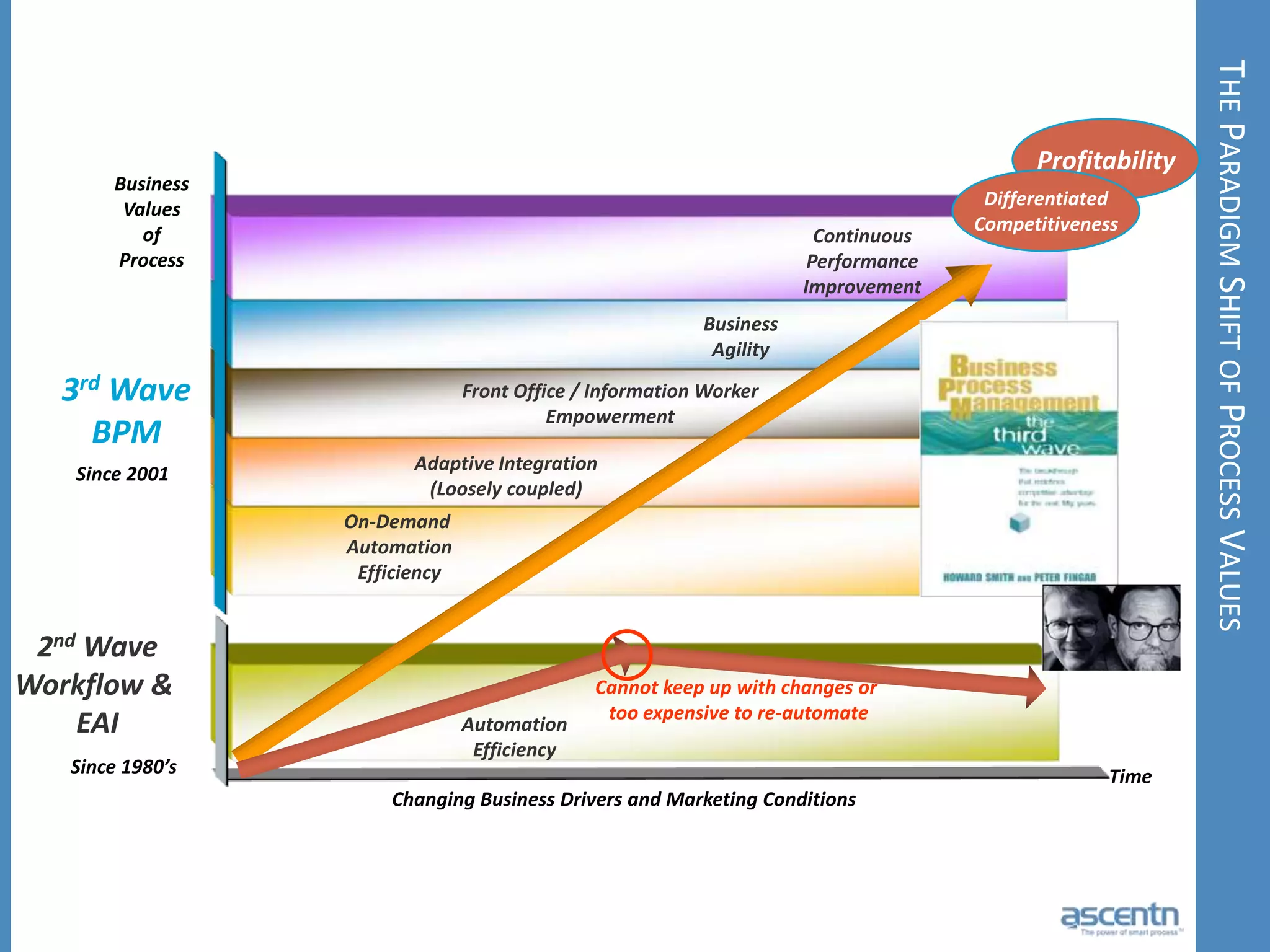
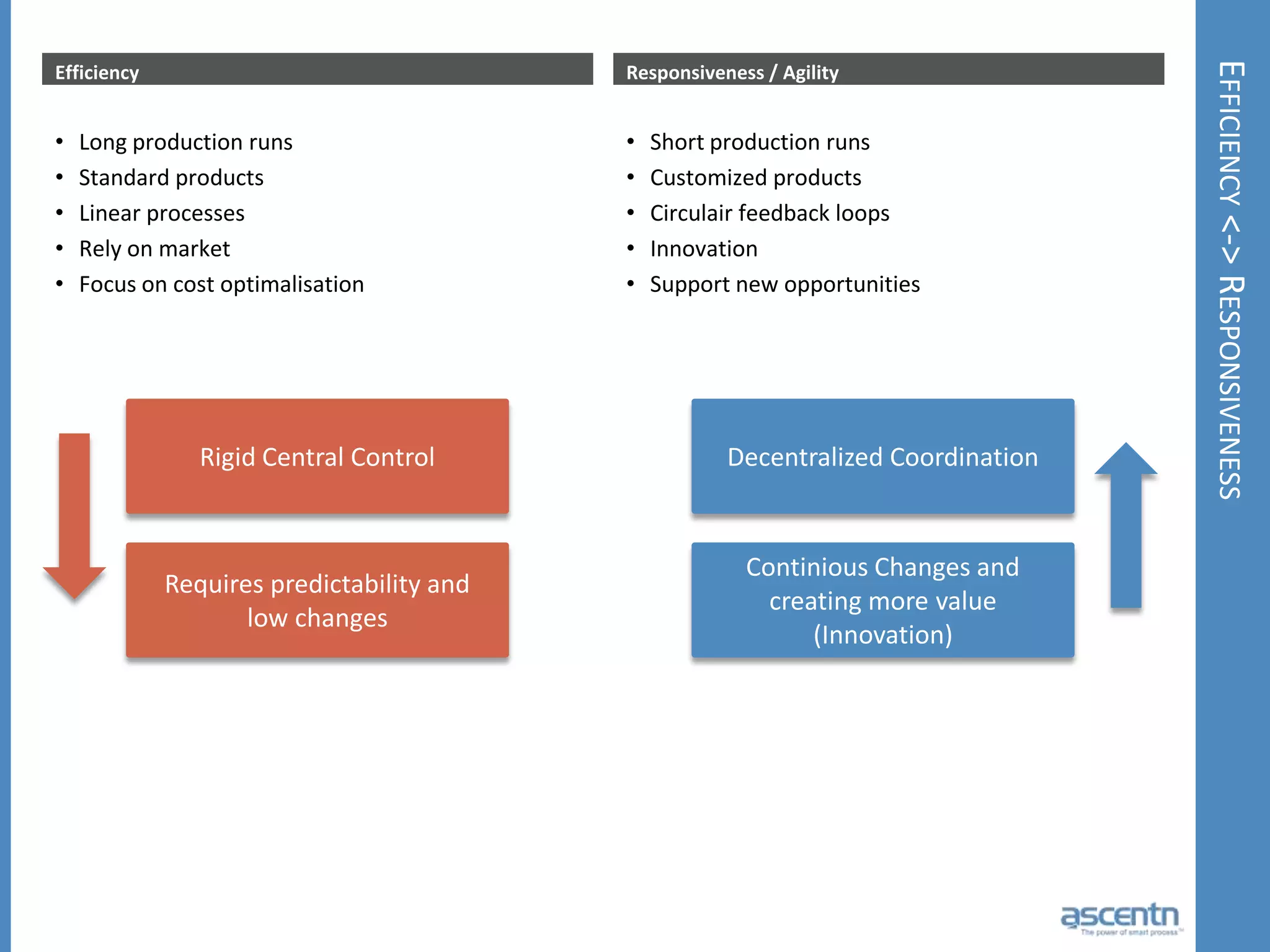
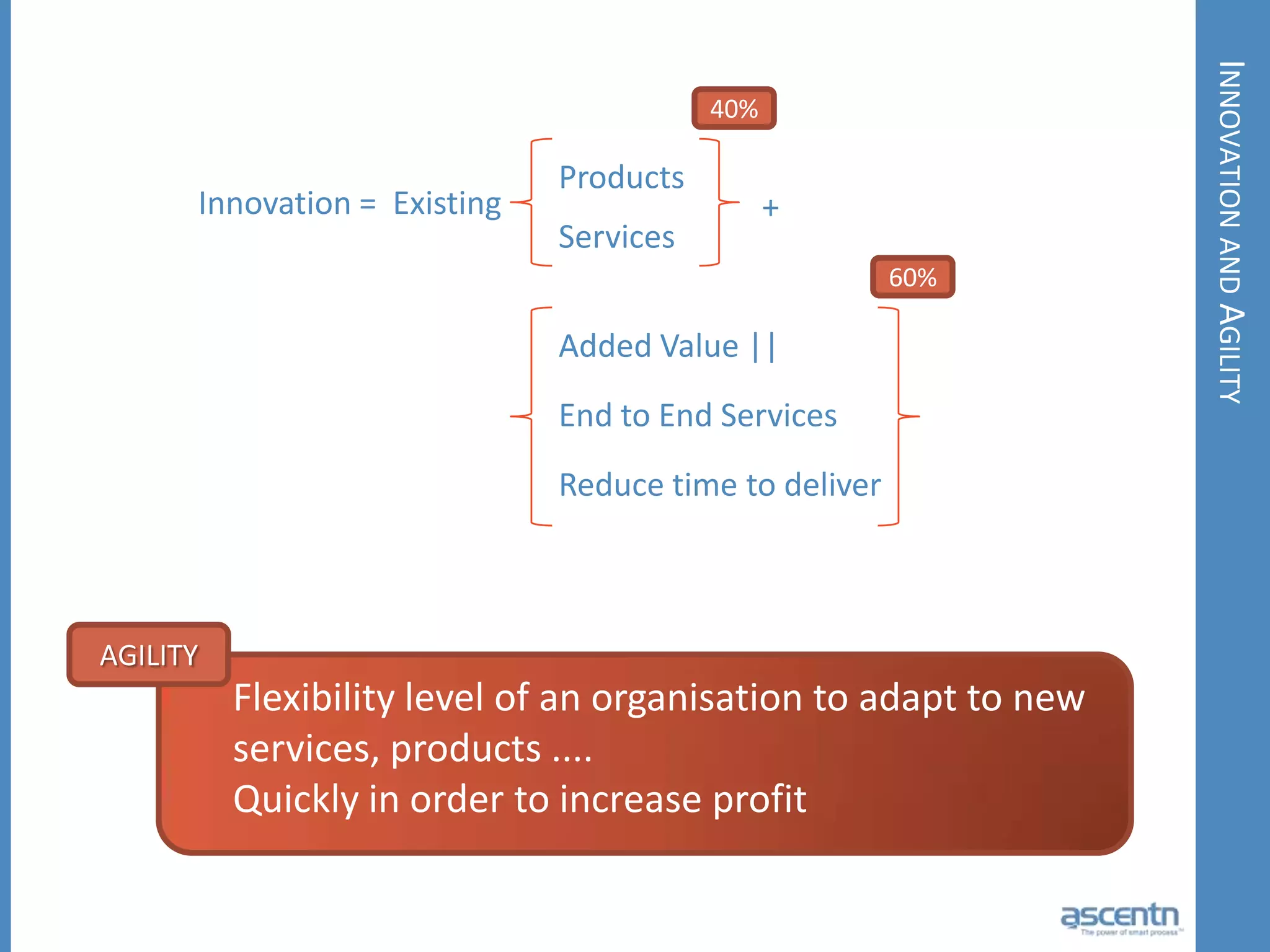
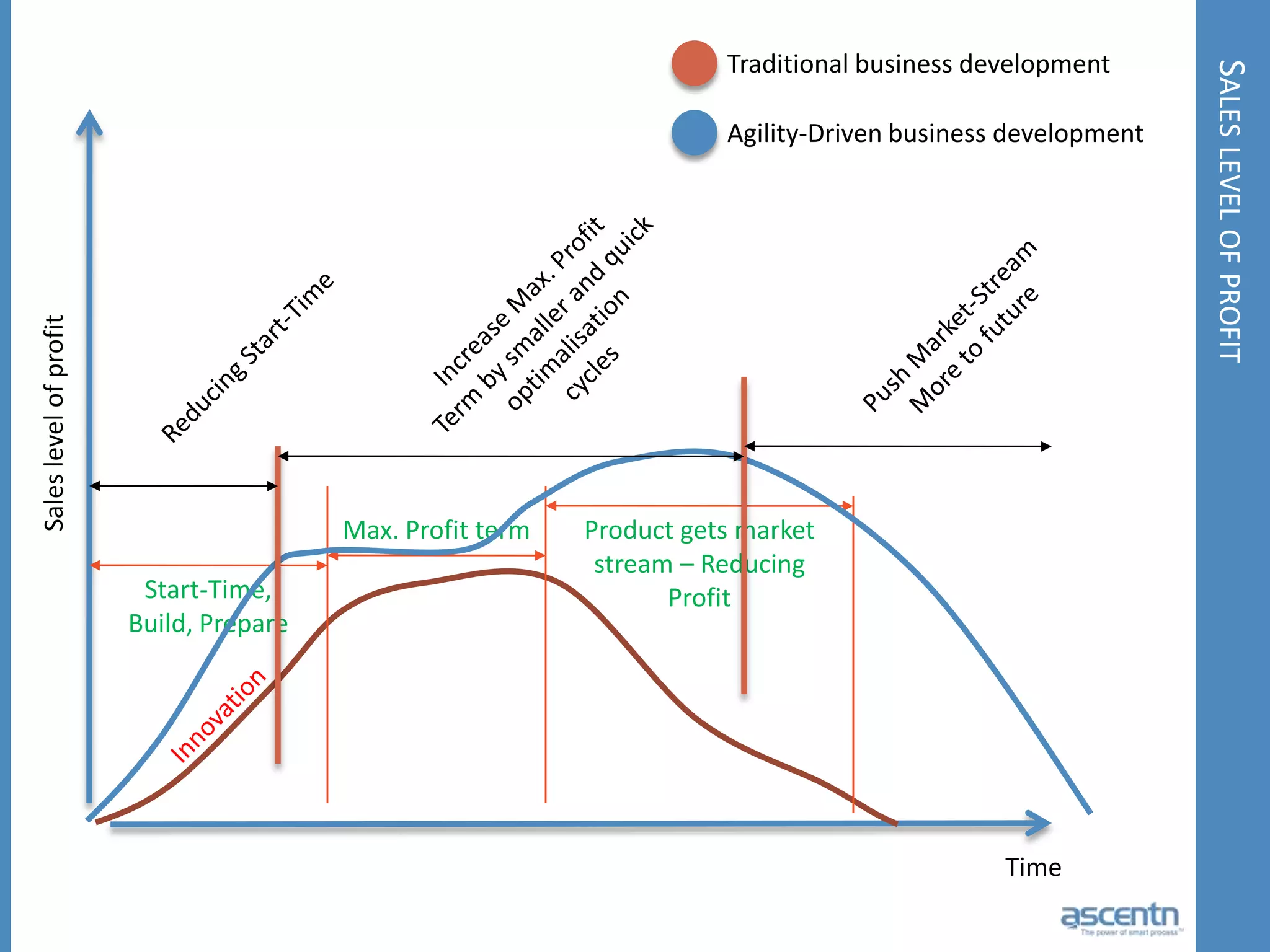
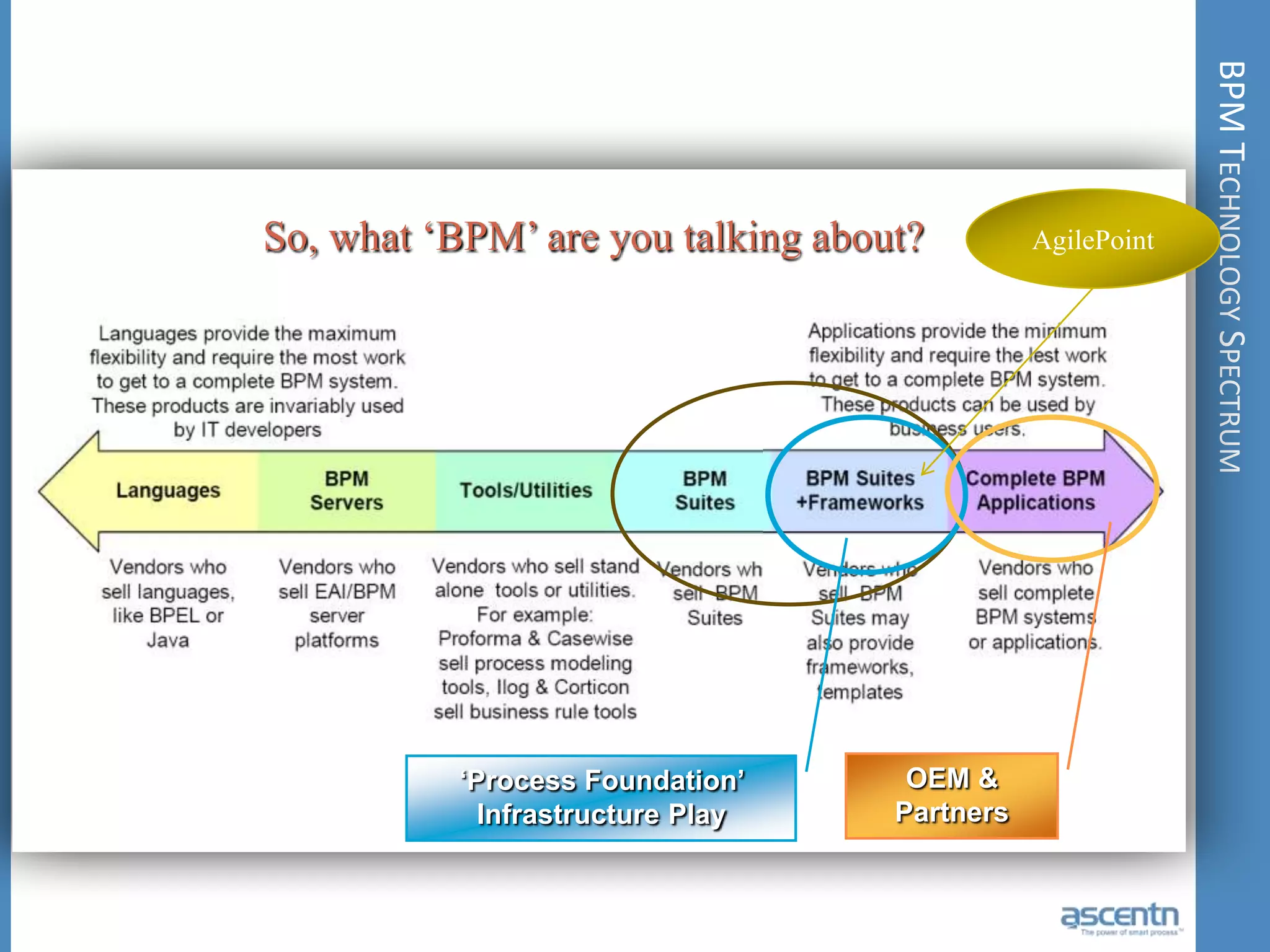
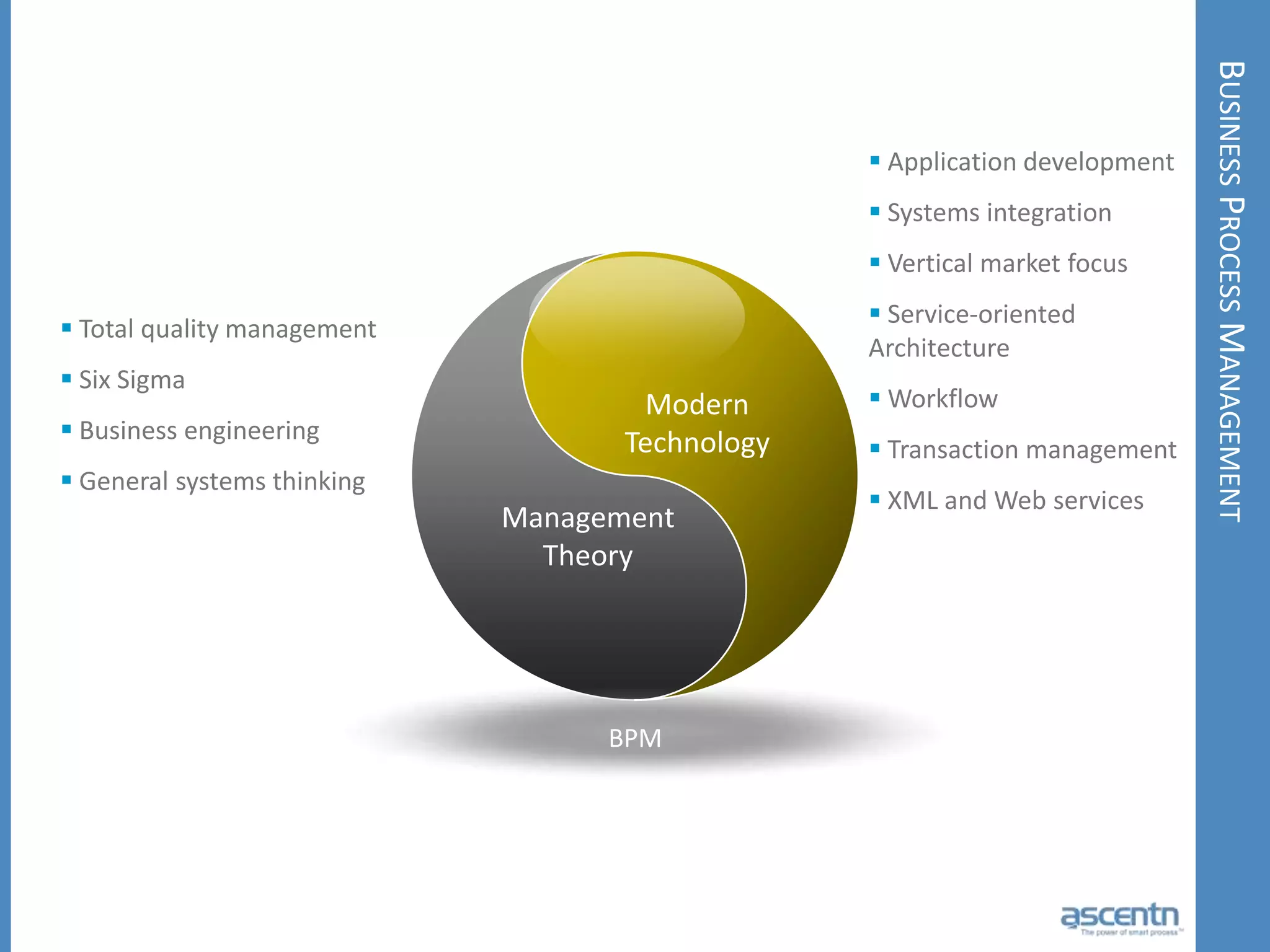
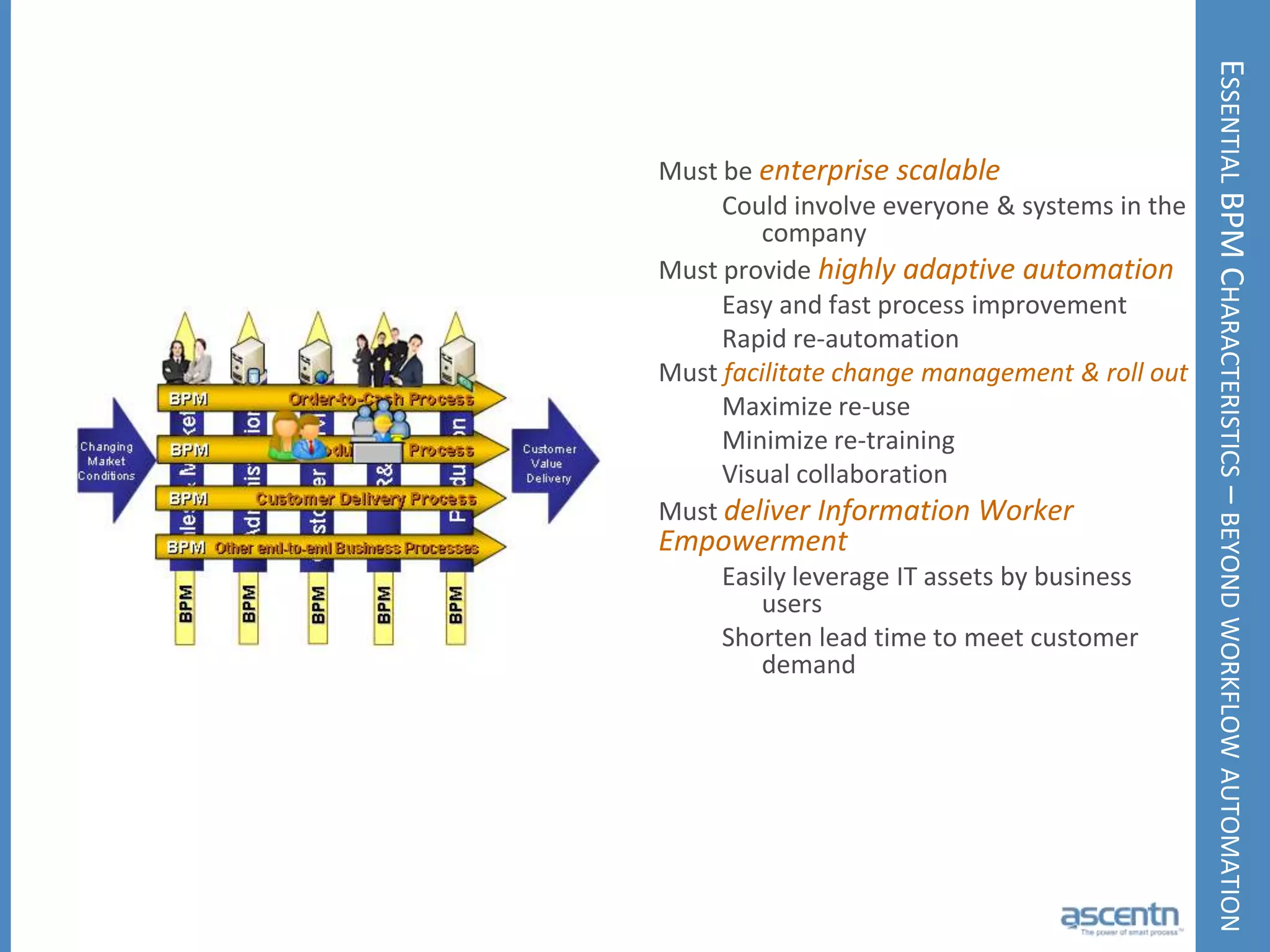
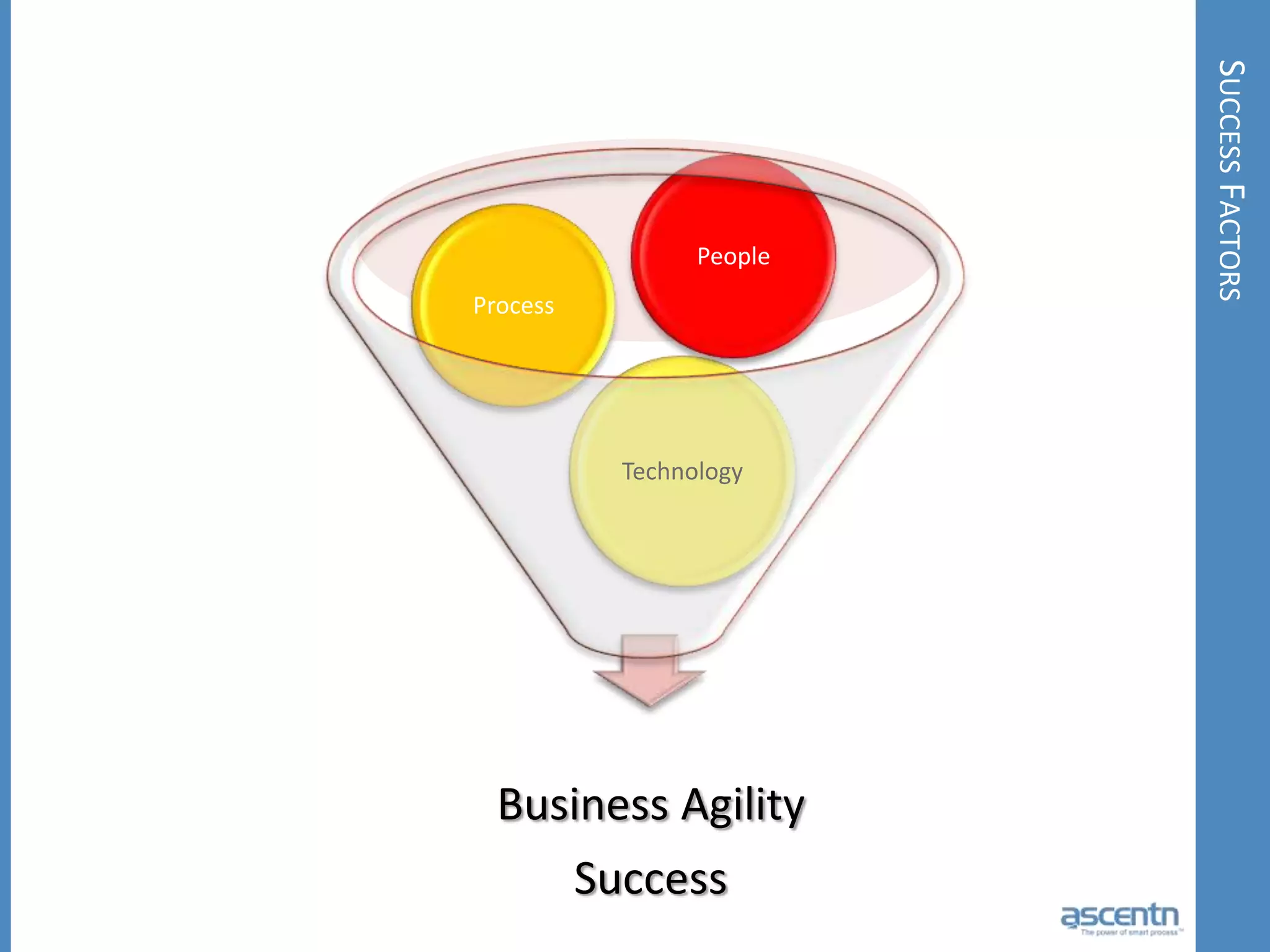
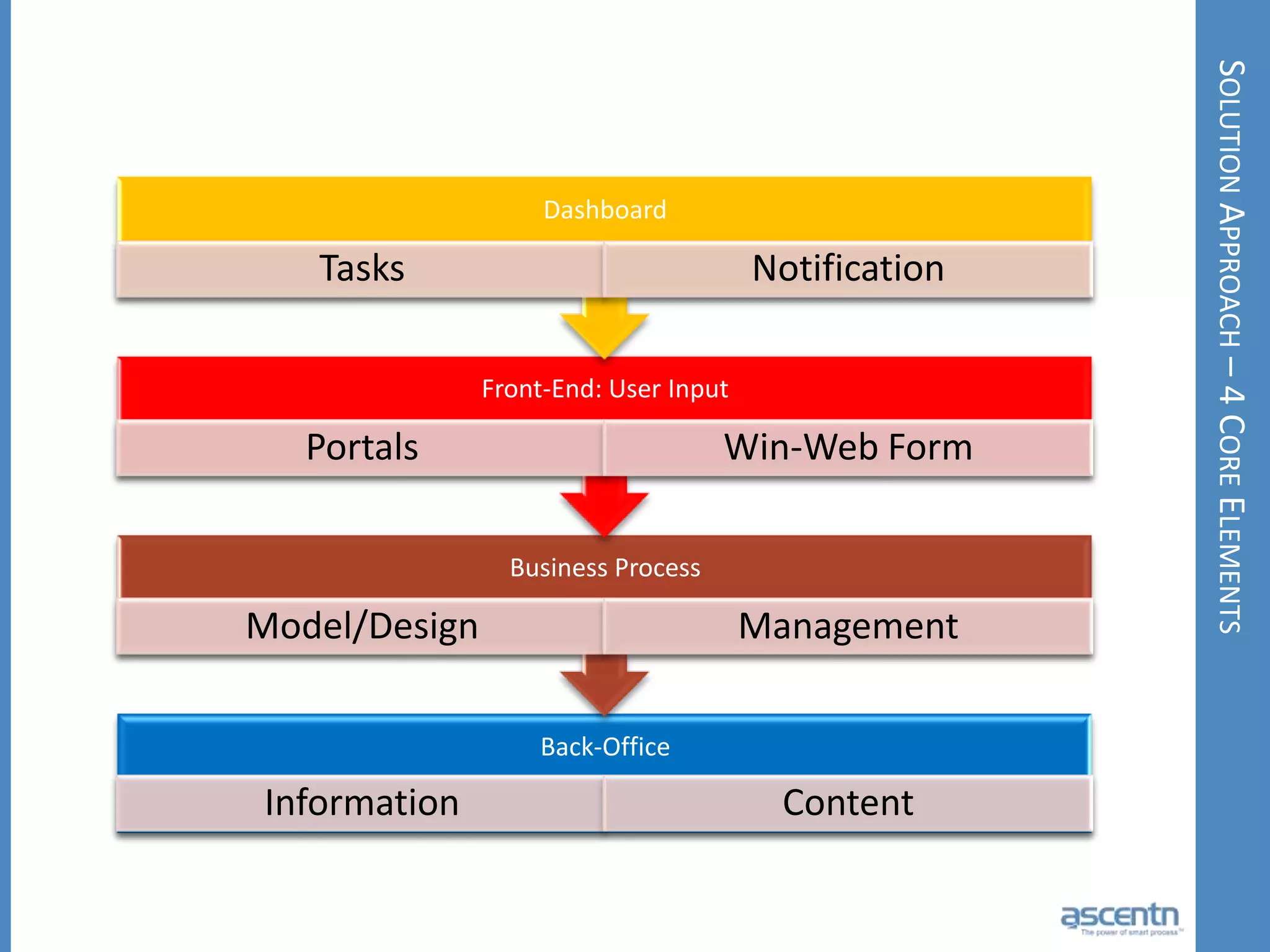
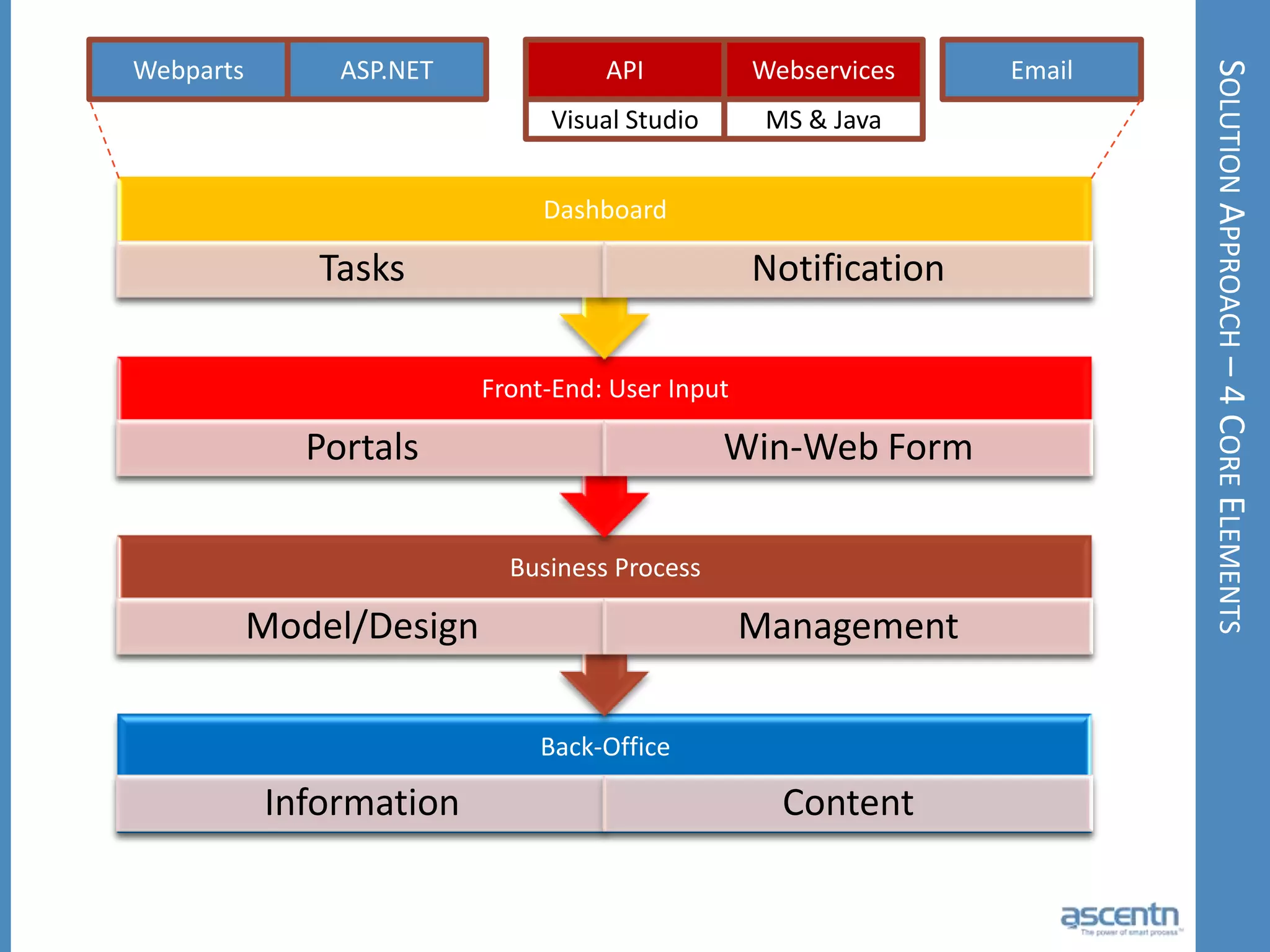
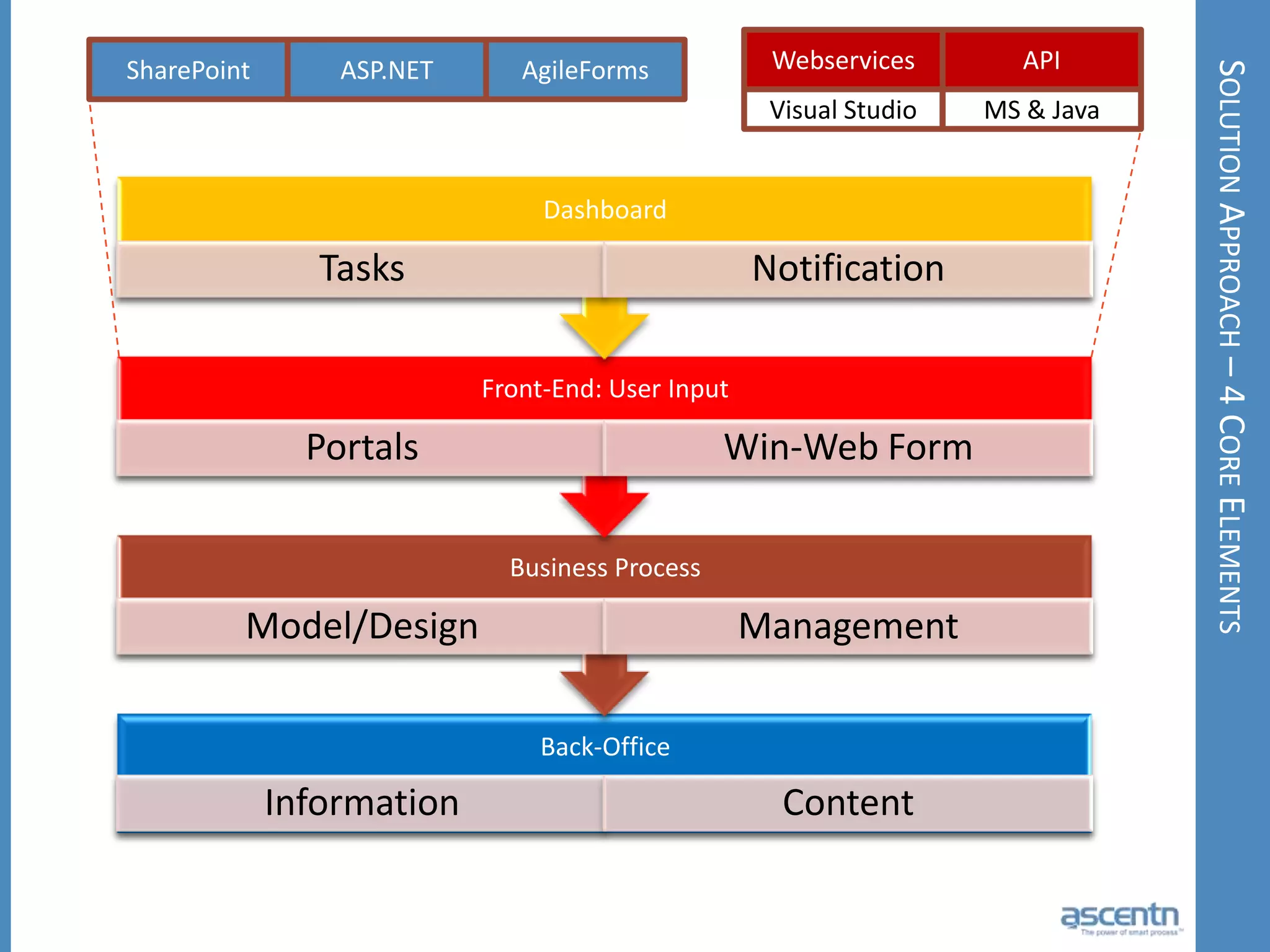
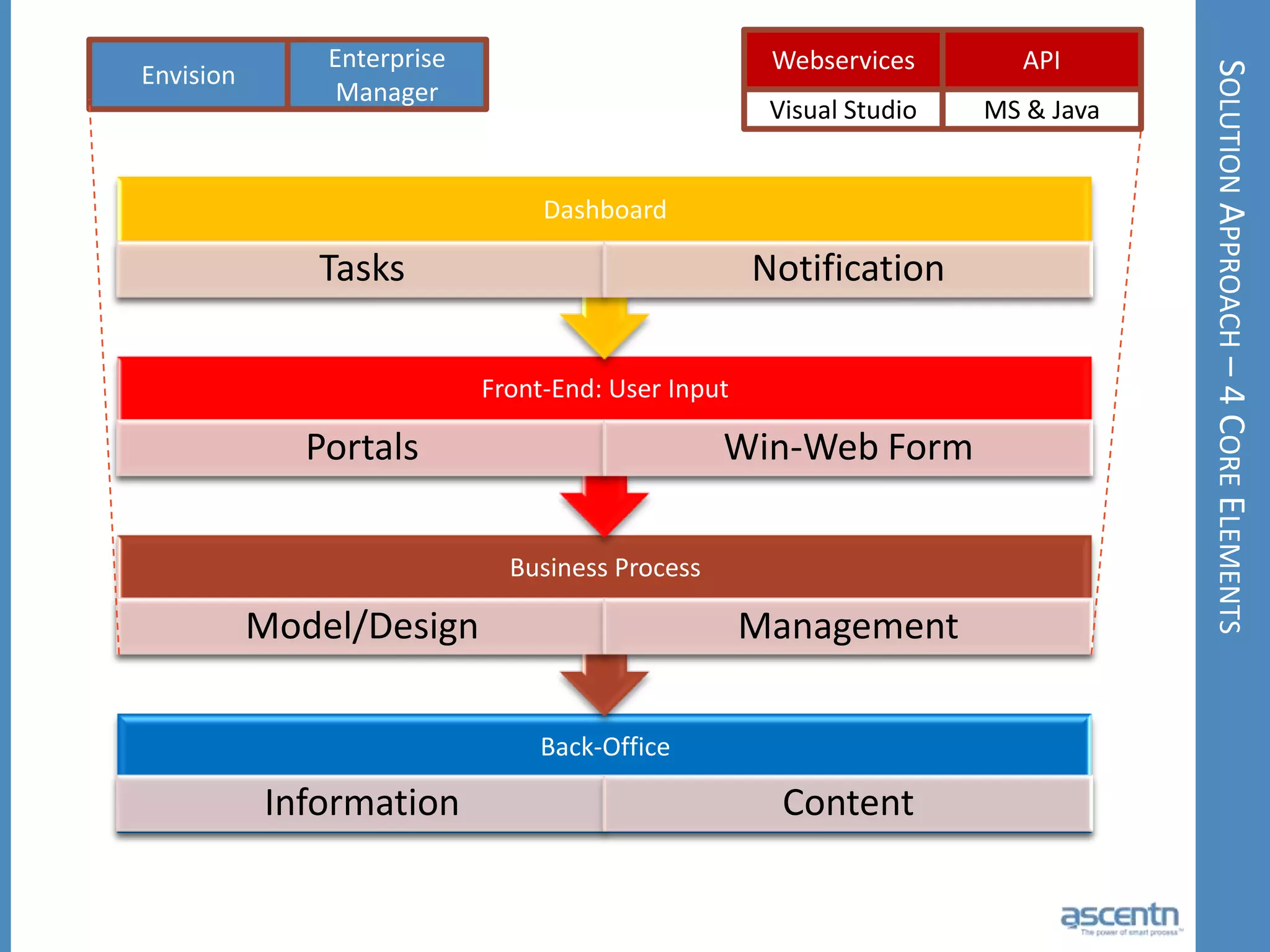
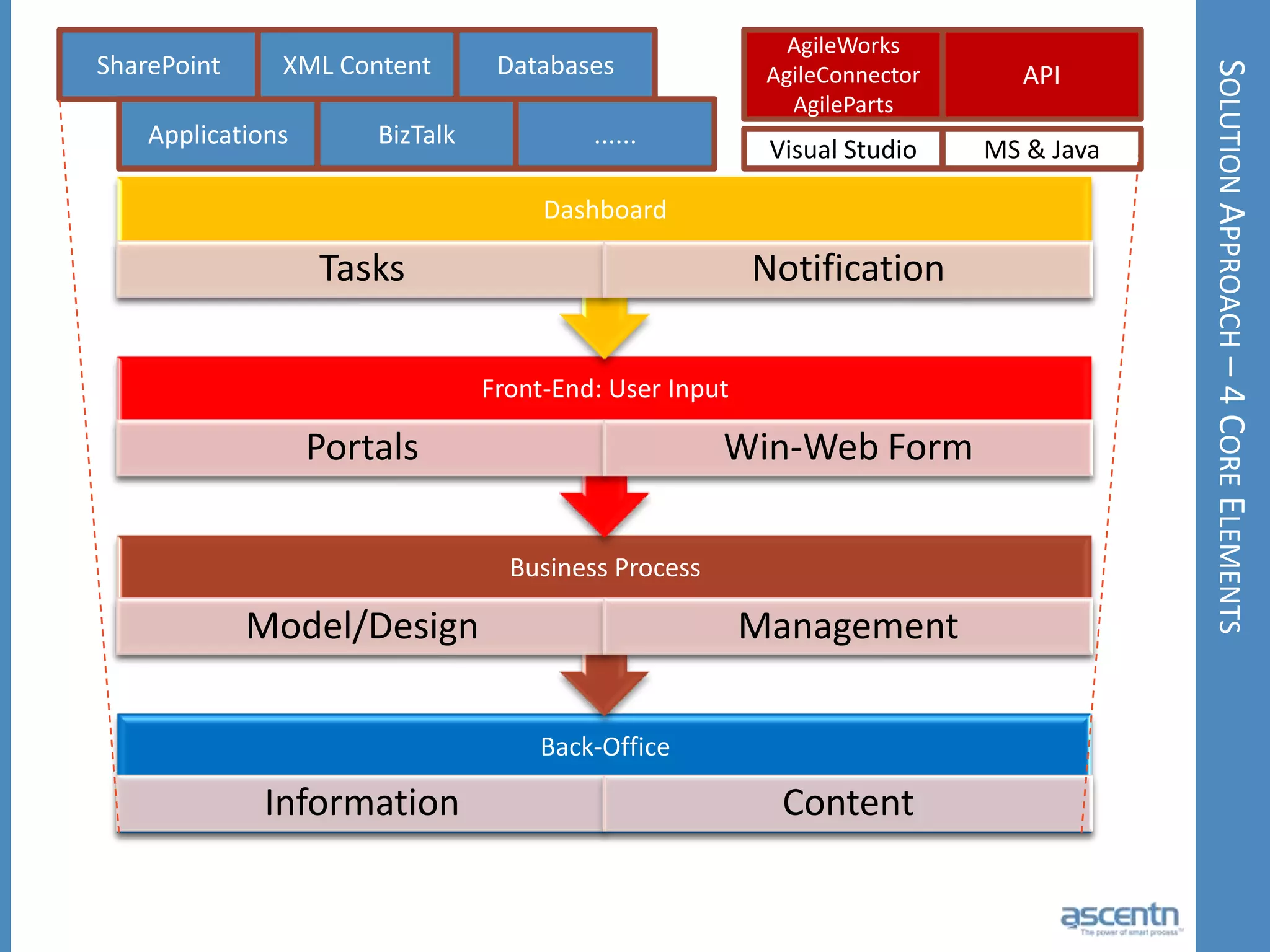
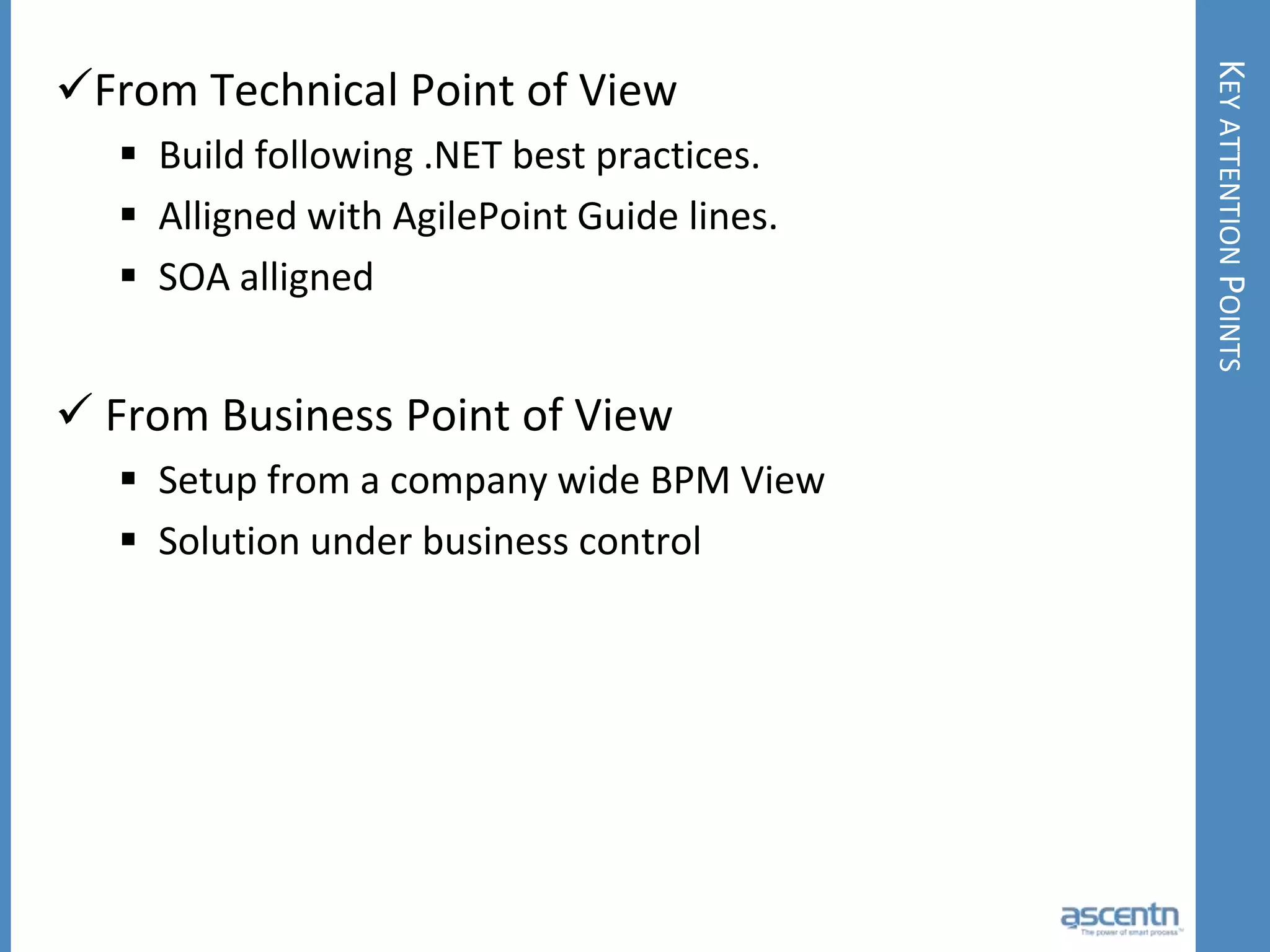
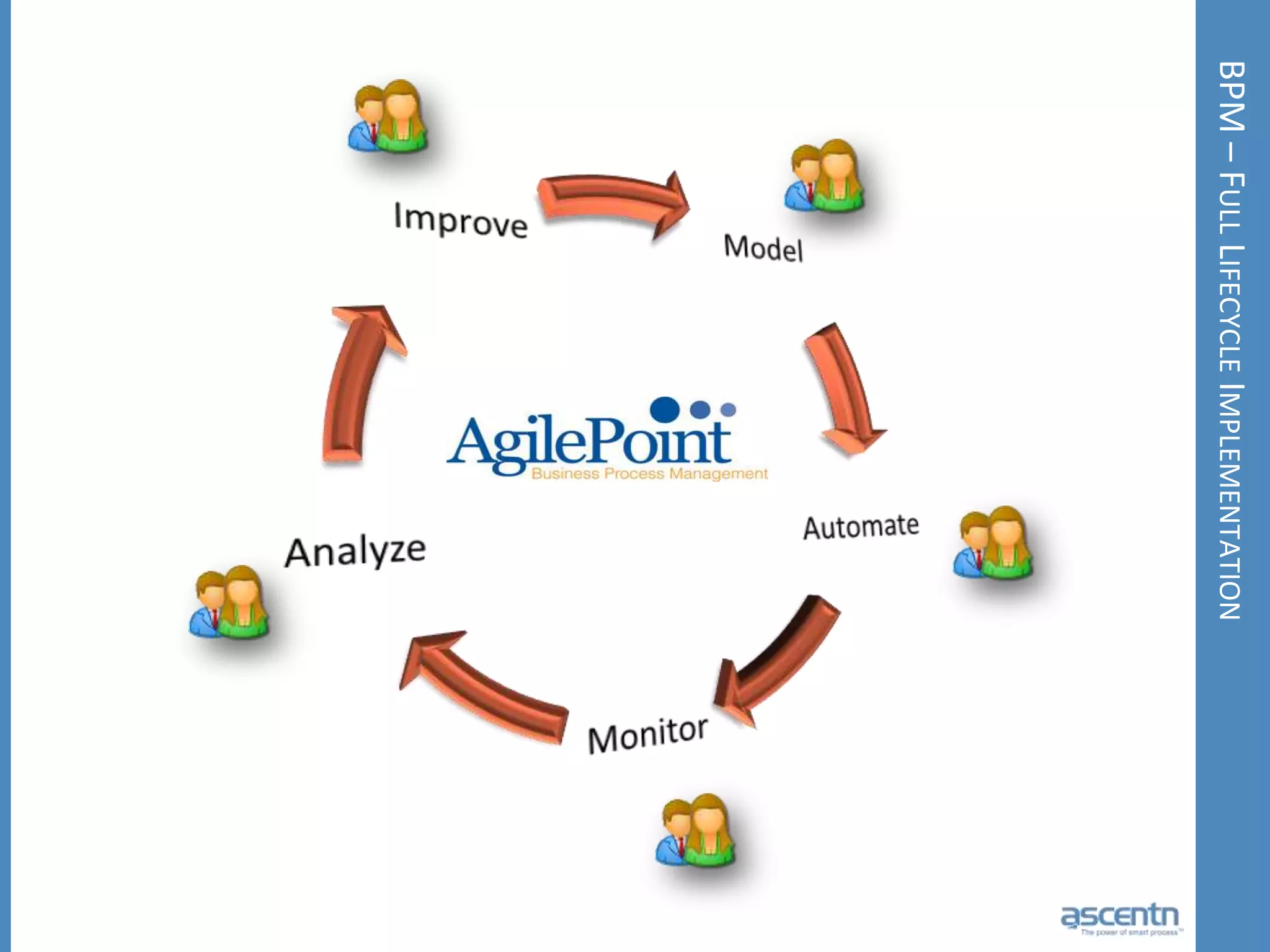
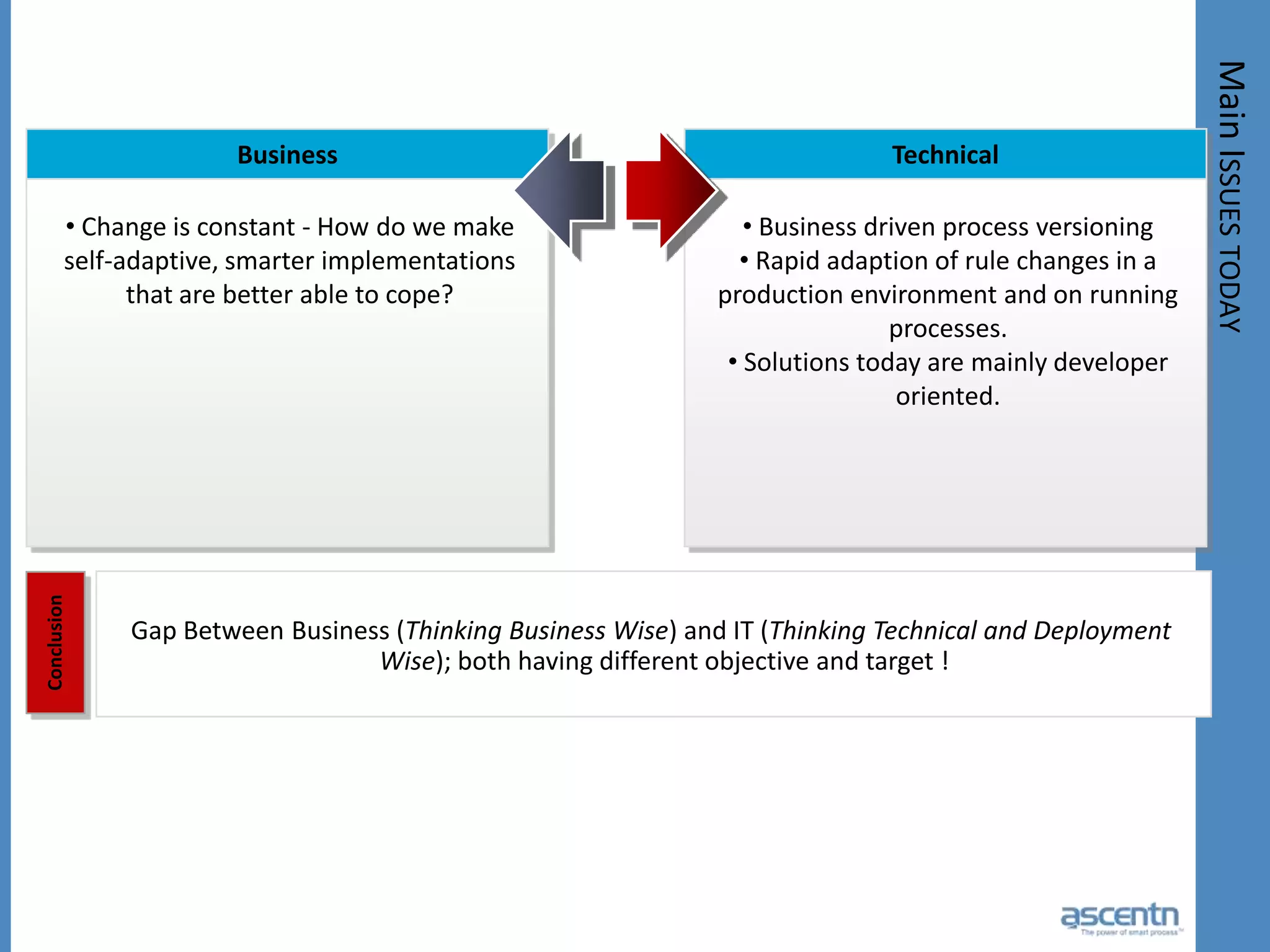
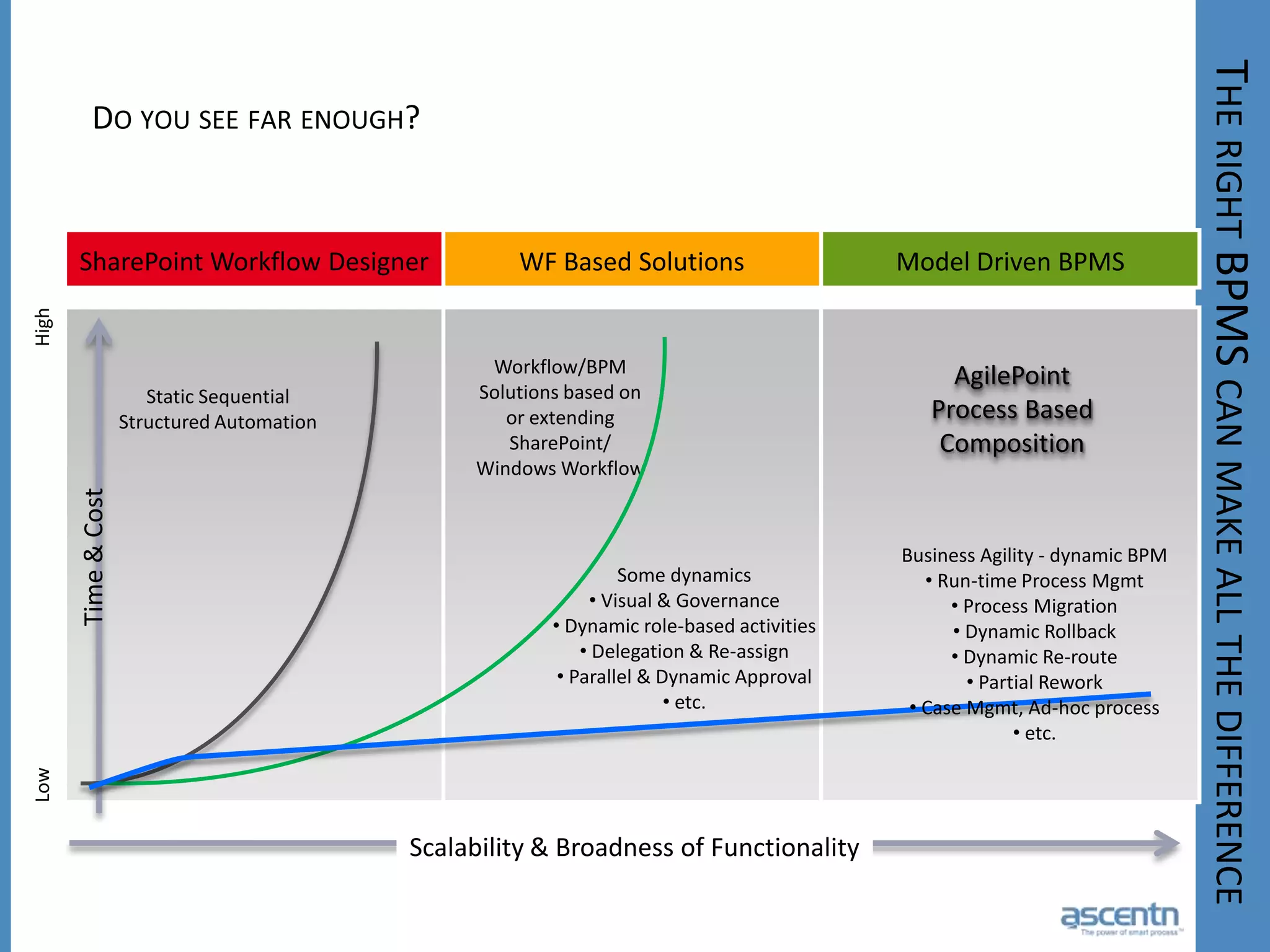
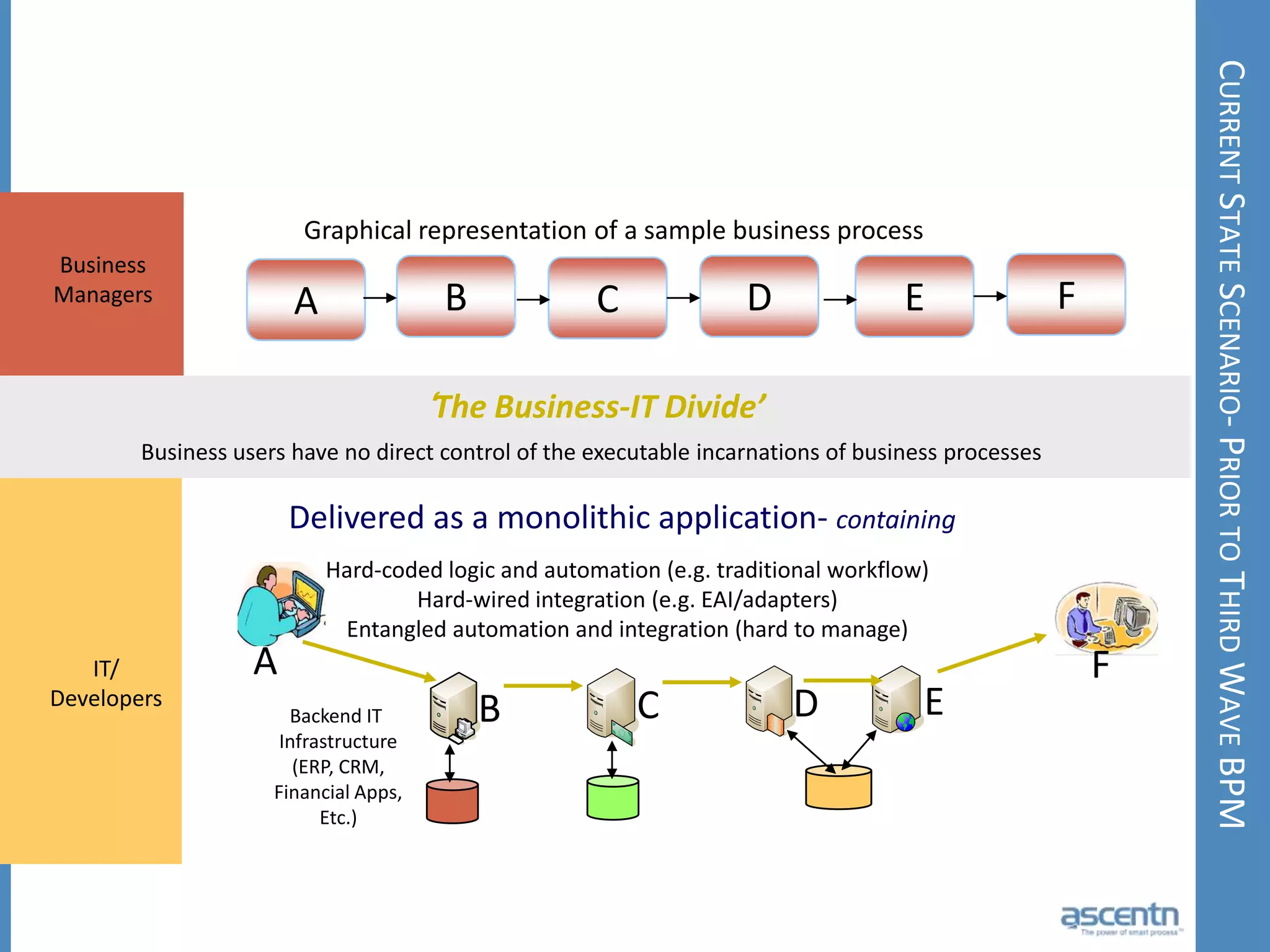
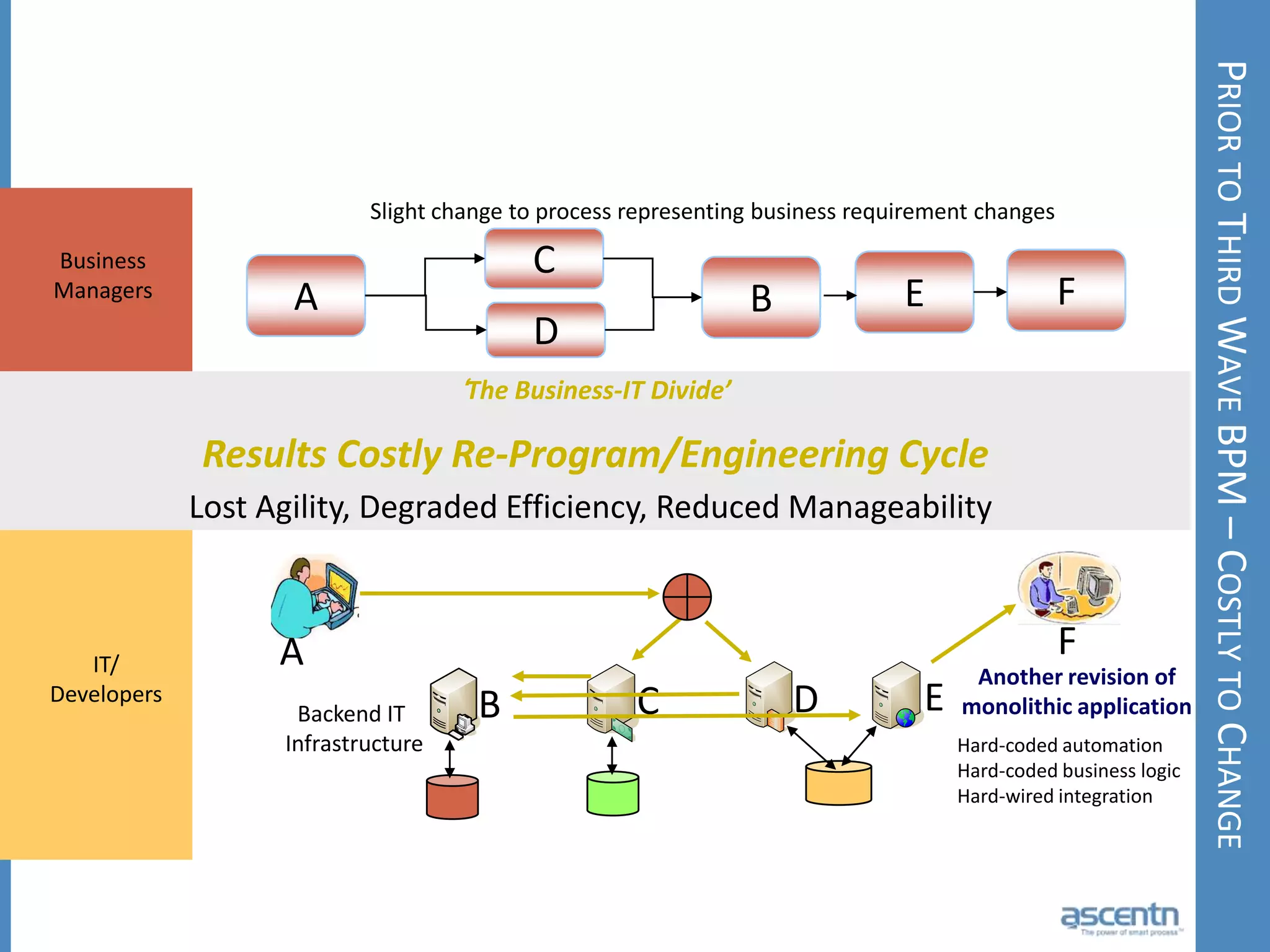
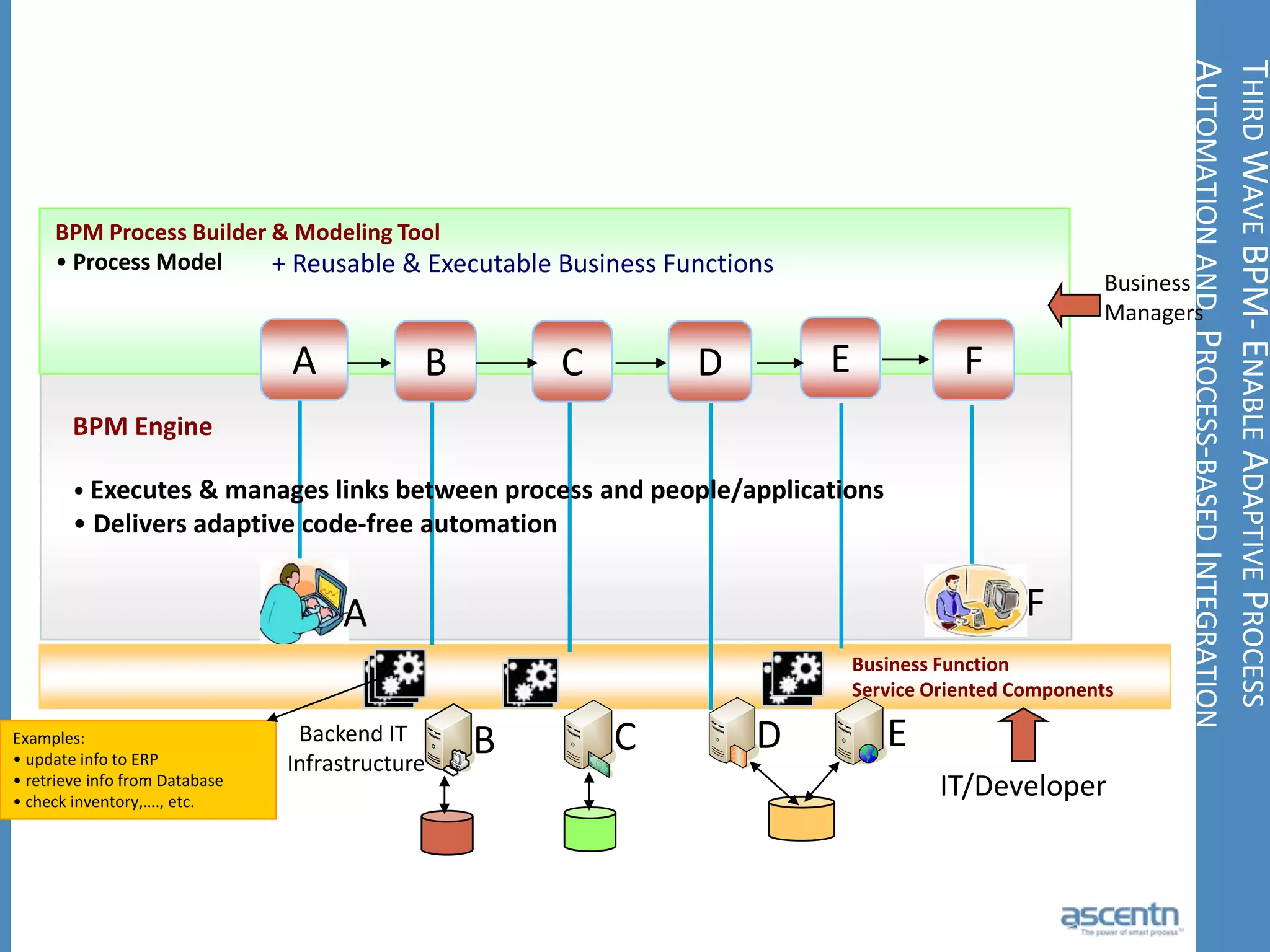
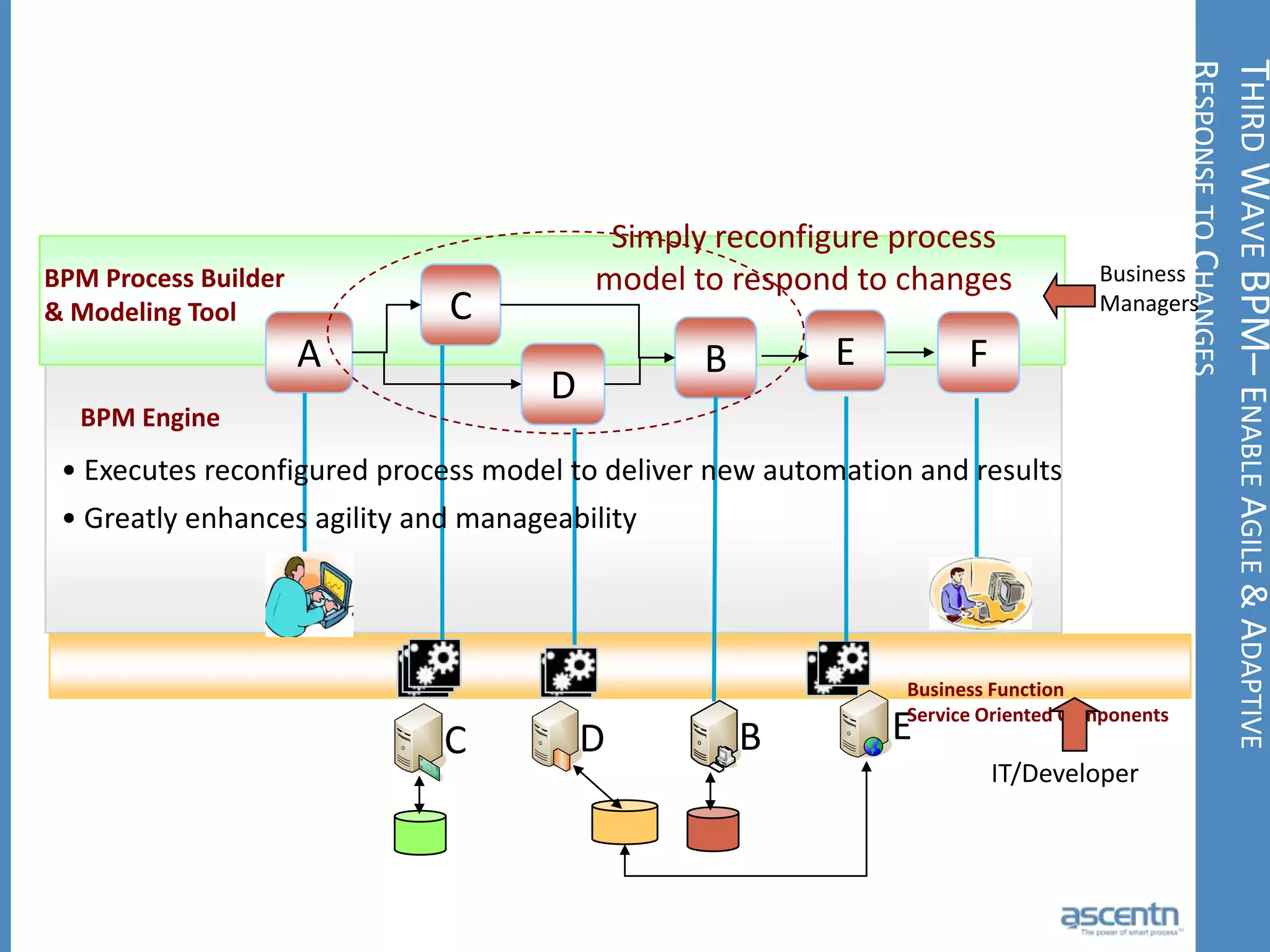
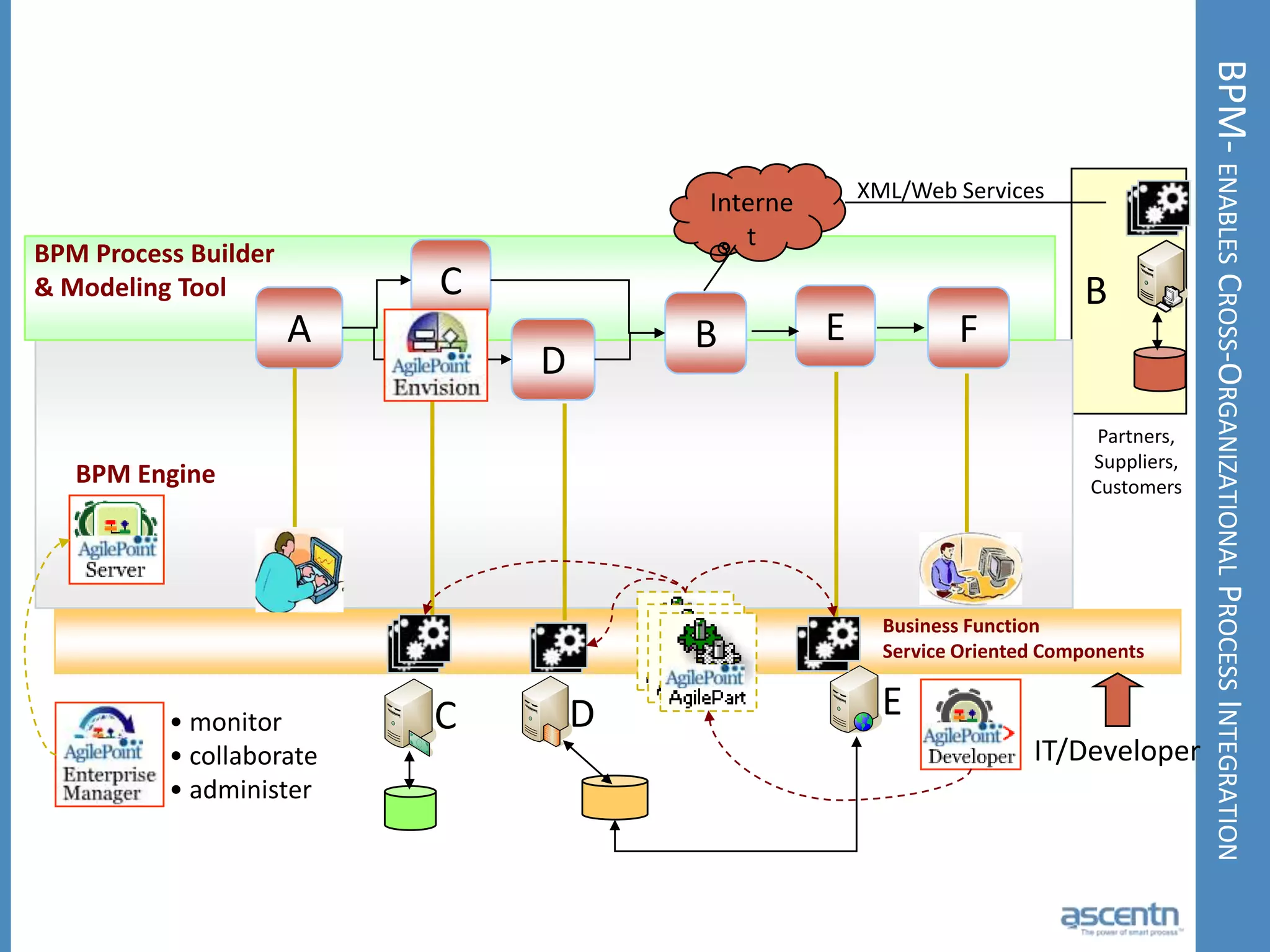
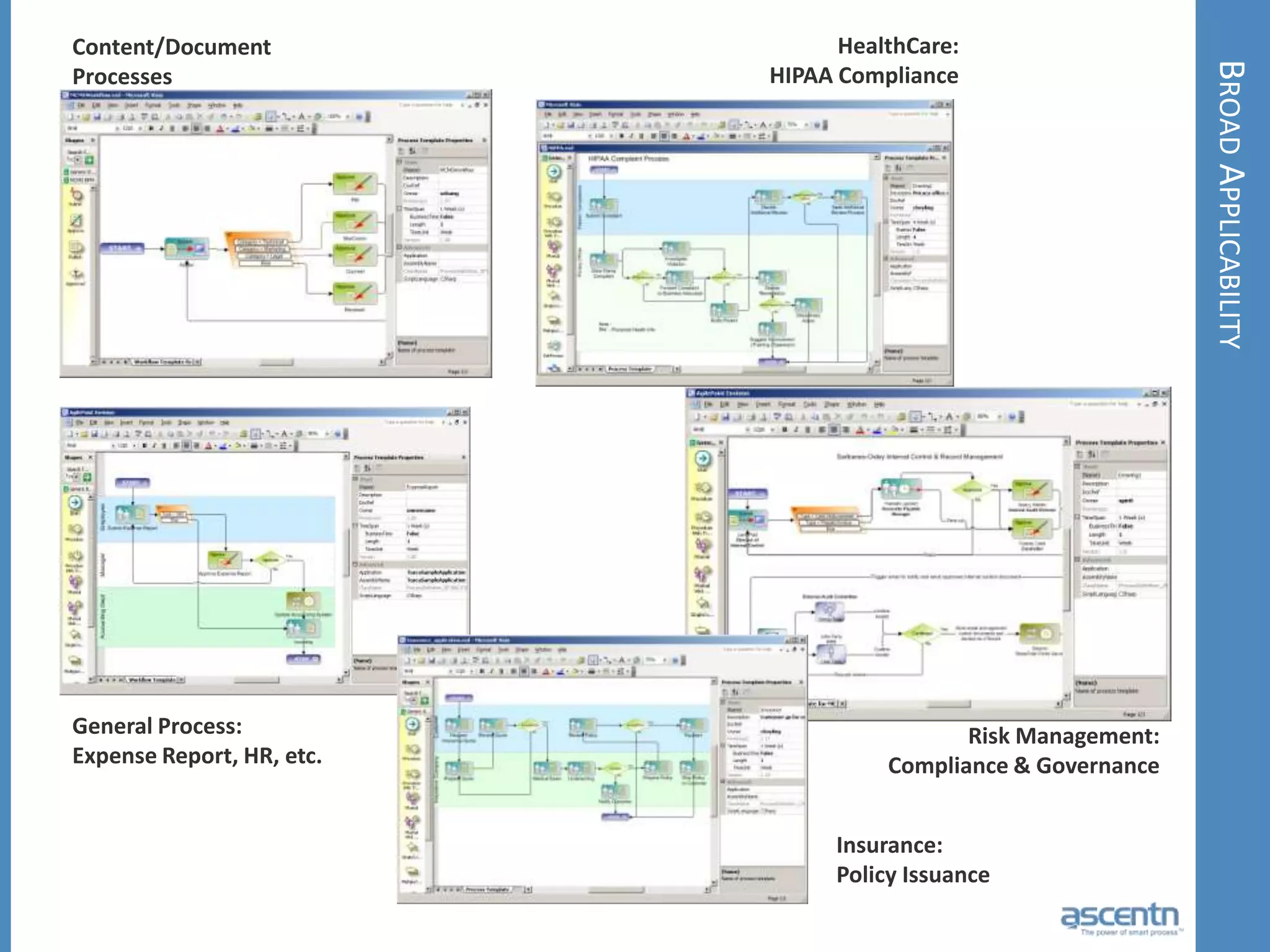
The document discusses business process management systems (BPMS) and how they enable agile and process-managed enterprises. It provides an overview of what BPMS is, the benefits it provides like increased efficiency and responsiveness, and how it allows businesses to adapt more quickly. The document also outlines key elements needed for a BPMS like a process engine and user directory, and tips for getting started with BPMS like taking a pragmatic approach, defining a dedicated team, and looking for quick win projects.