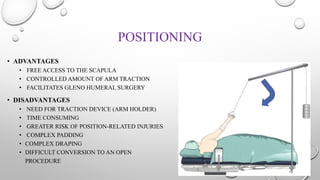
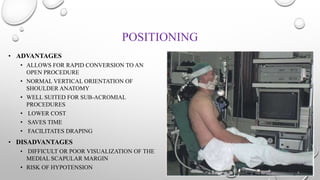
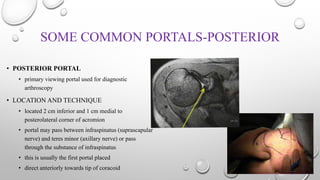
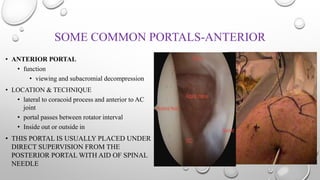
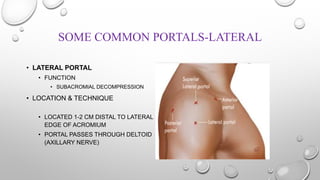
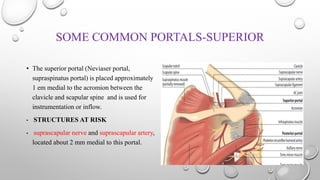
The document outlines the setup, positioning, and portal techniques for shoulder arthroscopy, highlighting its historical developments and various therapeutic indications. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different positioning methods and portals used during surgery, as well as potential complications associated with each approach. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of documentation and visualization techniques for pre and post-operative assessment.