Embed presentation
Downloaded 130 times








The document discusses the epiphysis, which is one of the three parts of a long bone. It develops through enchondral ossification from secondary ossification centers. Lesions can occur at the epiphysis, including tumors and infections. Injuries to the epiphyseal plate in children are classified using the Salter-Harris system from Type I to V based on the fracture line. Rare types also exist. The epiphysis is an important part of long bone anatomy and development in the body.















Introduction to the epiphysis in long bones.
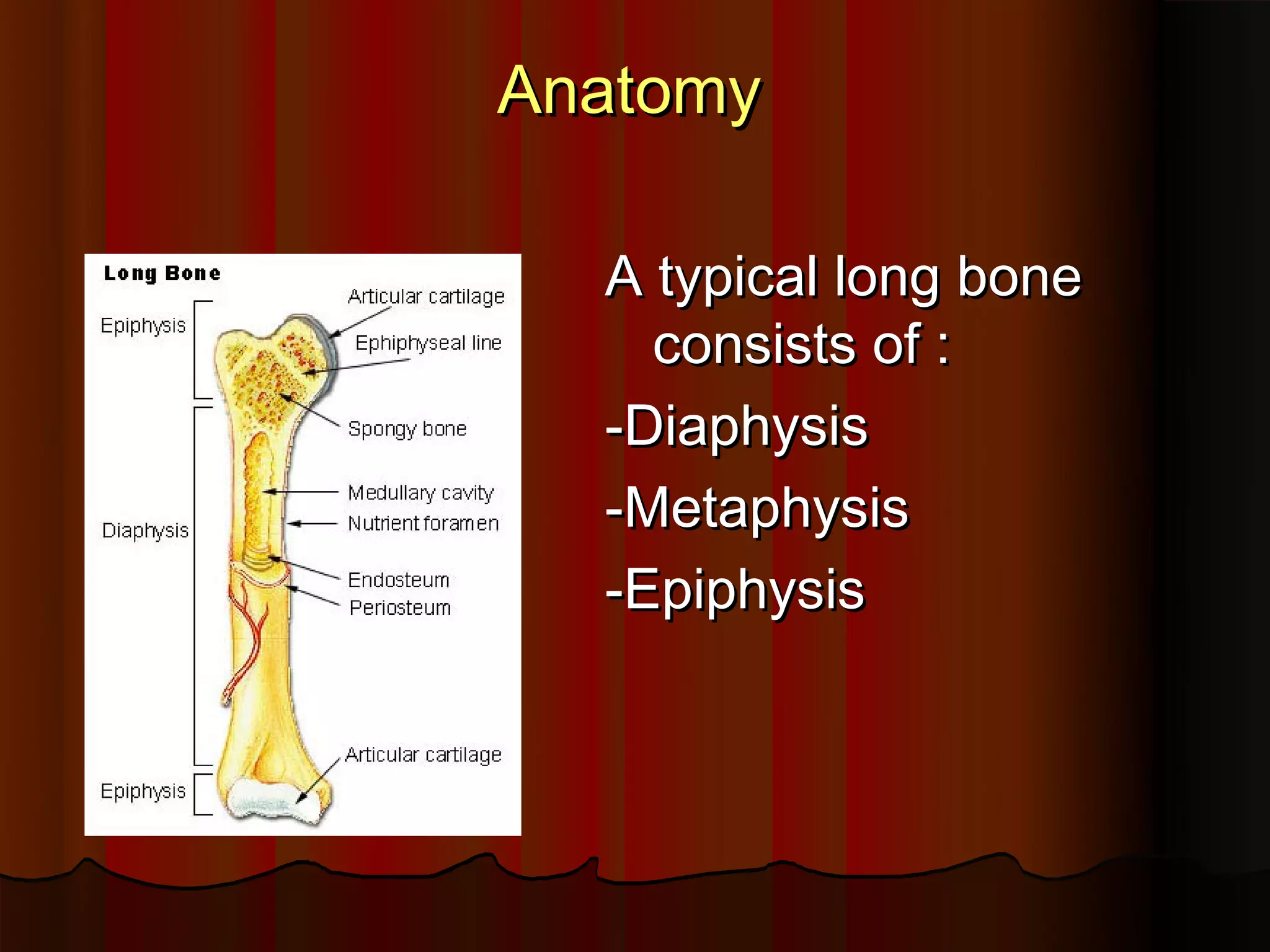
Structure of a typical long bone: Diaphysis, Metaphysis, Epiphysis.
Four types of epiphysis: Pressure, Traction, Atavistic, and Aberrant.
Epiphysis develops from secondary ossification centers via enchondral ossification.
Various lesions impacting the epiphysis: chondroblastoma, osteomyelitis, clear cell chondrosarcoma.
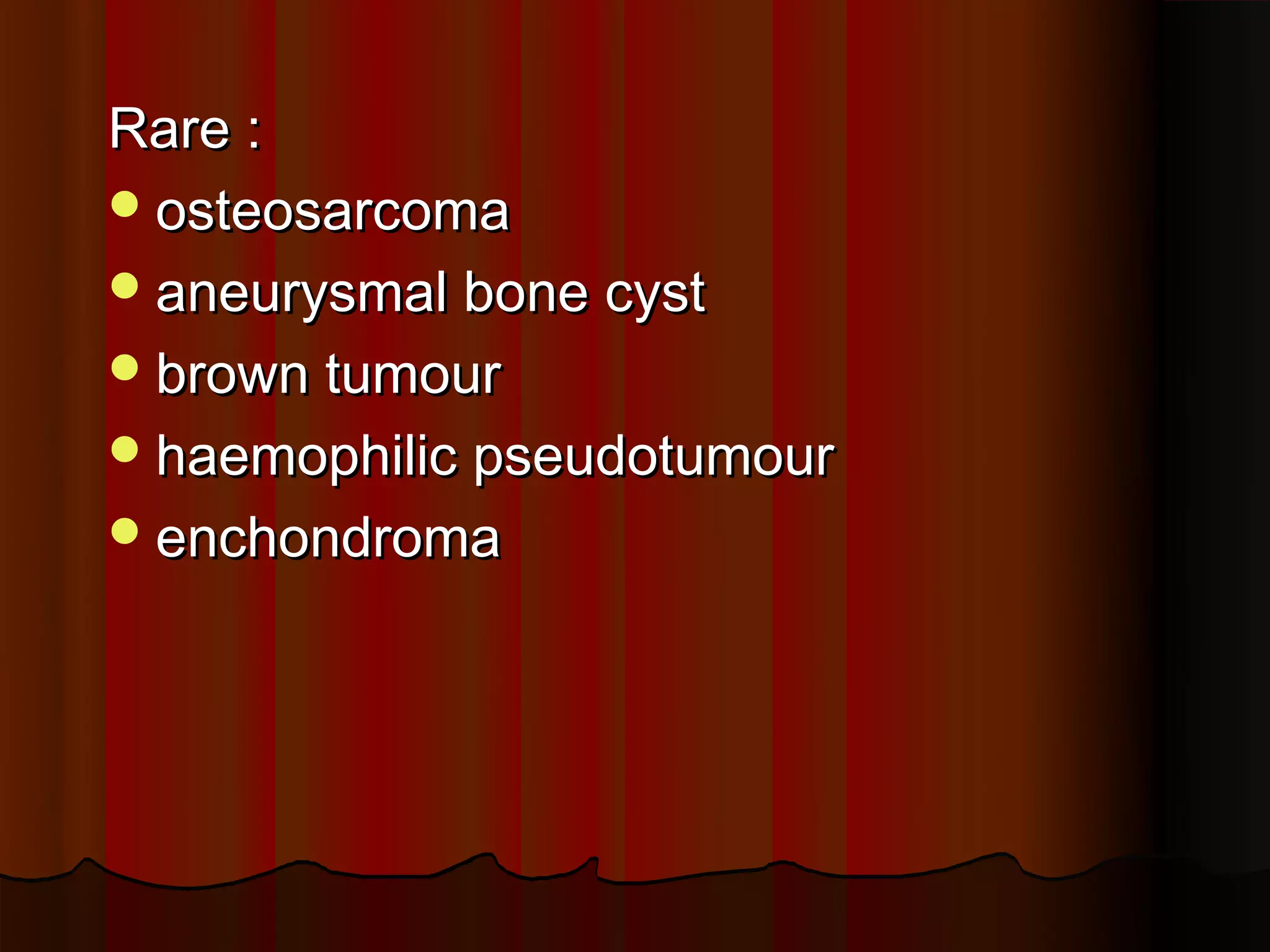
Rare epiphyseal lesions include osteosarcoma, aneurysmal bone cyst, and enchondroma.
Classifications of epiphyseal plate injuries in children, accounting for 15-20% of long bone fractures.
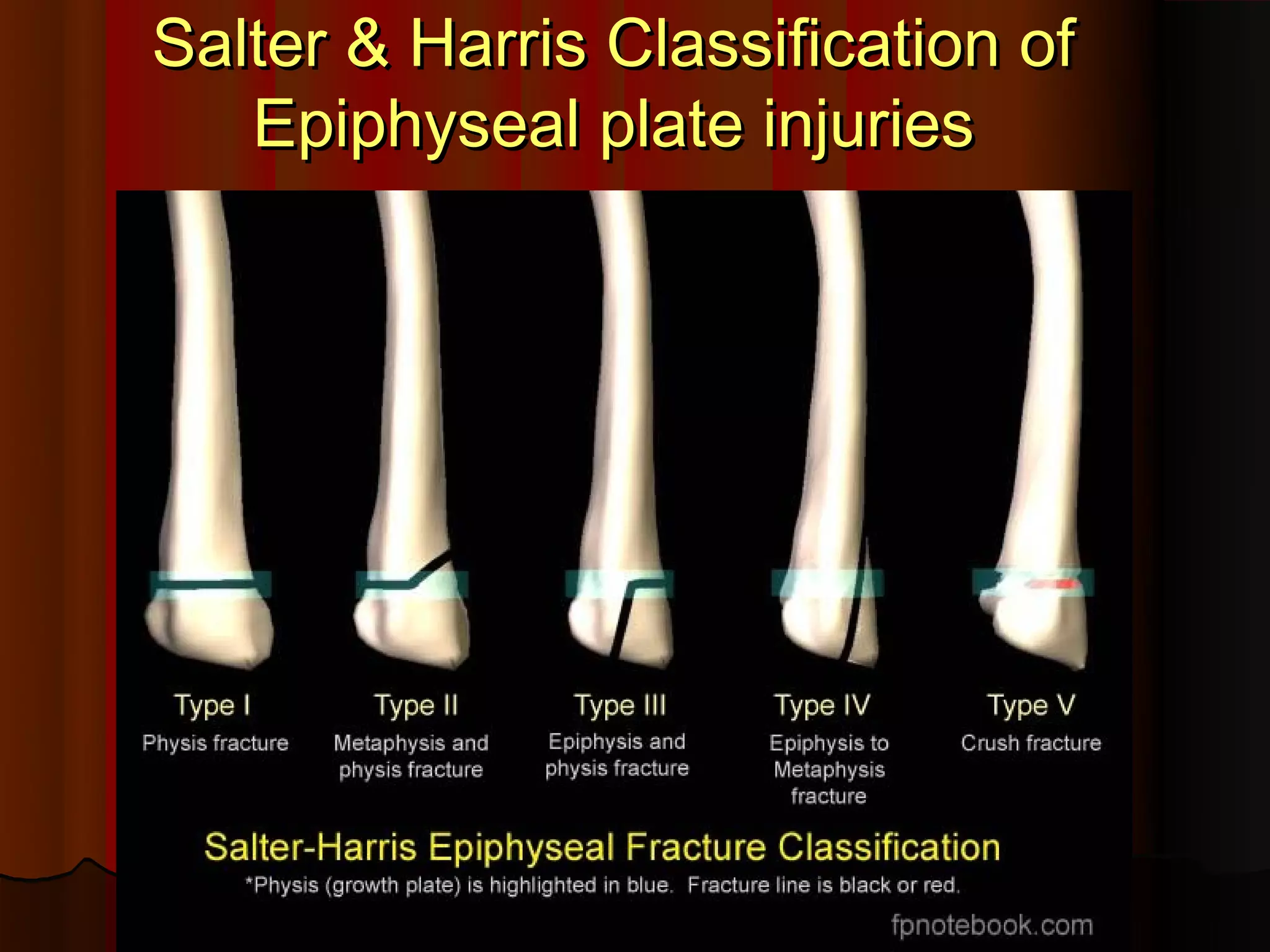
An overview of the Salter-Harris classification for epiphyseal plate injuries.
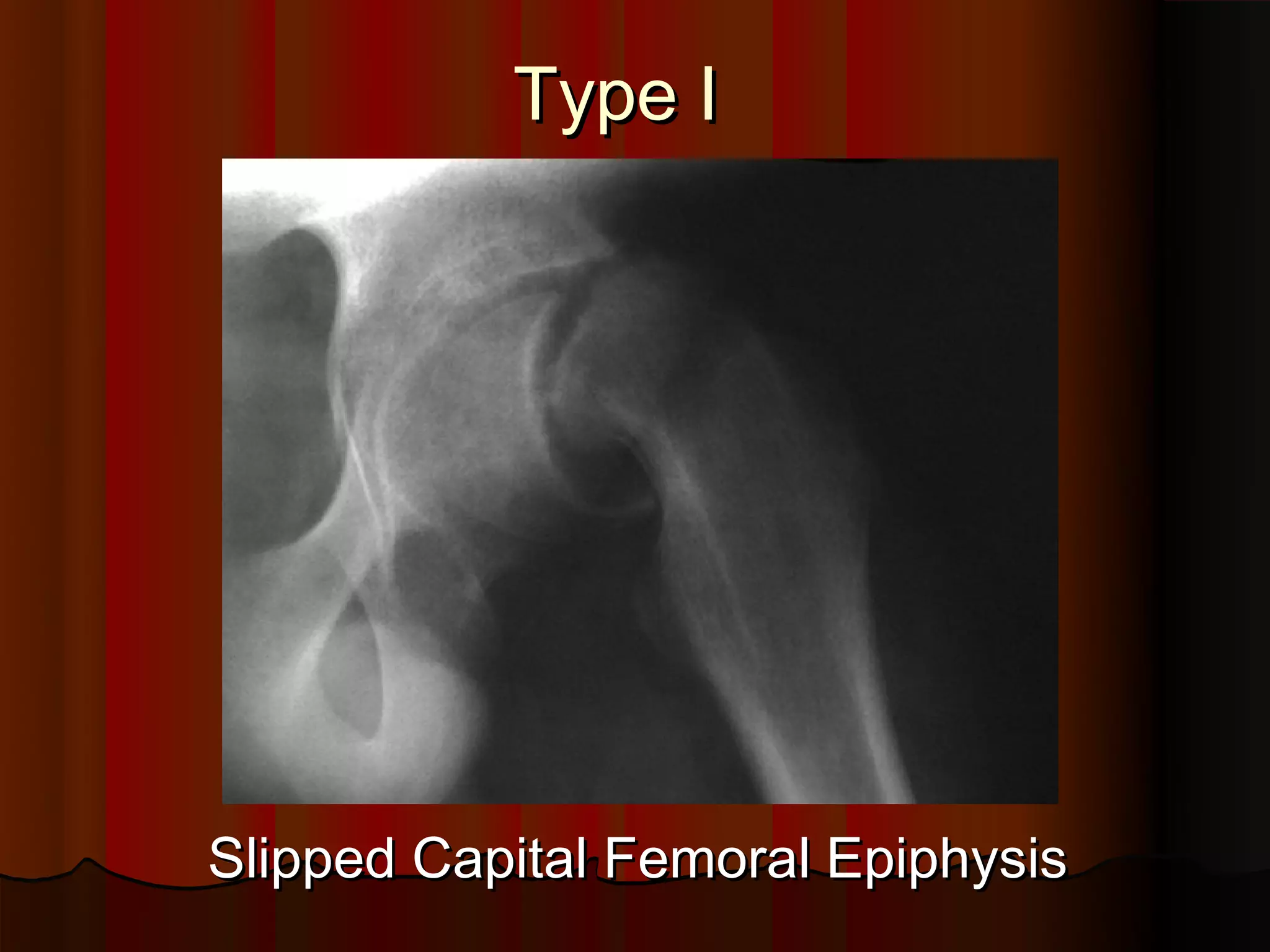
Description of Salter-Harris Type I injury: Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis.
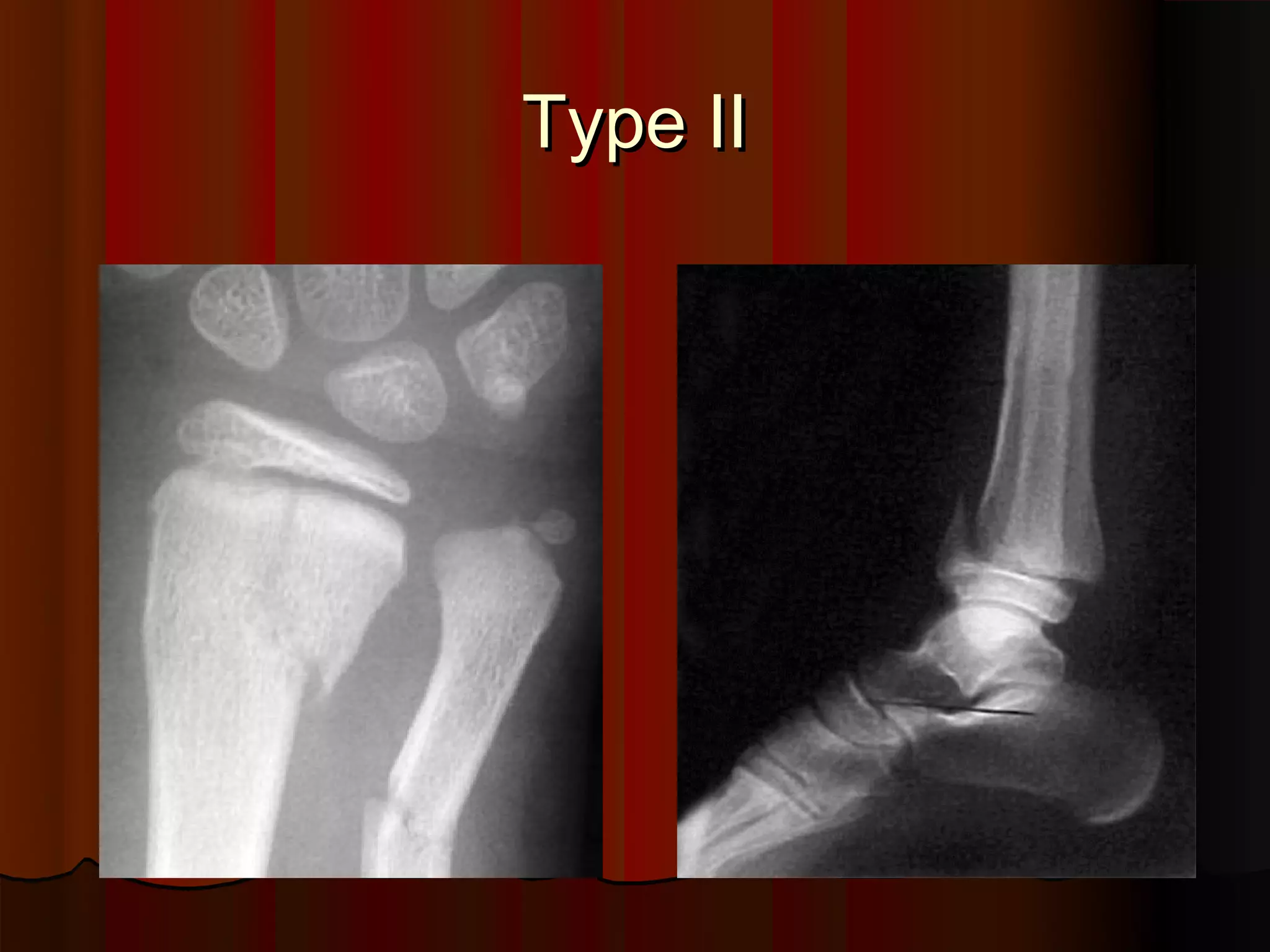
Description of Salter-Harris Type II injury.
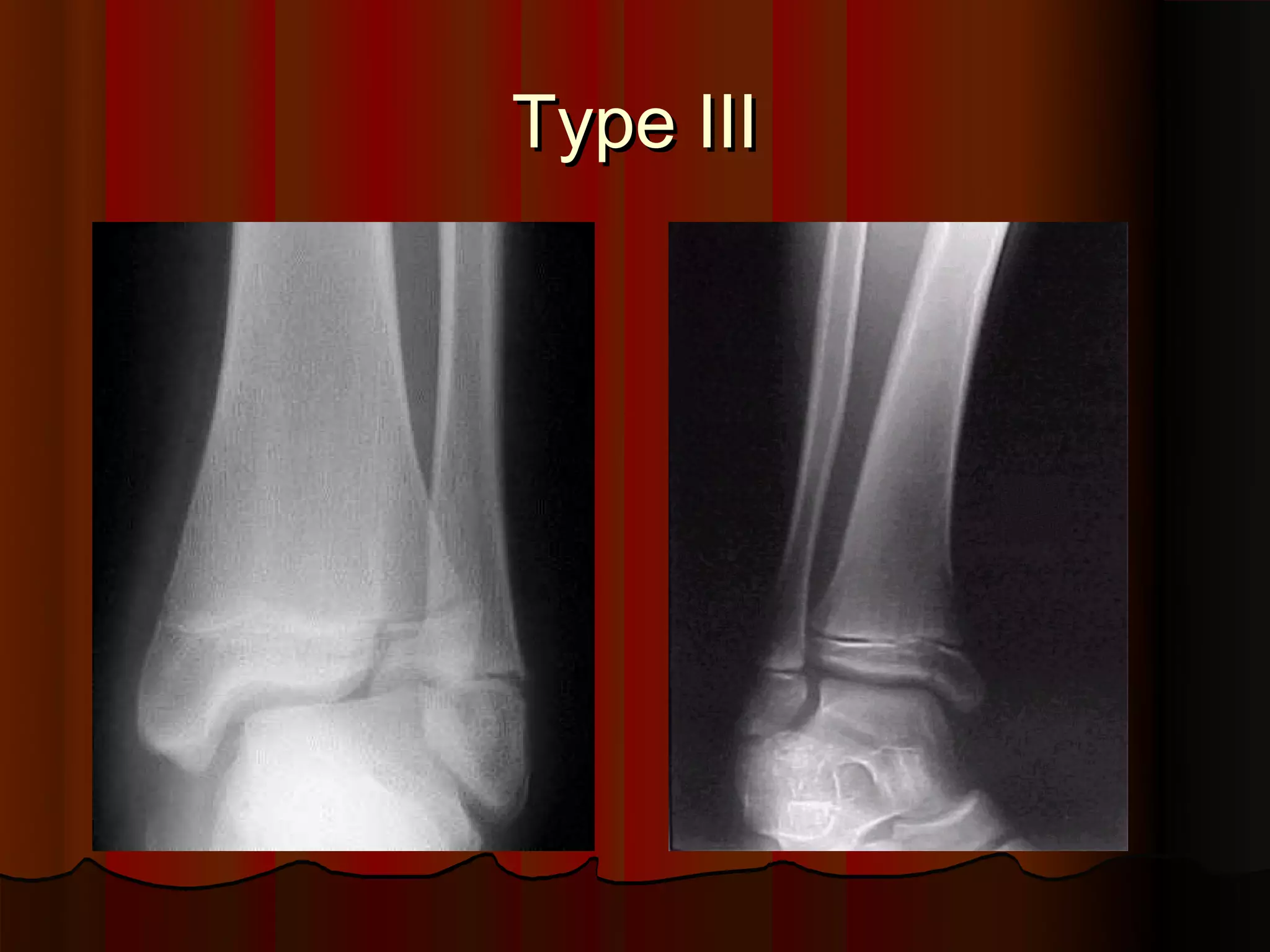
Description of Salter-Harris Type III injury.
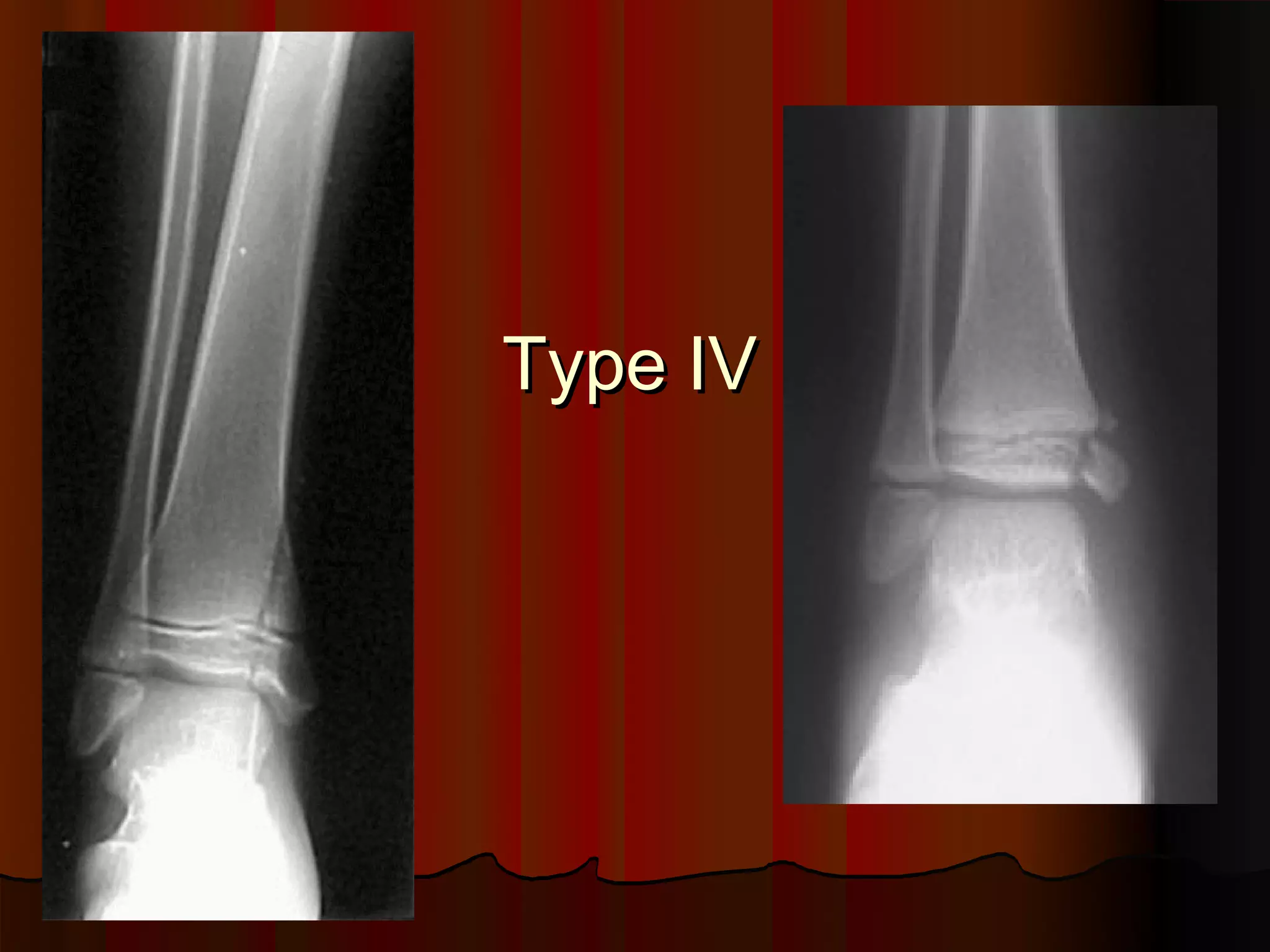
Description of Salter-Harris Type IV injury.
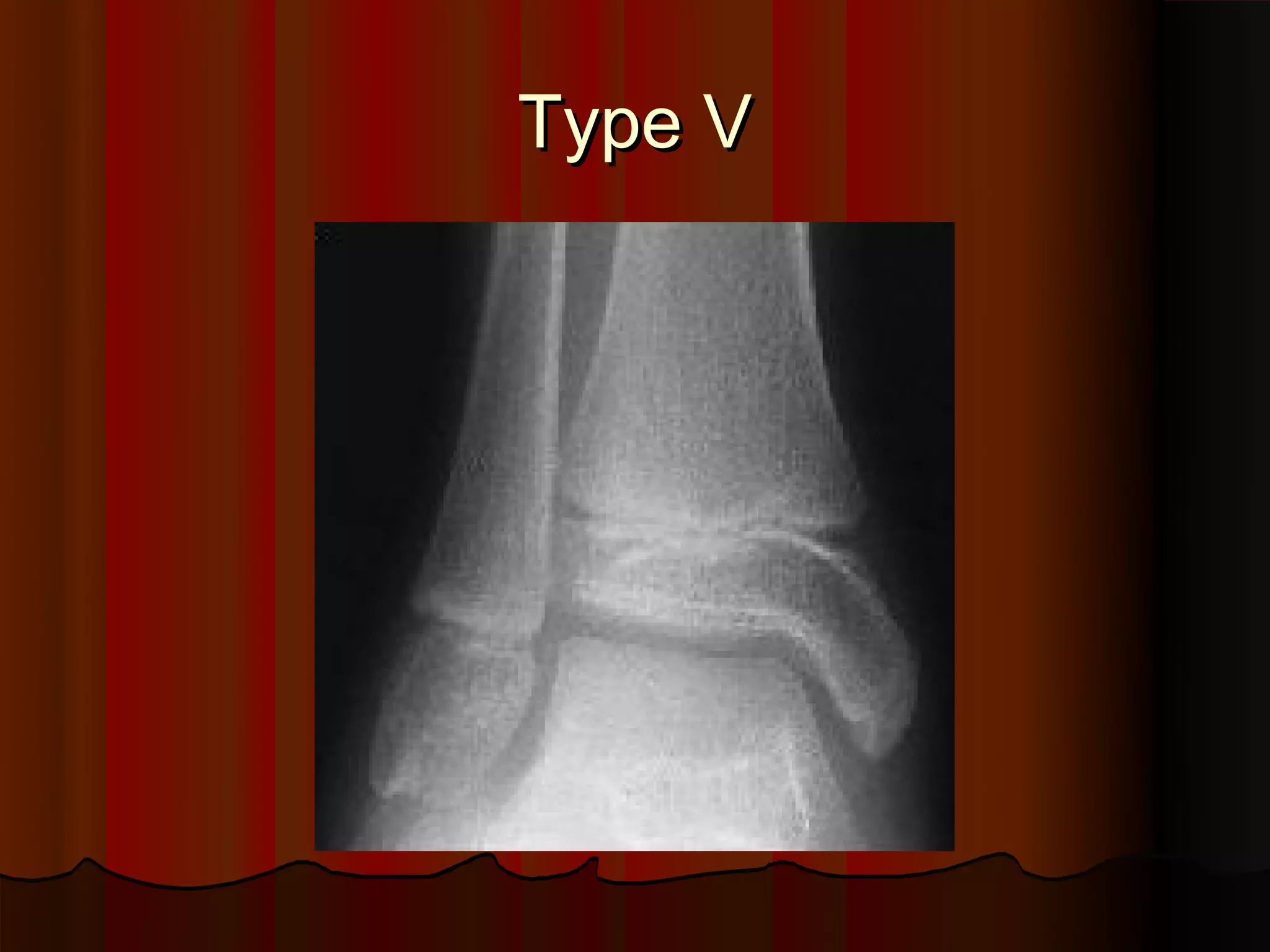
Description of Salter-Harris Type V injury.
Overview of rare fracture types: Type VI to IX, affecting perichondral structures and more.
Ending note or acknowledgment.