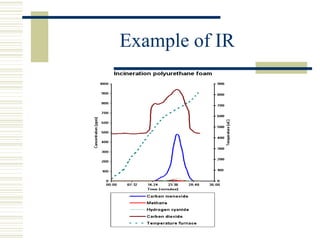
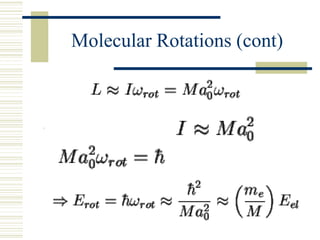
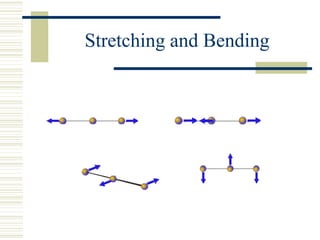
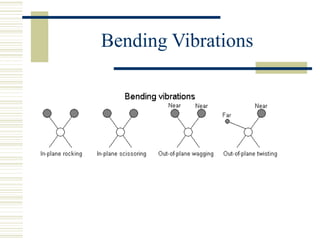
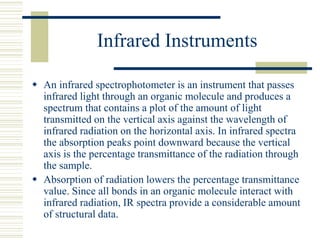
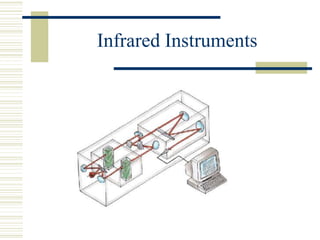
This document discusses infrared spectroscopy. It begins with definitions, explaining that infrared spectroscopy involves measuring the absorption of infrared light by a sample. It then covers the infrared spectroscopic process, theory of infrared absorption, examples of infrared spectra, and applications of infrared spectroscopy such as in chemistry, forensics, and testing pill quality. Advantages include being cheap and fast, while disadvantages include requiring sample preparation and being qualitative rather than quantitative. The conclusion restates that infrared spectroscopy identifies sample components by measuring their interaction with infrared radiation.