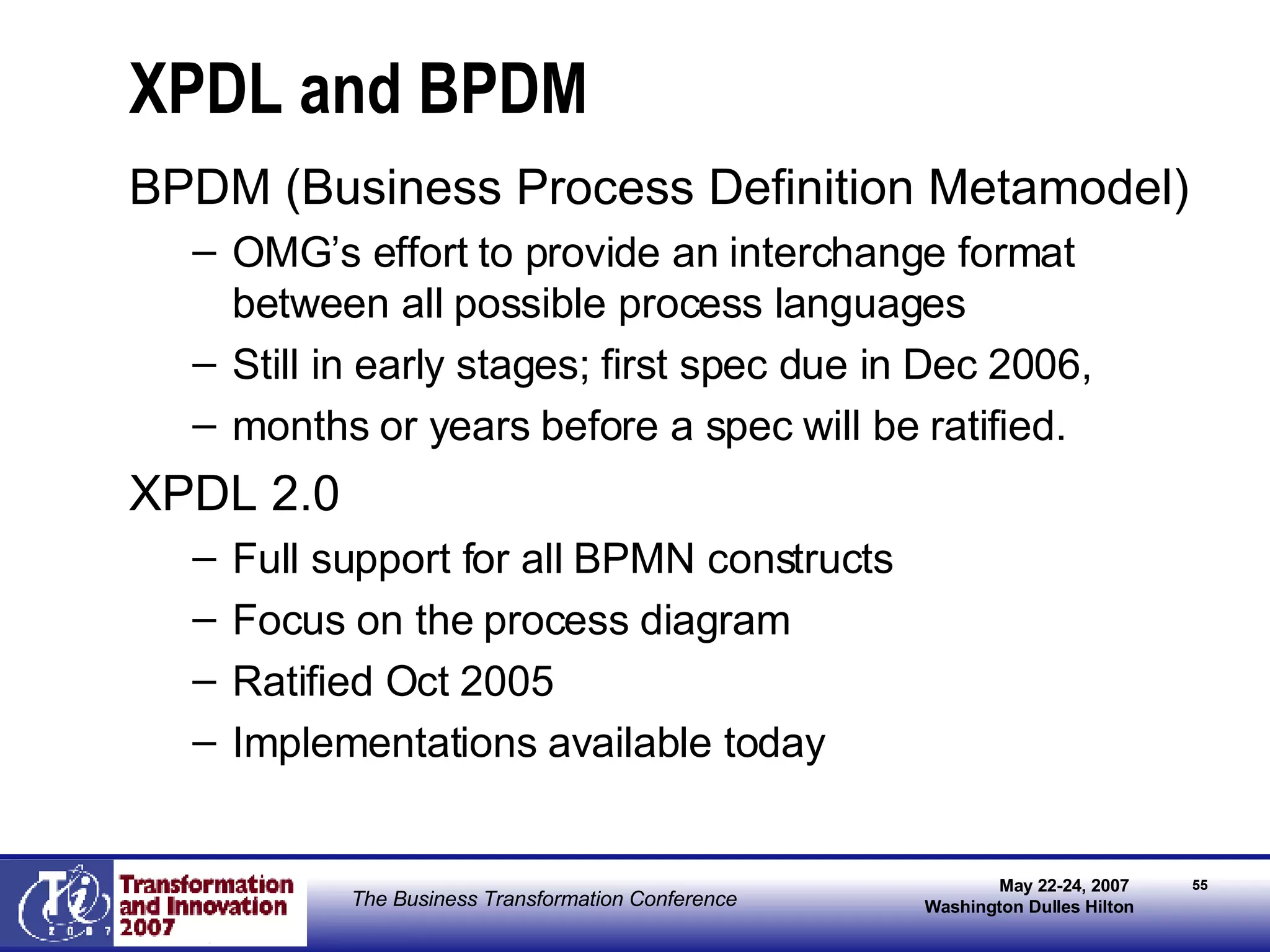
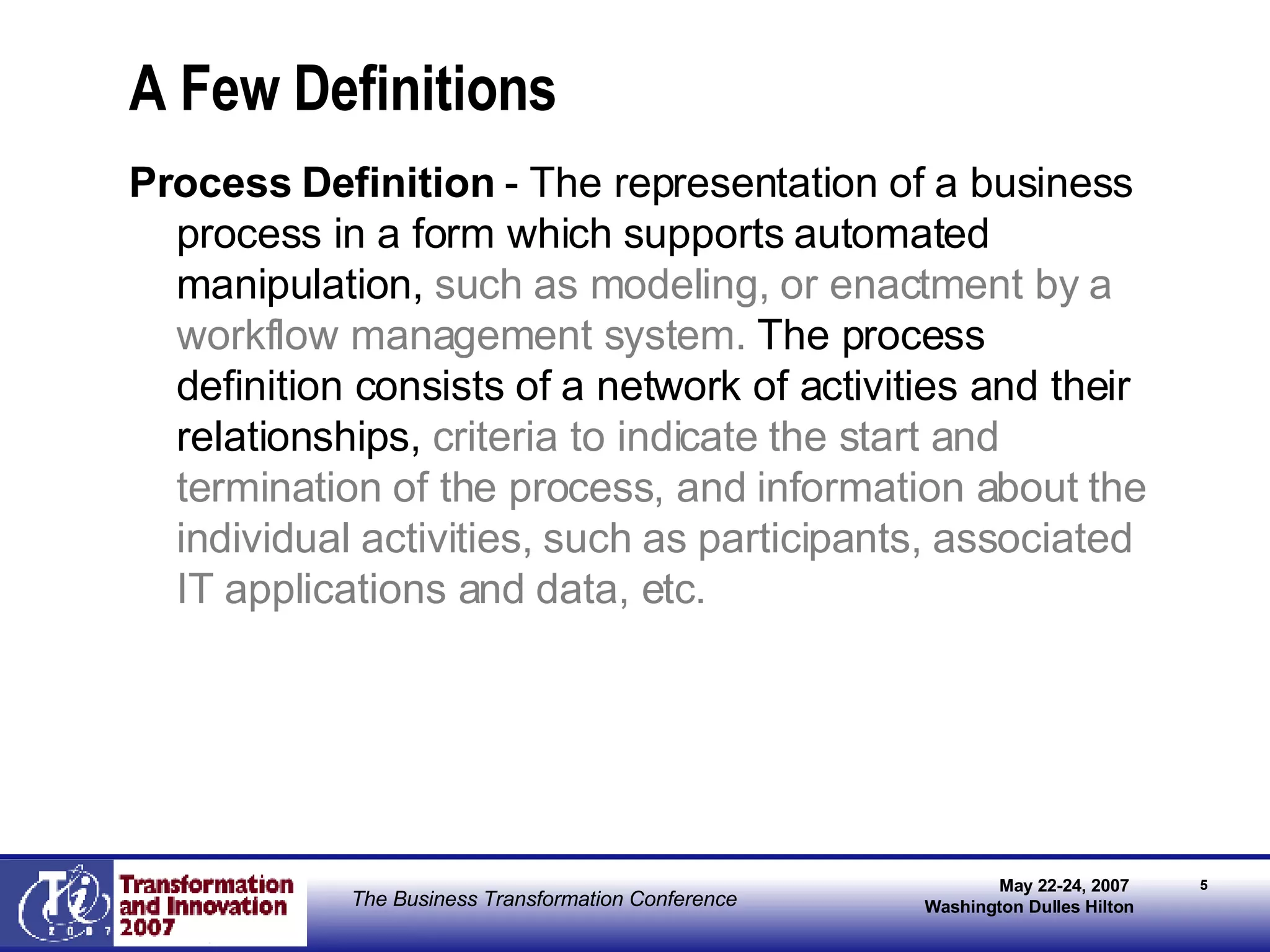
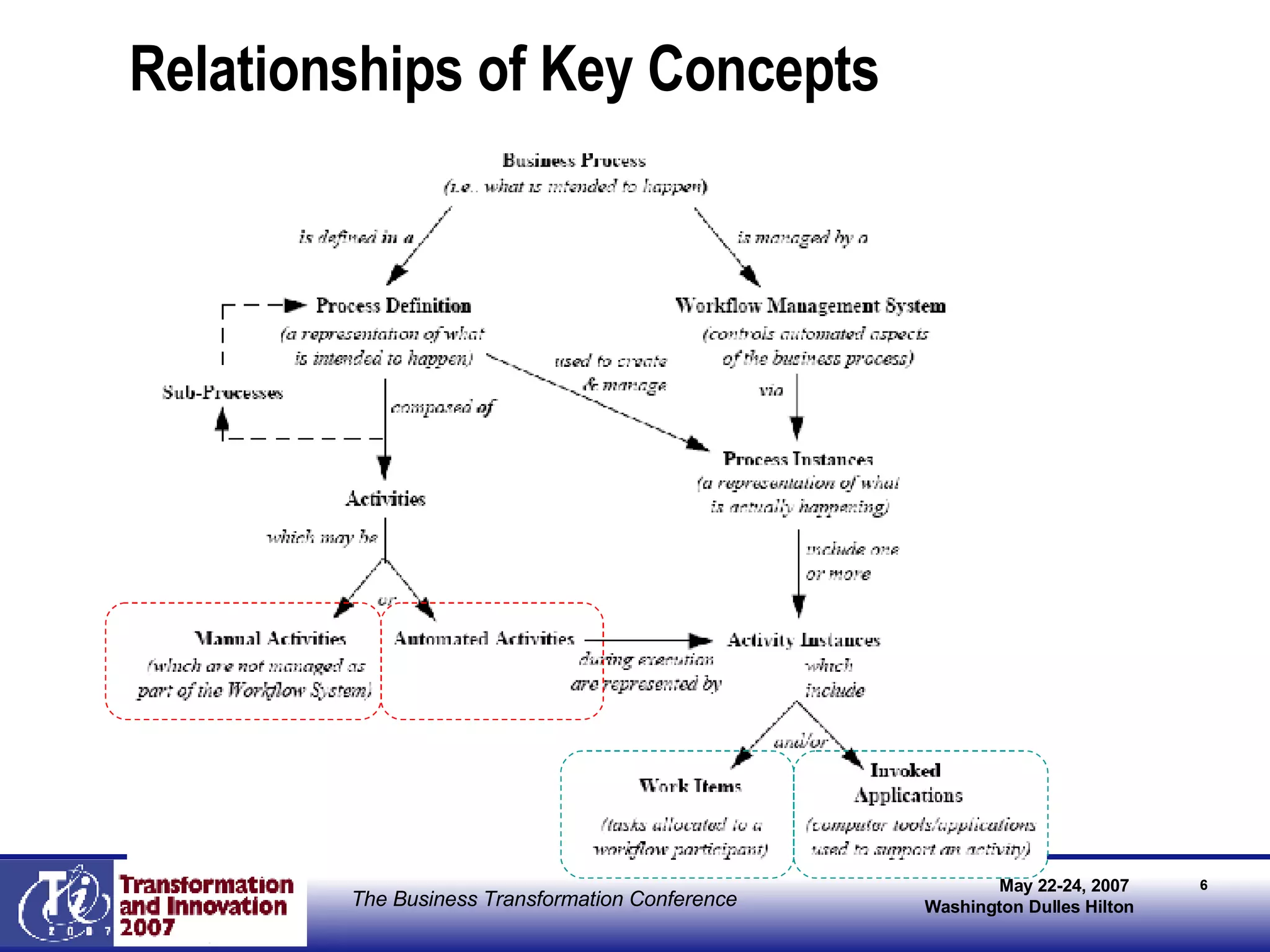
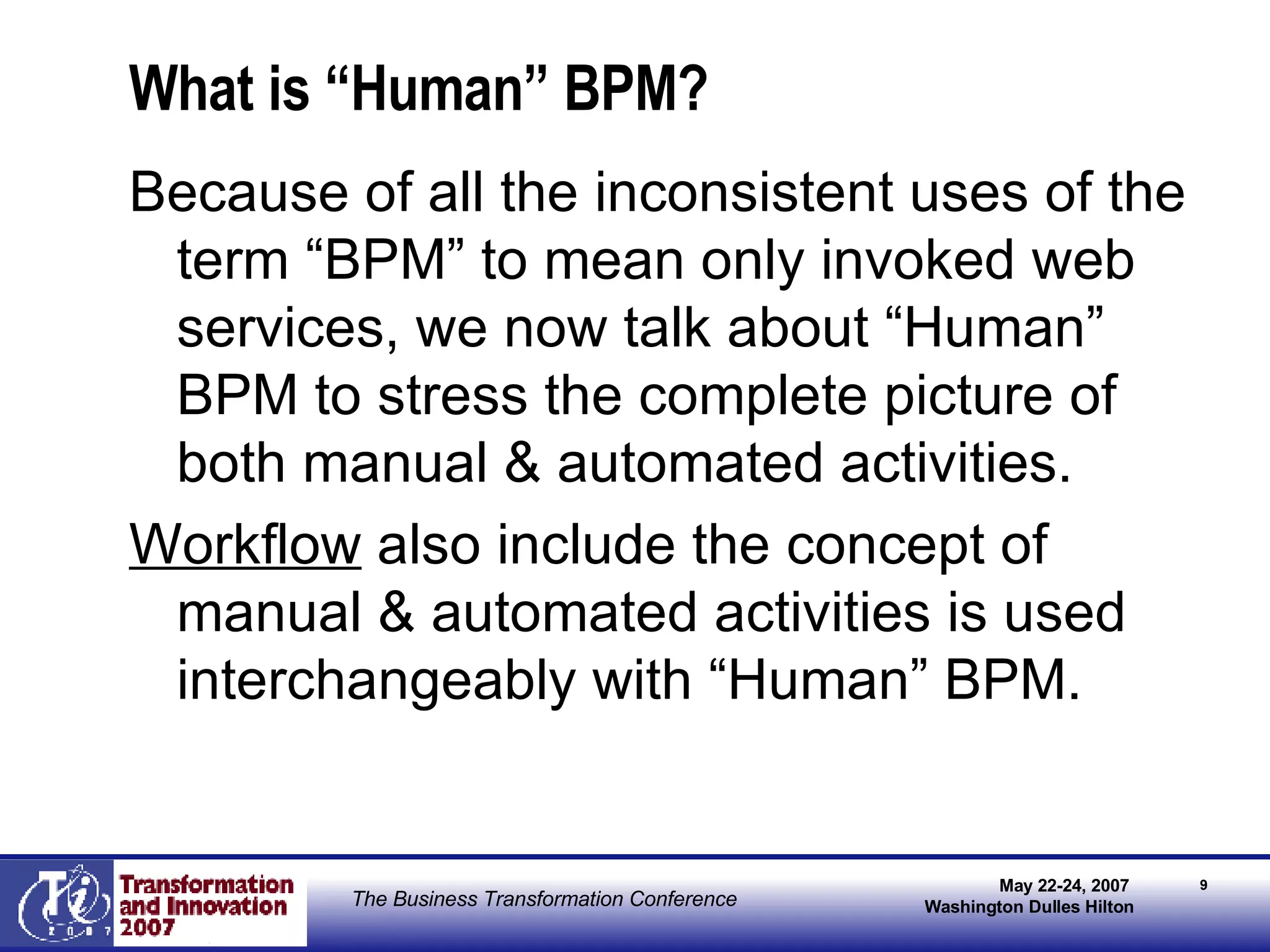
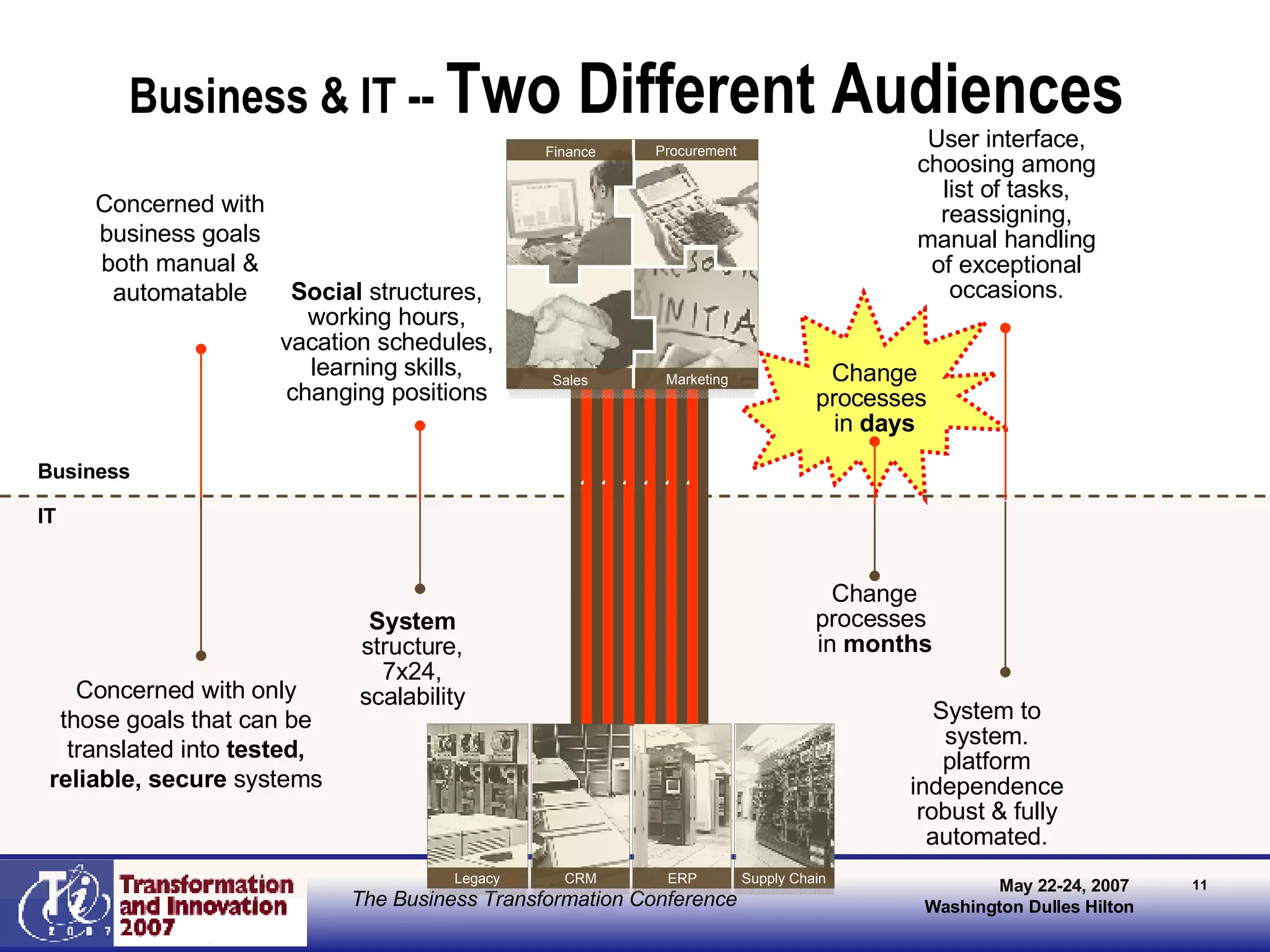
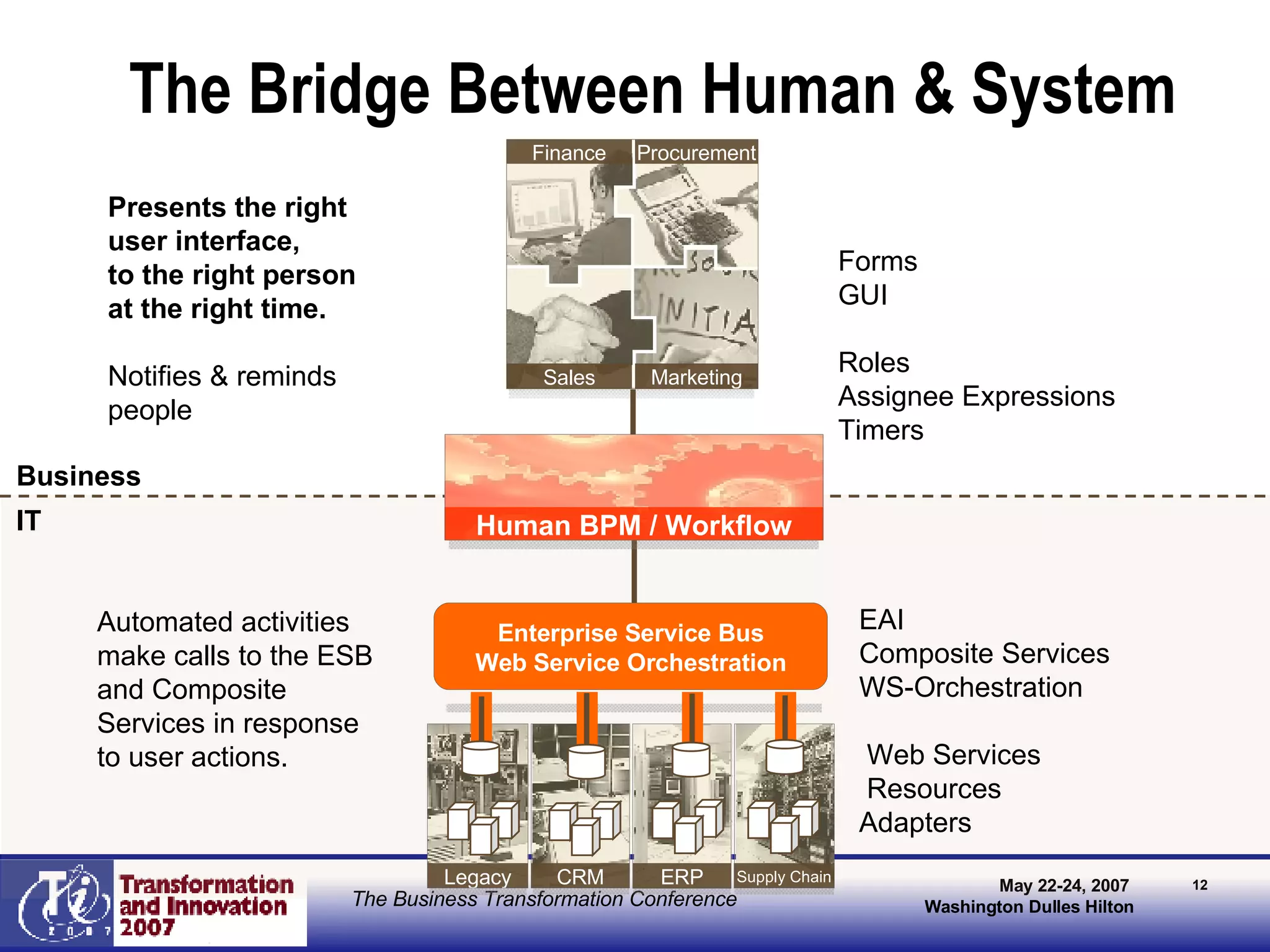
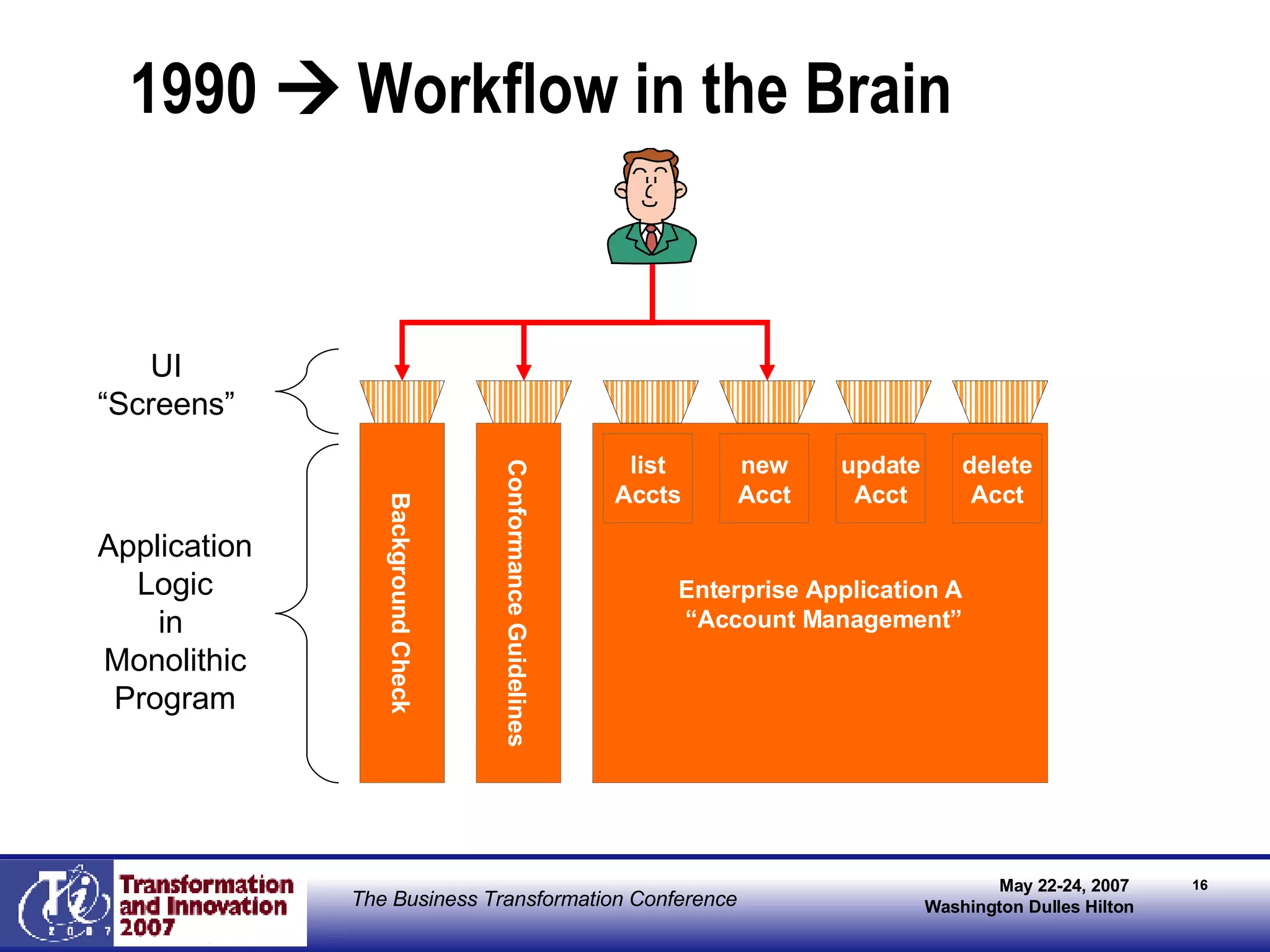
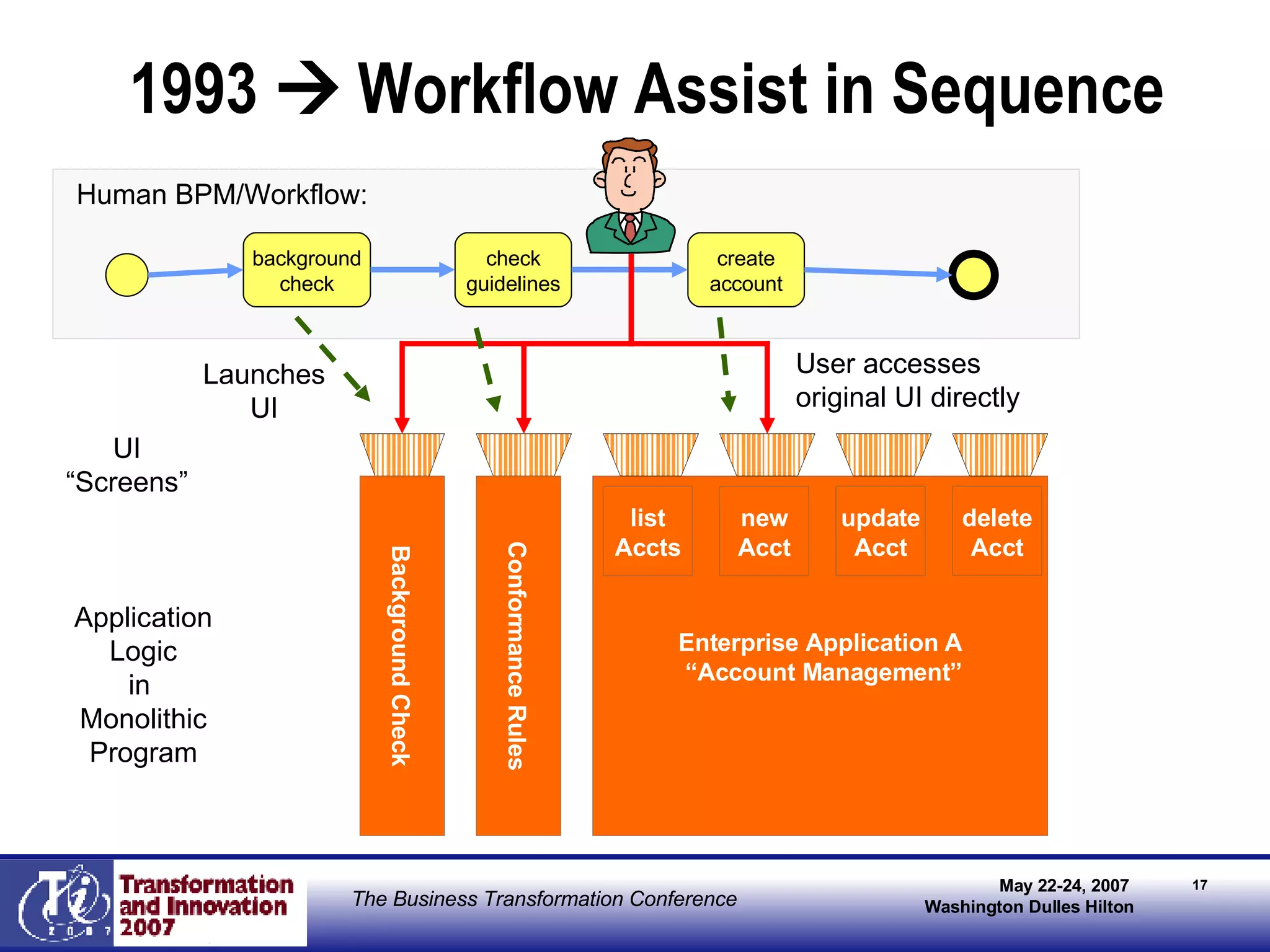
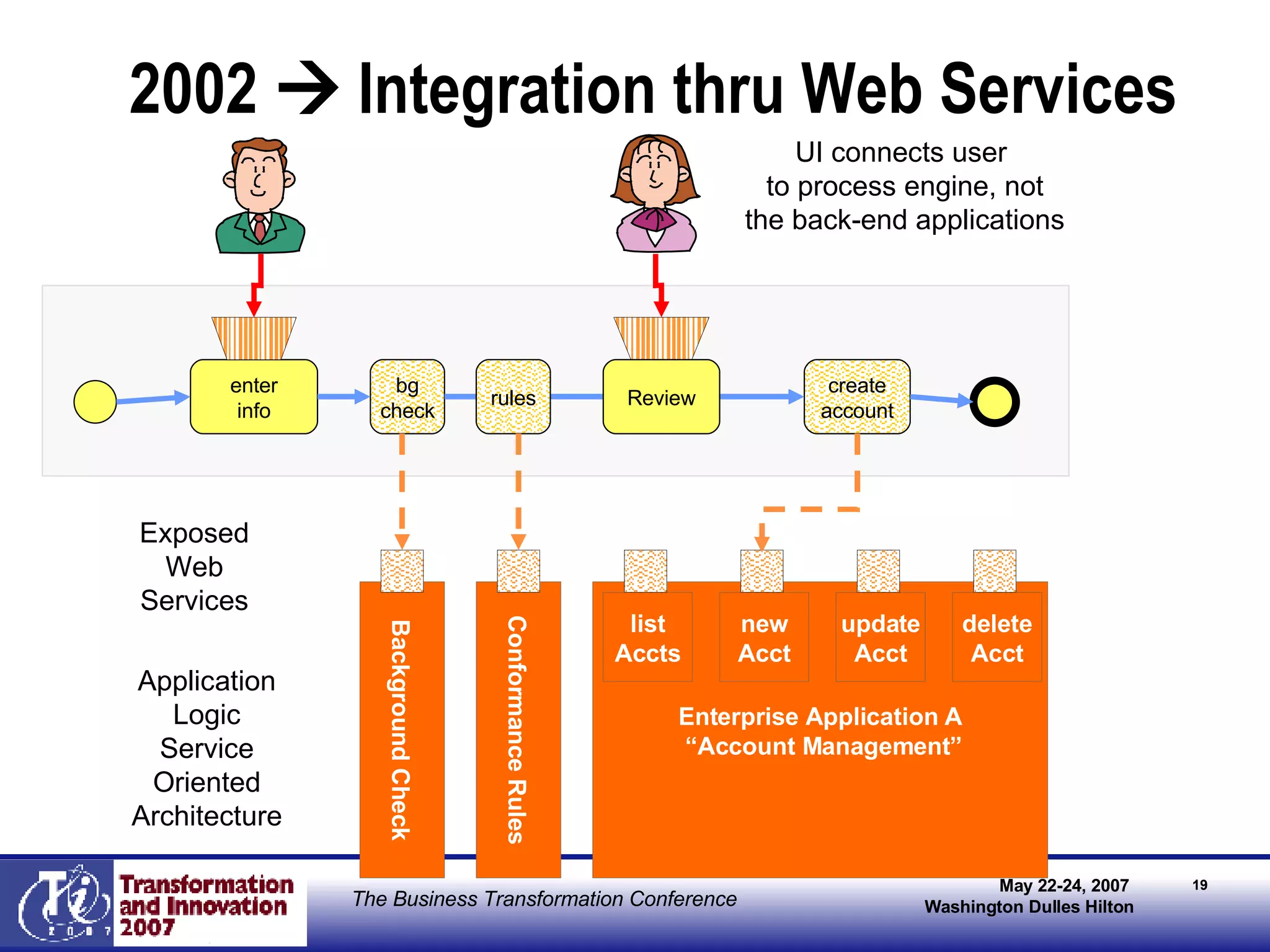
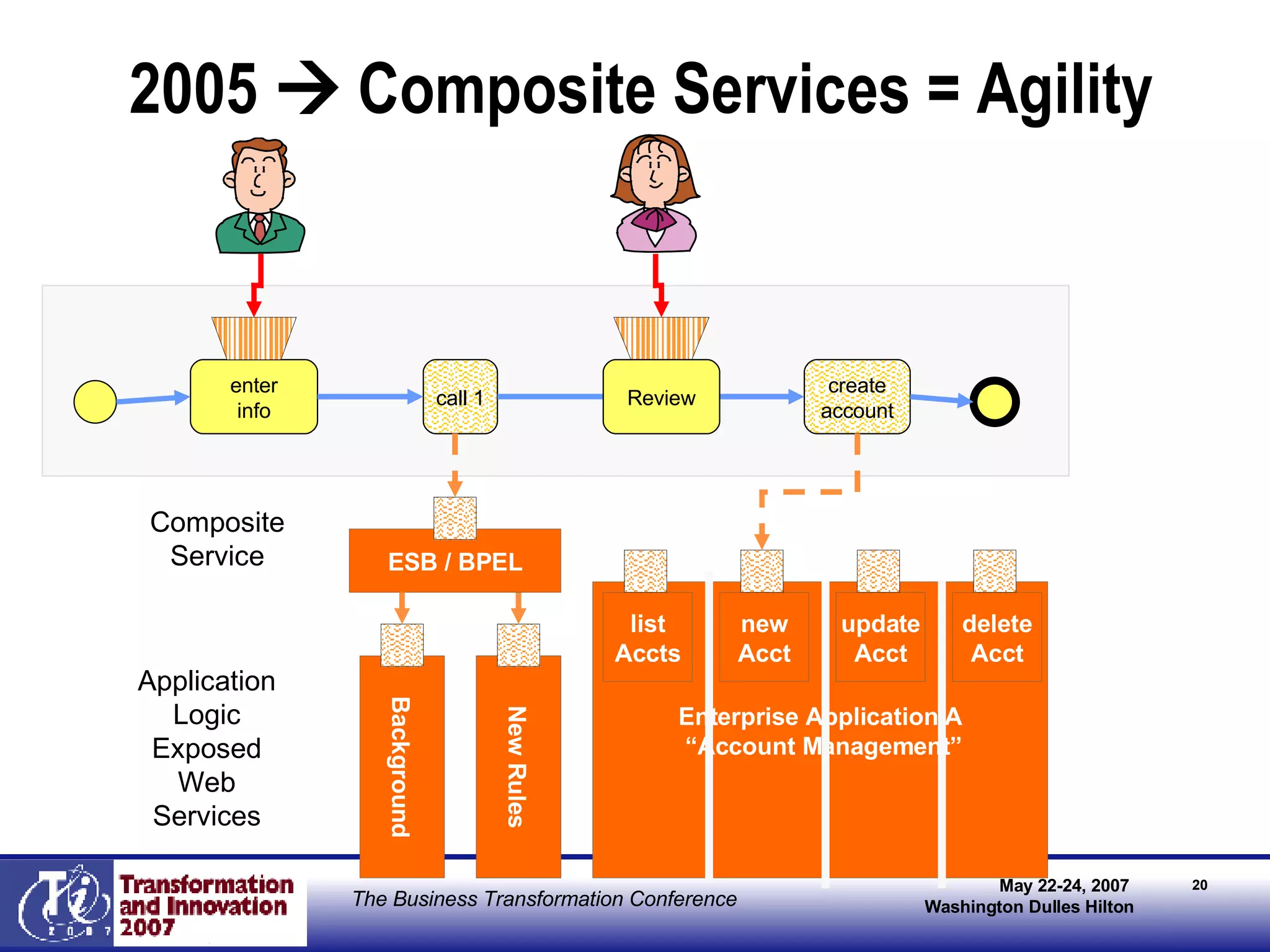
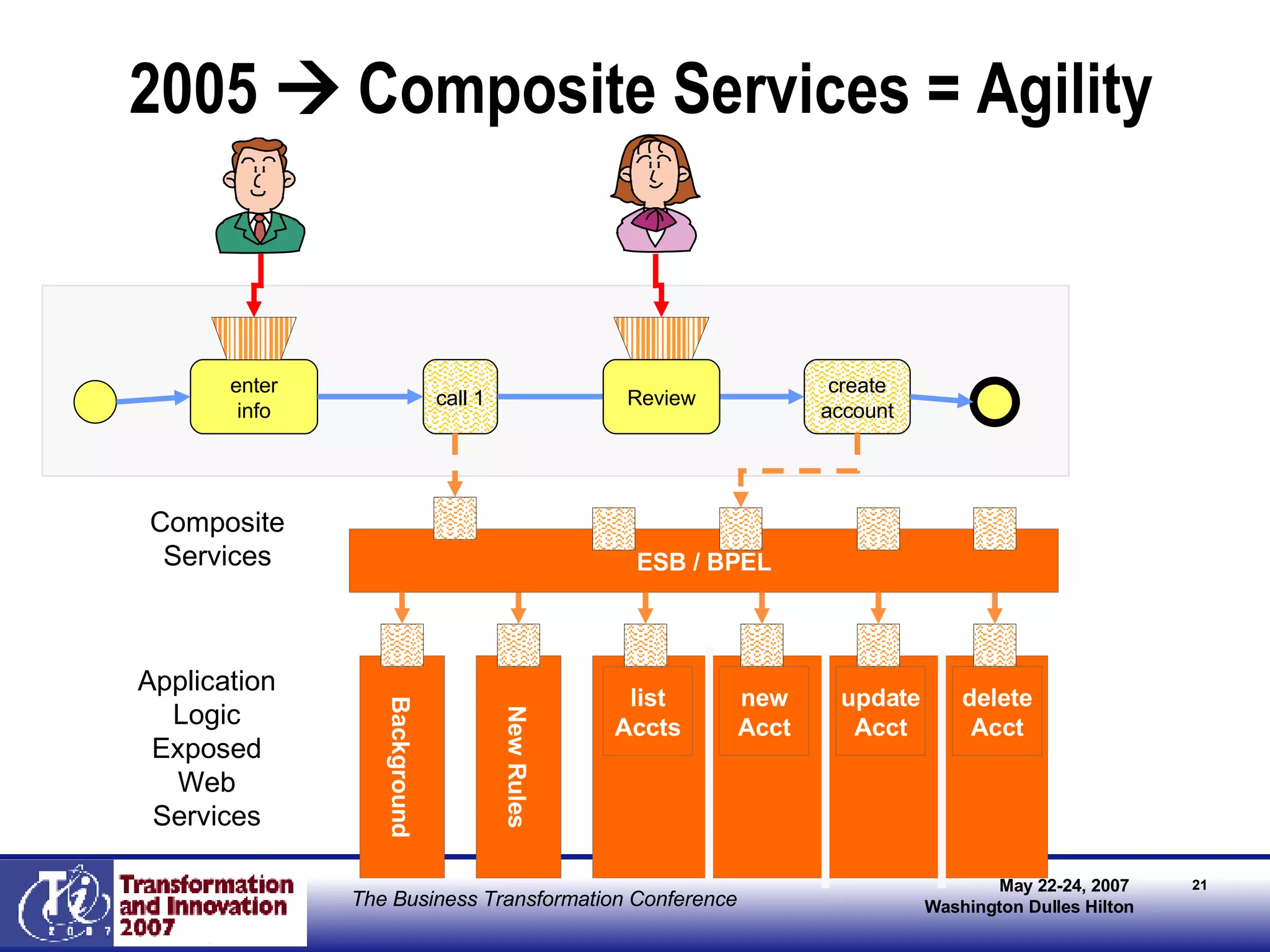
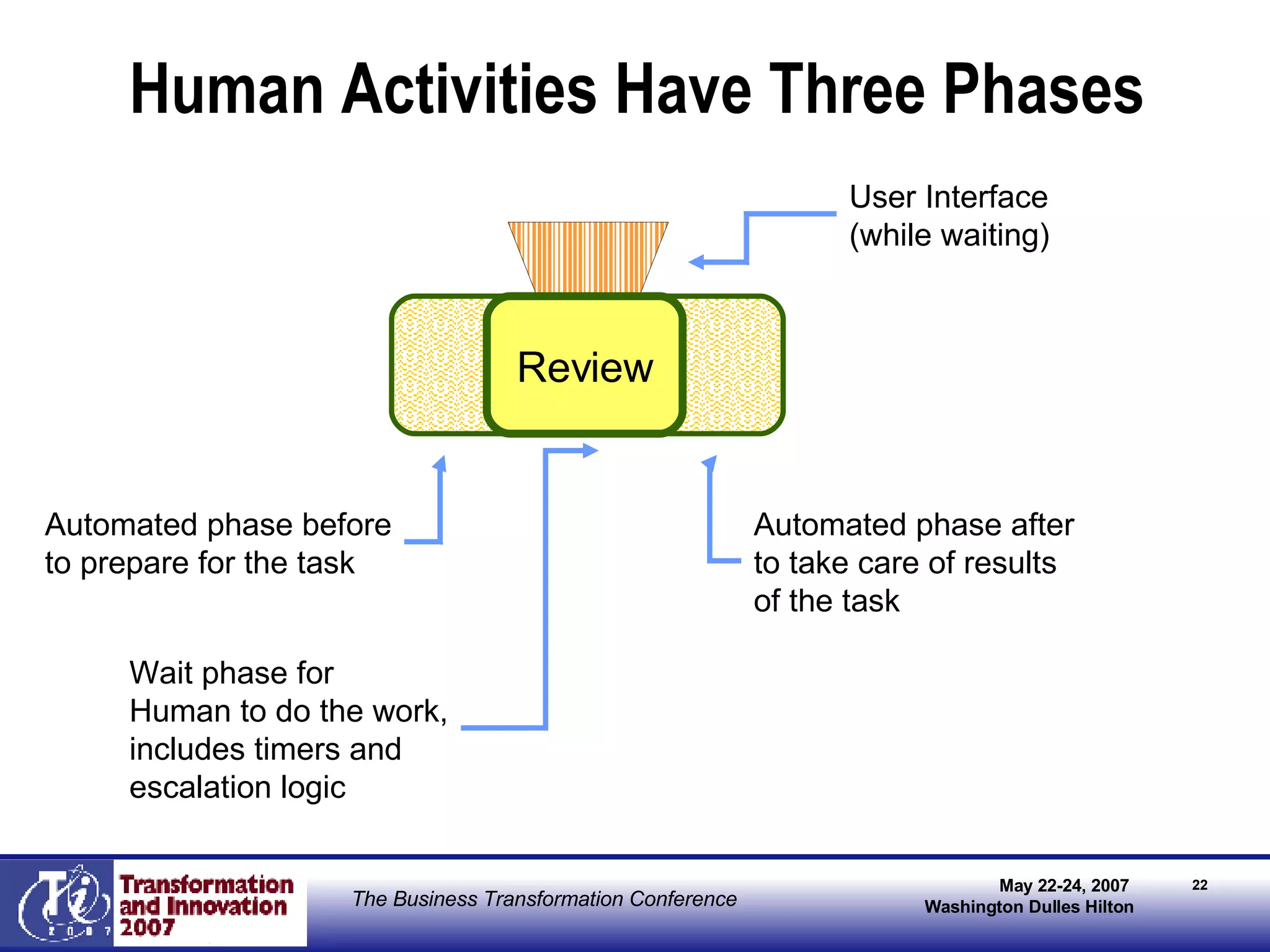
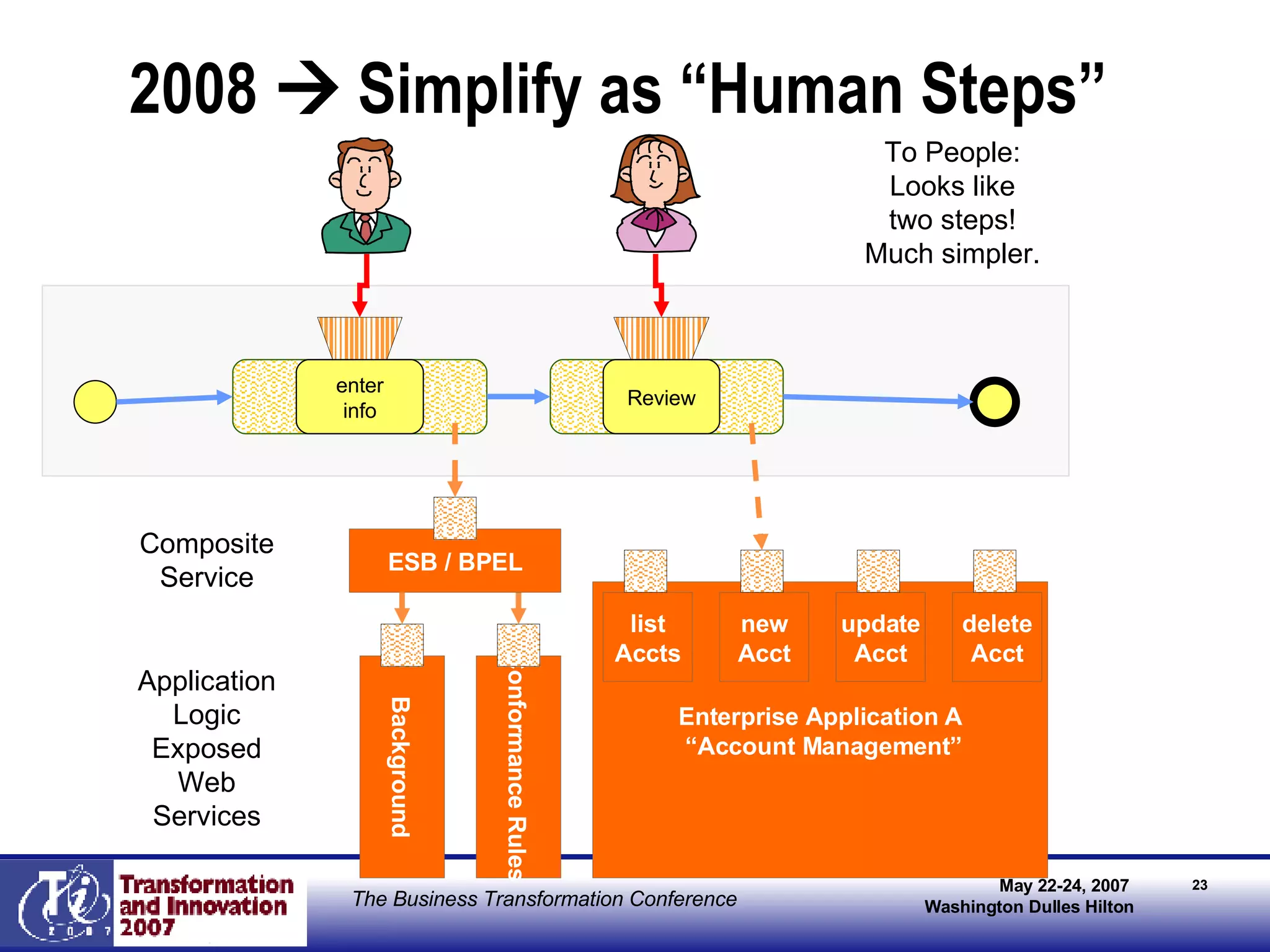
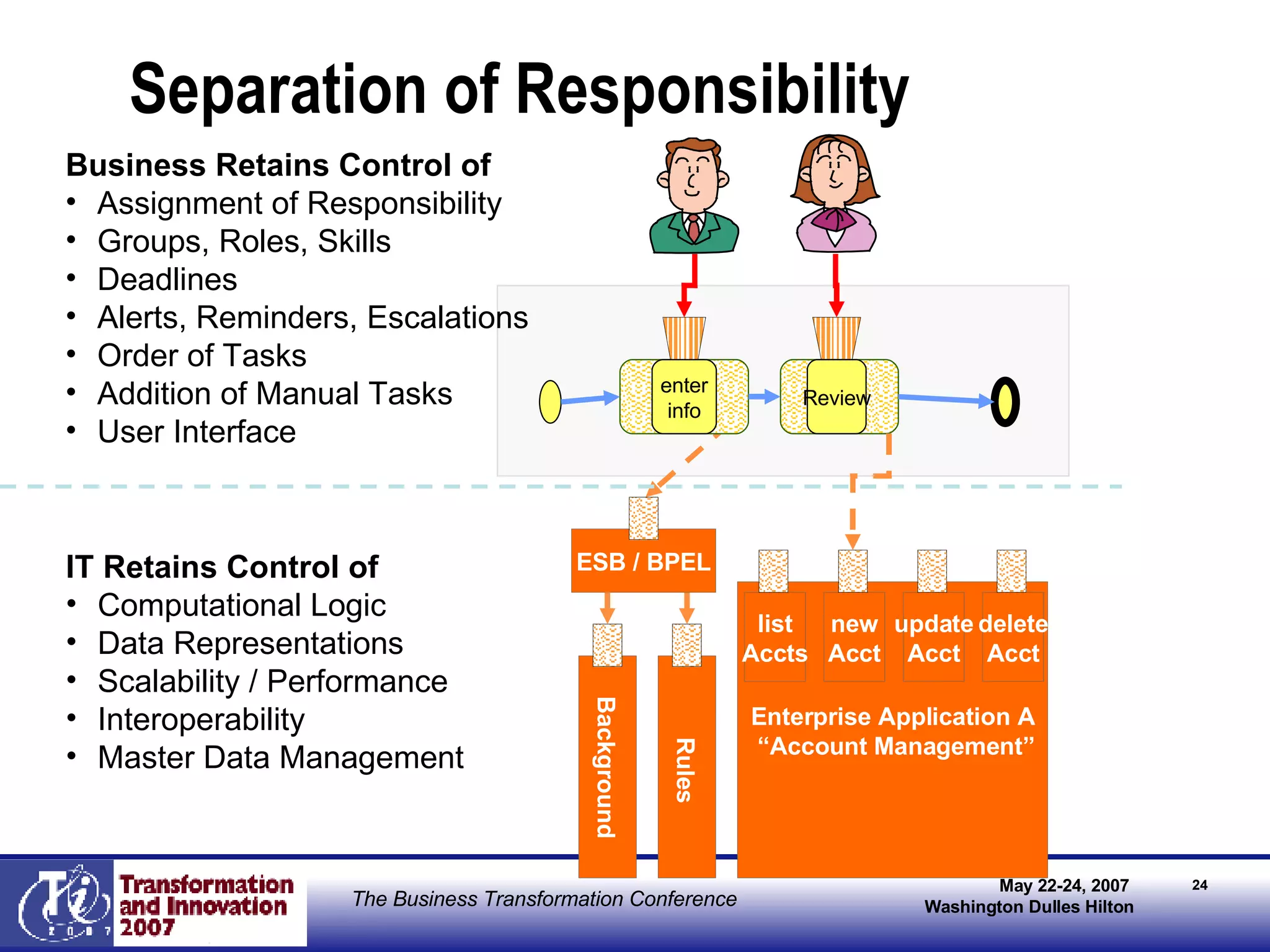
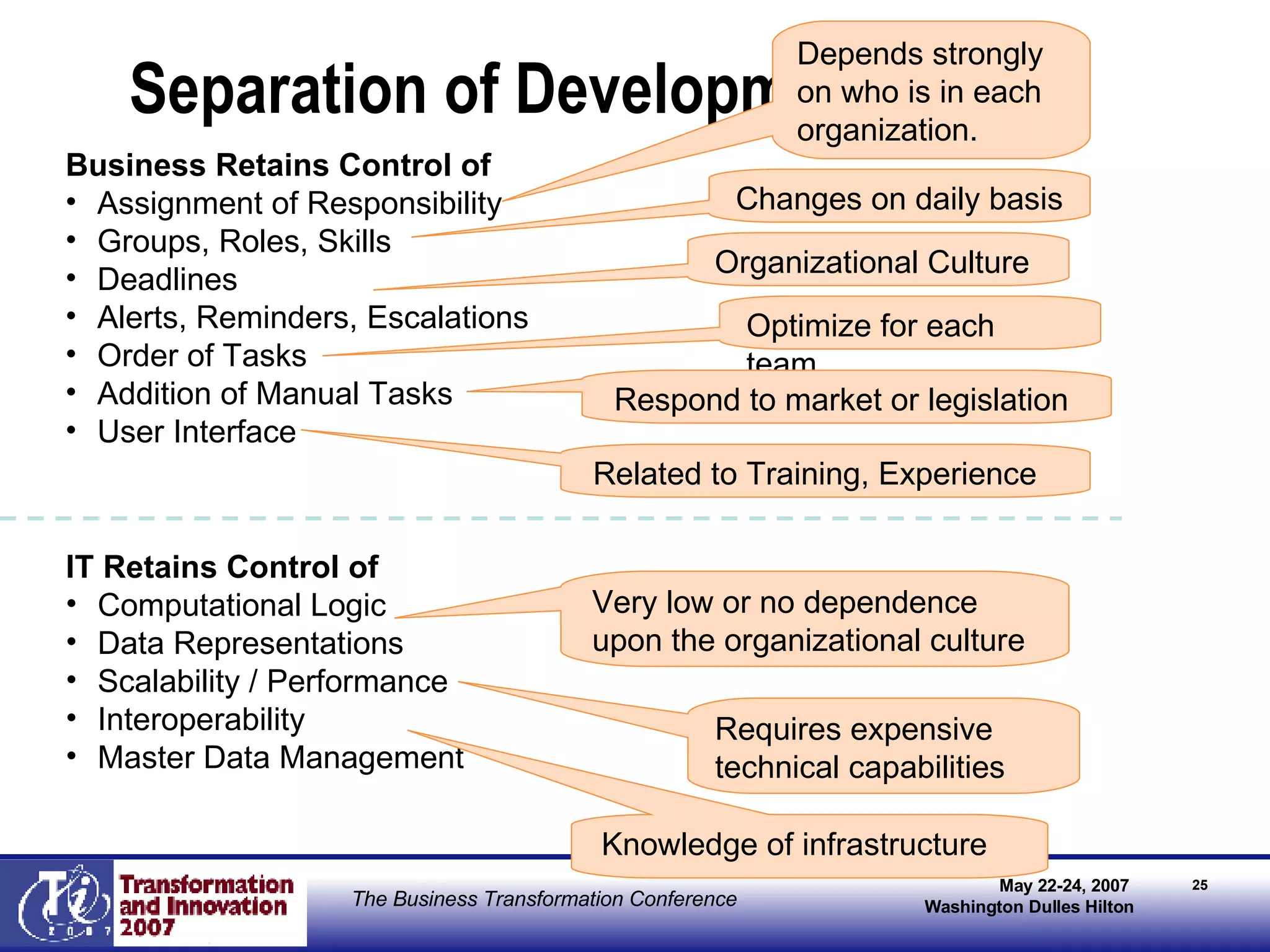
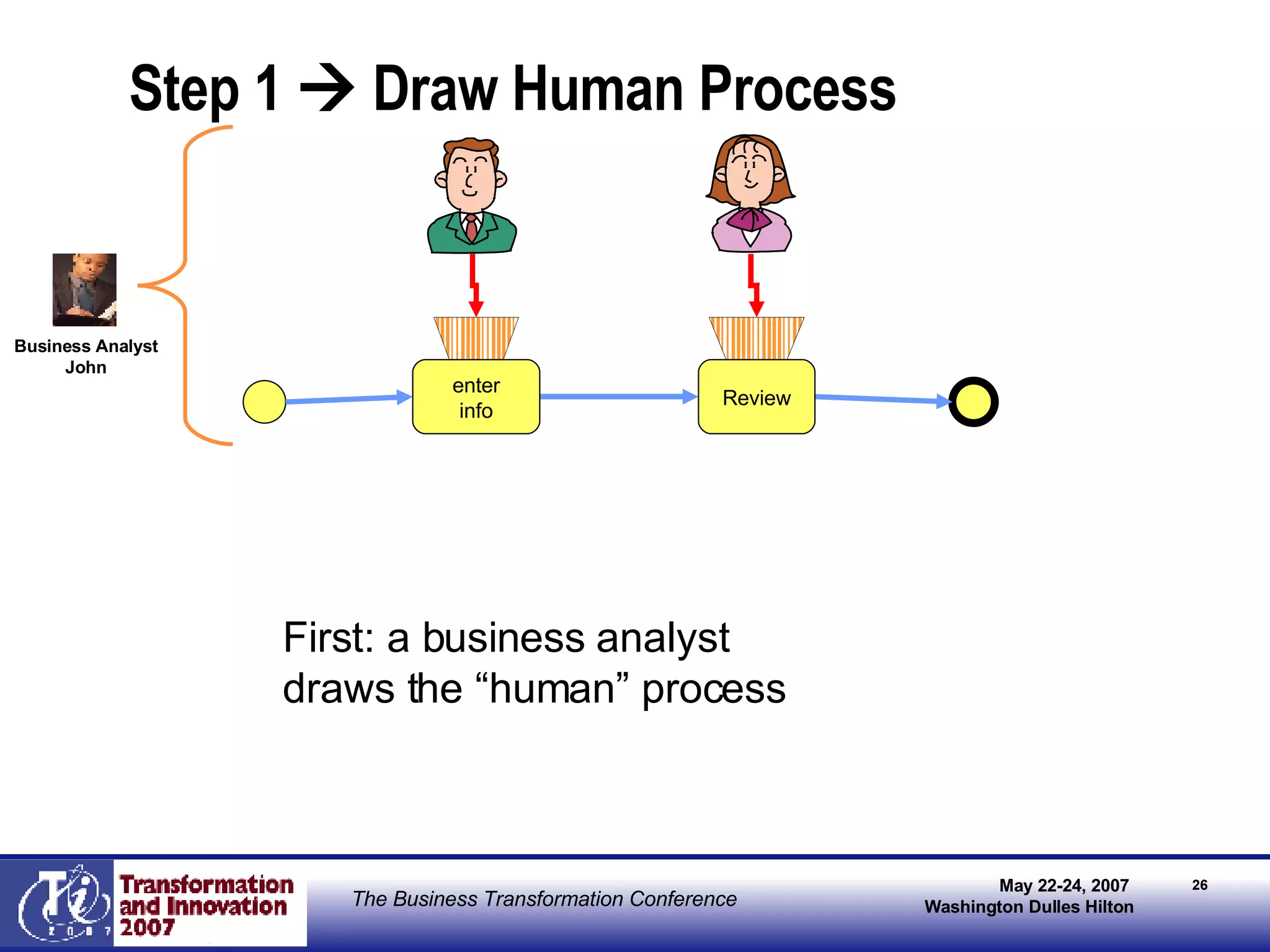
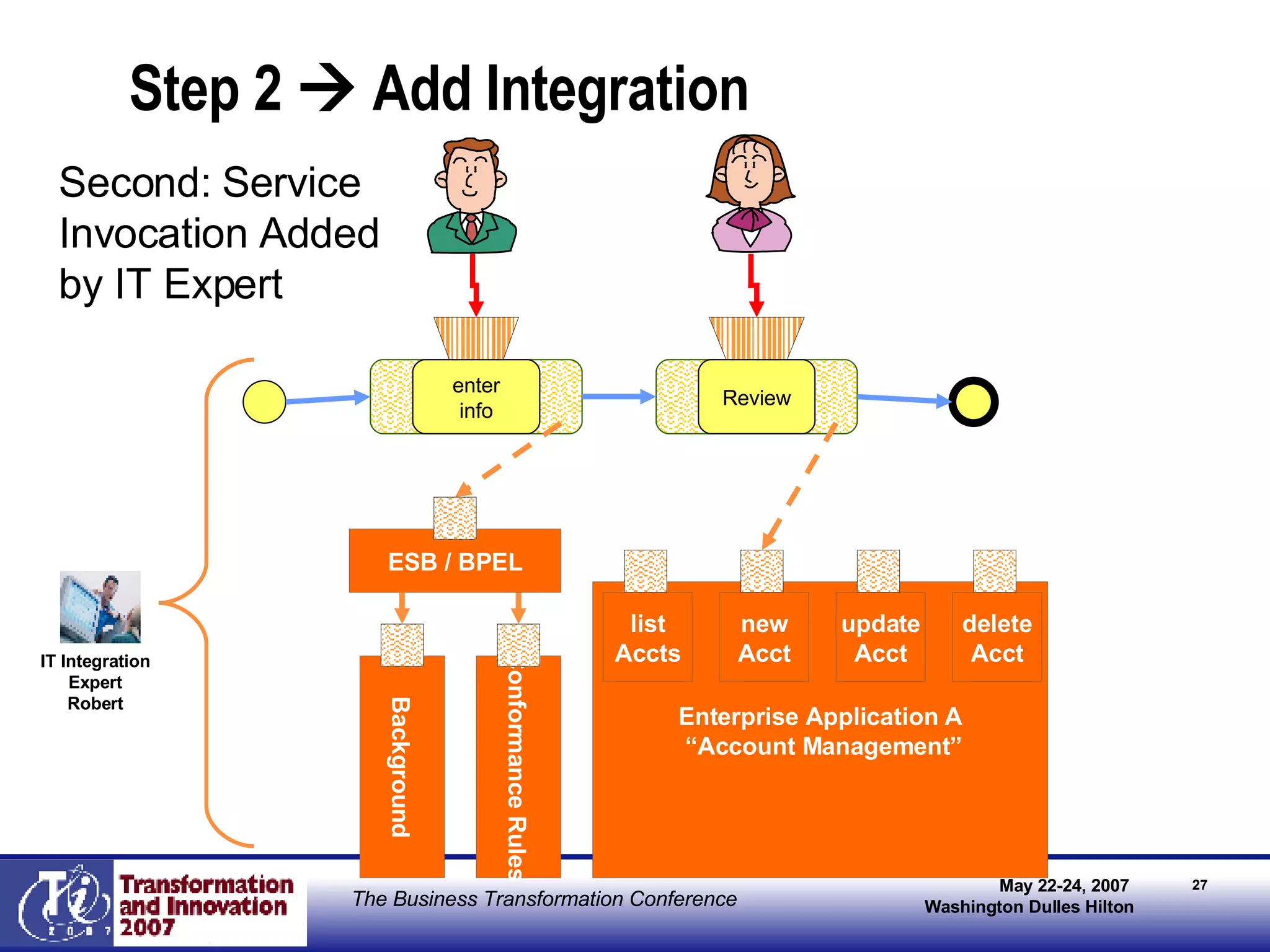
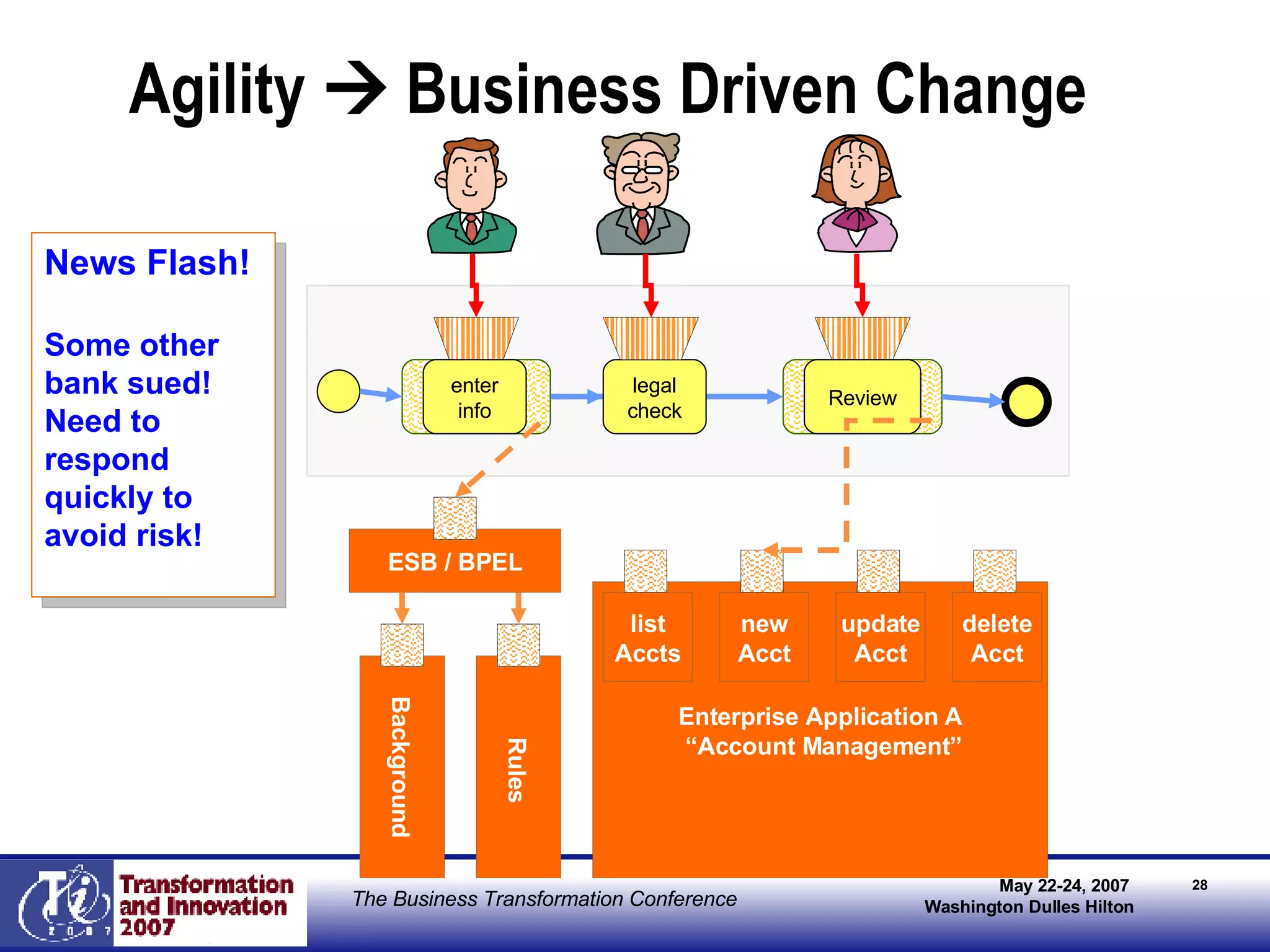
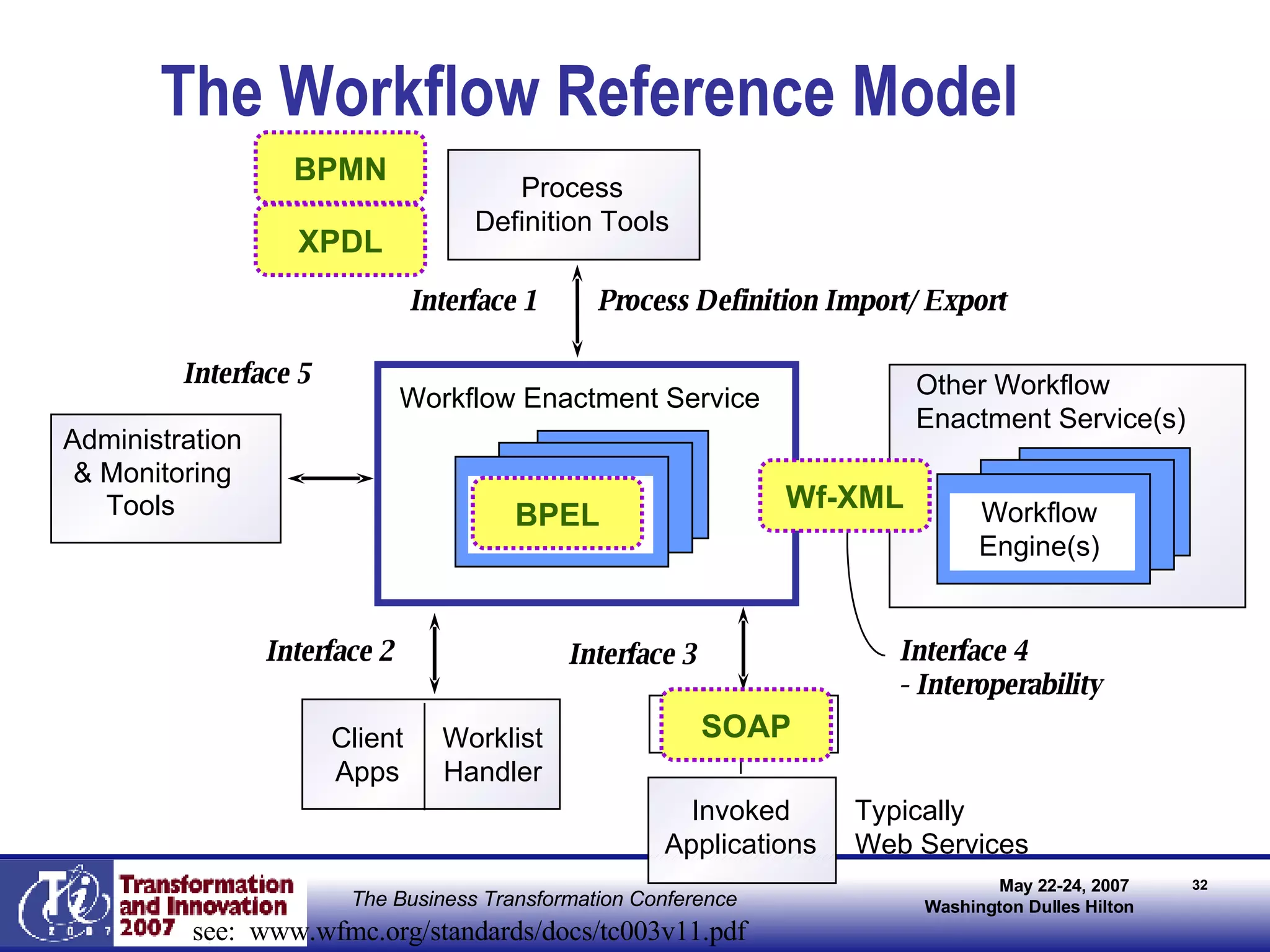
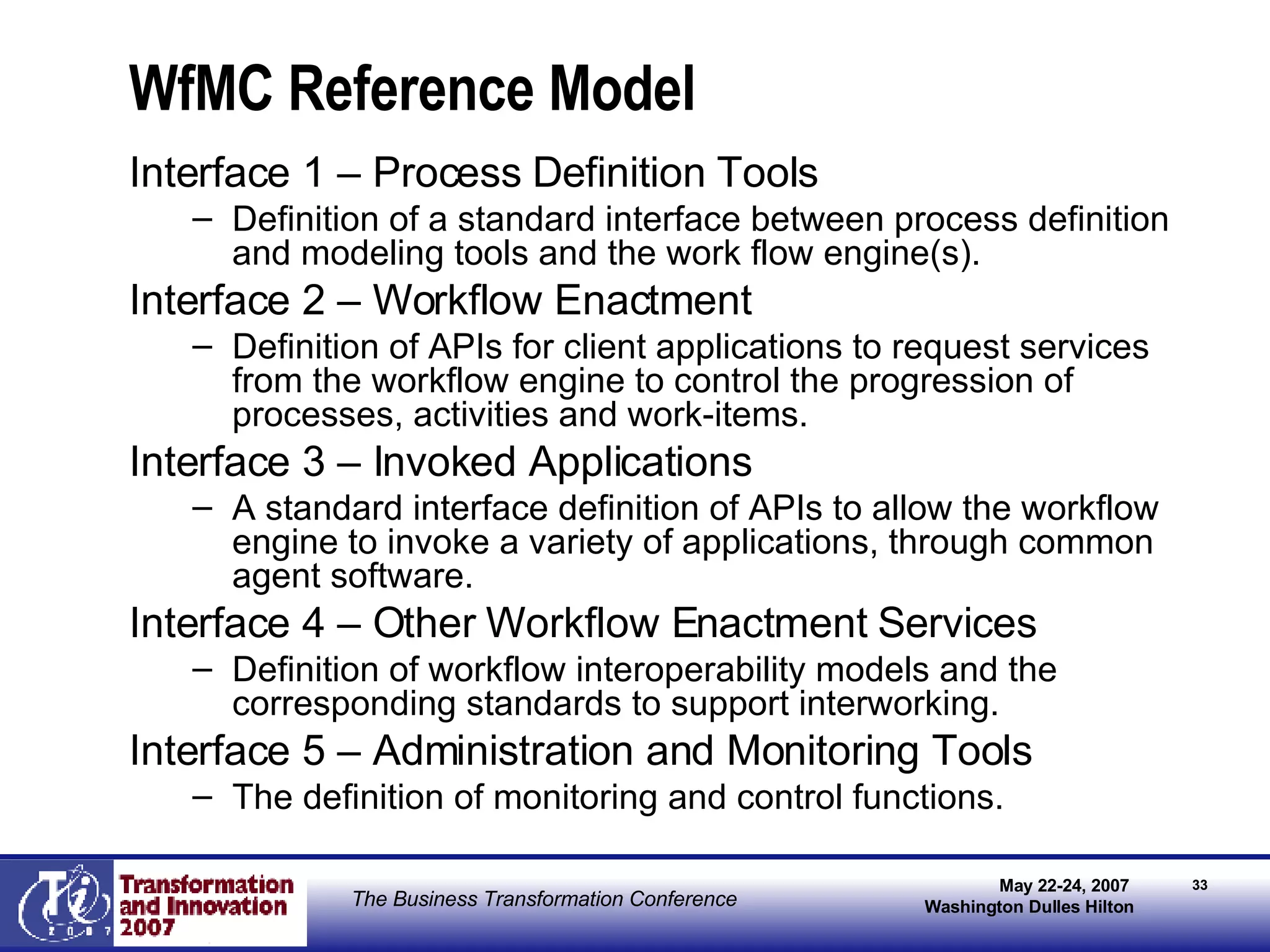
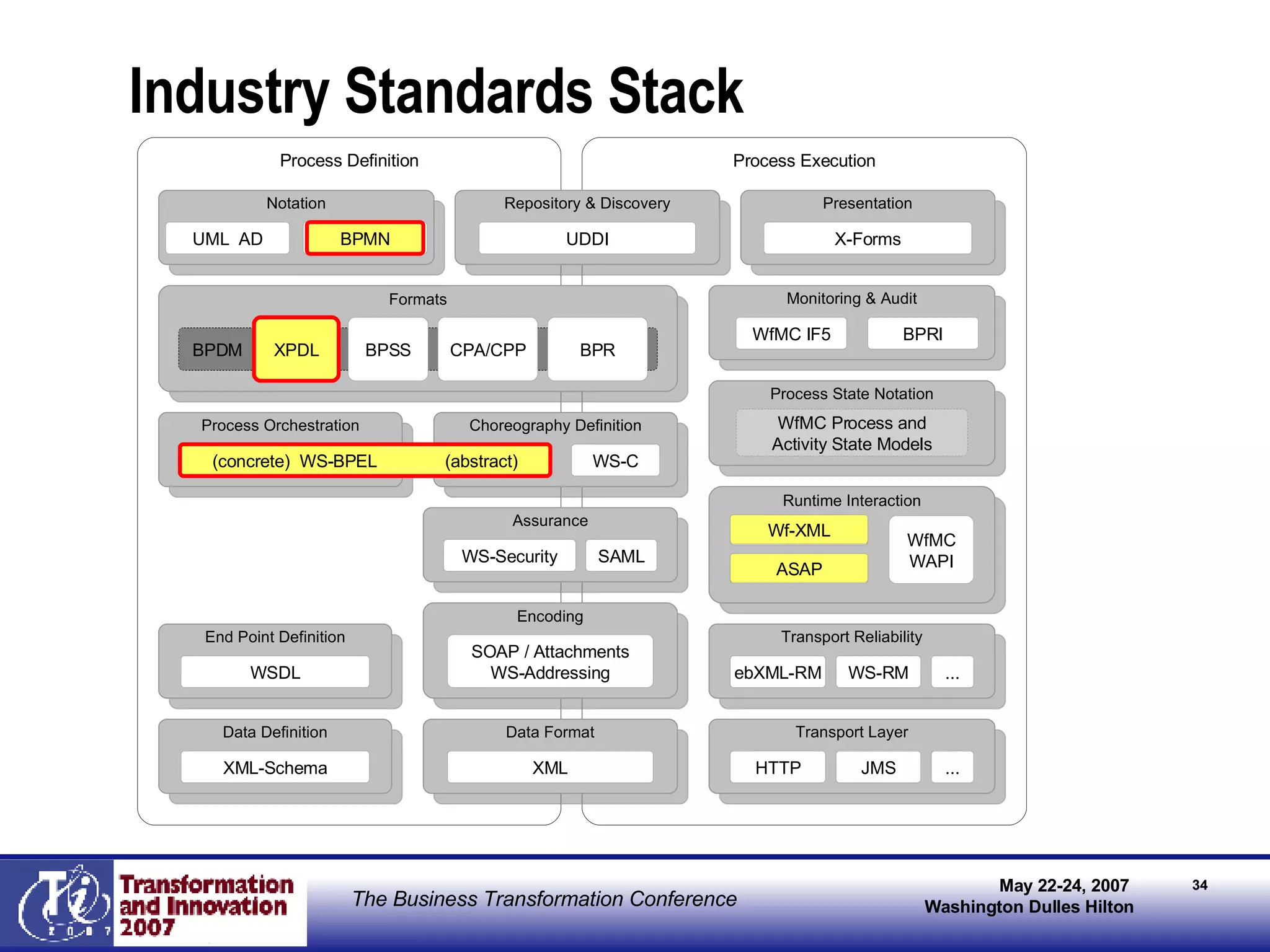
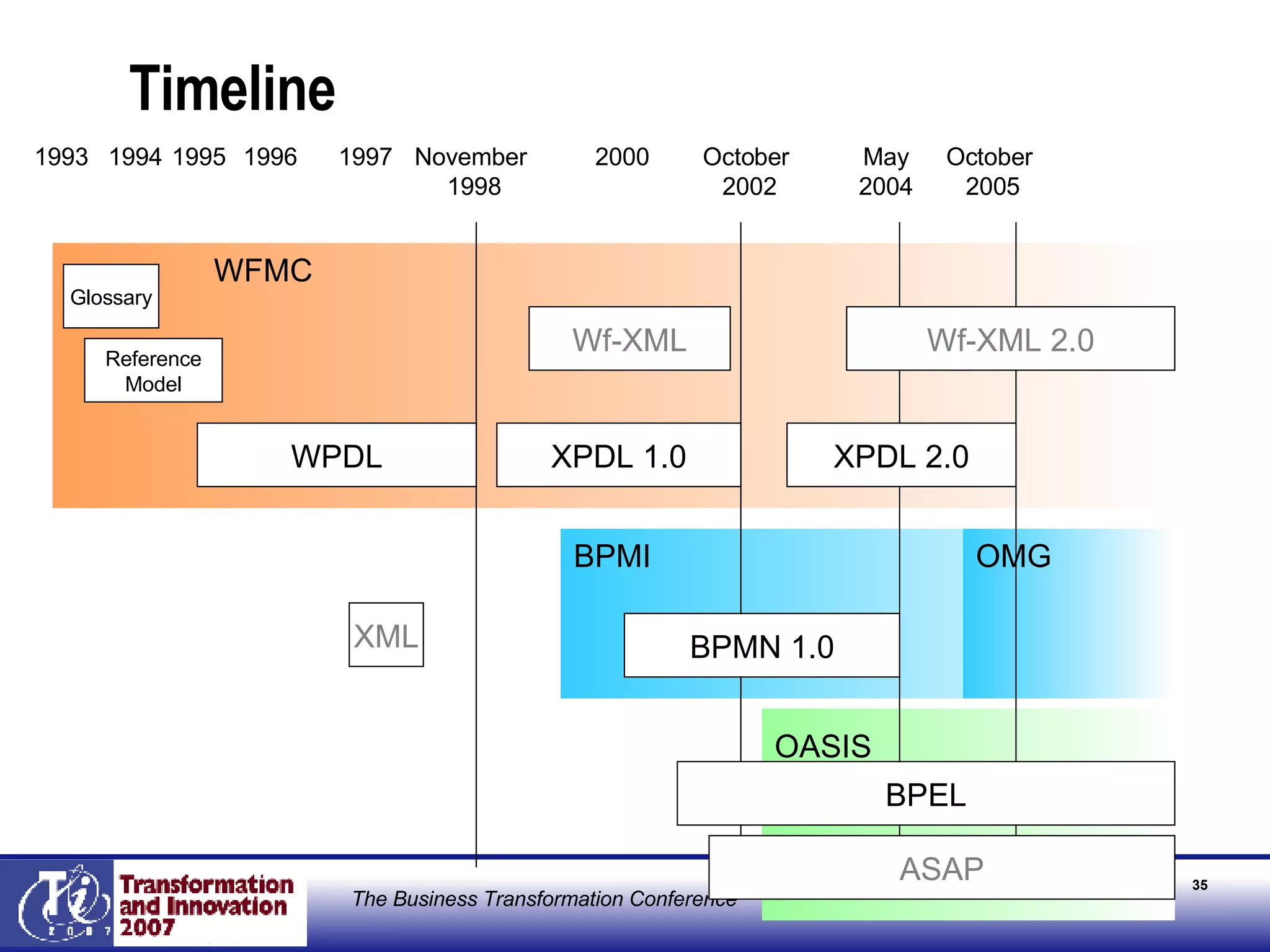
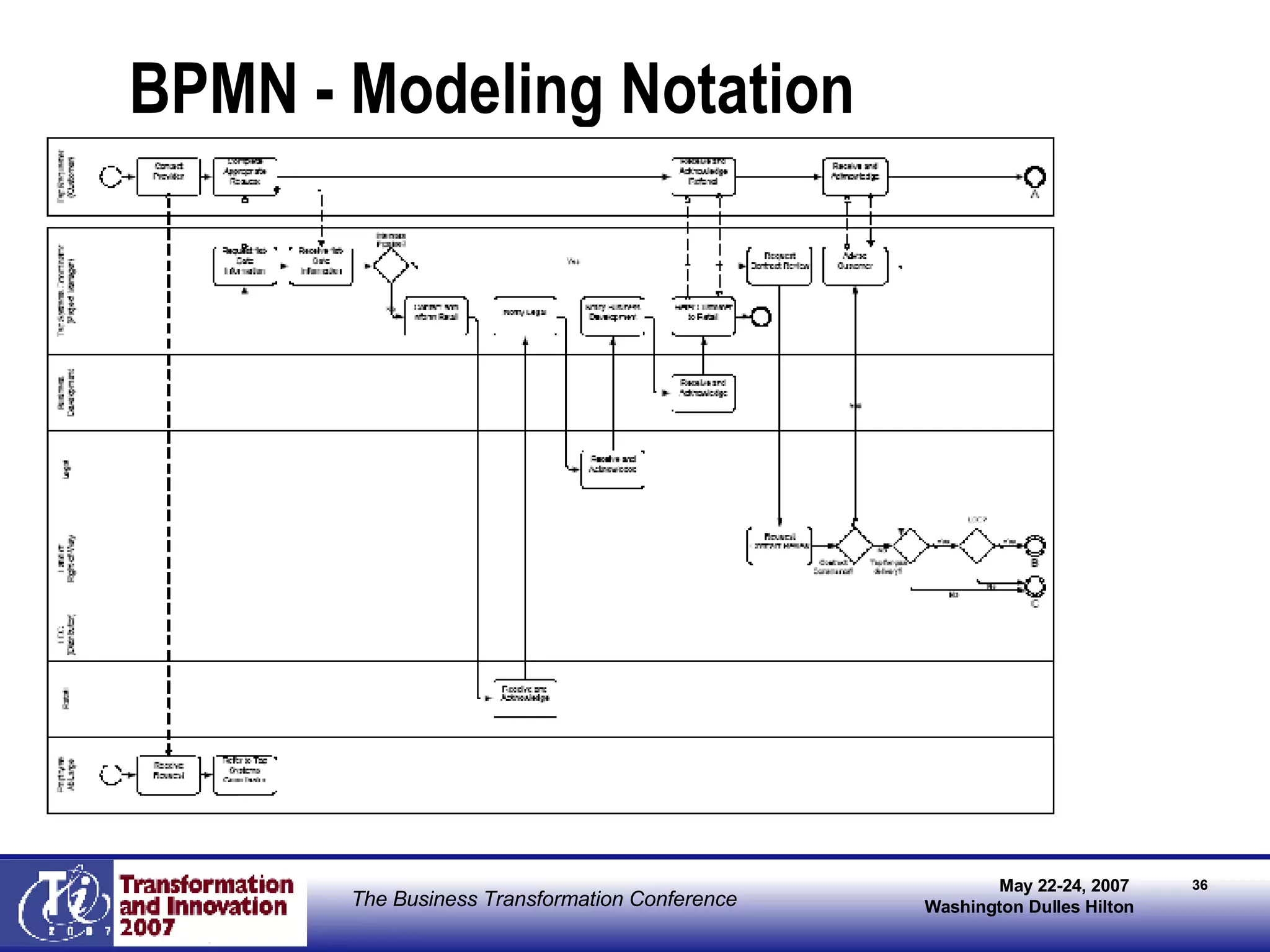
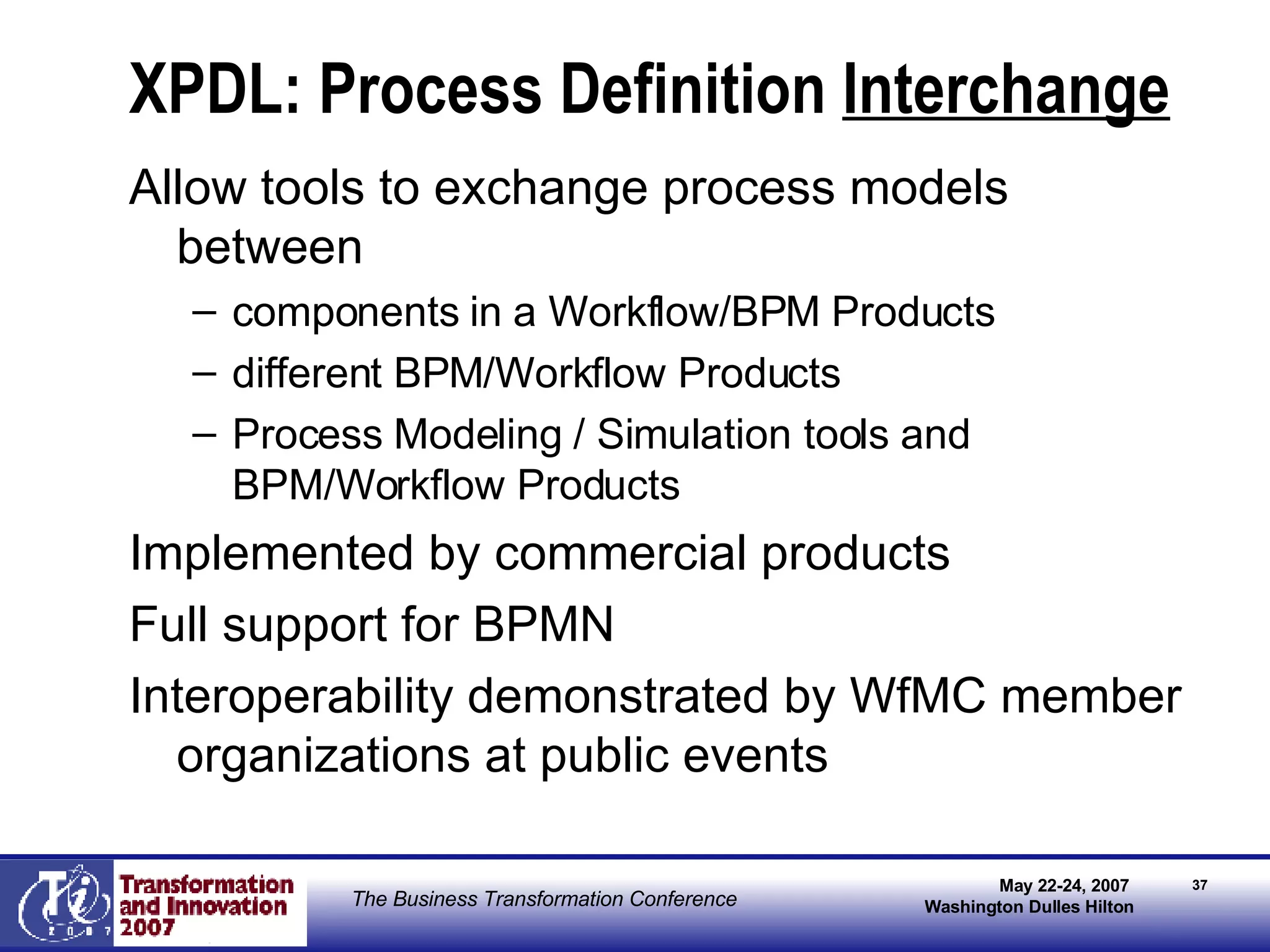
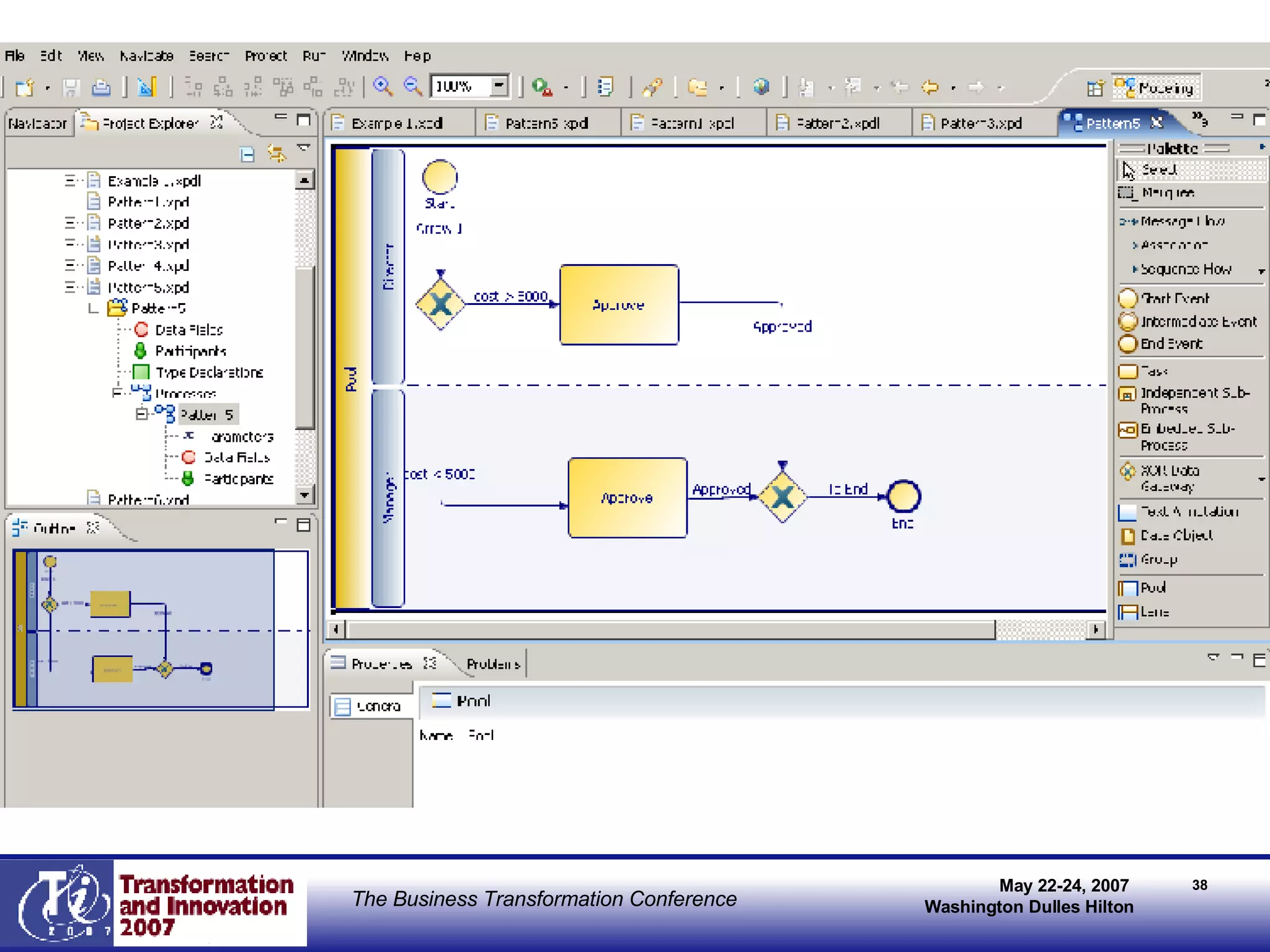
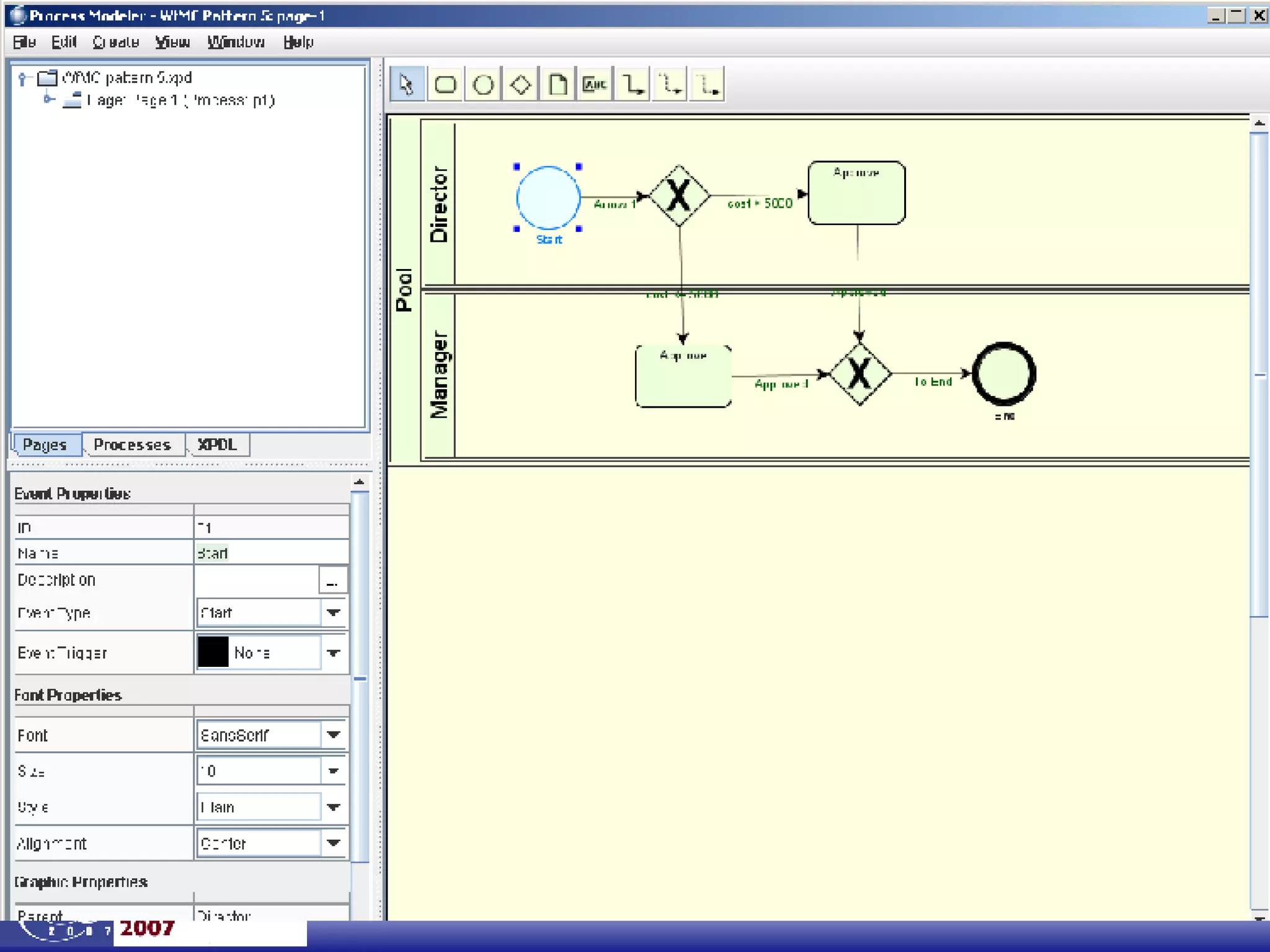
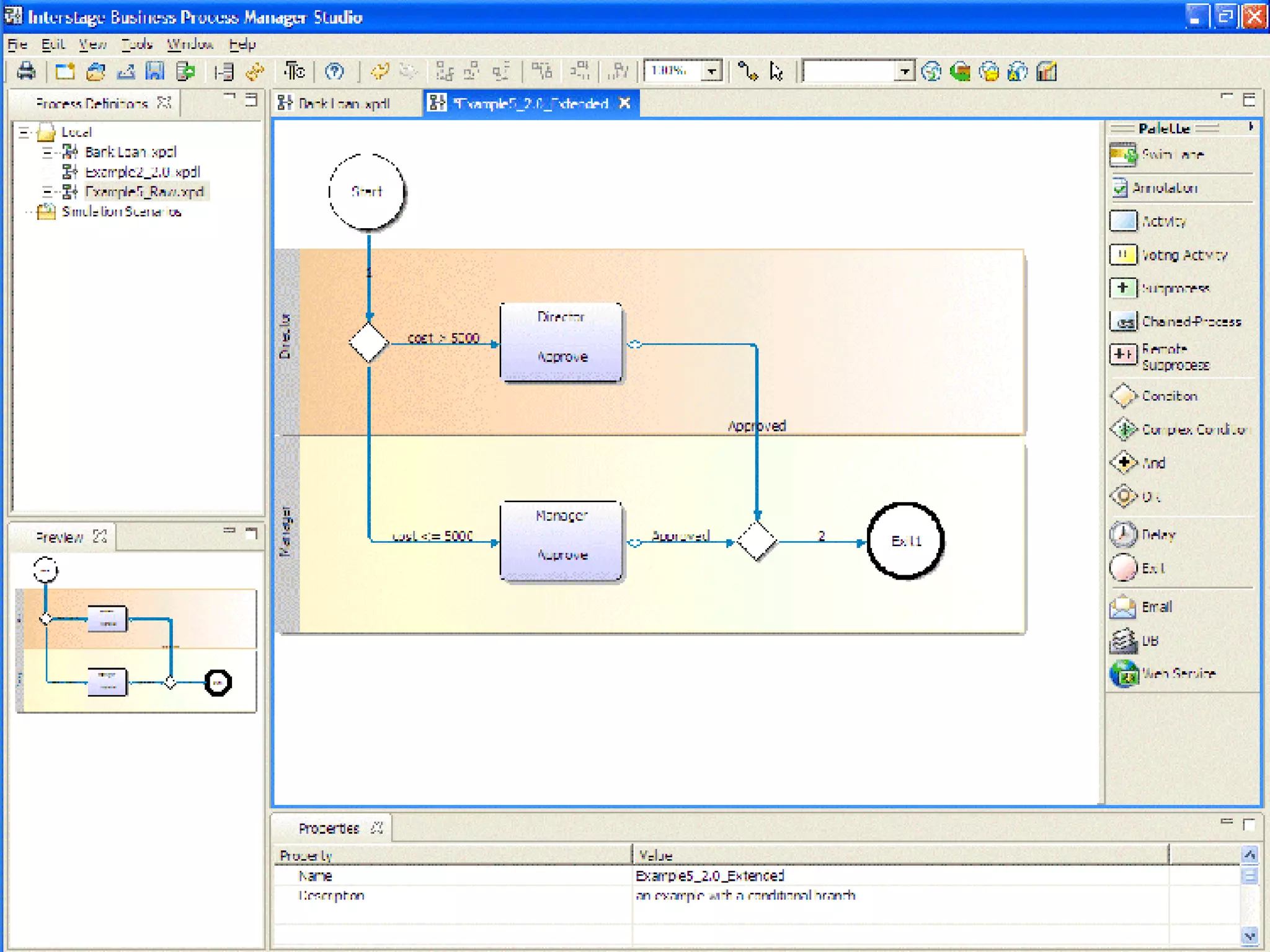
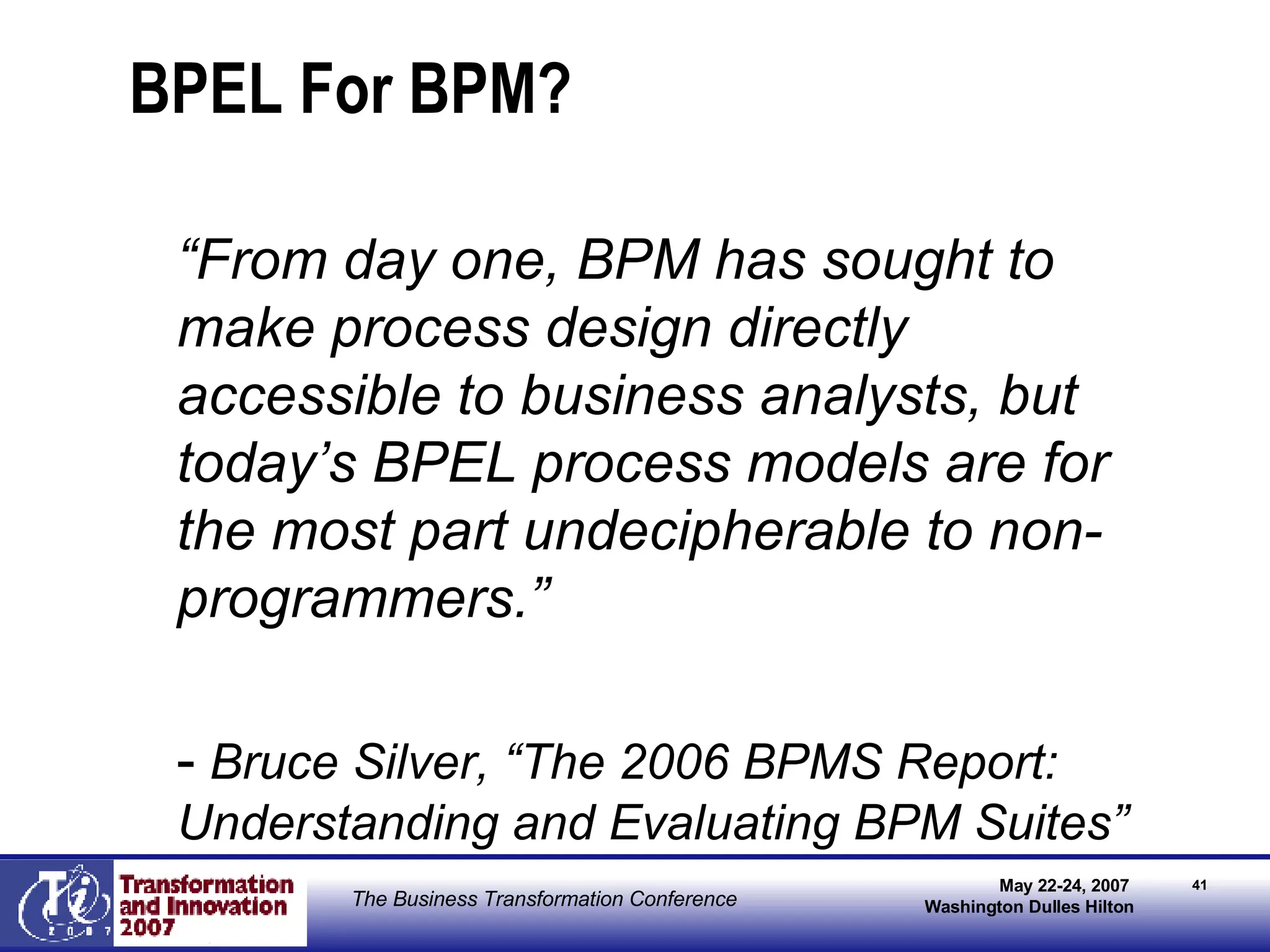
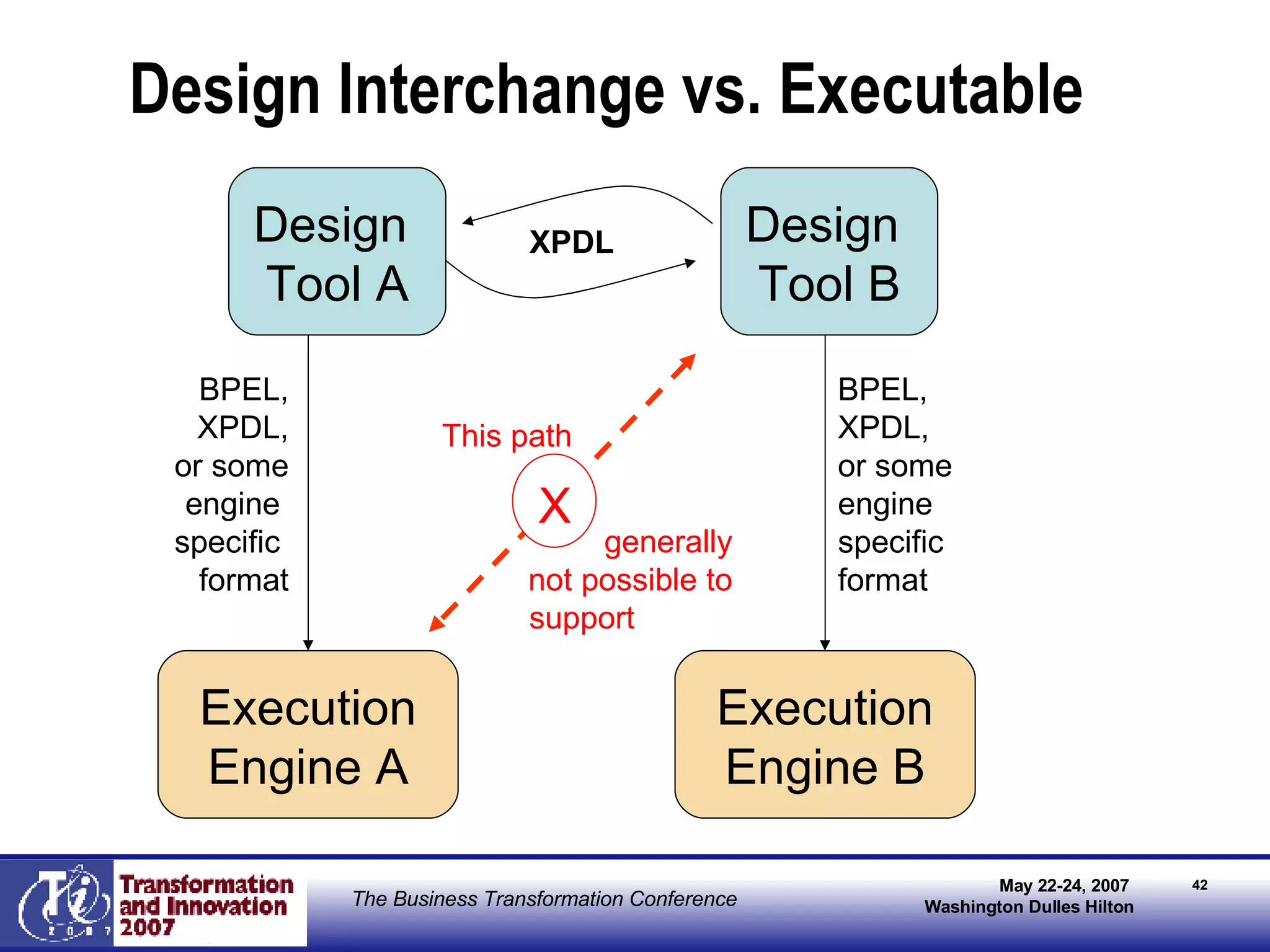
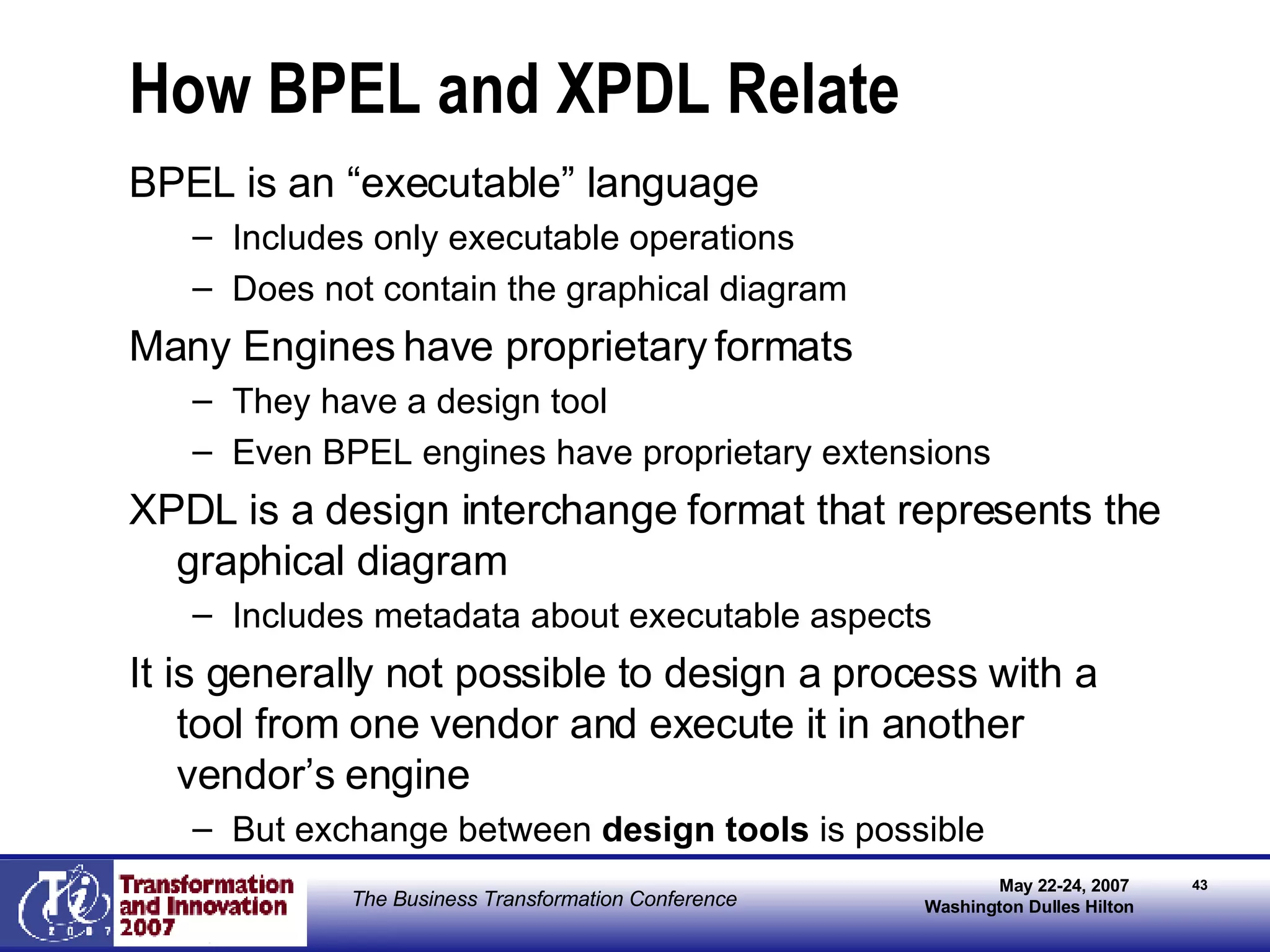
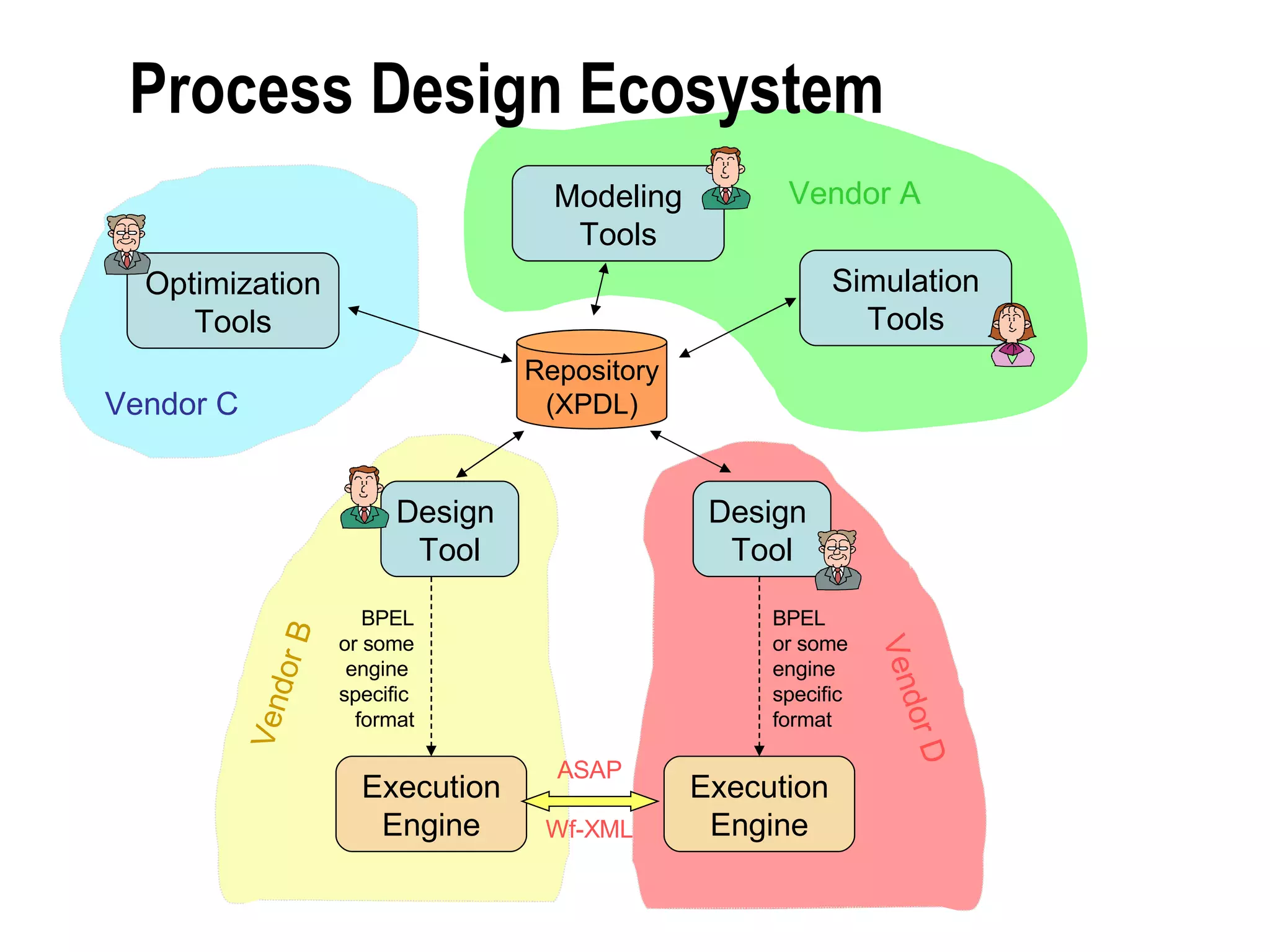
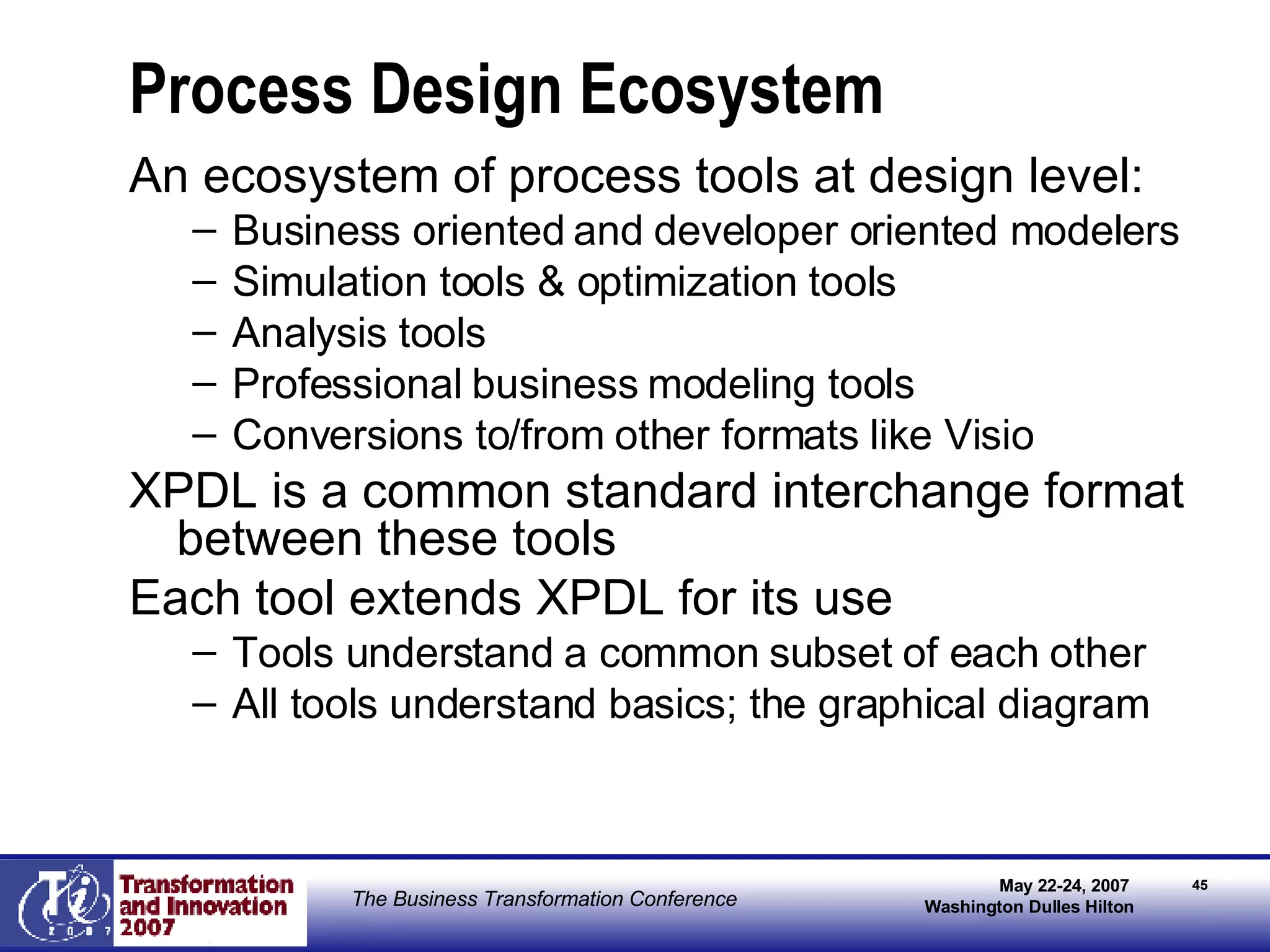
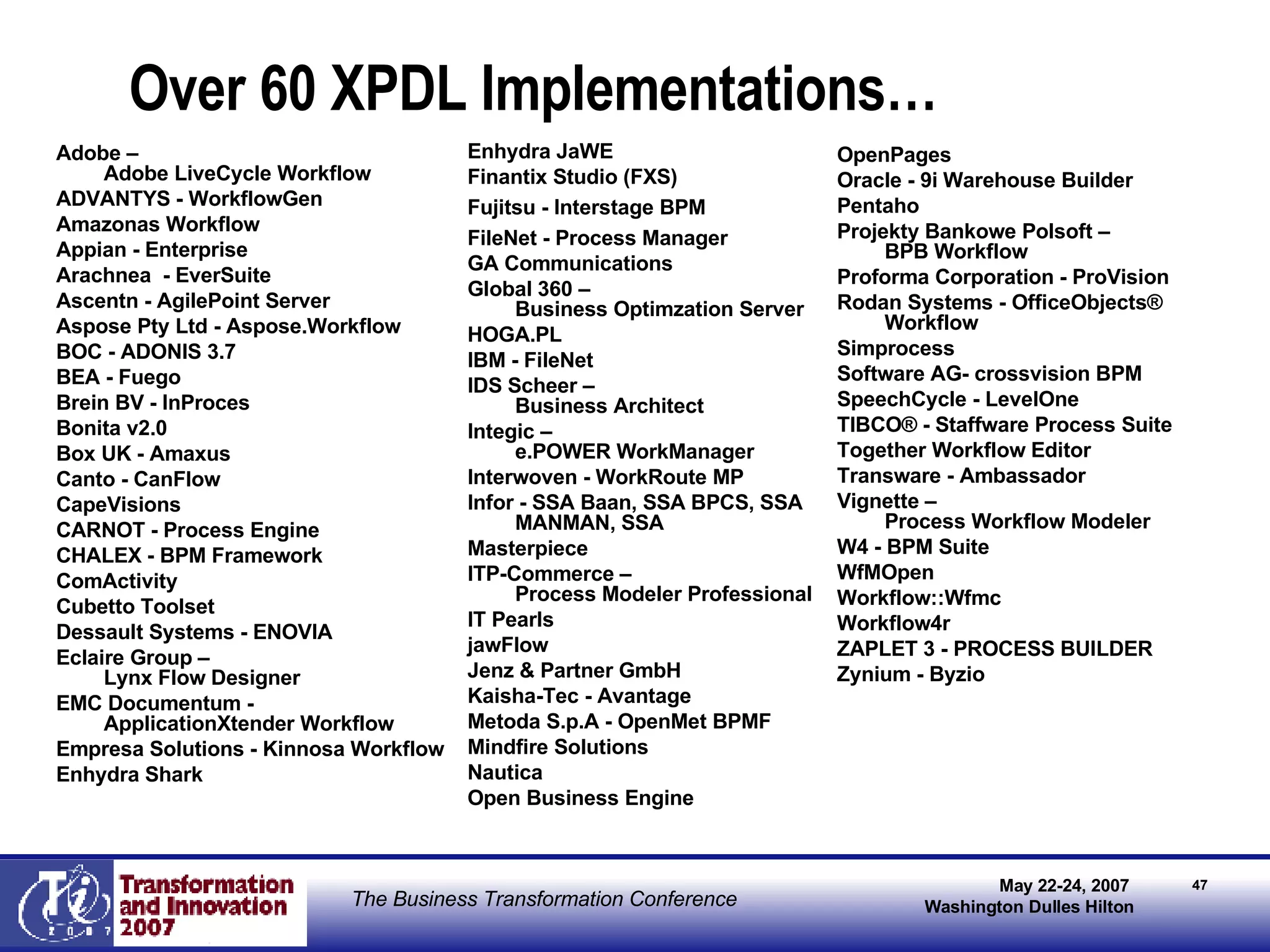
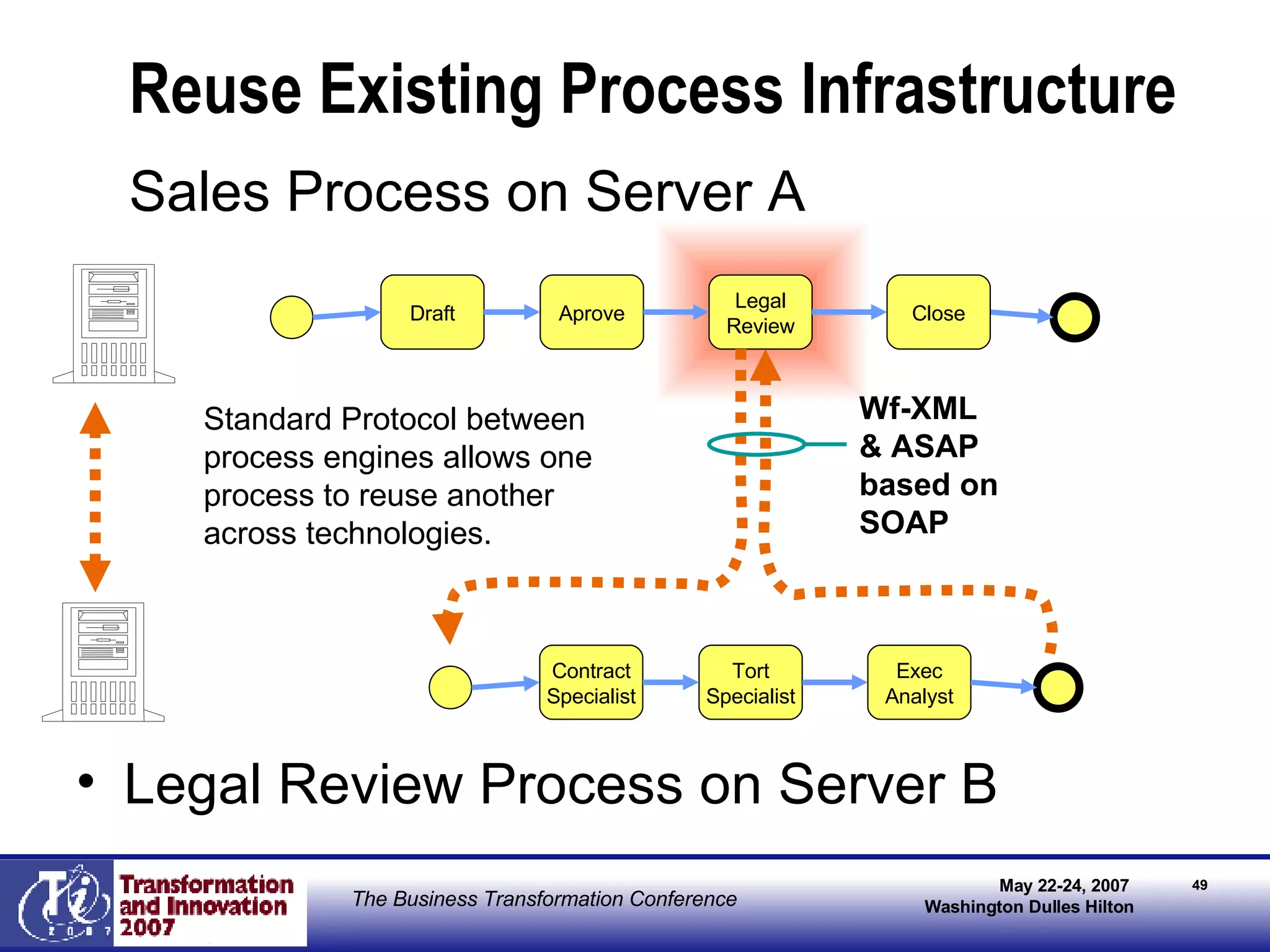
The document discusses the integration of business process management (BPM) and workflow within enterprise architecture, highlighting the gap between business needs and IT capabilities. It emphasizes the importance of standards like BPMN, XPDL, and BPEL for ensuring interoperability, enabling business professionals to modify processes independently from IT. The presentation outlines the evolution of workflow technology and the necessity for a cohesive understanding of both automated and human-centric BPM practices to foster agility and visibility in business processes.


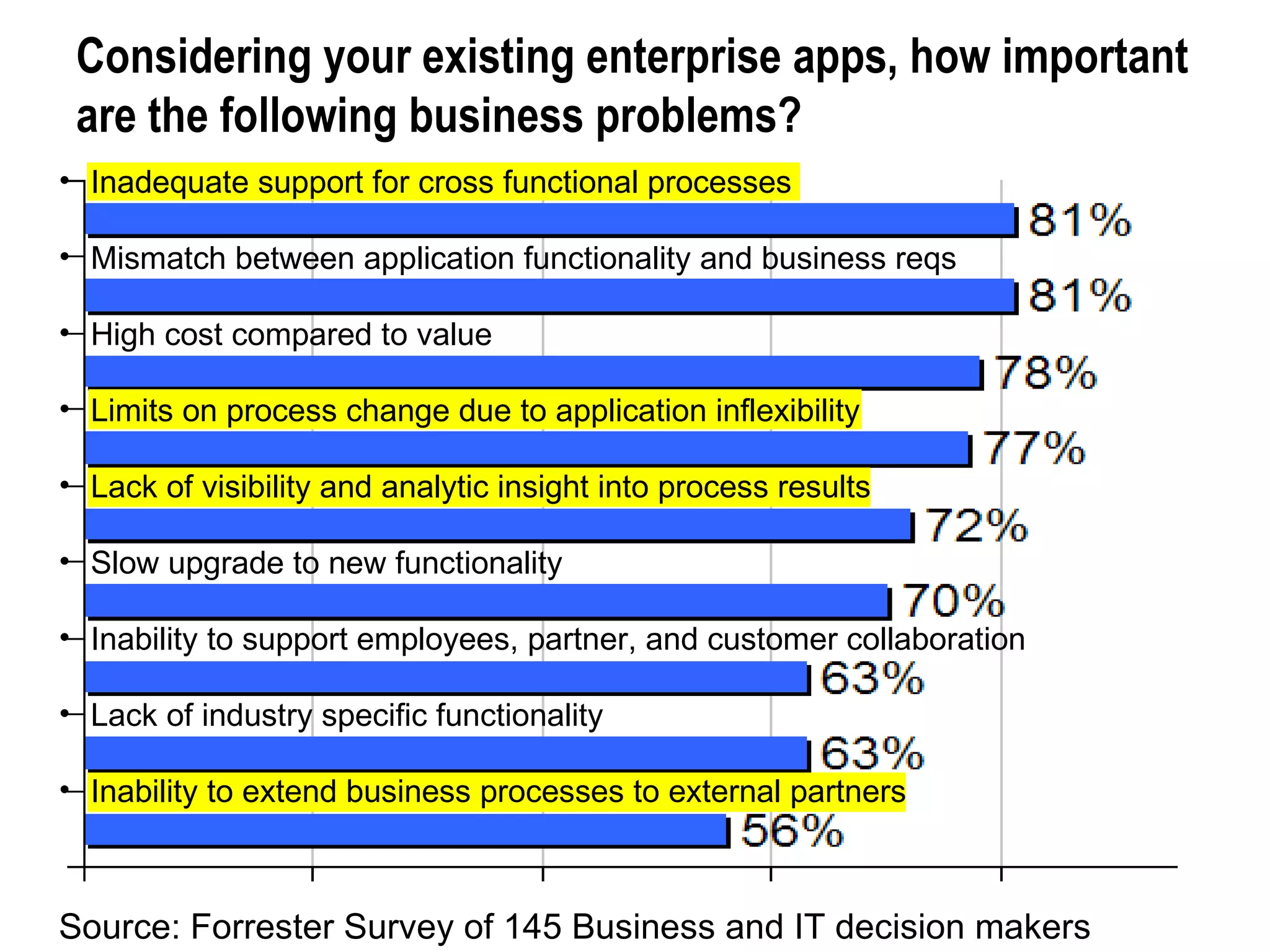





![Where is it Going? By 2009, 20 percent of business processes in the Global 2000 will be supported on BPMS[*]. These processes will be predominantly those that involve a lot of human work, that differentiate the company from its competitors and that are poorly supported by existing IT systems (0.7 probability). Janelle Hill, Gartner * BPMS is defined as a suite that handles both human and system processes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workflow-and-bpm-in-the-new-enterprise-architecture3374/75/Workflow-and-BPM-in-the-New-Enterprise-Architecture-14-2048.jpg)






![Thank Y Kith D Swenson VP Fujtisu Computer Systems Technical Committee Chair, WfMC Contact Information: +1 408 859 1005 [email_address] ou Process Thought Leadership Thank Y ou](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workflow-and-bpm-in-the-new-enterprise-architecture3374/75/Workflow-and-BPM-in-the-New-Enterprise-Architecture-53-2048.jpg)