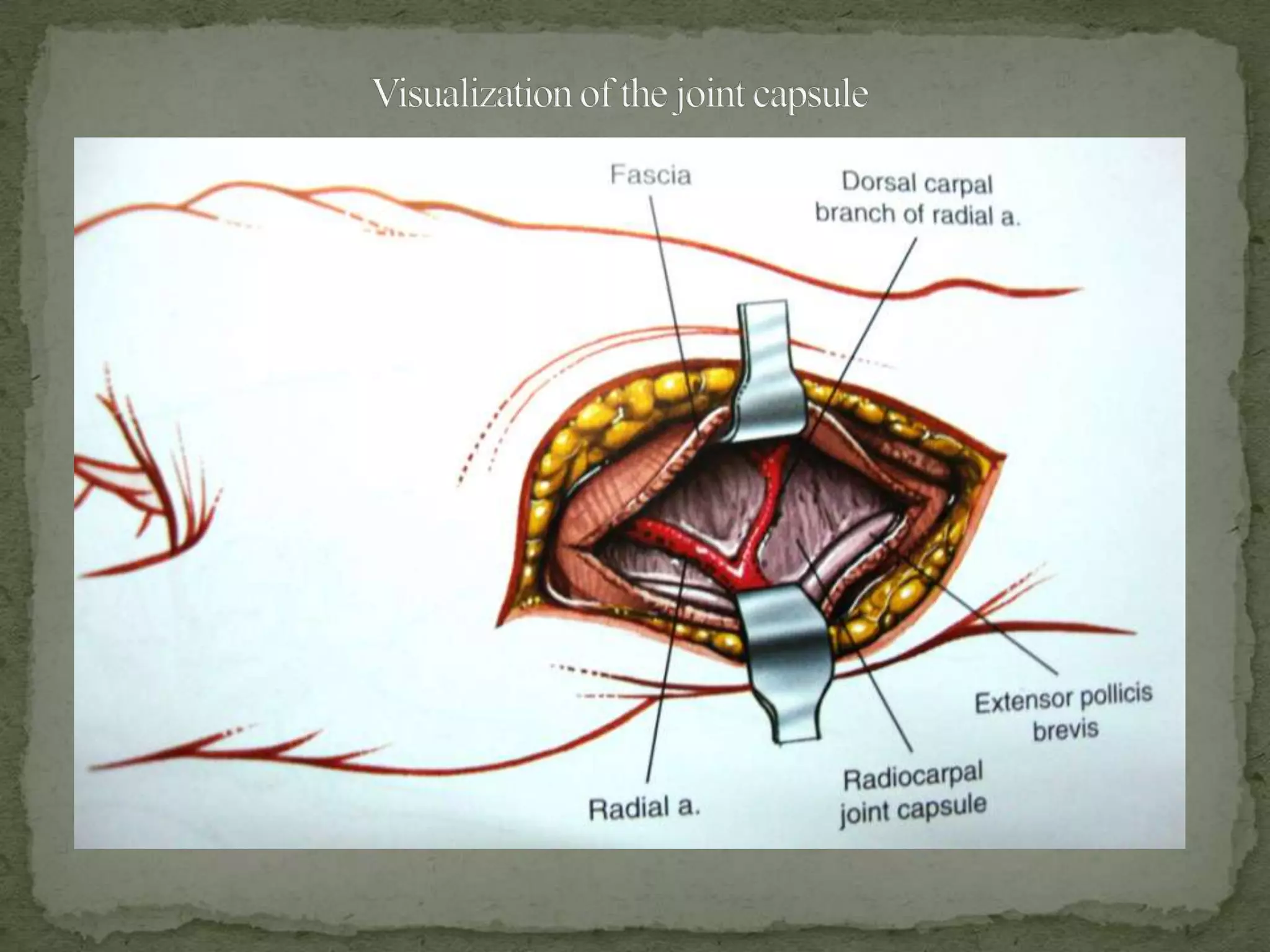
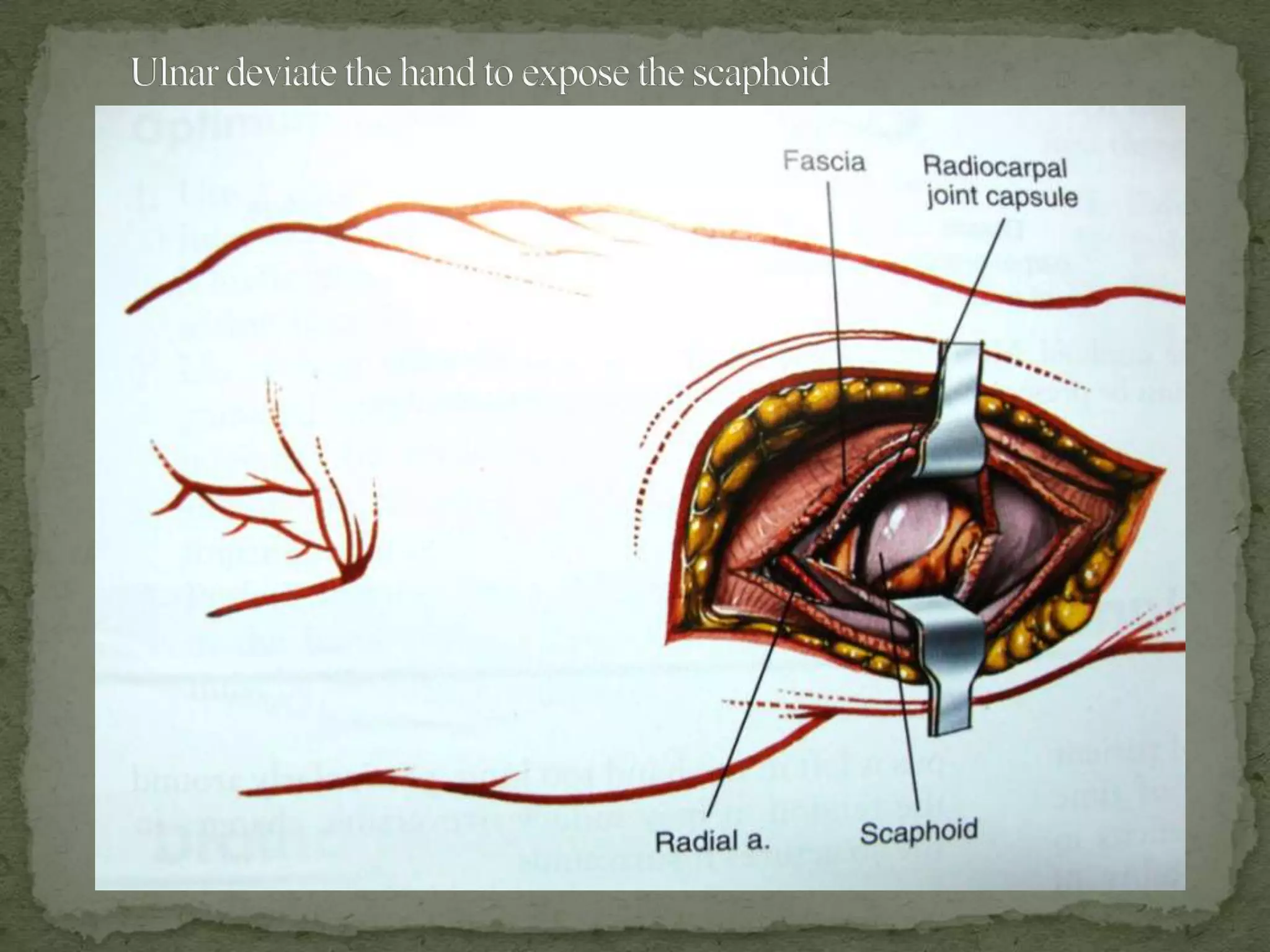
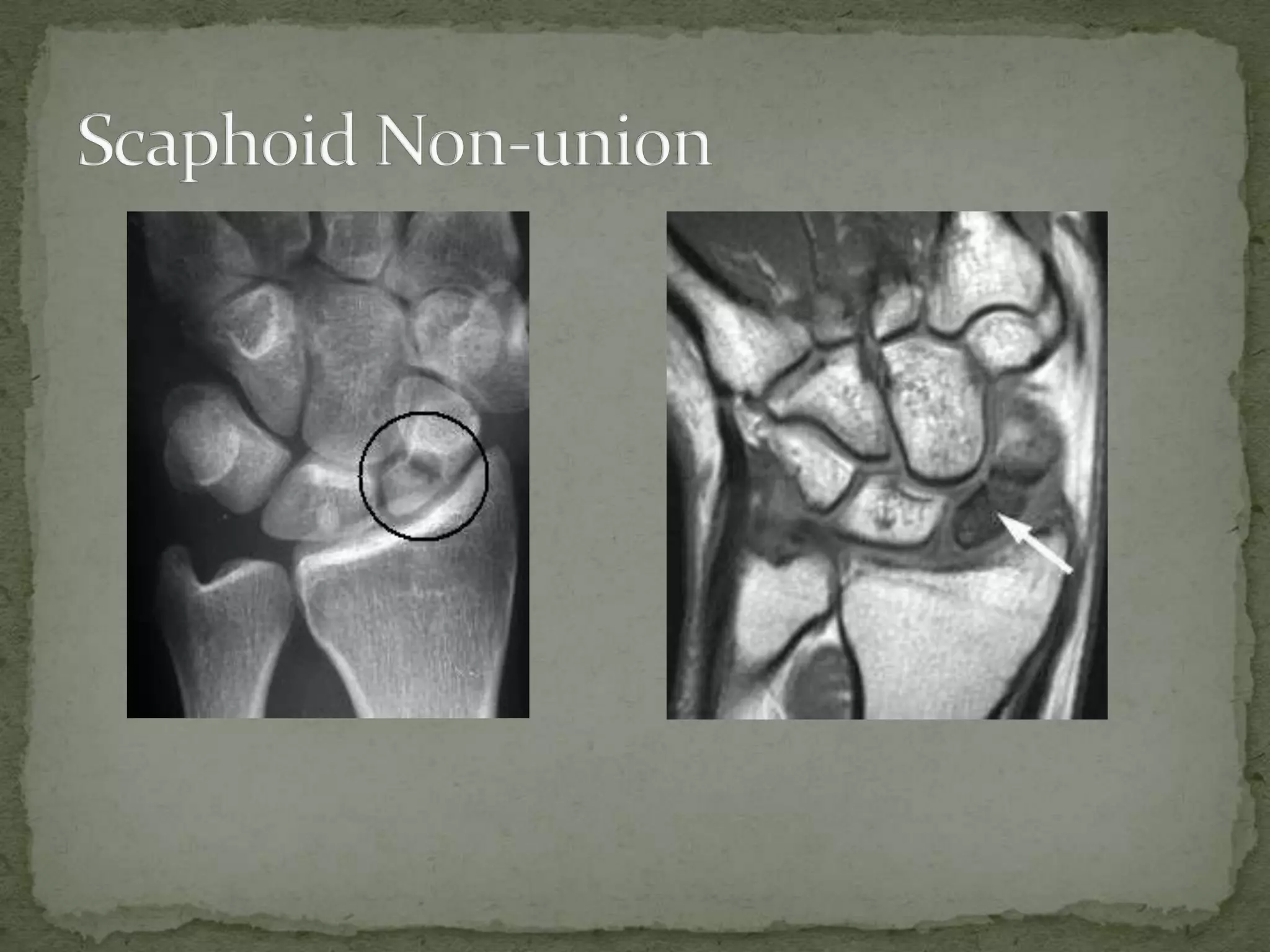
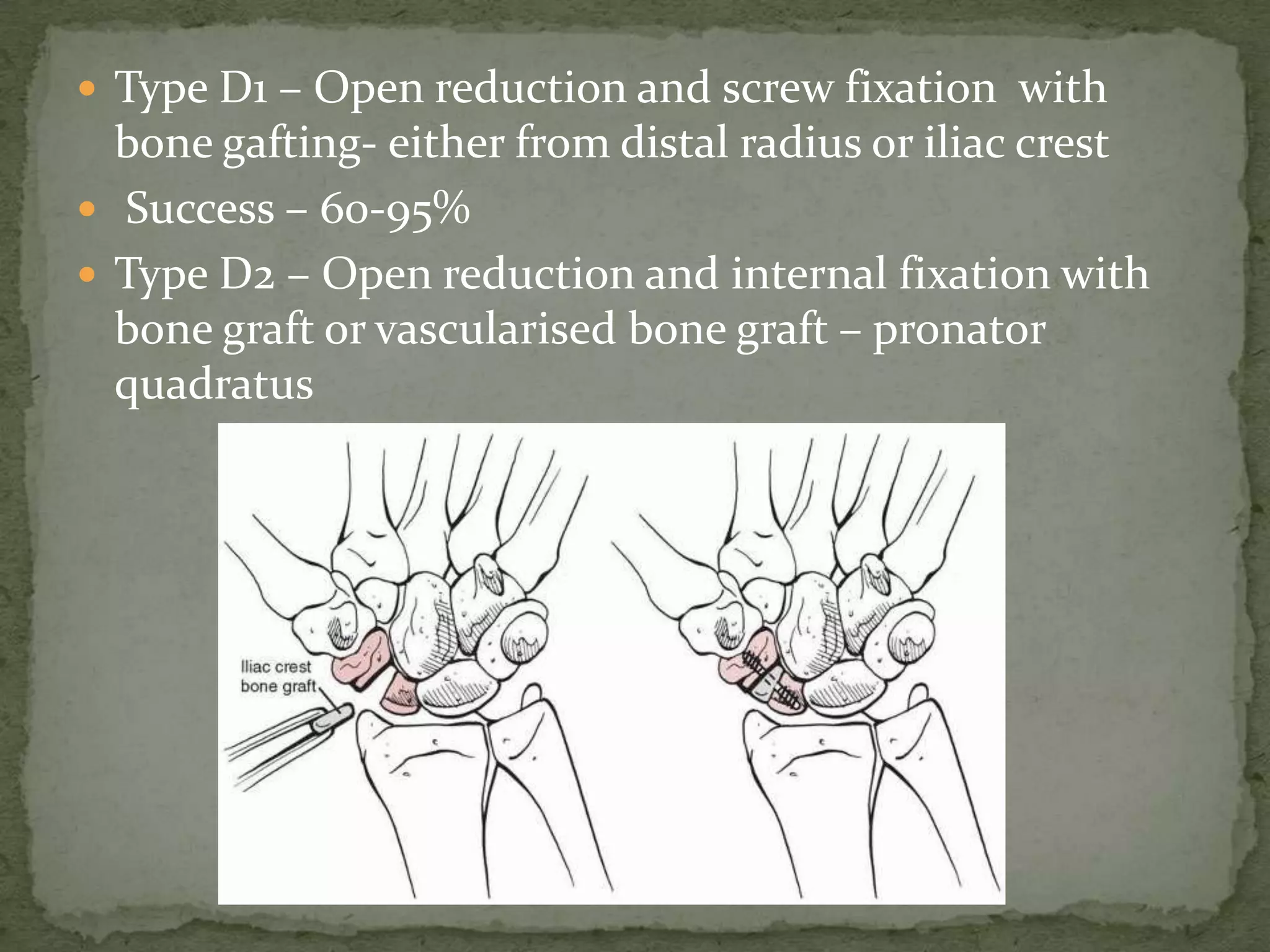
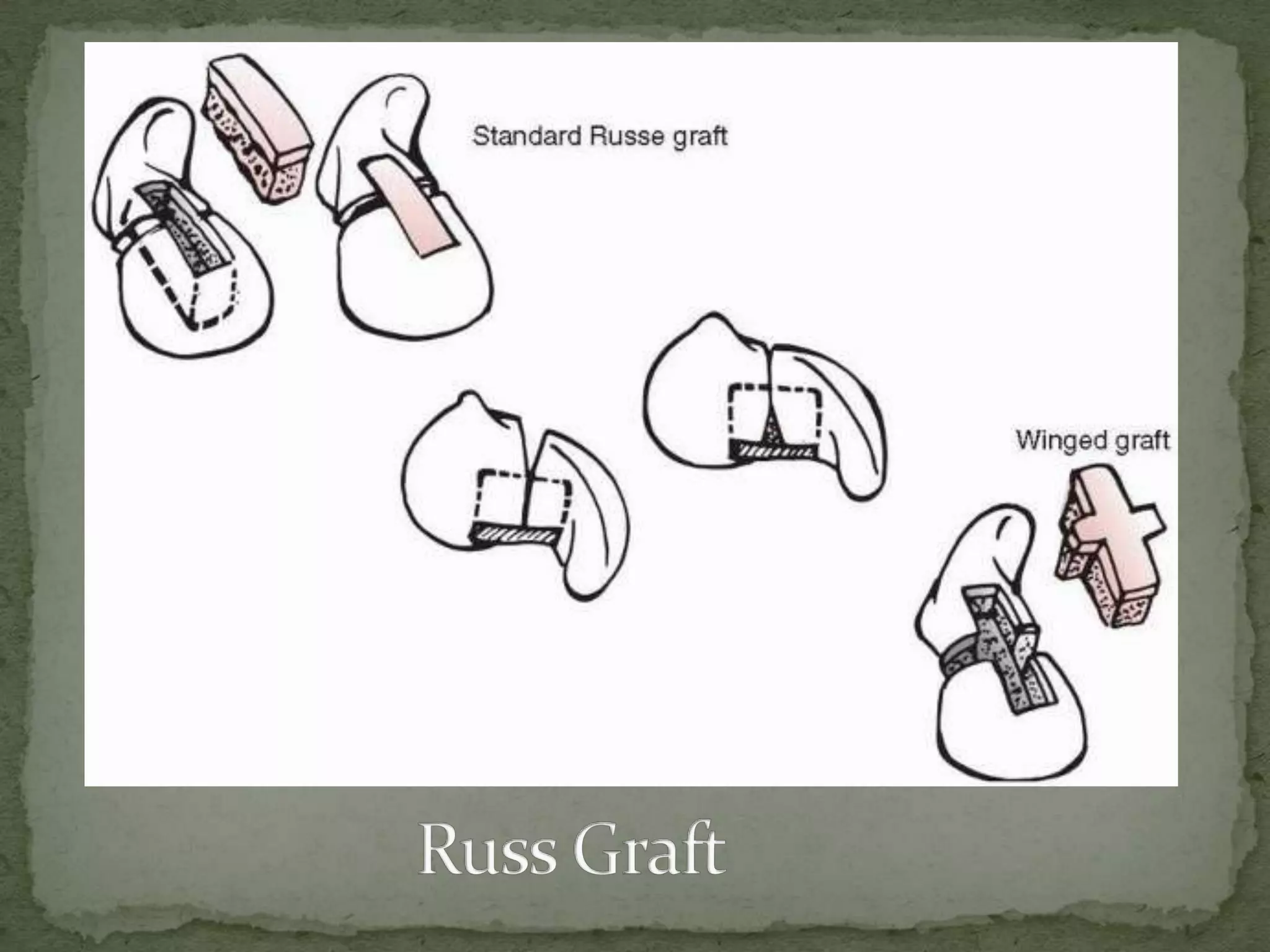
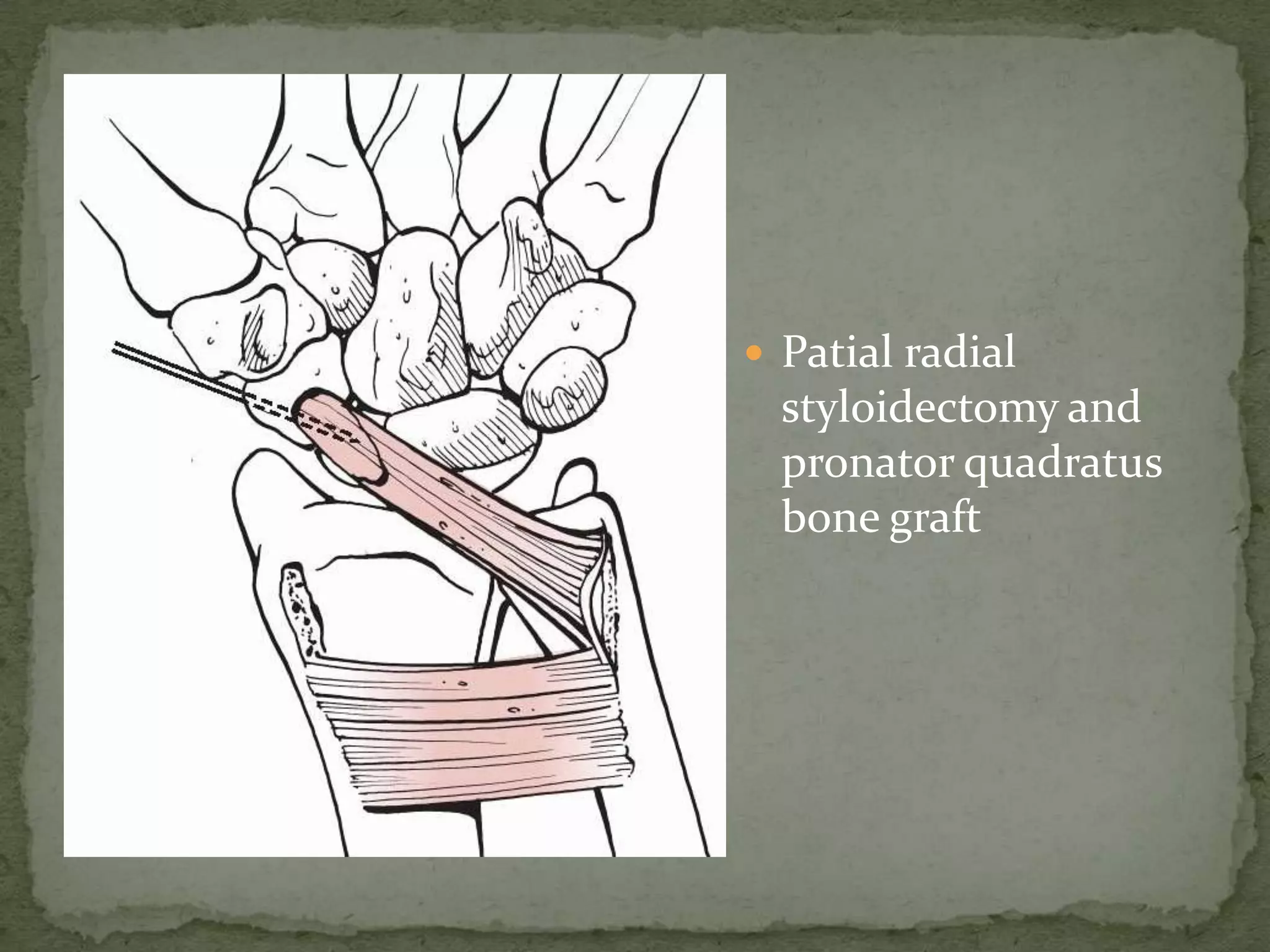
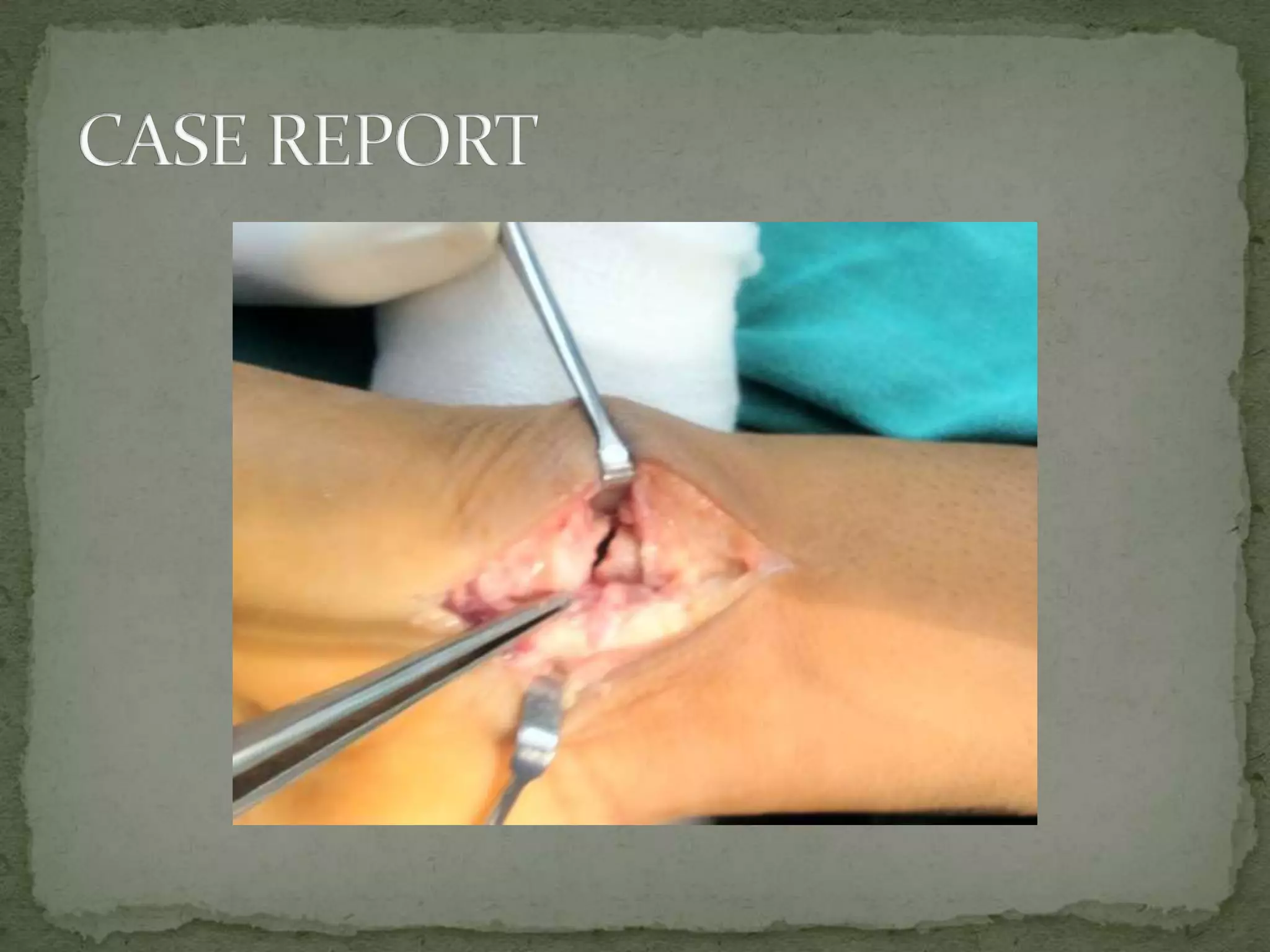
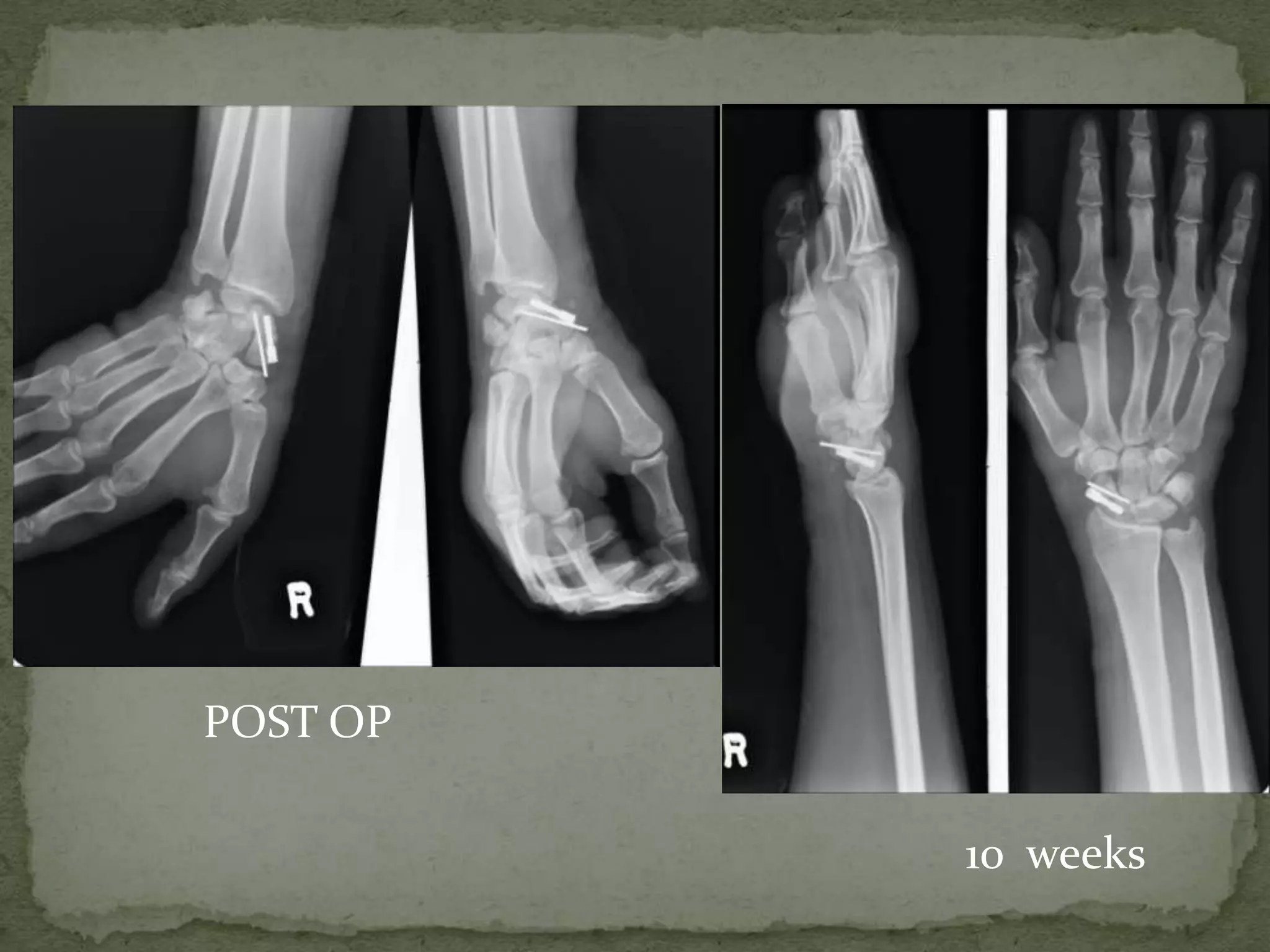
This document discusses the anatomy, classification, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of scaphoid fractures. Some key points:
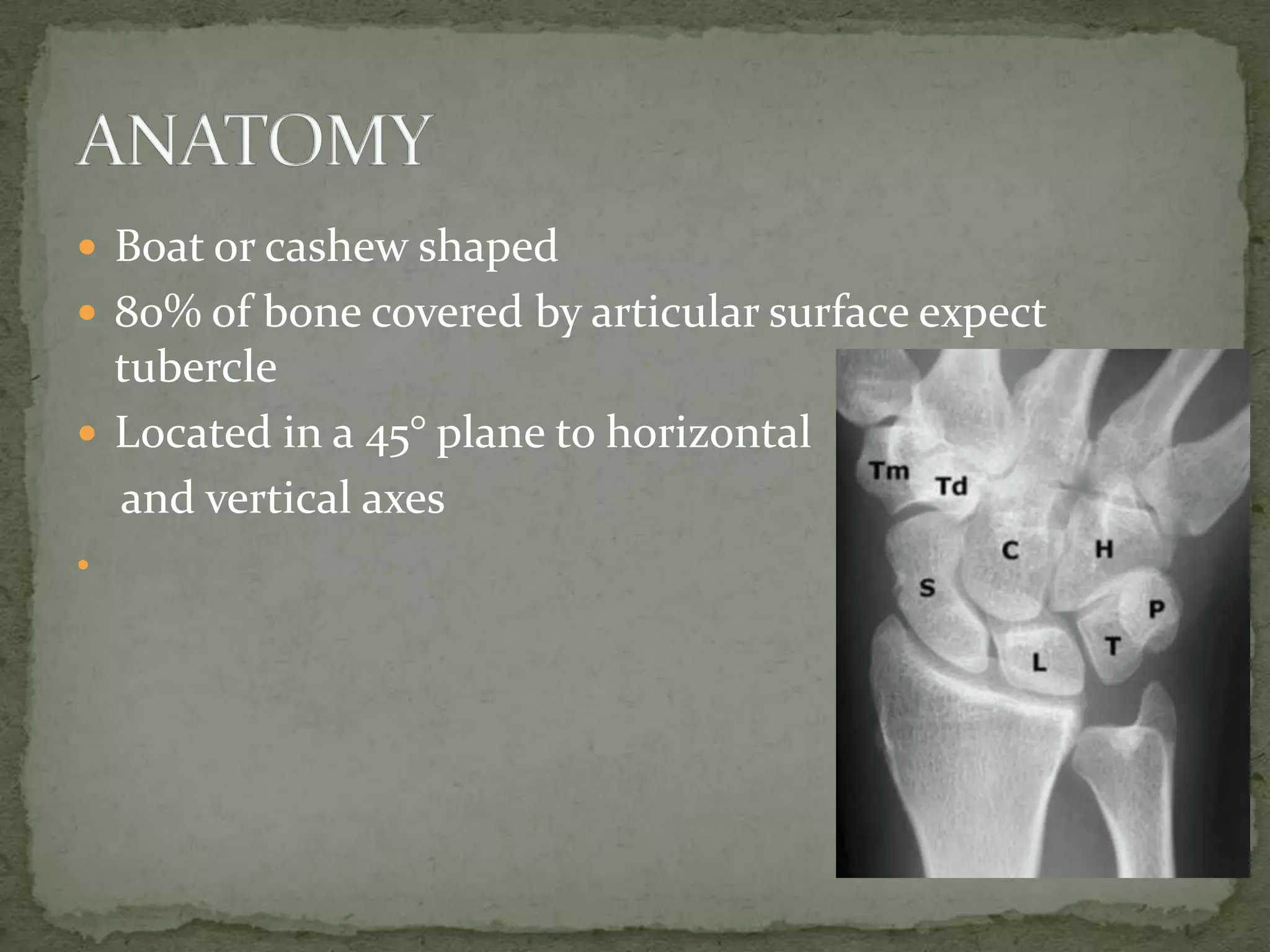
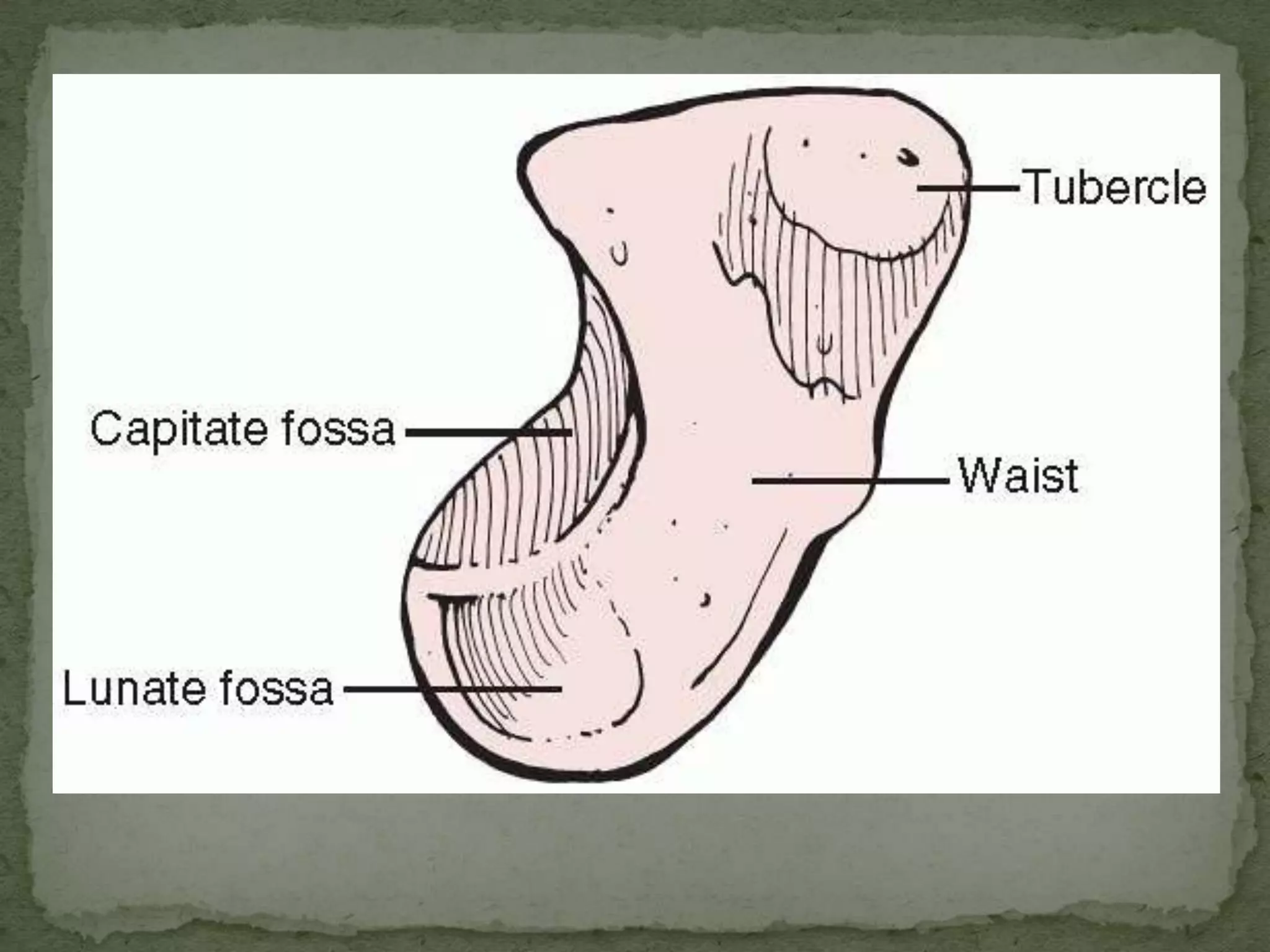
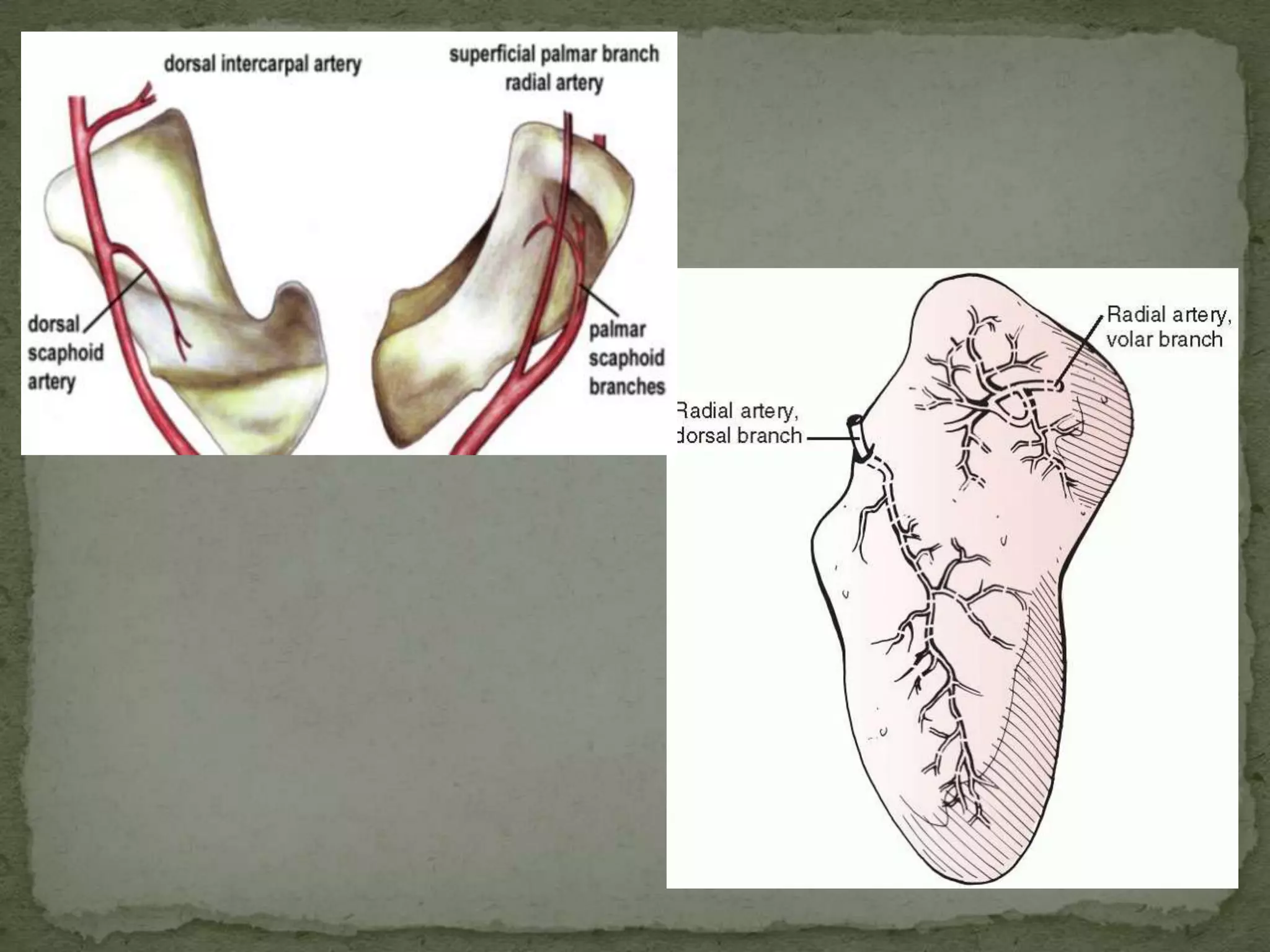
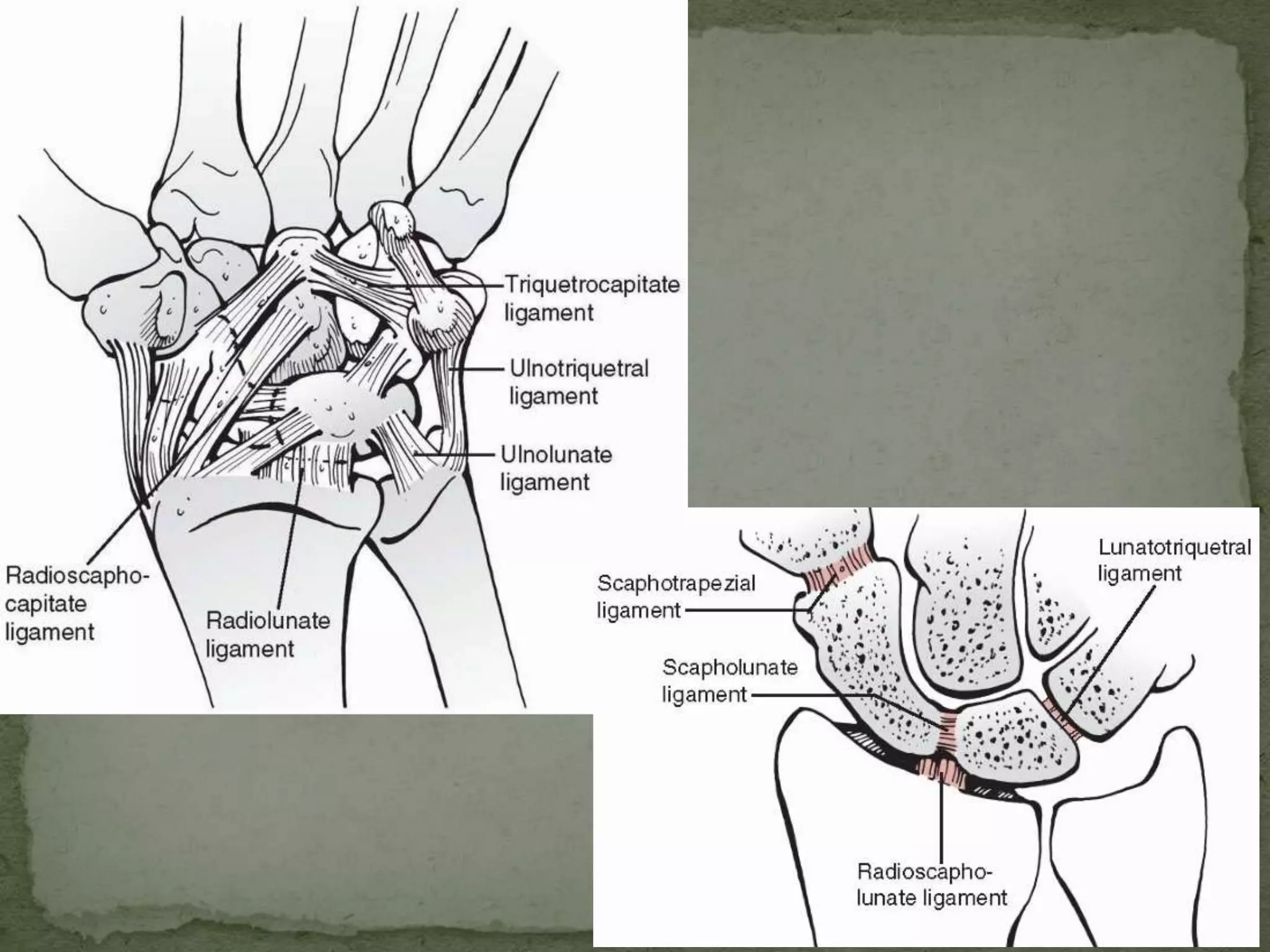
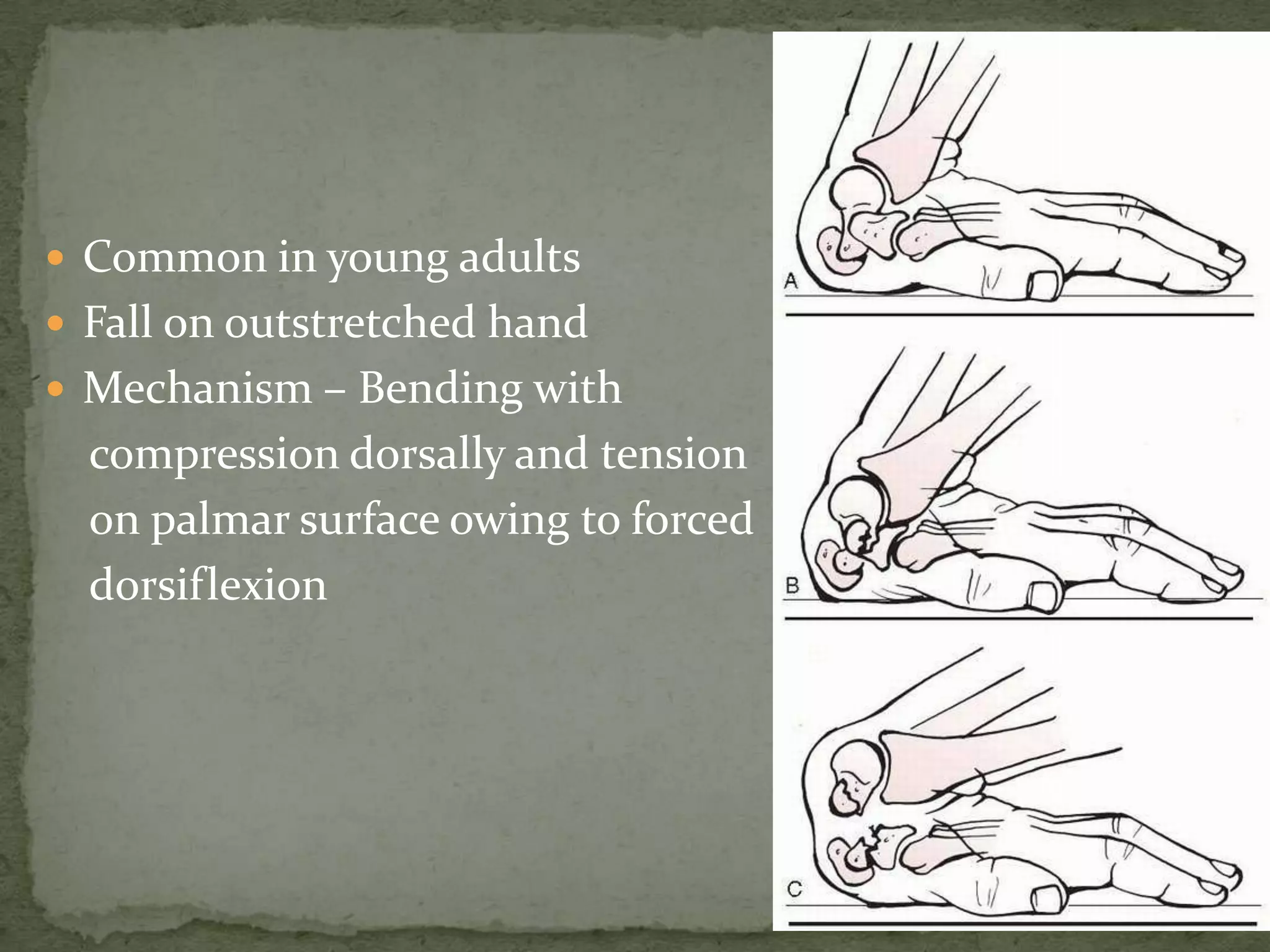
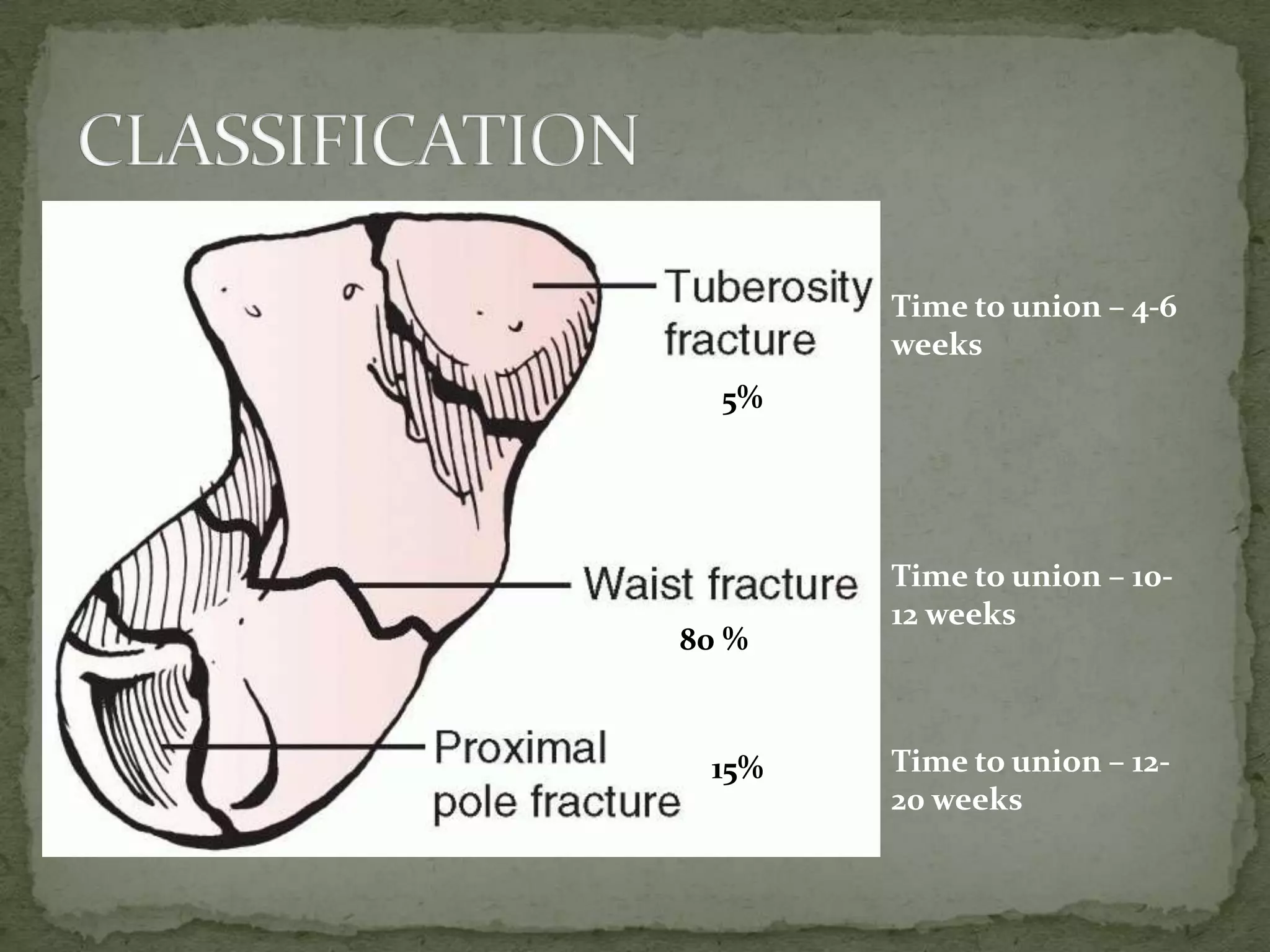
- The scaphoid bone has a boat or cashew shape and accounts for 70% of carpal fractures.
- Scaphoid fractures are commonly caused by a fall on an outstretched hand and result from forced dorsiflexion.
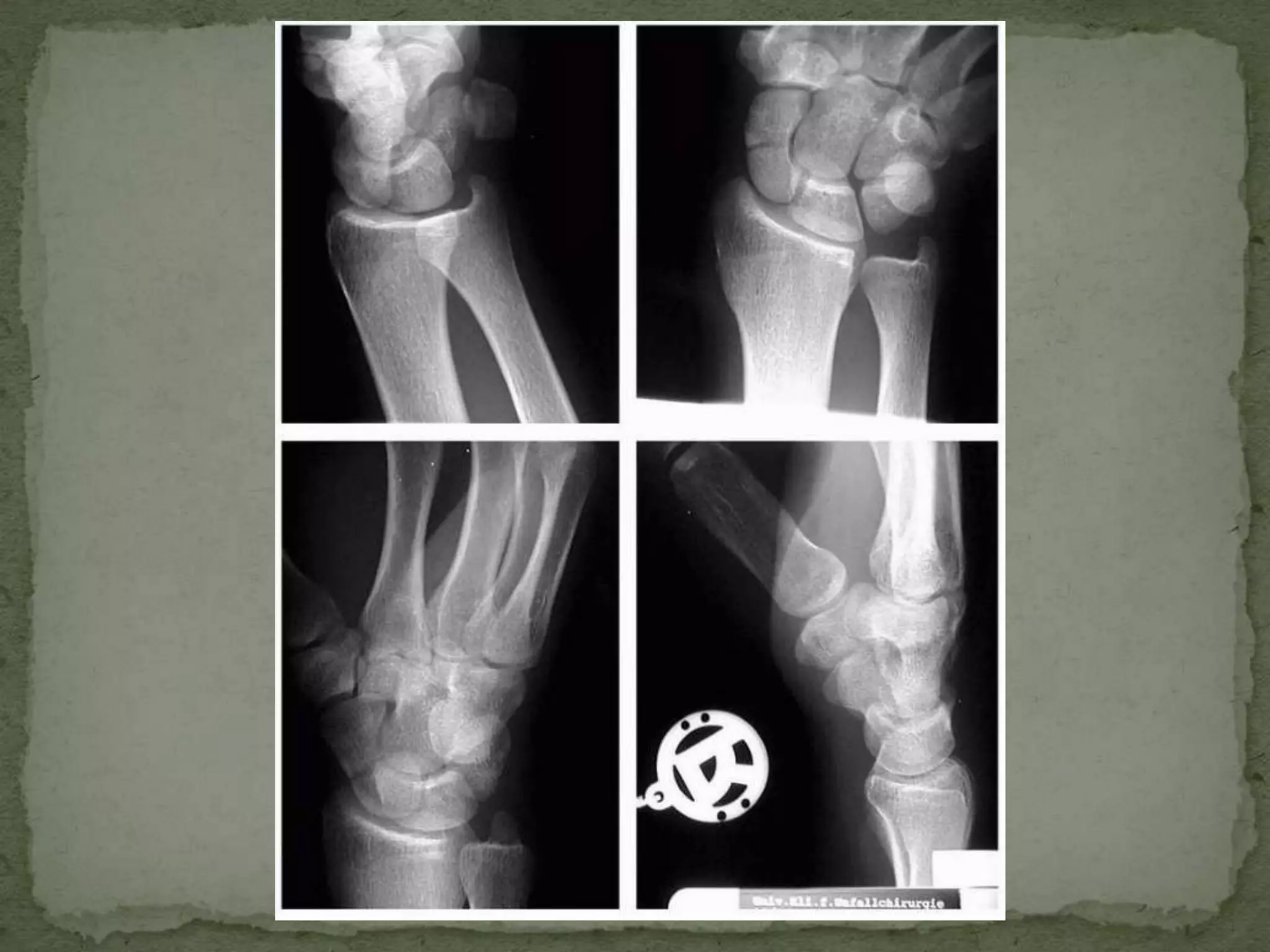
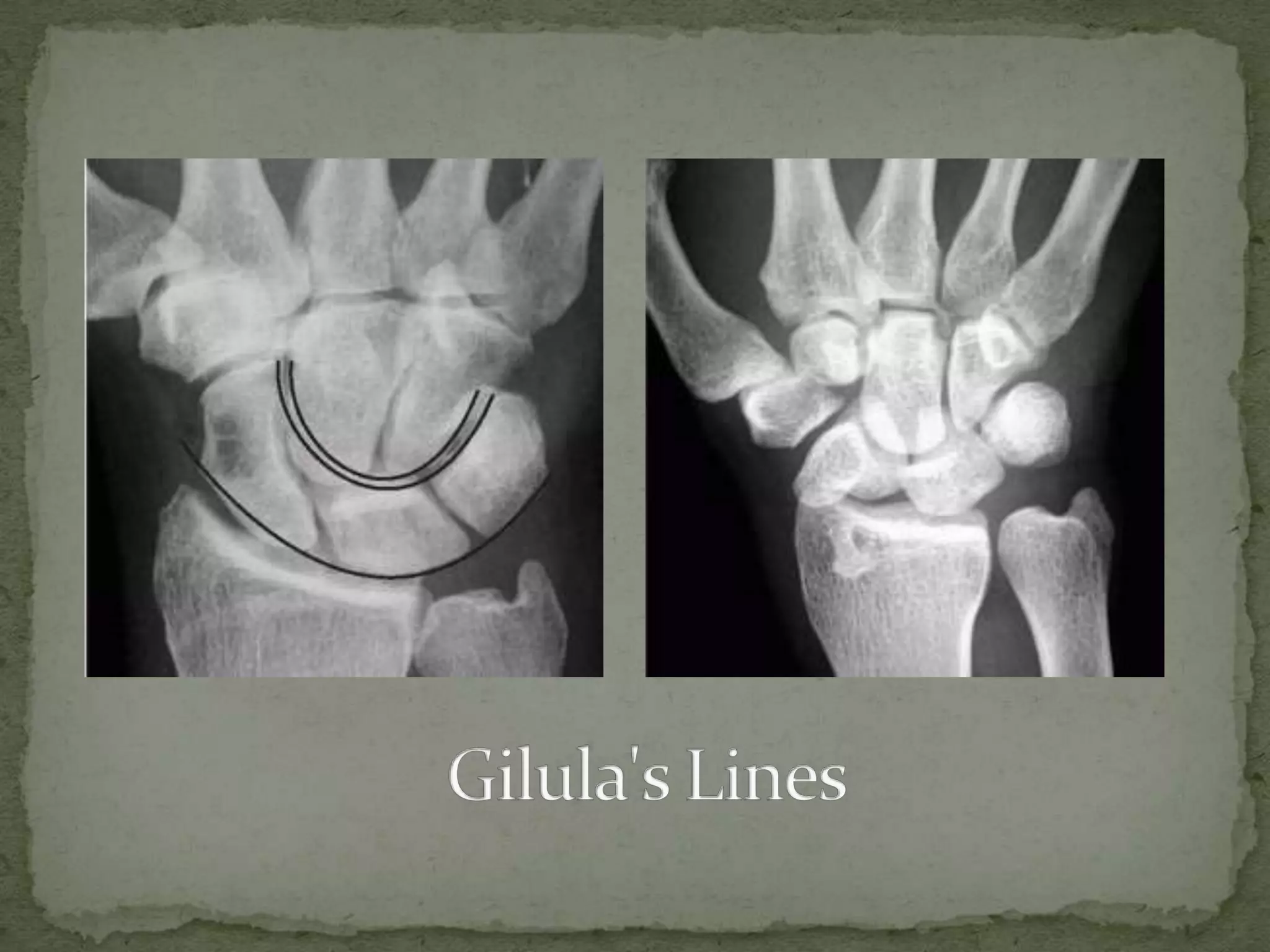
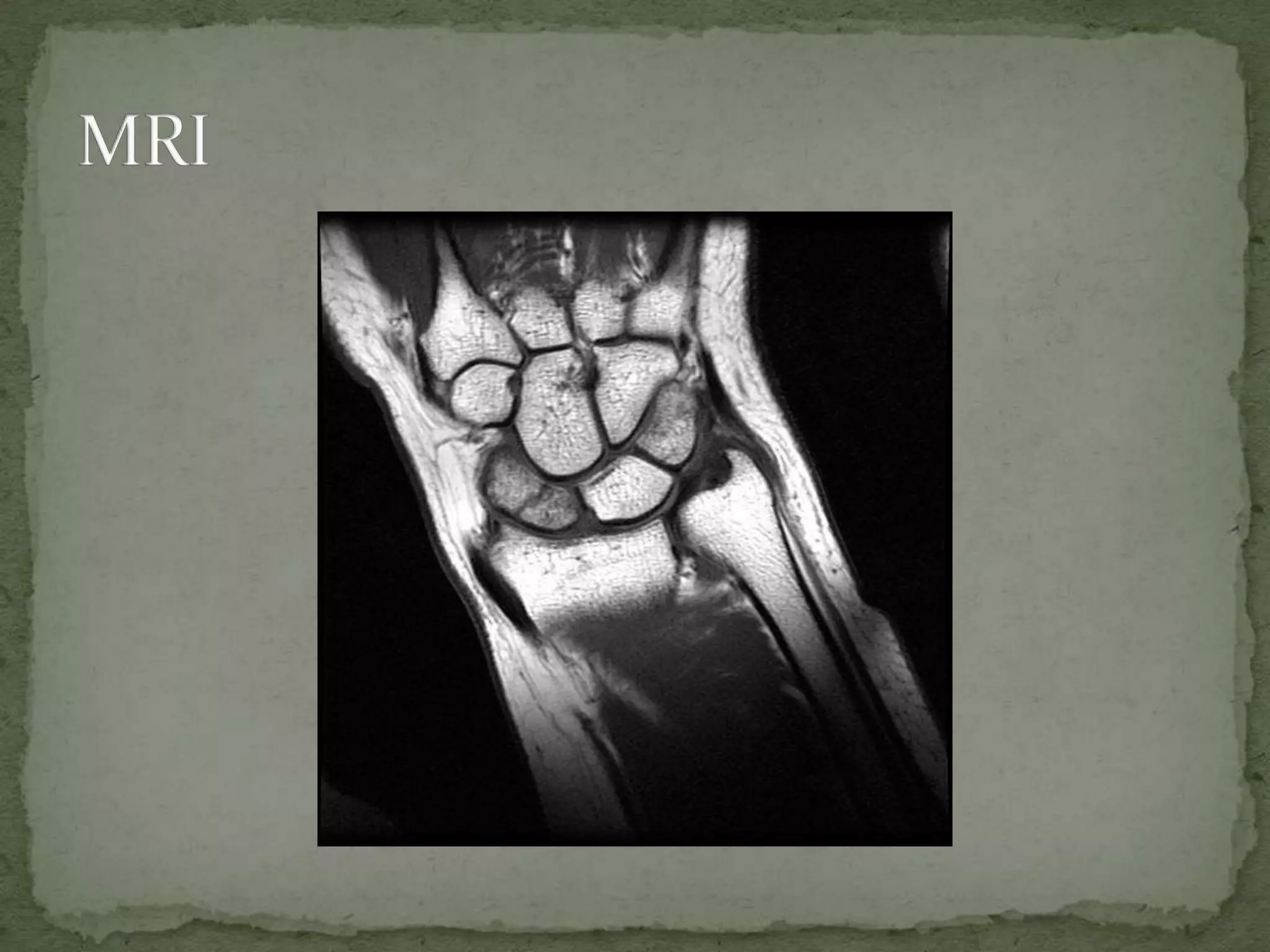
- Diagnosis involves history, clinical exam, and imaging like X-rays, MRI, or bone scans.
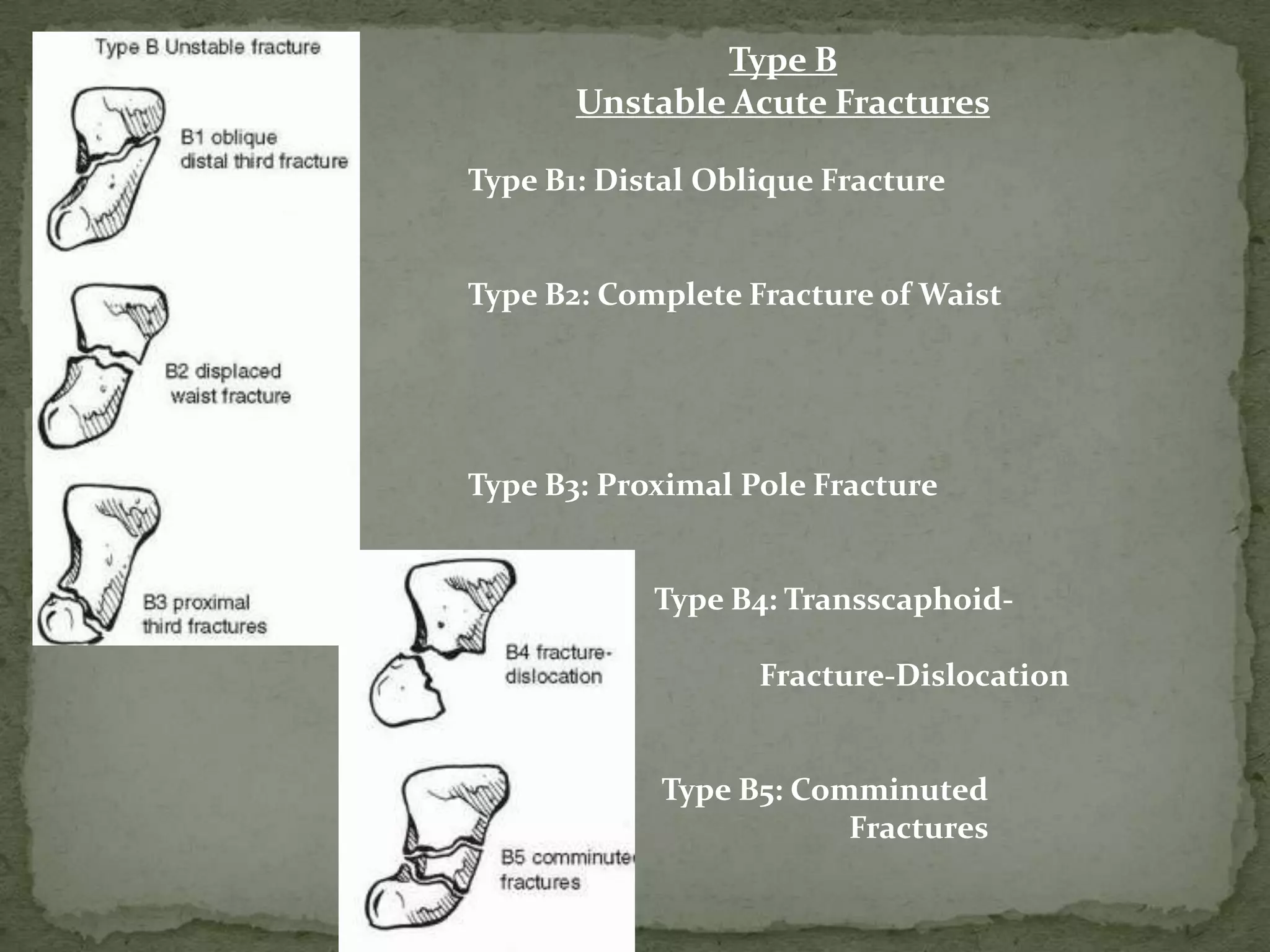
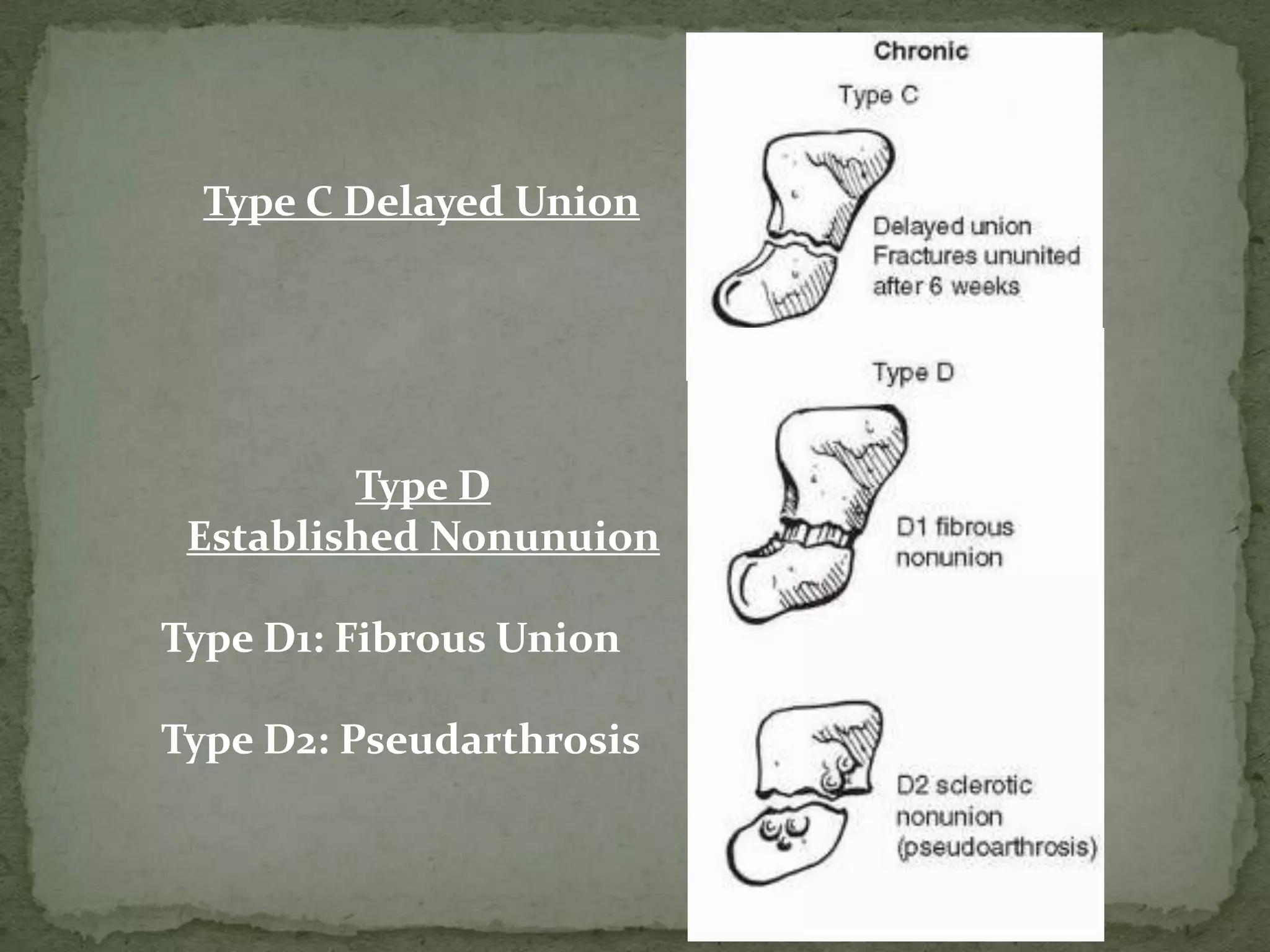
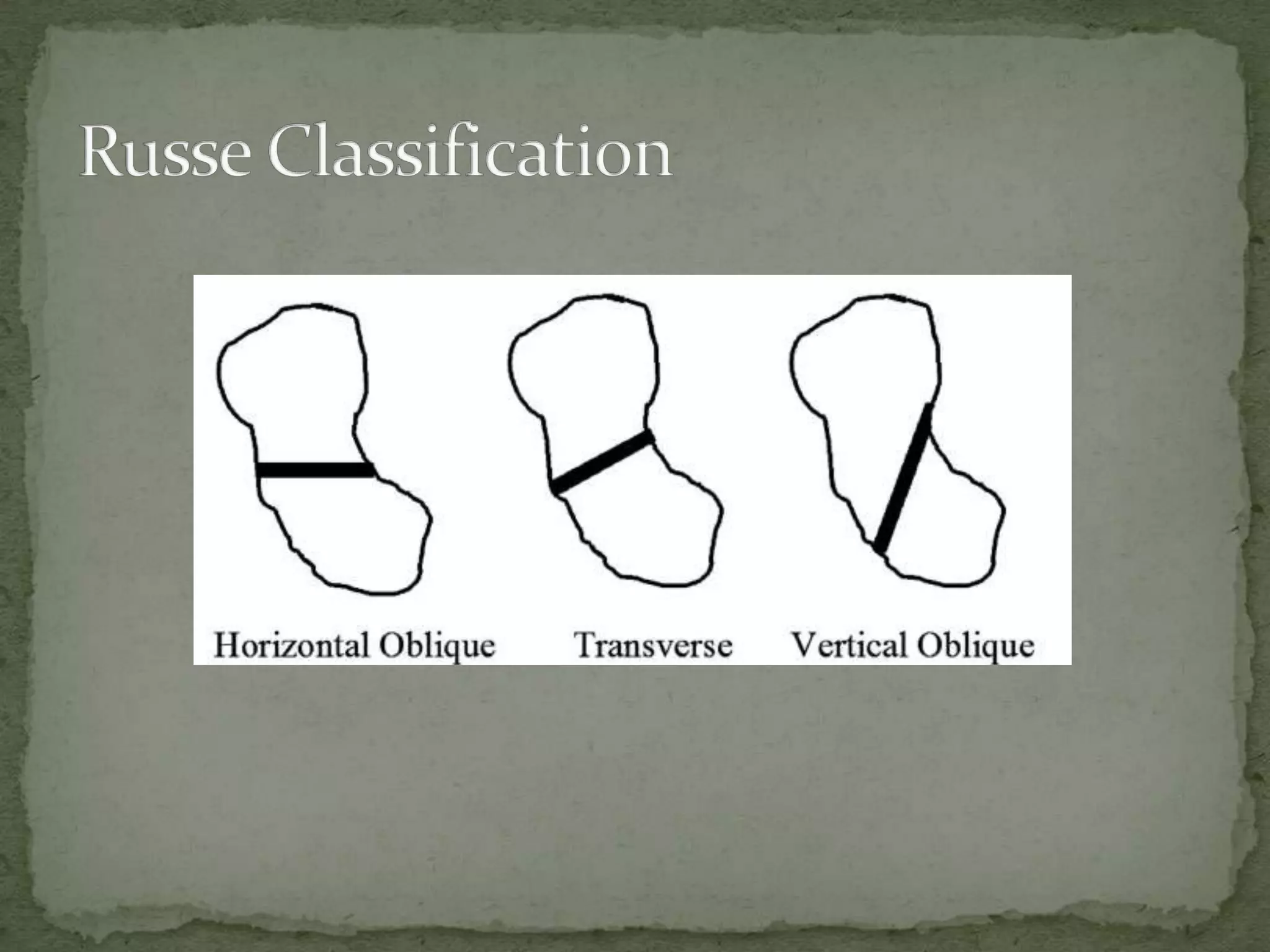
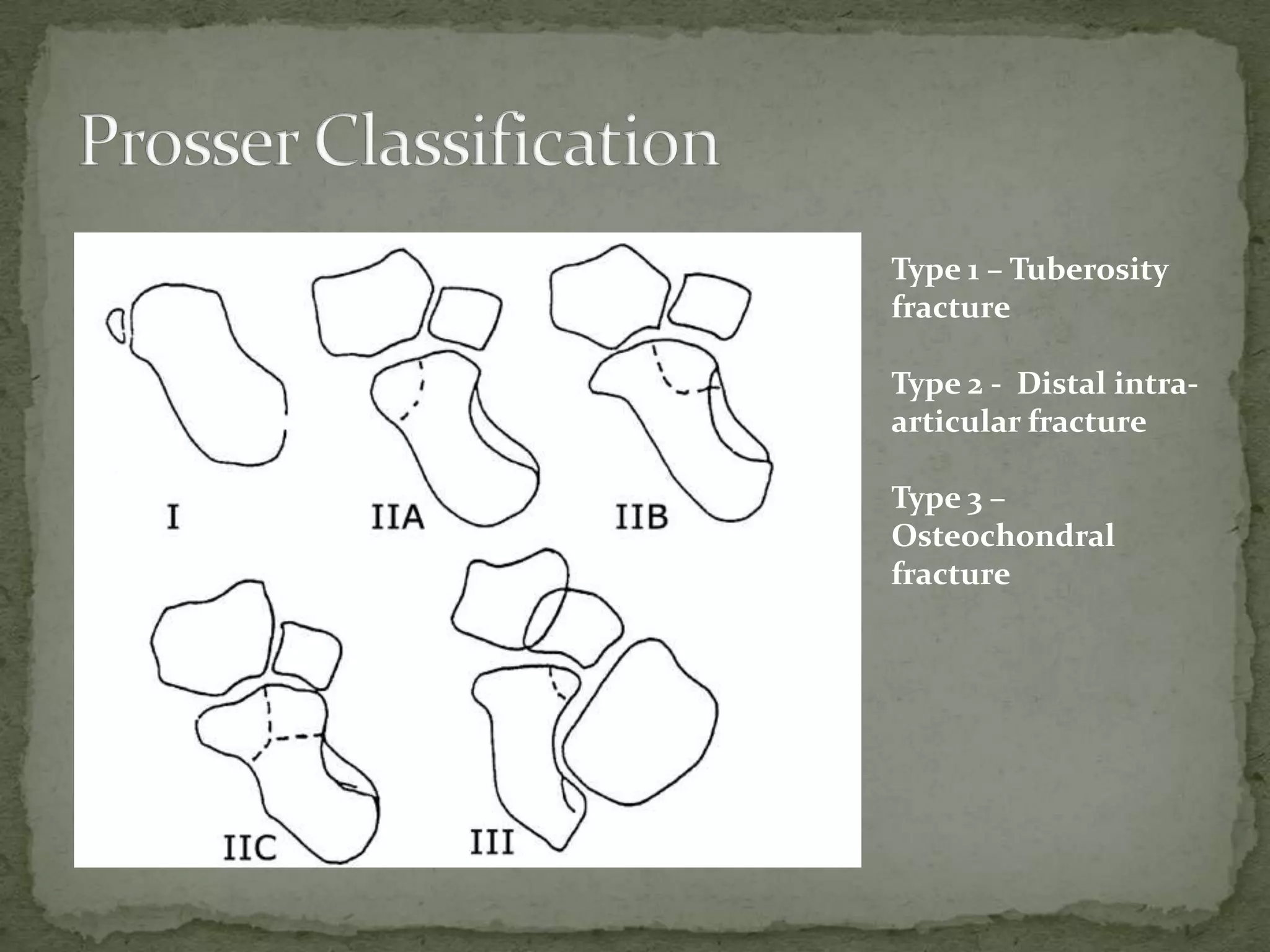
- Fractures are classified by the Herbert and Fisher system into stable or unstable acute fractures, delayed unions, and nonunions.
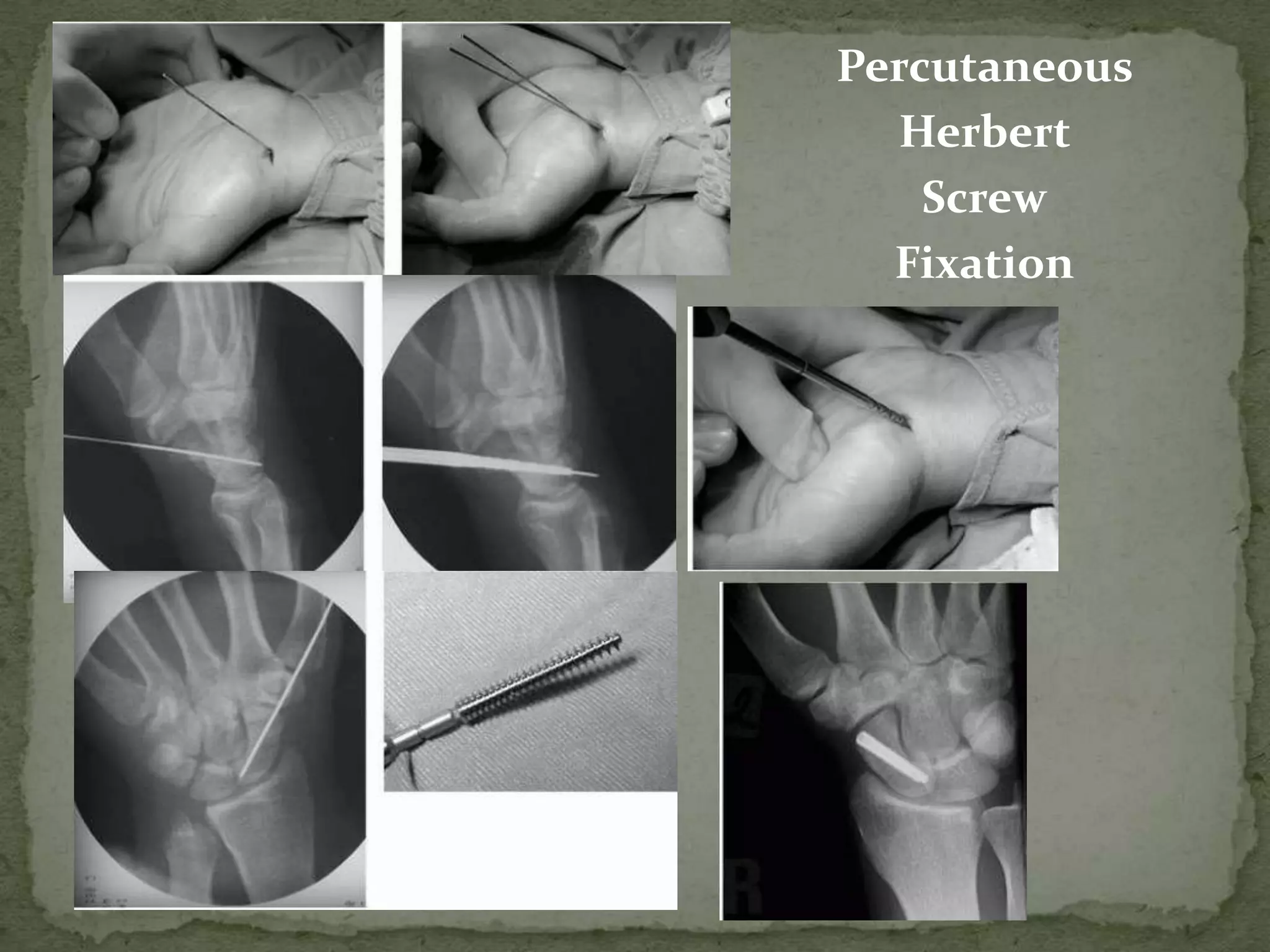
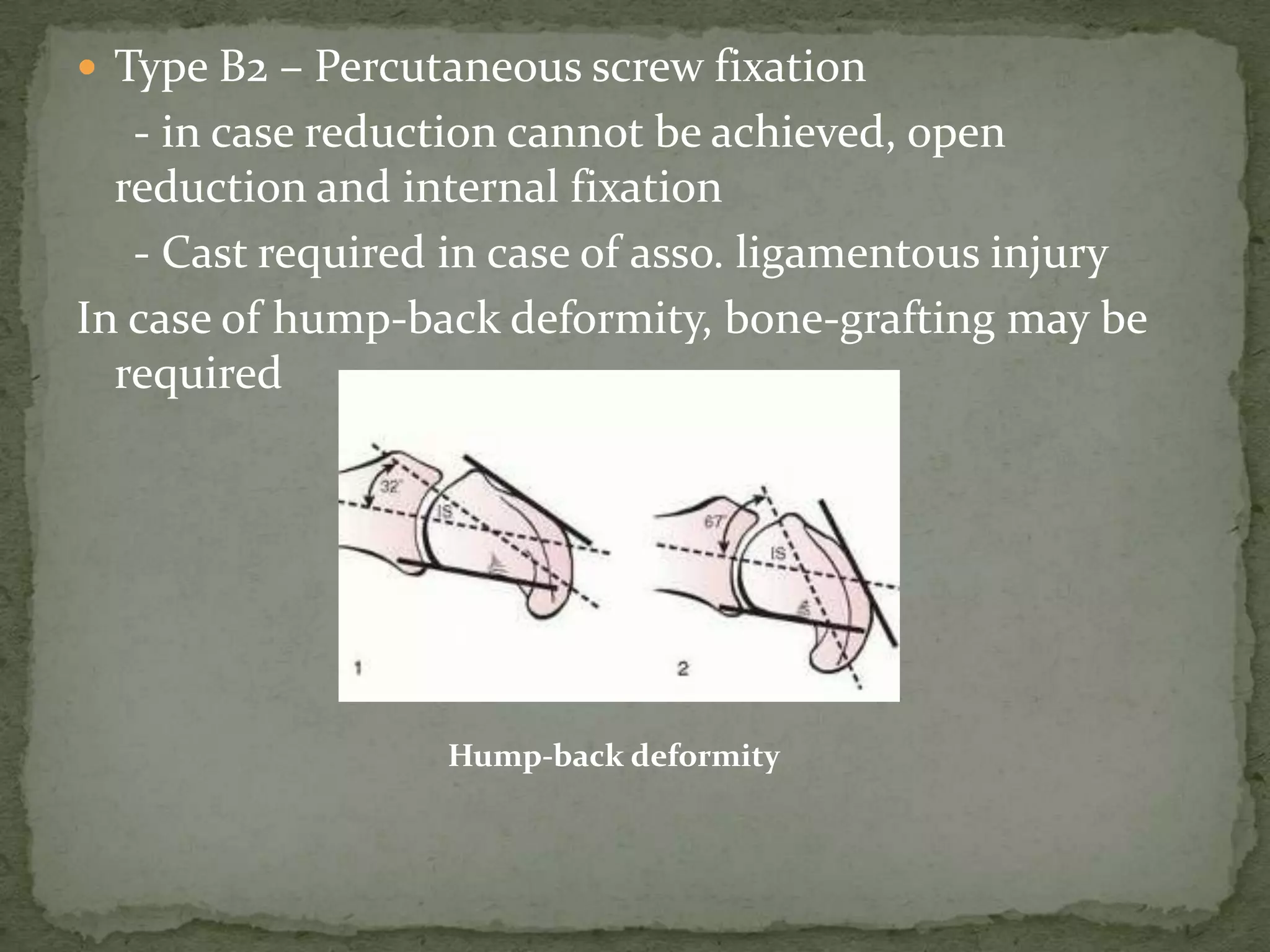
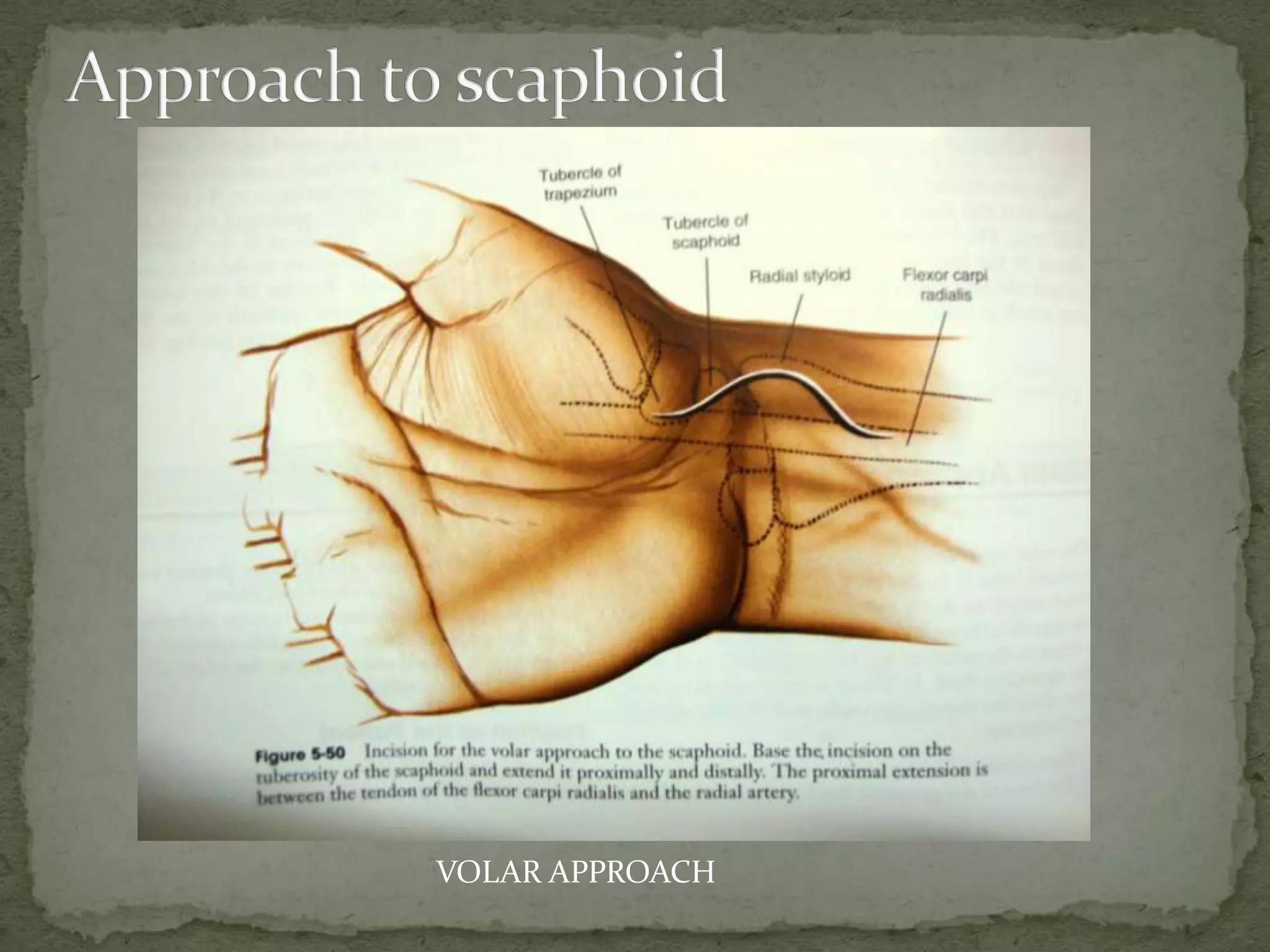
- Treatment depends on the type but may include casting