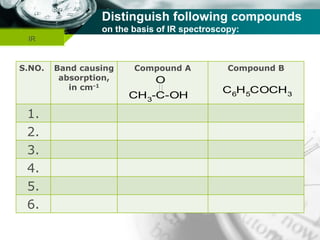
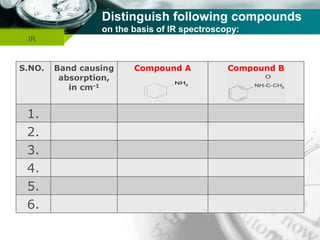
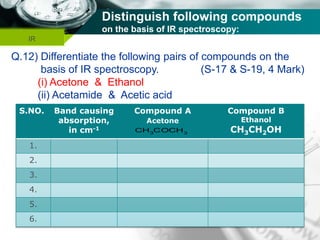
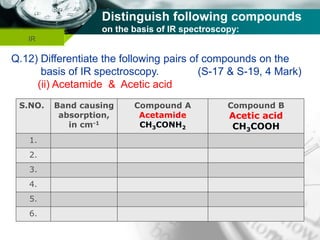
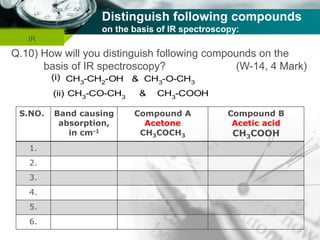
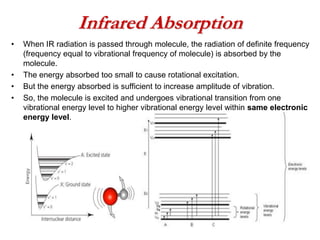
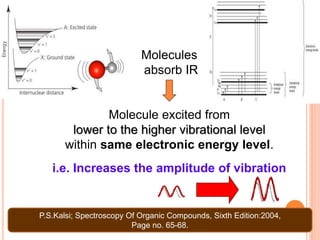
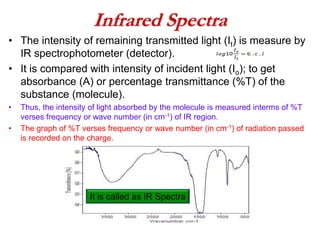
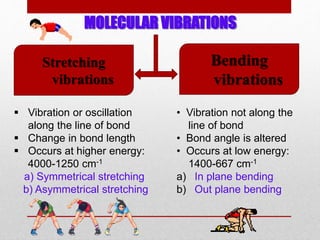
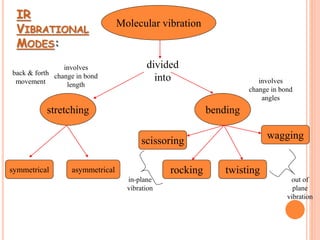
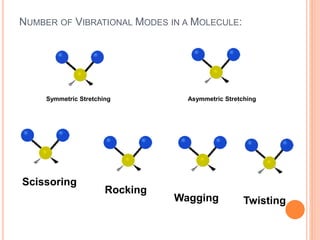
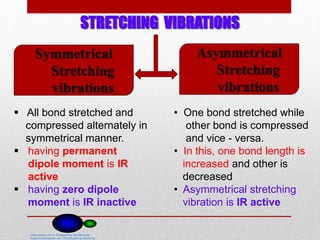
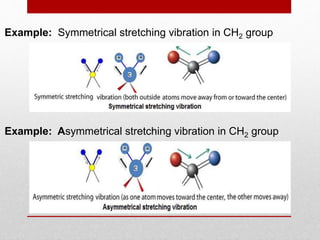
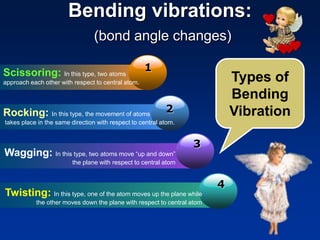
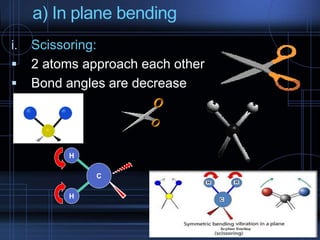
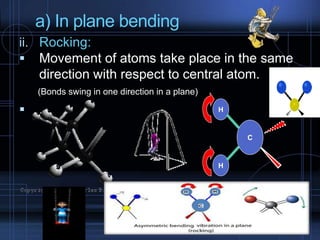
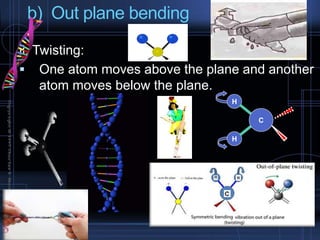
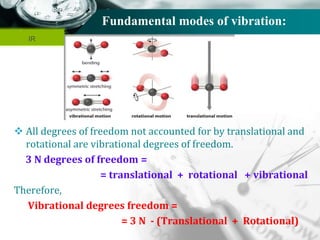
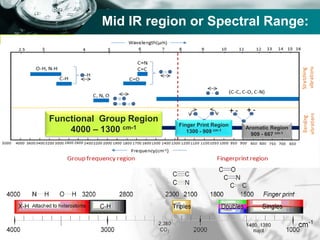
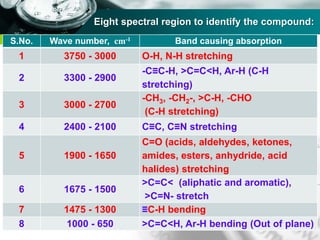
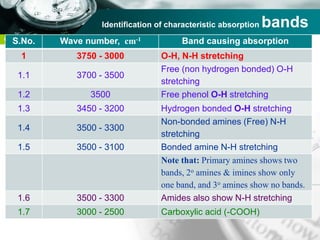
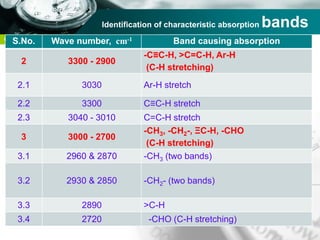
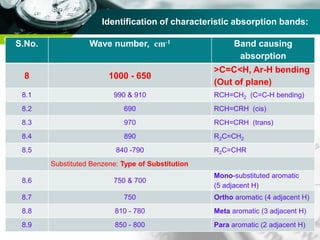
Infrared spectroscopy is a technique used to identify functional groups in a compound based on the vibrational transitions of bonds observed in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The most common technique is absorption spectroscopy, where infrared radiation is passed through a sample and the frequencies at which absorption occurs are measured. For a molecule to absorb infrared radiation, the vibration must cause a change in the dipole moment of the molecule. There are two main types of vibrations observed - stretching vibrations which change bond lengths, and bending vibrations which change bond angles. Stretching vibrations are further divided into symmetrical and asymmetrical types. Bending vibrations include in-plane and out-of-plane types such as scissoring,





































![Company name
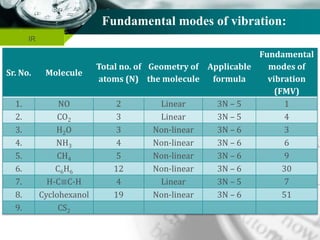
Structure of Organic Compounds:
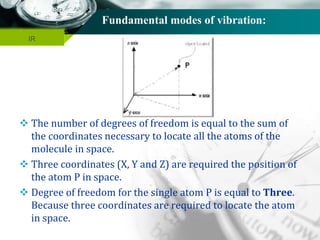
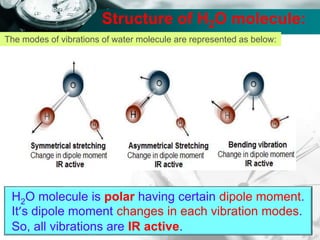
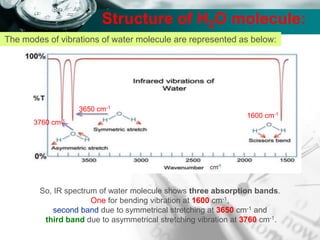
Structure of H2O molecule:
The total fundamental mode of vibration of
non-linear, H2O molecule are (3N-6) =
= [(3 x 3) – 6] = 3
Out of three fundamental mode of vibration;
The molecule containing N number of total
atom has (N-1) number of stretching vibration.
i.e., (3-1) = 2 vibration are stretching vibration
and one vibration is bending vibration.
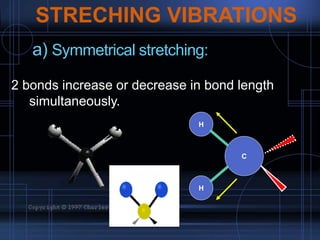
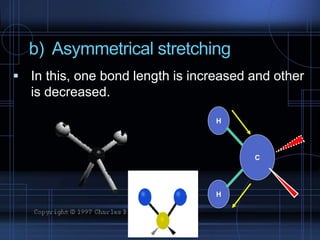
Out of two stretching vibration; one is
symmetrical stretching vibration and another is
asymmetrical stretching vibration.
IR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irspectroscopybydr-200306185703/85/Ir-spectroscopy-by-dr-pramod-r-padole-81-320.jpg)

![Company name
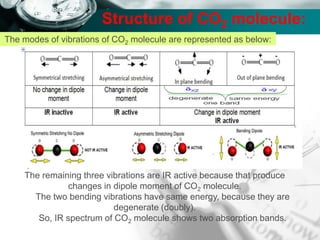
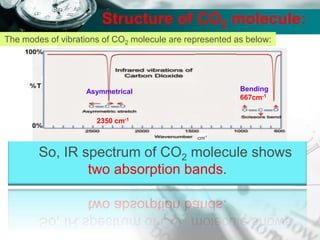
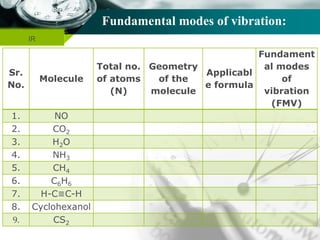
Structure of CO2 molecule:
The modes of vibrations of CO2 molecule are represented as below:
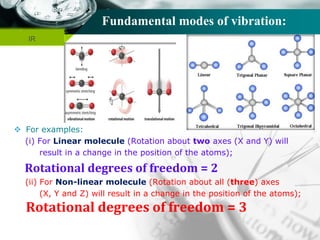
Structure of CO2 molecule: (Linear molecule)
The Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a linear molecule.
CO2 molecule has fundamental modes of vibration =(3N-5)
= [(3 x 3) - 5] = 4.
Out of four fundamental mode of vibration;
The molecule containing N number of total atom has (N-1)
number of stretching vibration.
i.e., (3-1) = 2 vibration are stretching vibration and two
are bending vibration.
Out of two stretching vibration; one is symmetrical
stretching vibration and another is asymmetrical stretching
vibration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irspectroscopybydr-200306185703/85/Ir-spectroscopy-by-dr-pramod-r-padole-85-320.jpg)