectrum is a graph of band intensities on ordinate versus position
of band on abscissa.
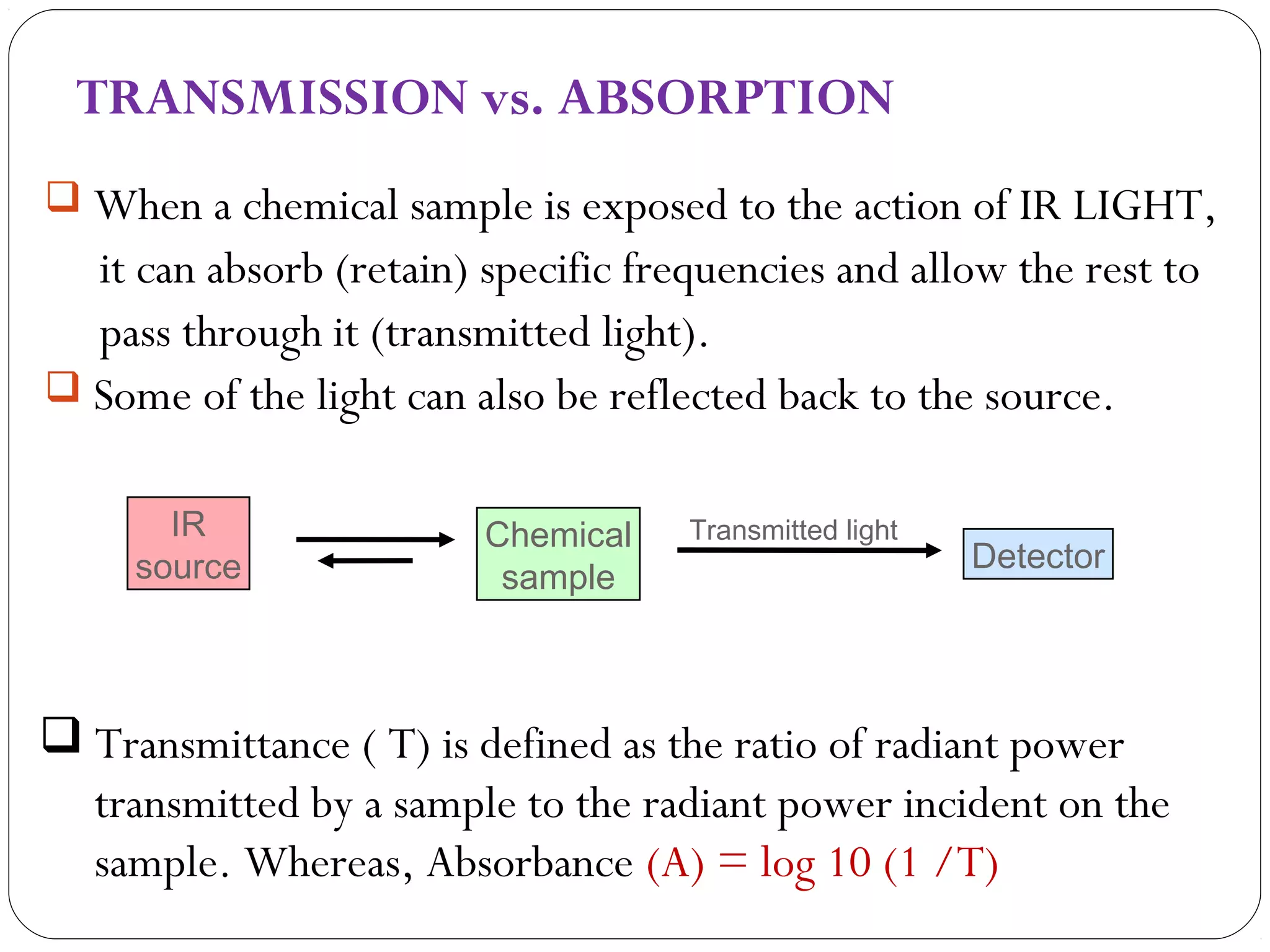
Band intensities can be given in terms of transmittance(T) or
absorbance(A).
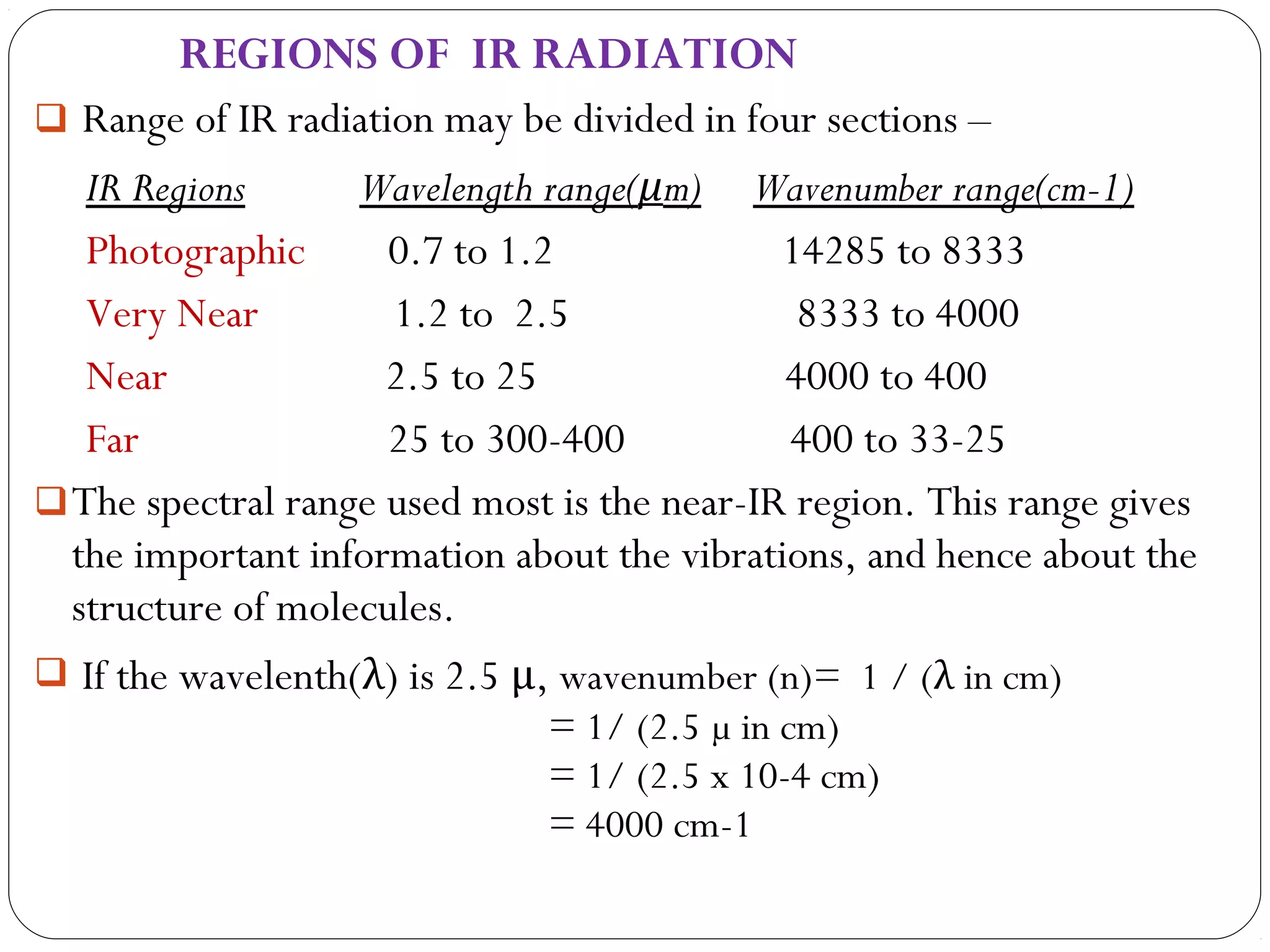
Position of band can be expressed in terms of wave number (n) or
wavelength(λ).
In IR spectra, wave numbers (n) are used instead of wavelength (λ)
for mentioning the characteristic peak as this unit has advantage of
being linear with energy of radiation (E) .
E = h c/ λ or, E= h c n
[ n = 1/λ, c= velocity of light, h= Planck’s constant ]
NATURE OF IR SPECTRA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theoryofirspectroscopy-160622080111/75/Theory-of-IR-spectroscopy-5-2048.jpg)