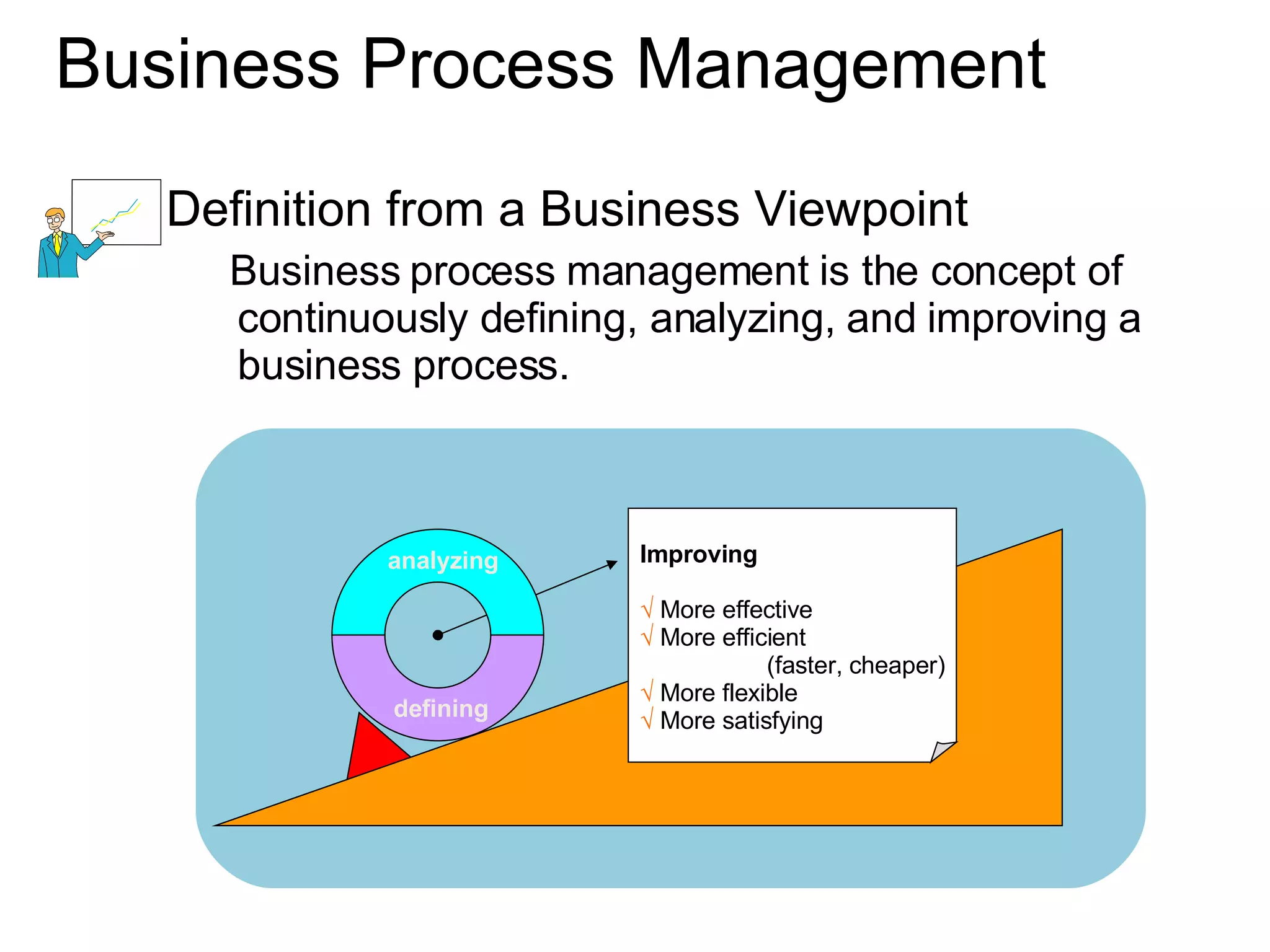
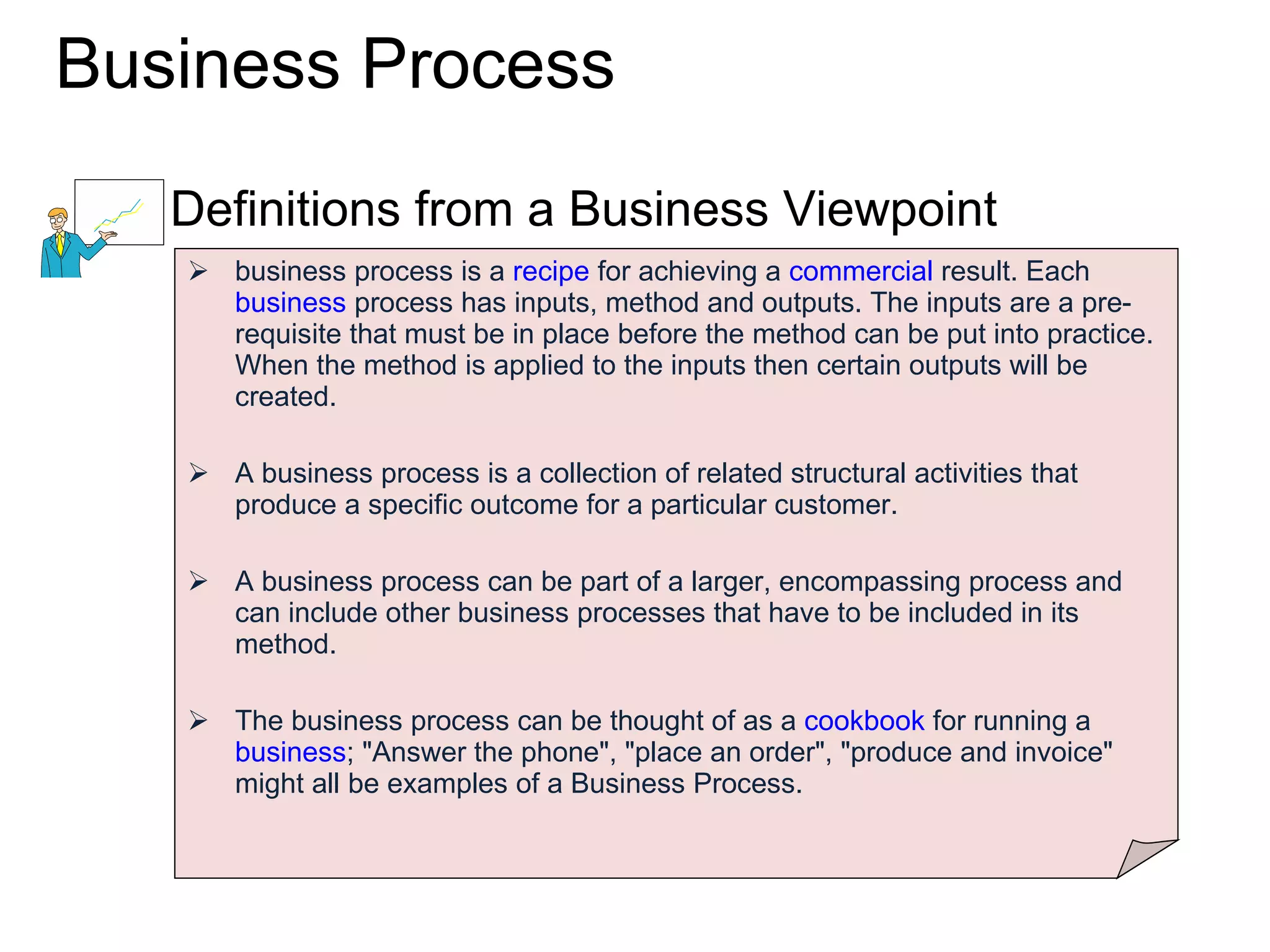
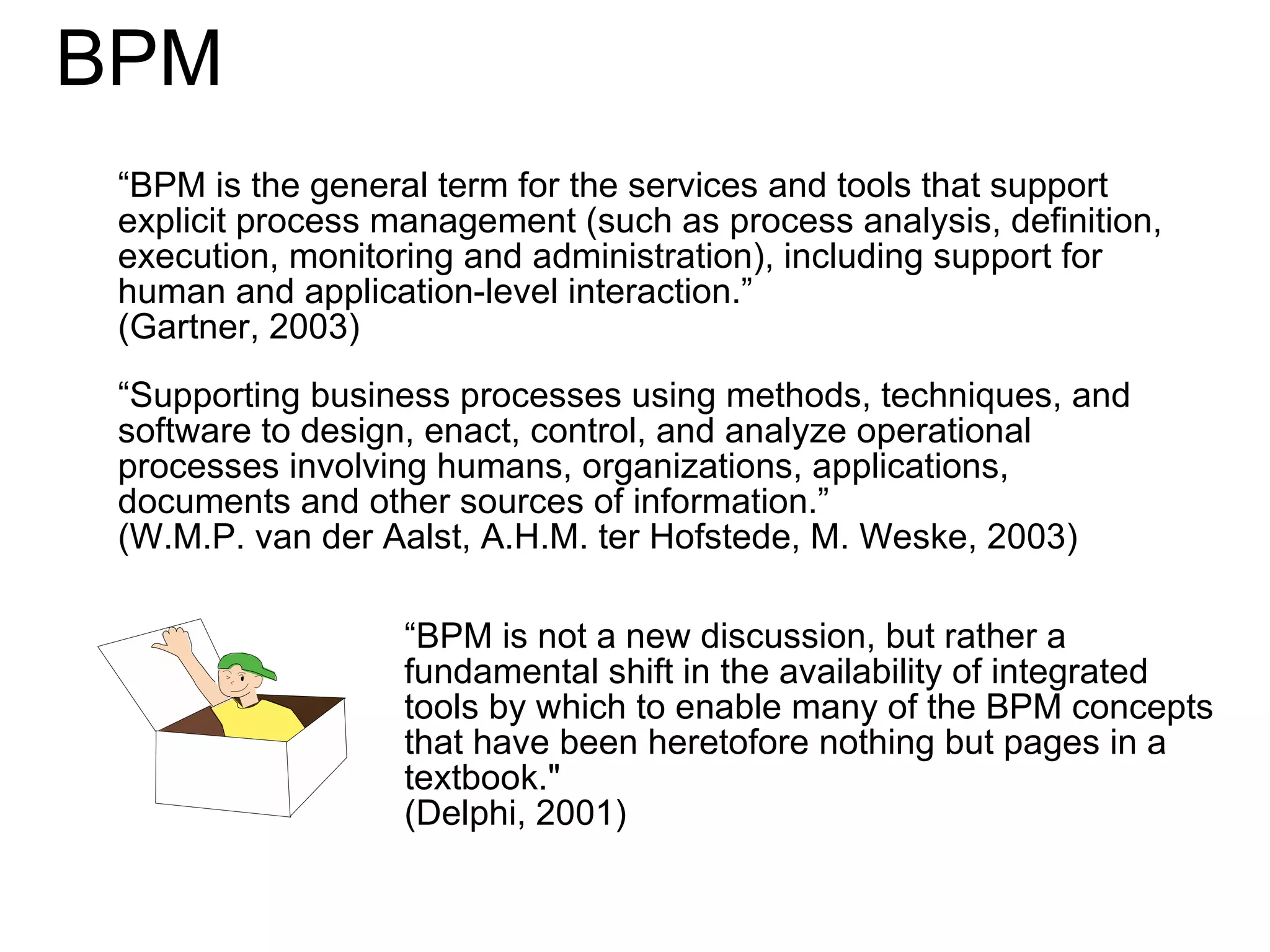
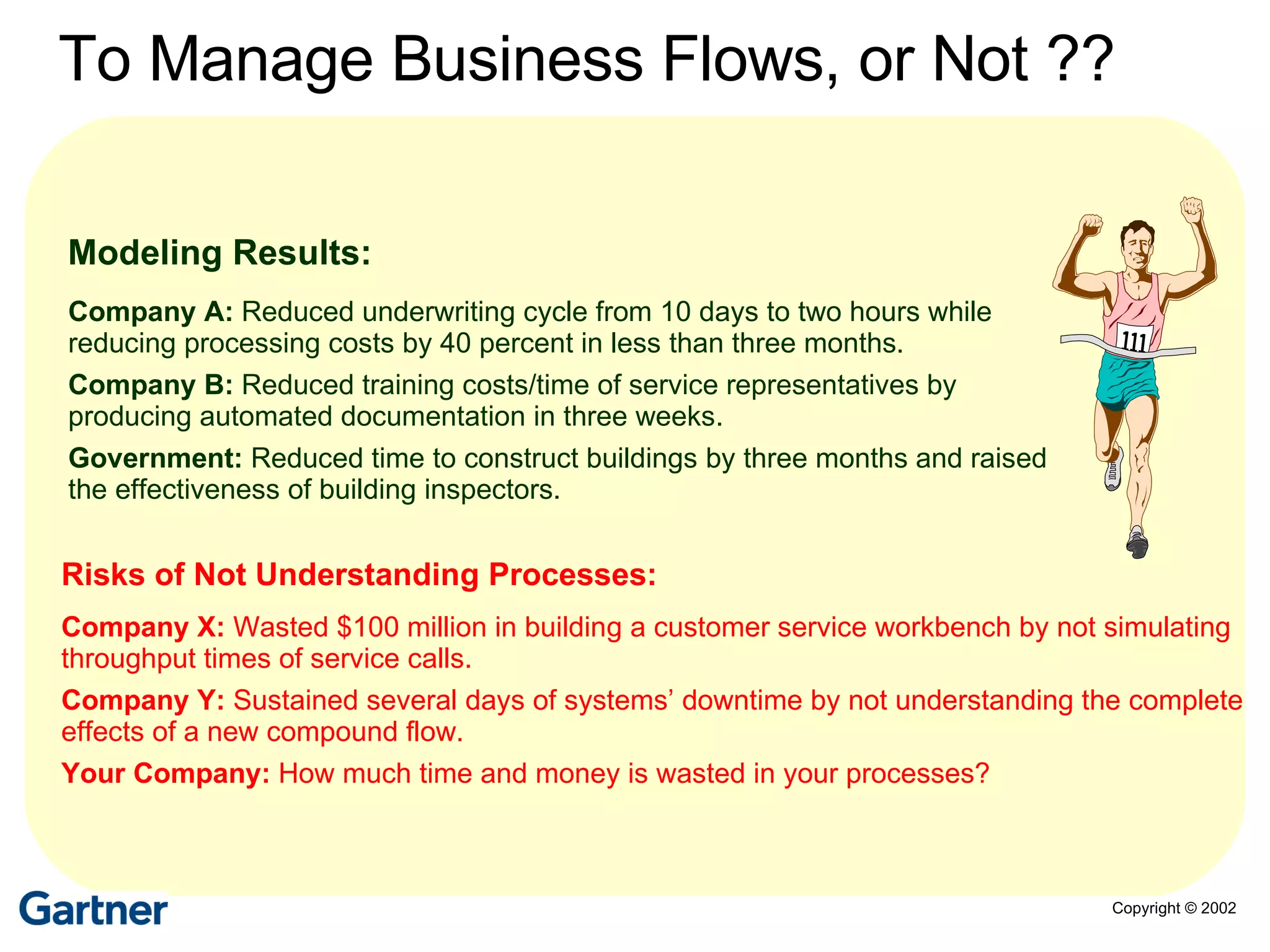
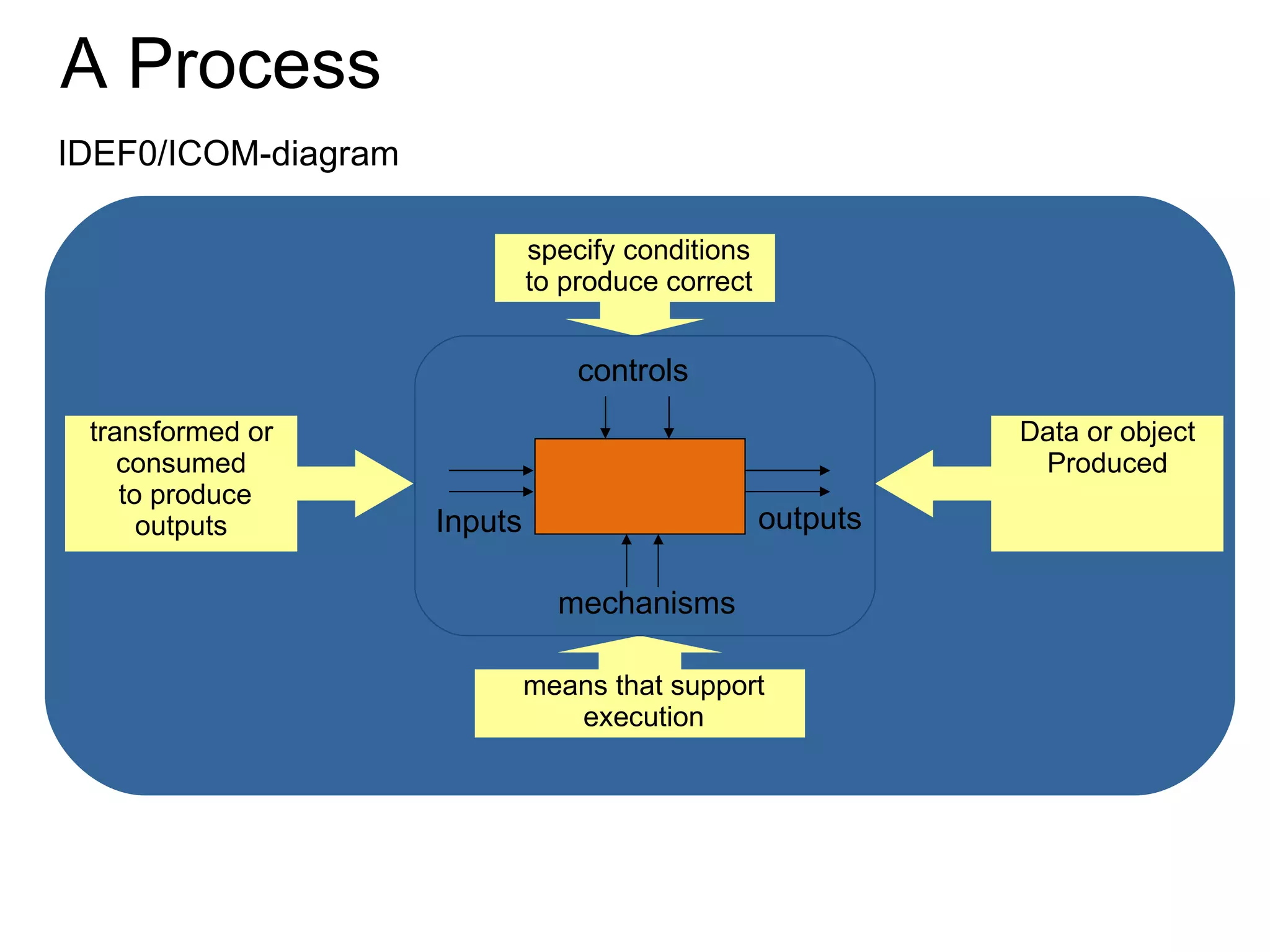
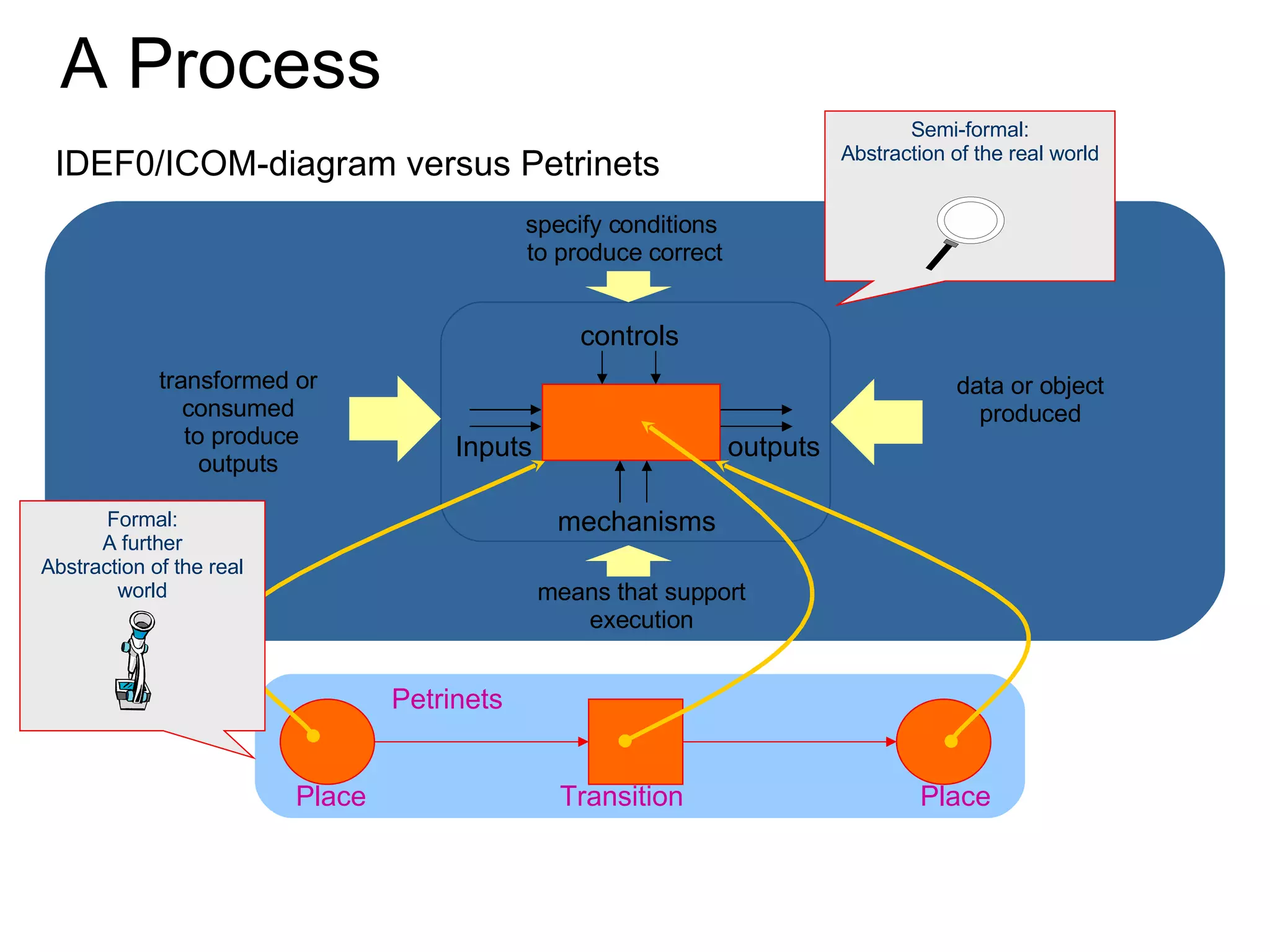
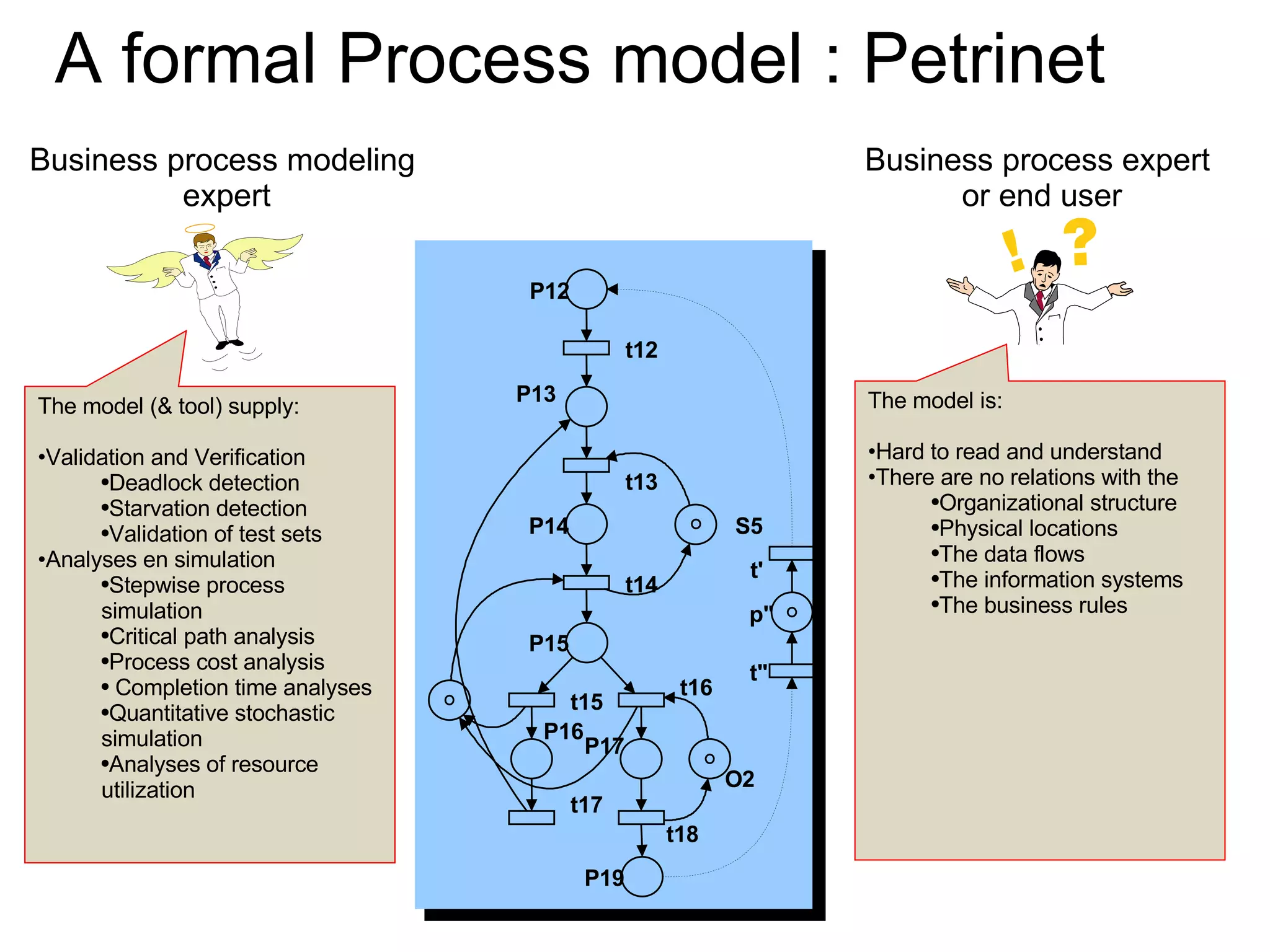
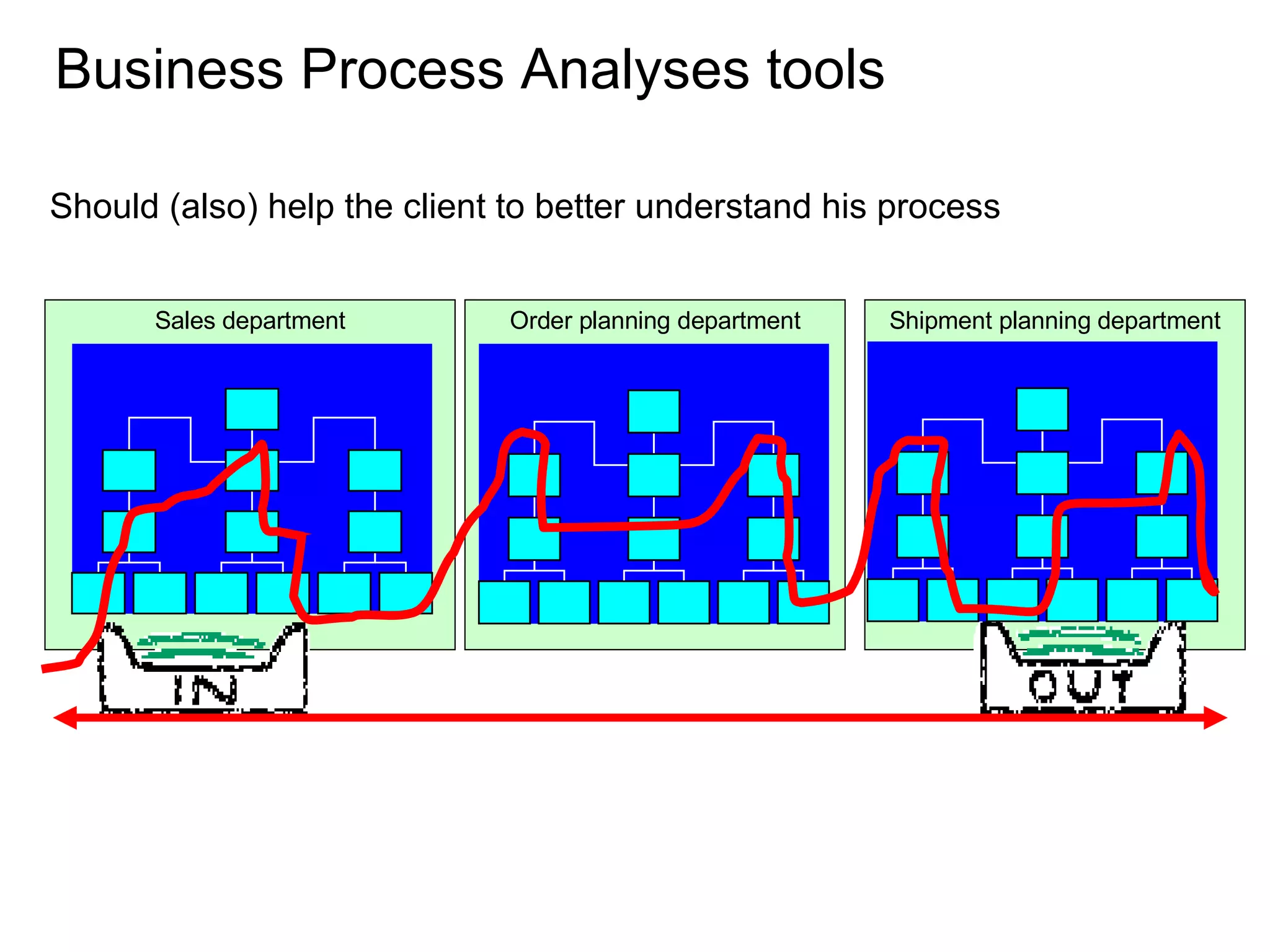
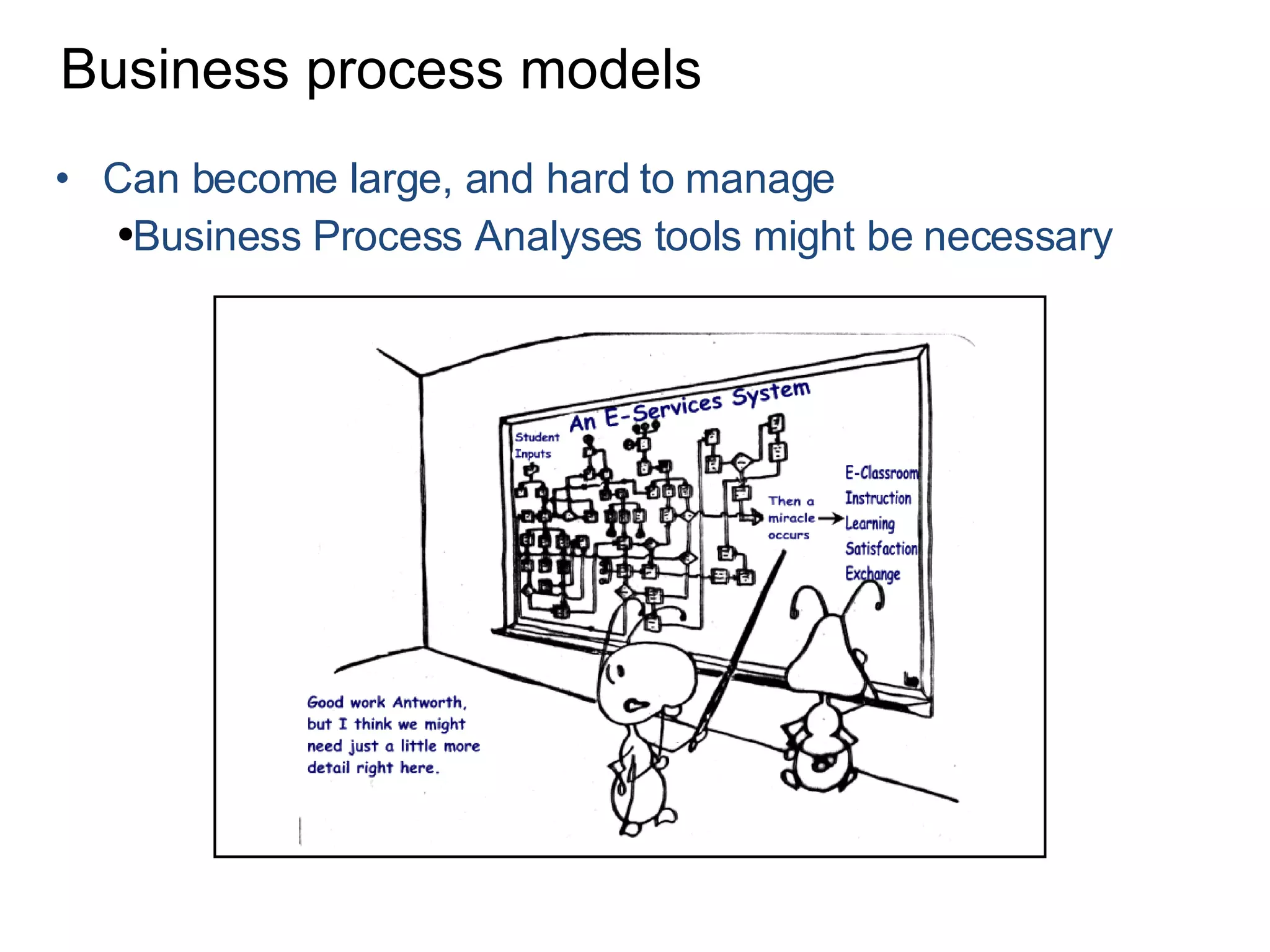
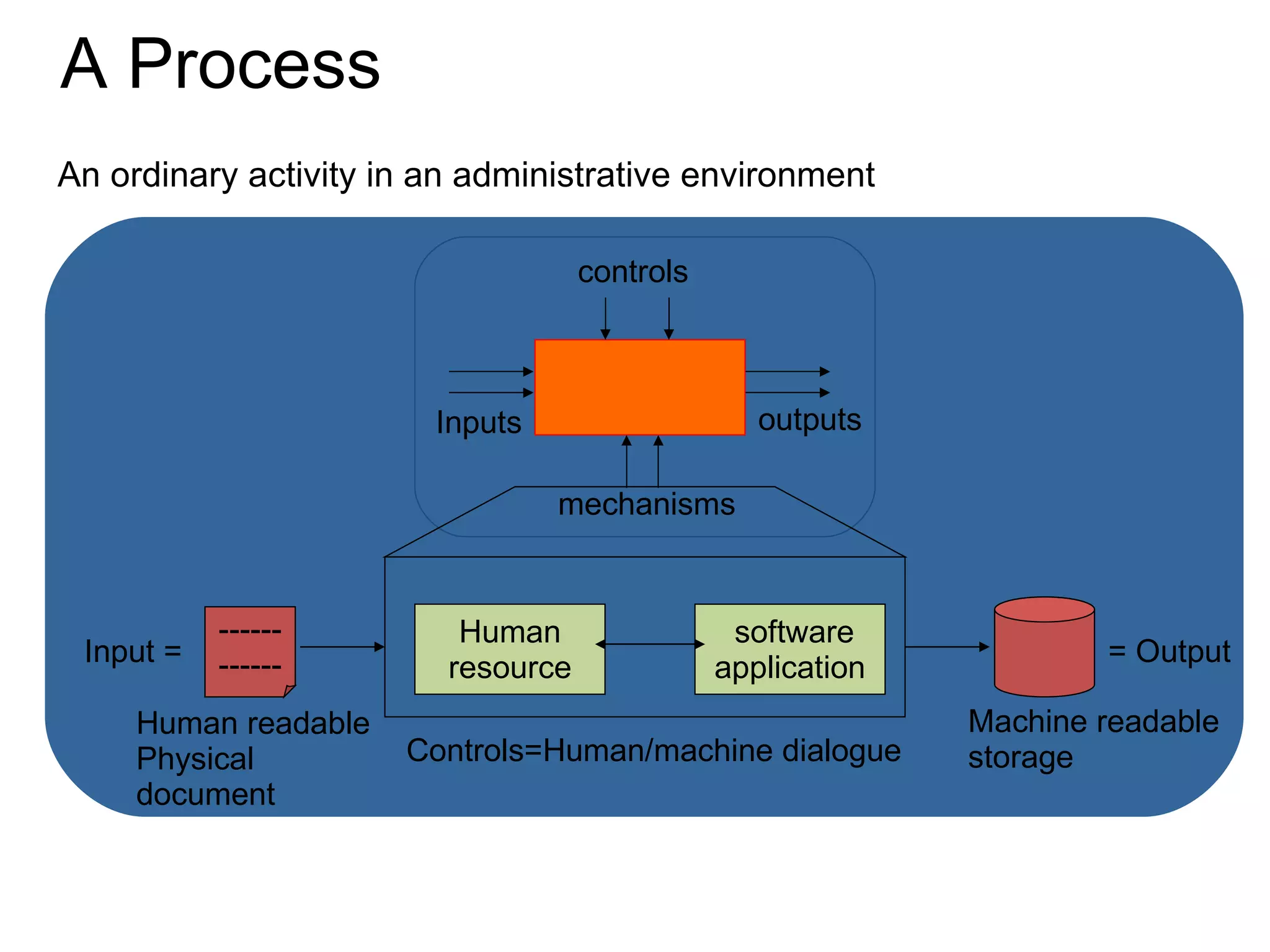
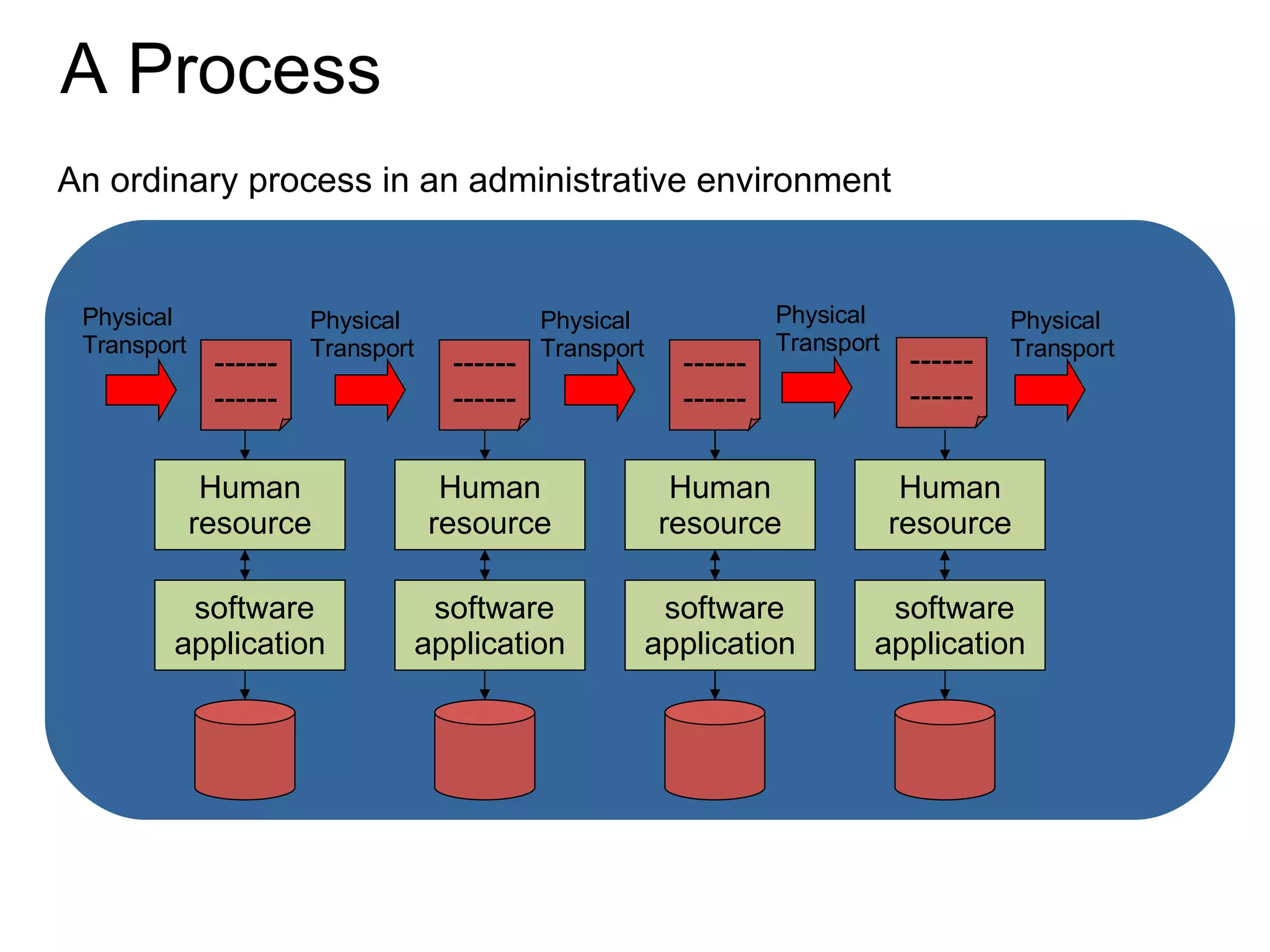
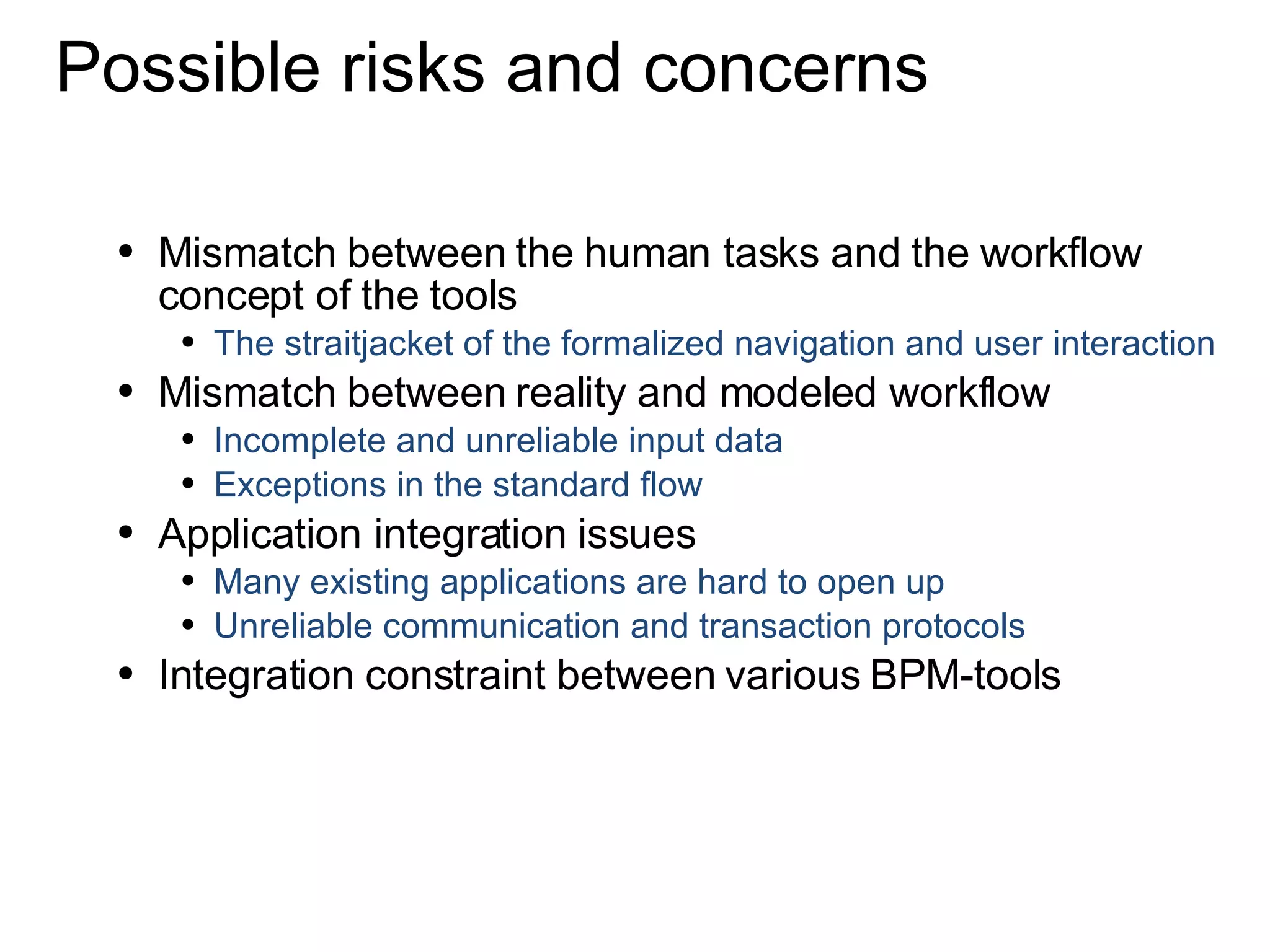
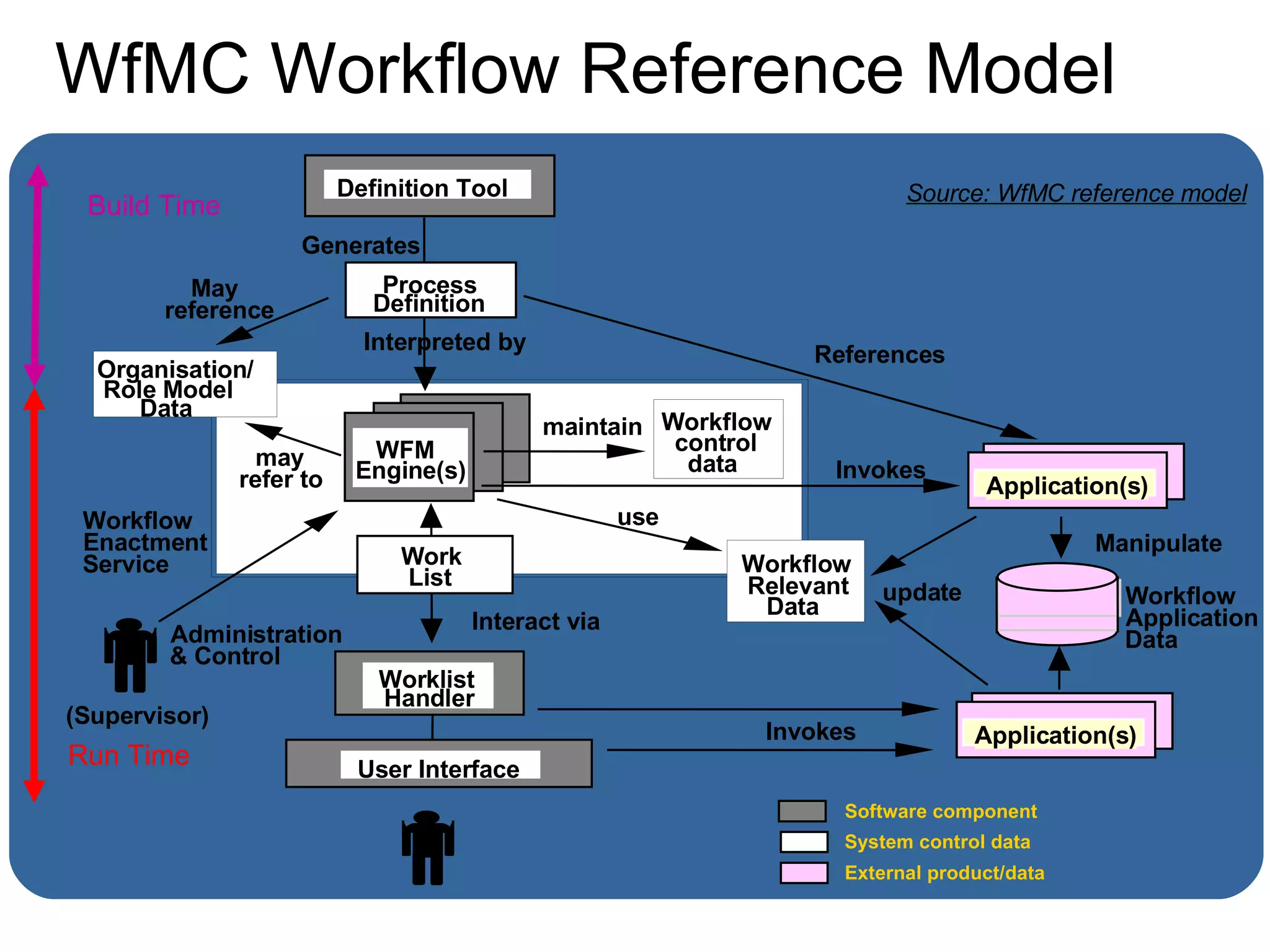
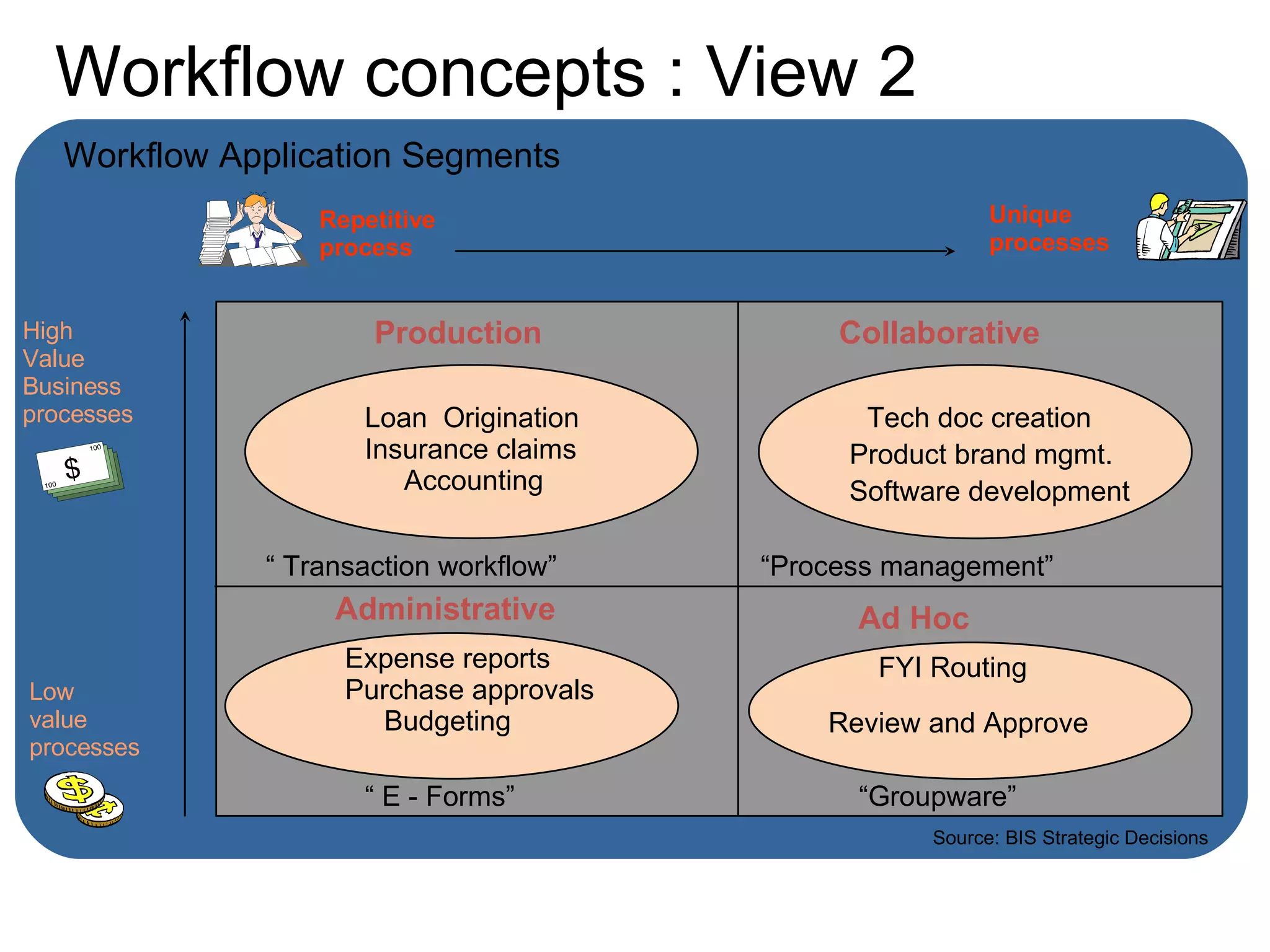
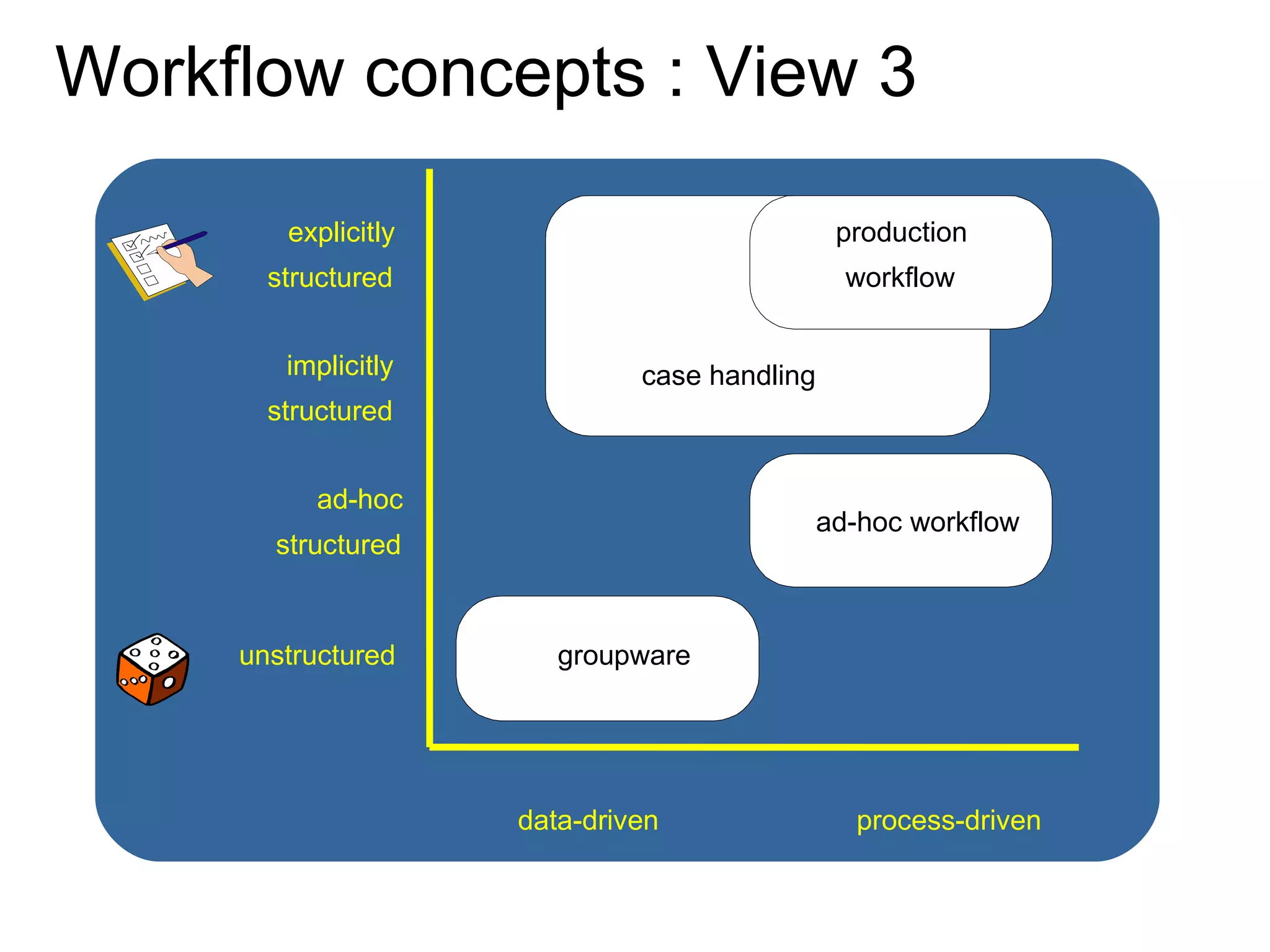
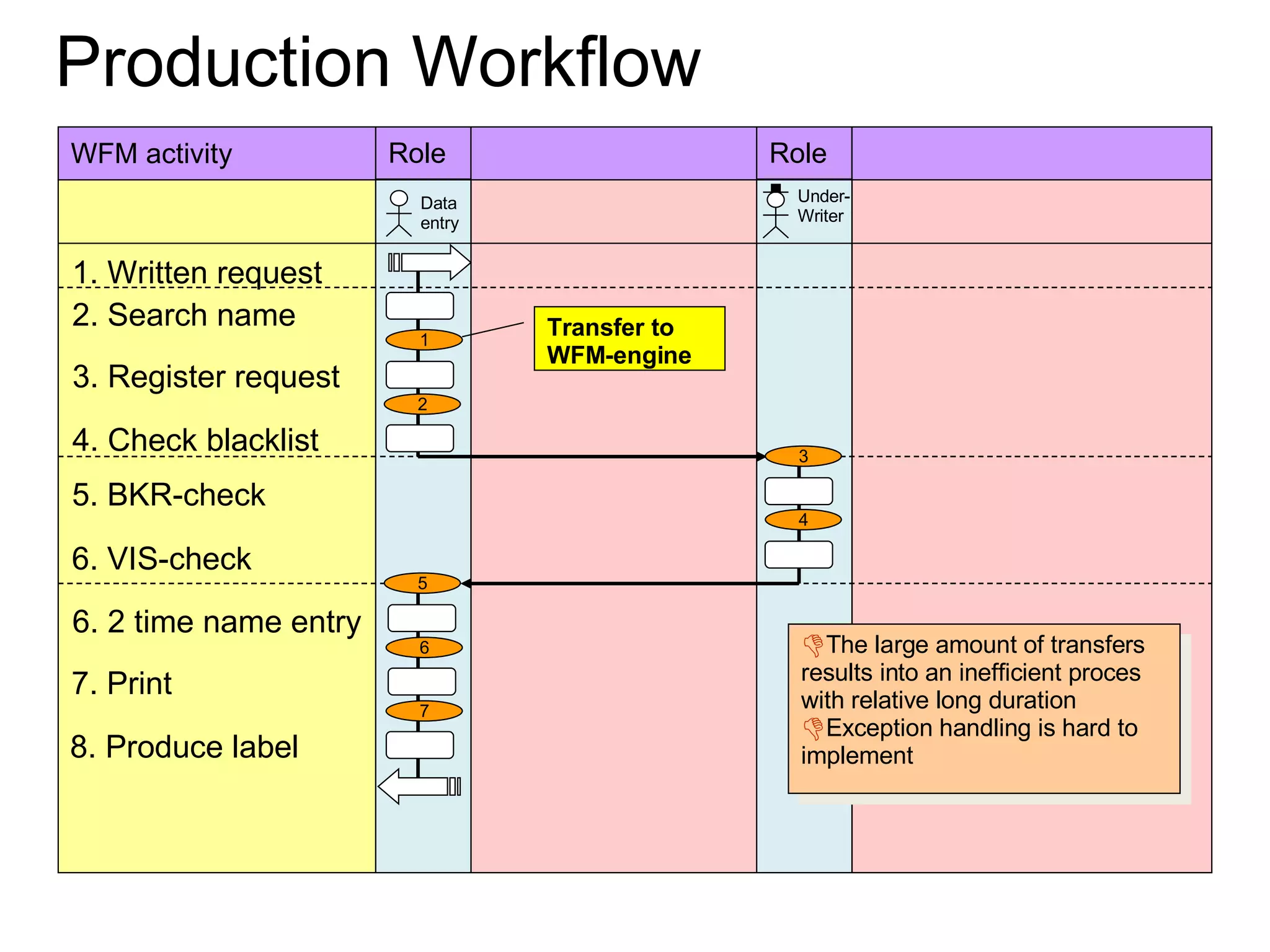
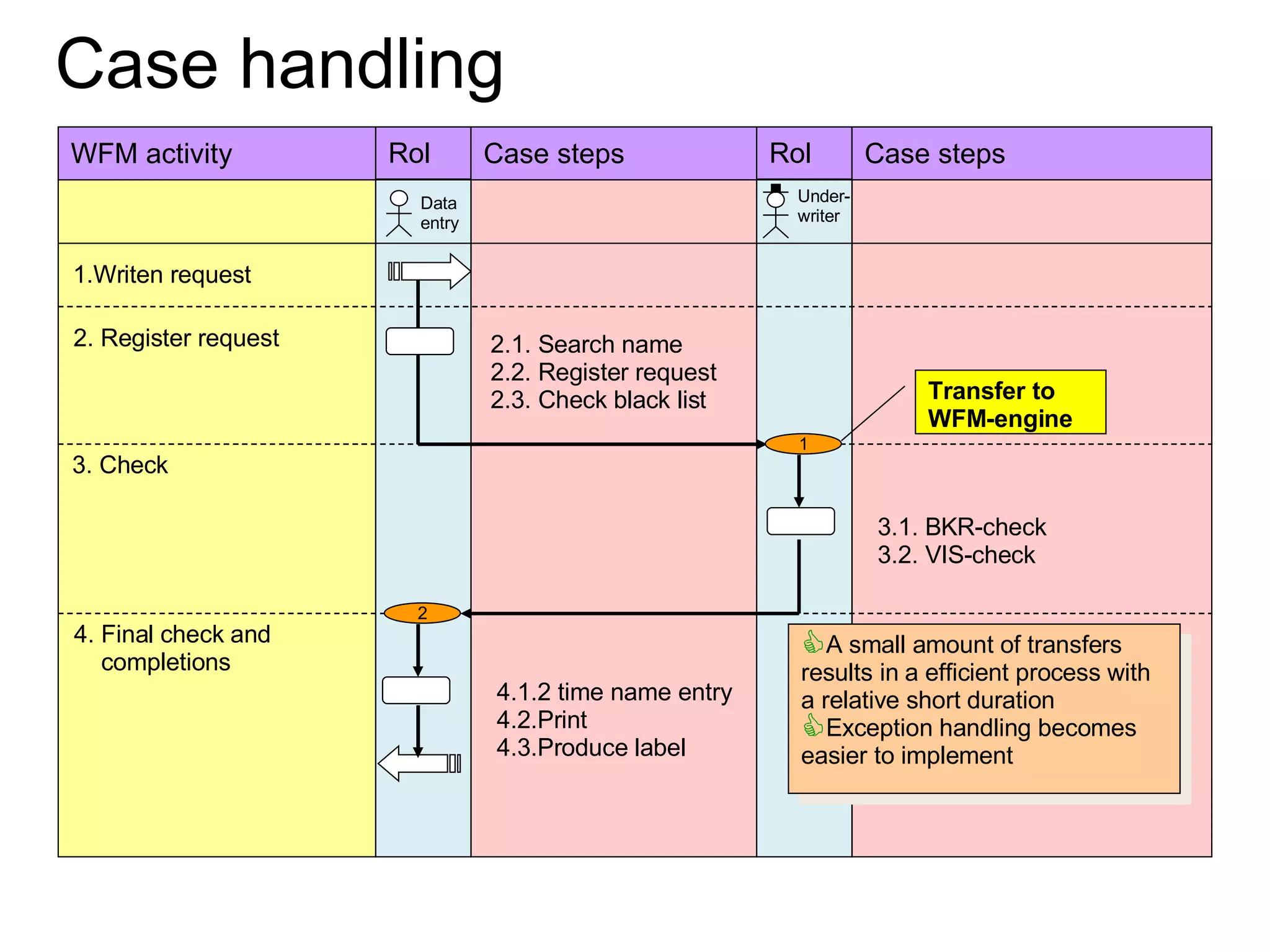
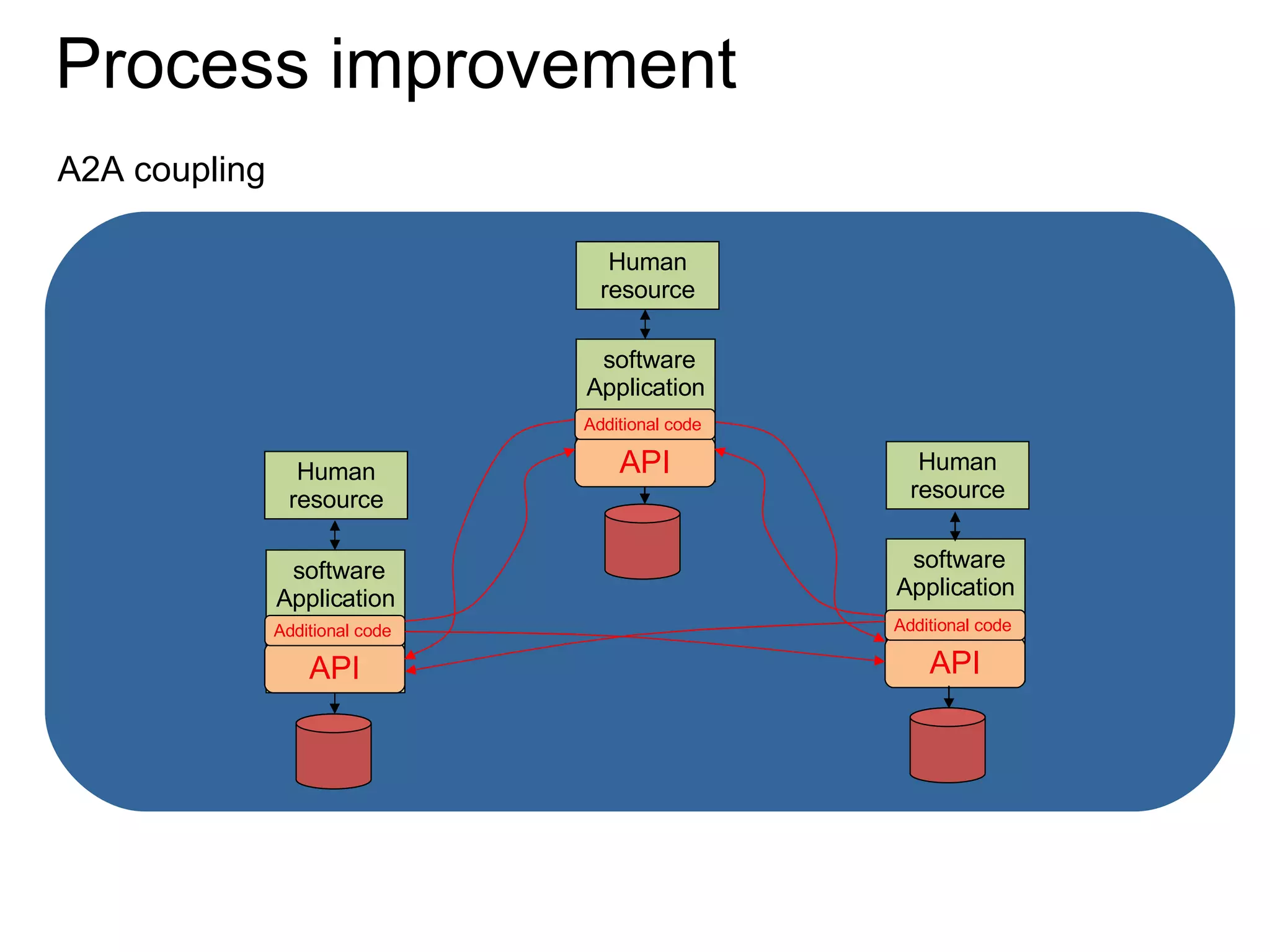
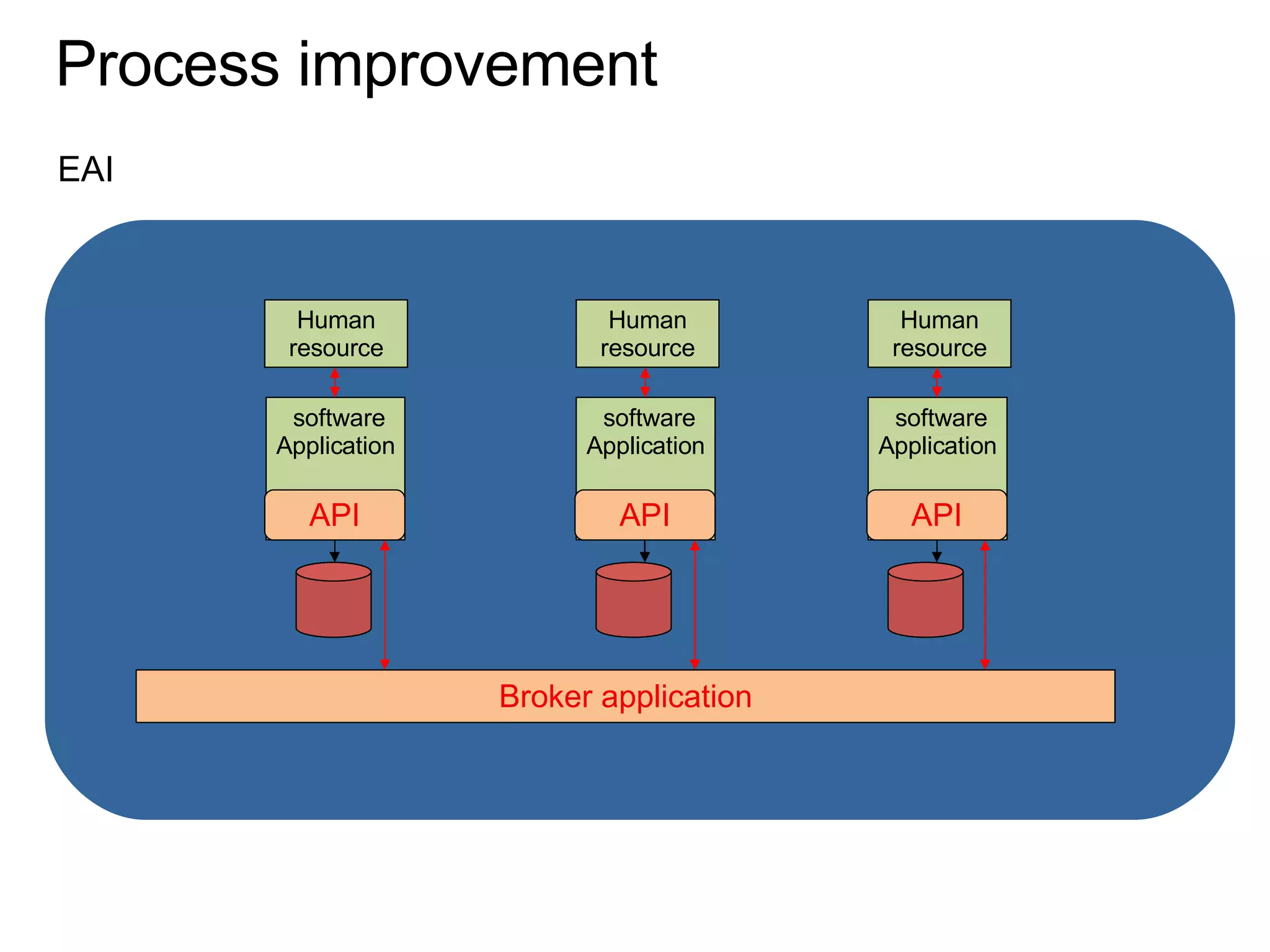
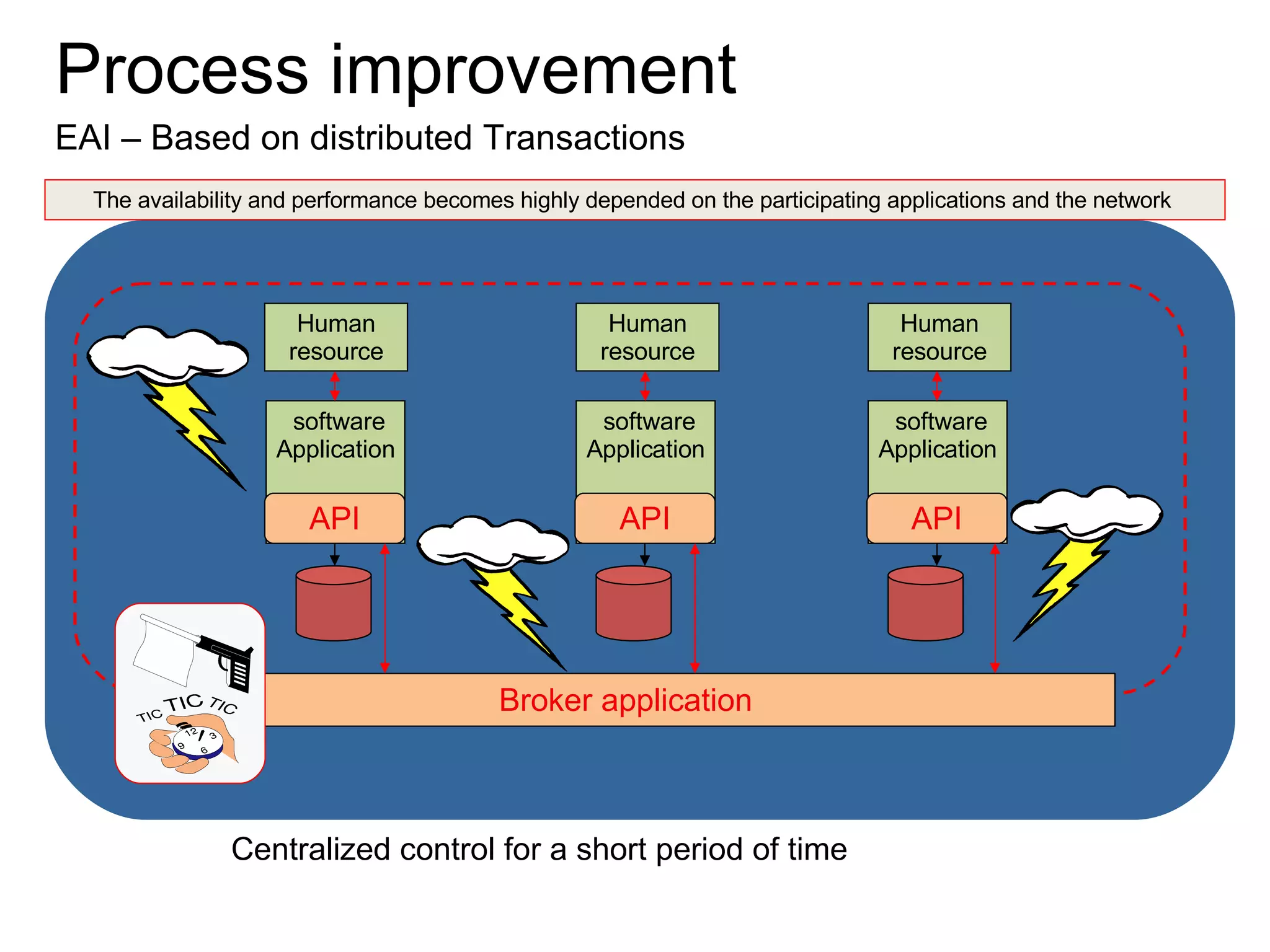
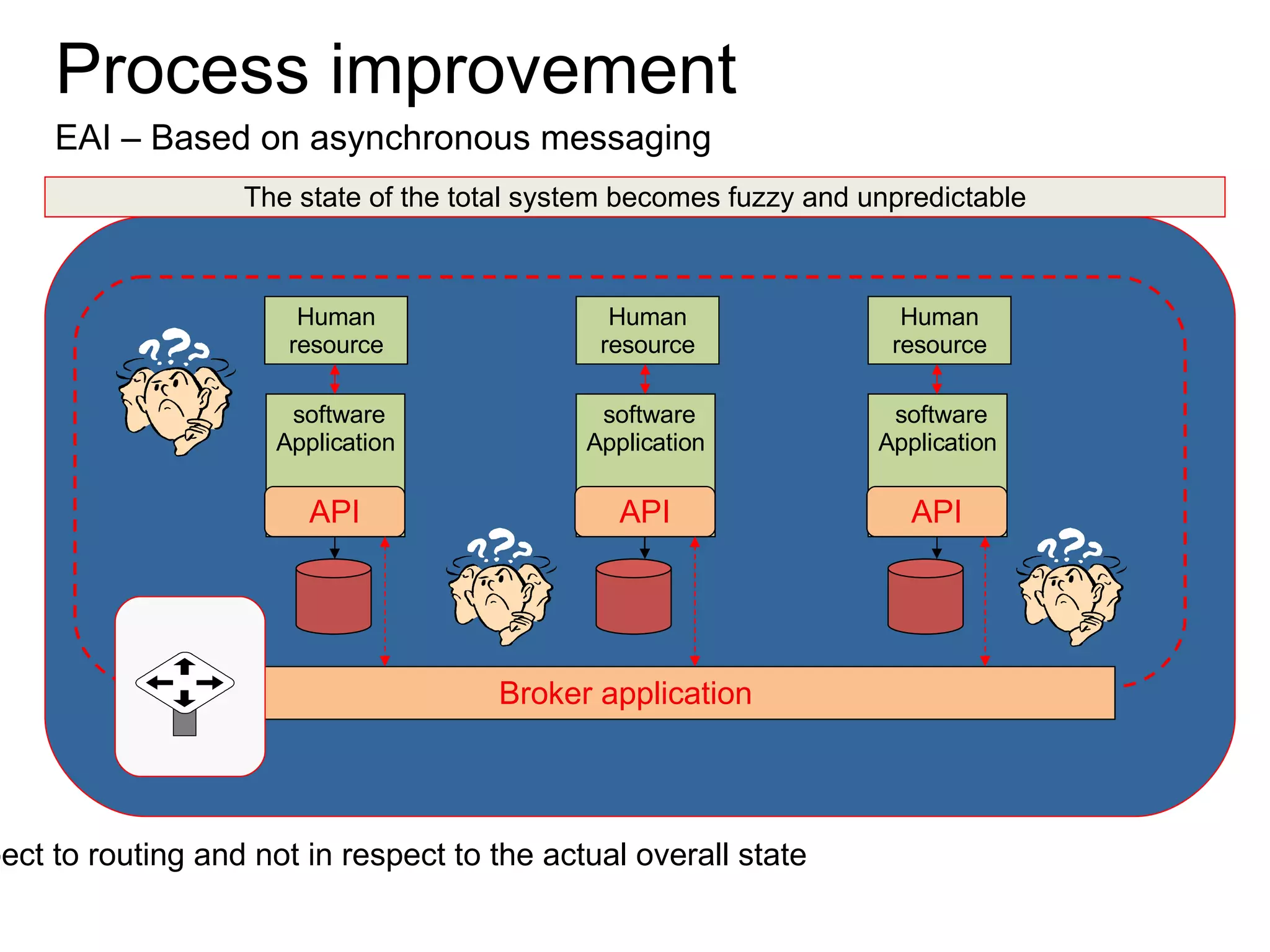
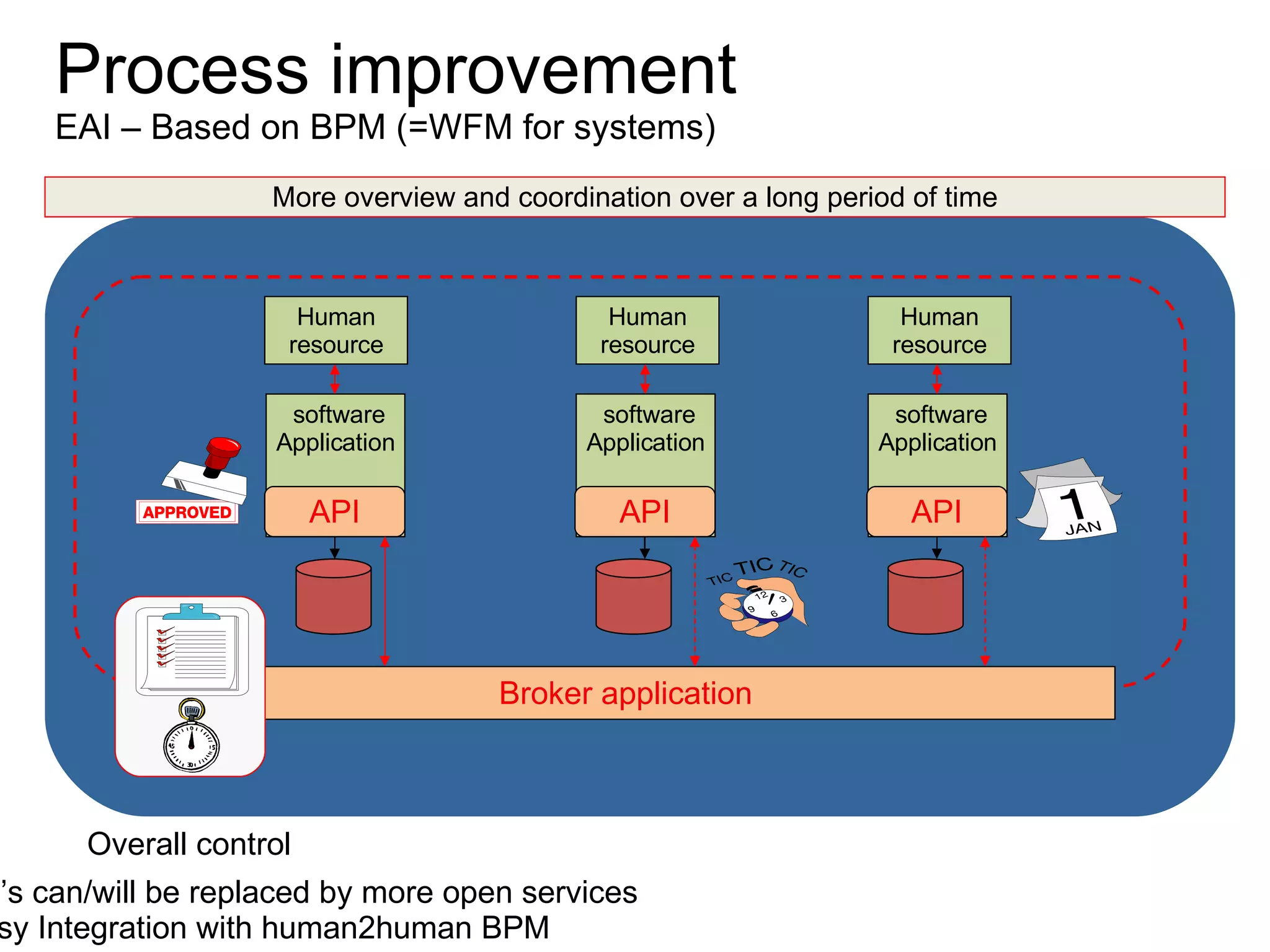
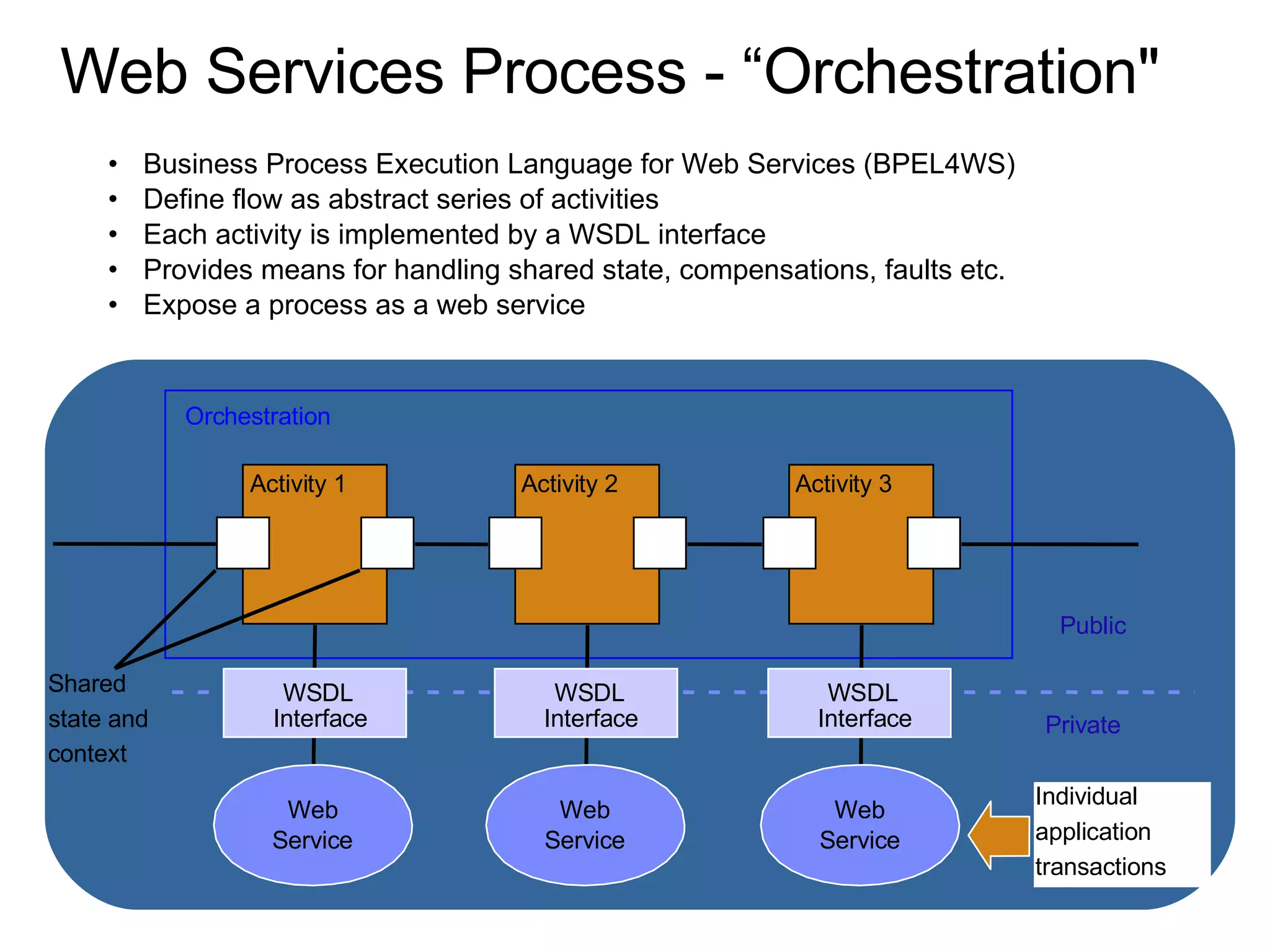
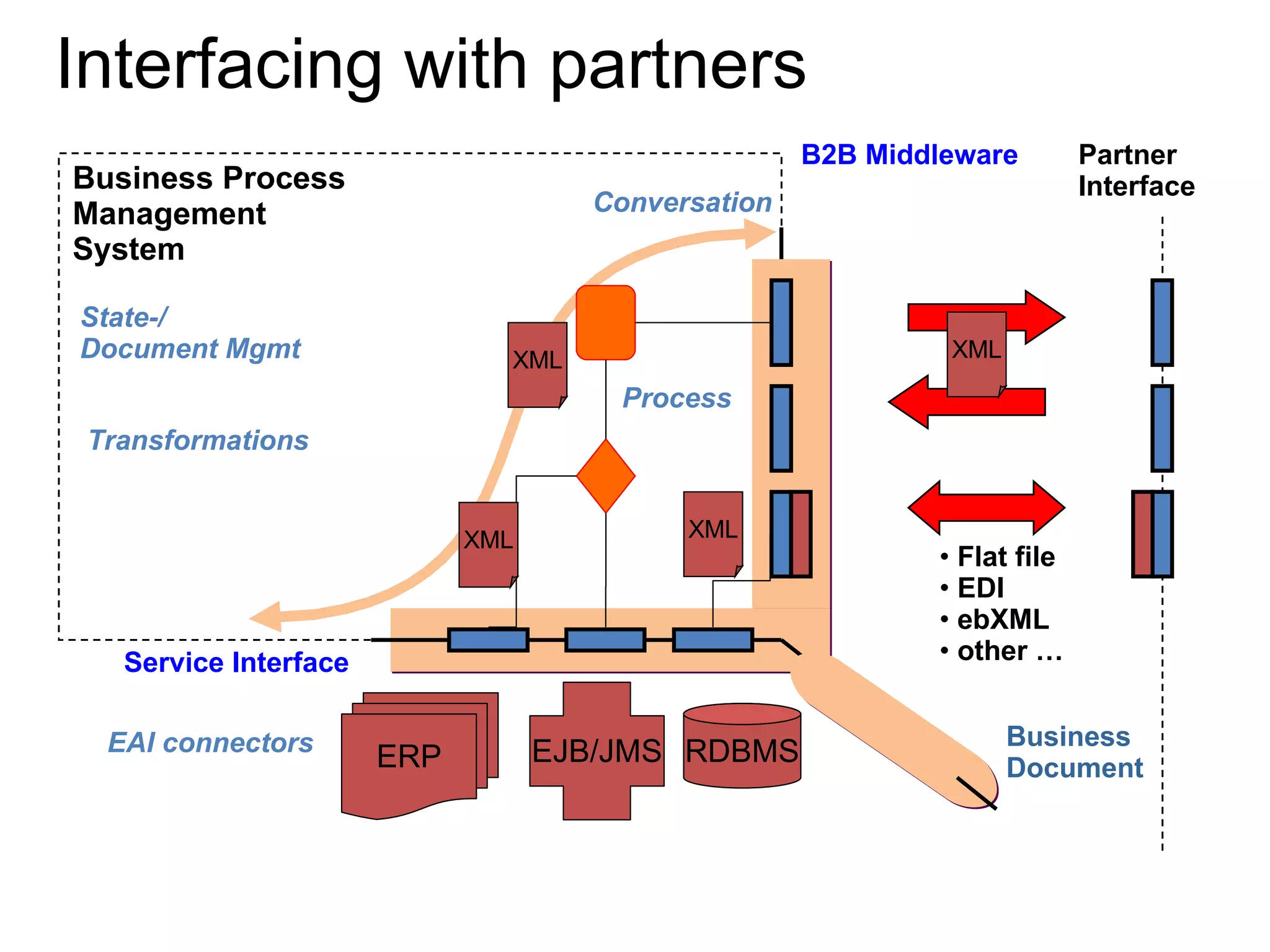
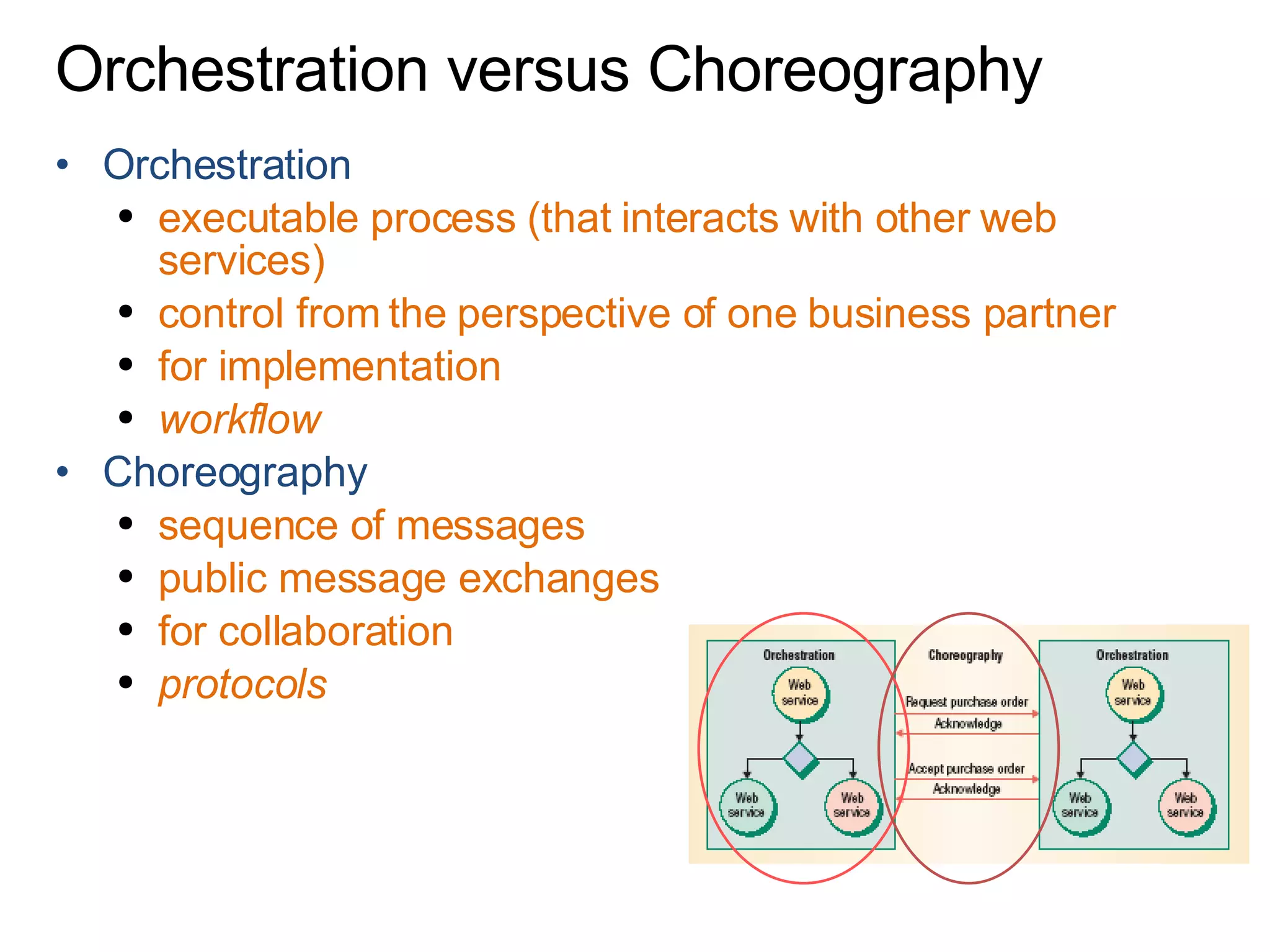
The document discusses various business process management (BPM) tools and concepts. It describes tools for modeling processes like IDEF0 and Petri nets. It also covers workflow management systems, enterprise application integration (EAI), web services, and B2B integration. The key tools and approaches discussed are for analyzing, improving, and automating business processes involving both human and system interactions.