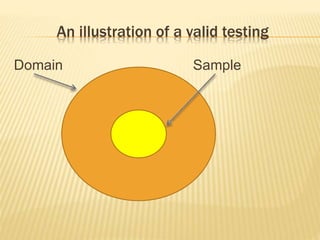
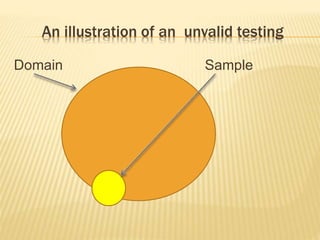
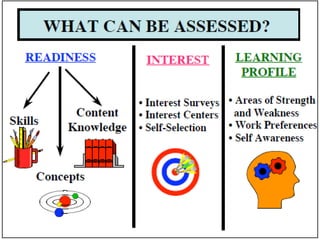
The document outlines the significance and components of diagnostic assessment within the curriculum, including its definition and benefits. It distinguishes between evaluation, measurement, and assessment while providing examples and various assessment tools and types. Additionally, it discusses the objectives and procedures involved in implementing diagnostic assessments and suggests strategies for remedial work to enhance student learning.