A good test should have the following key characteristics:
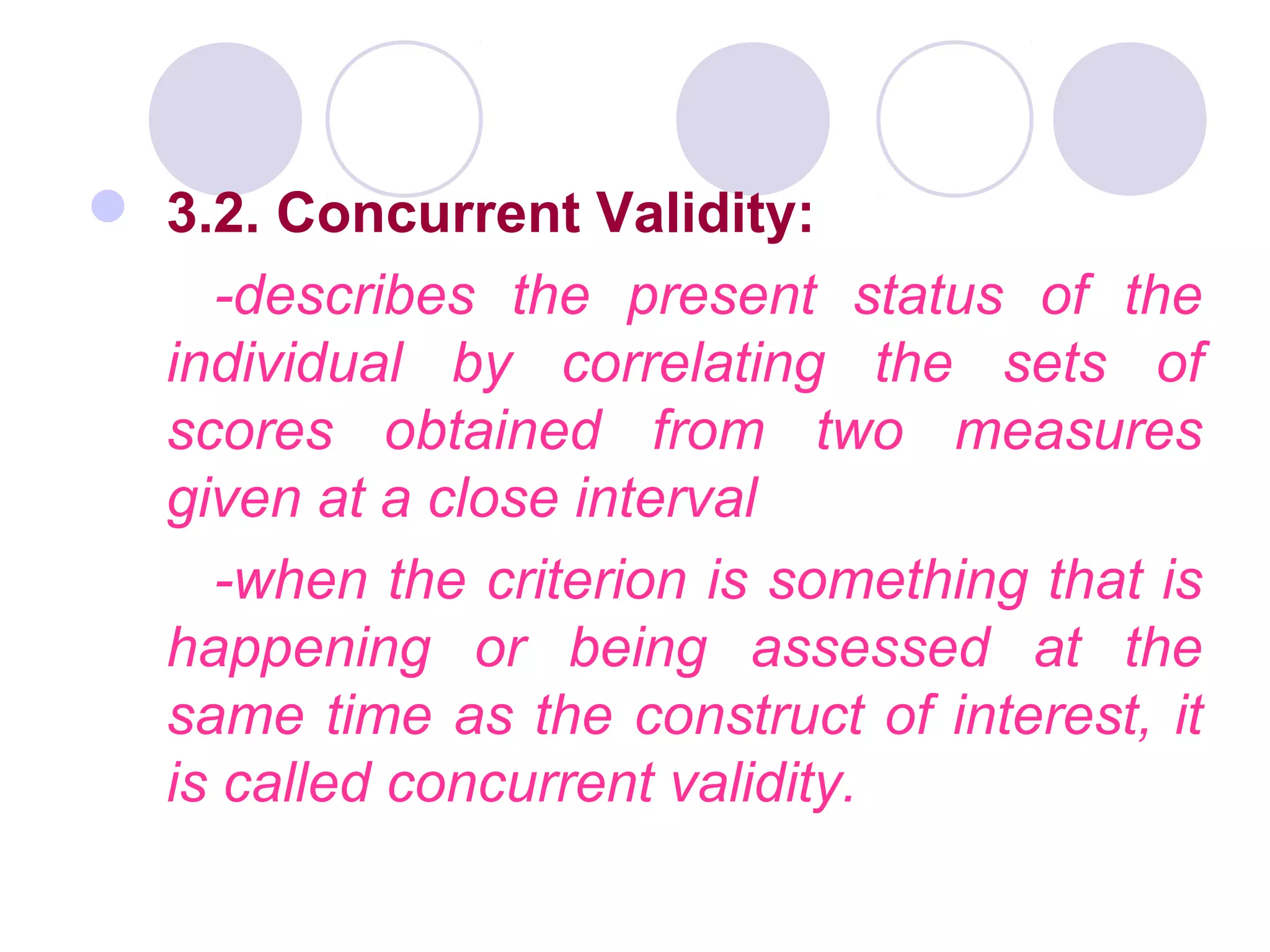
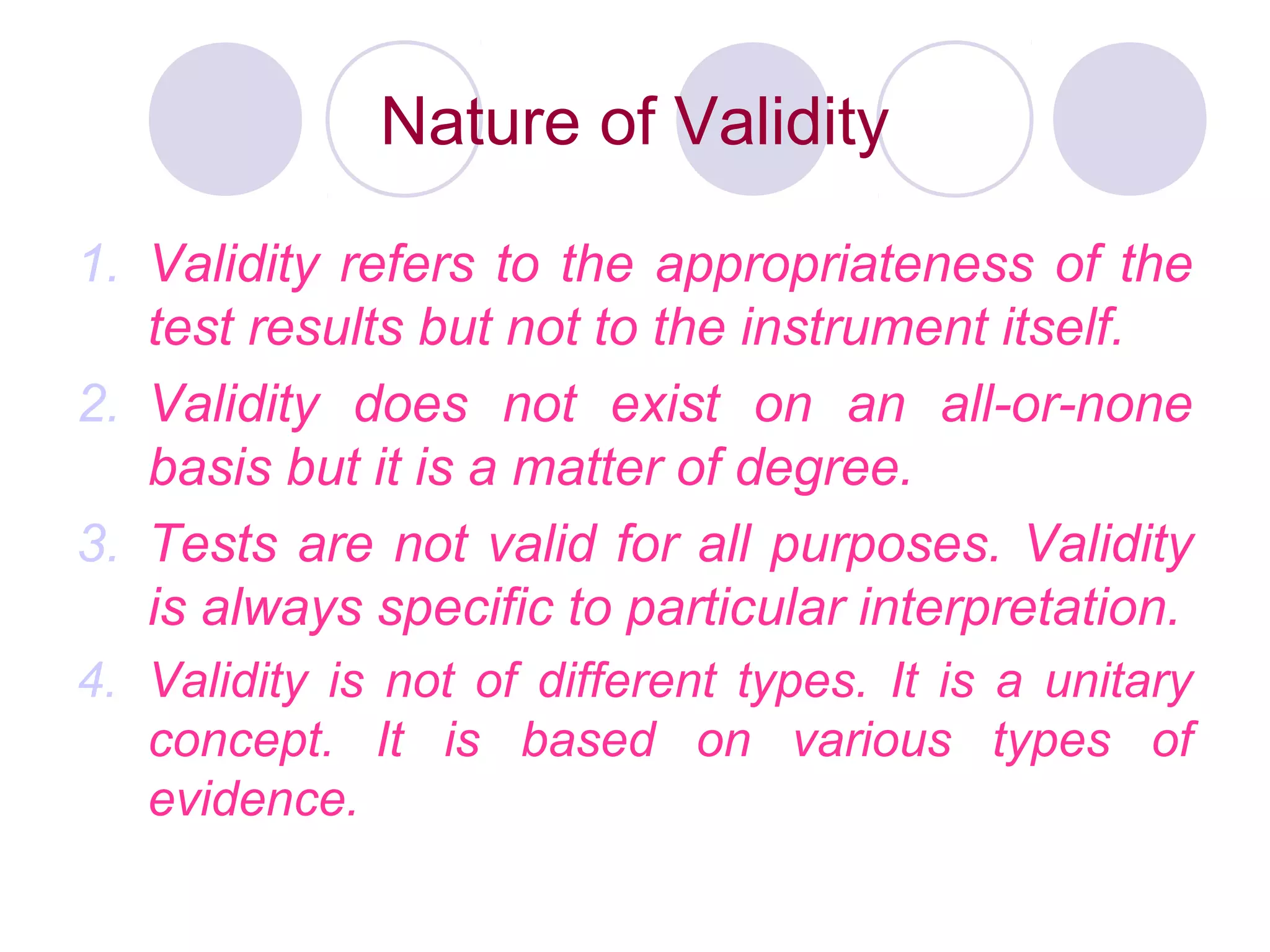
1. It should be a valid instrument that accurately measures what it is intended to measure as evidenced by various types of validity like content validity.
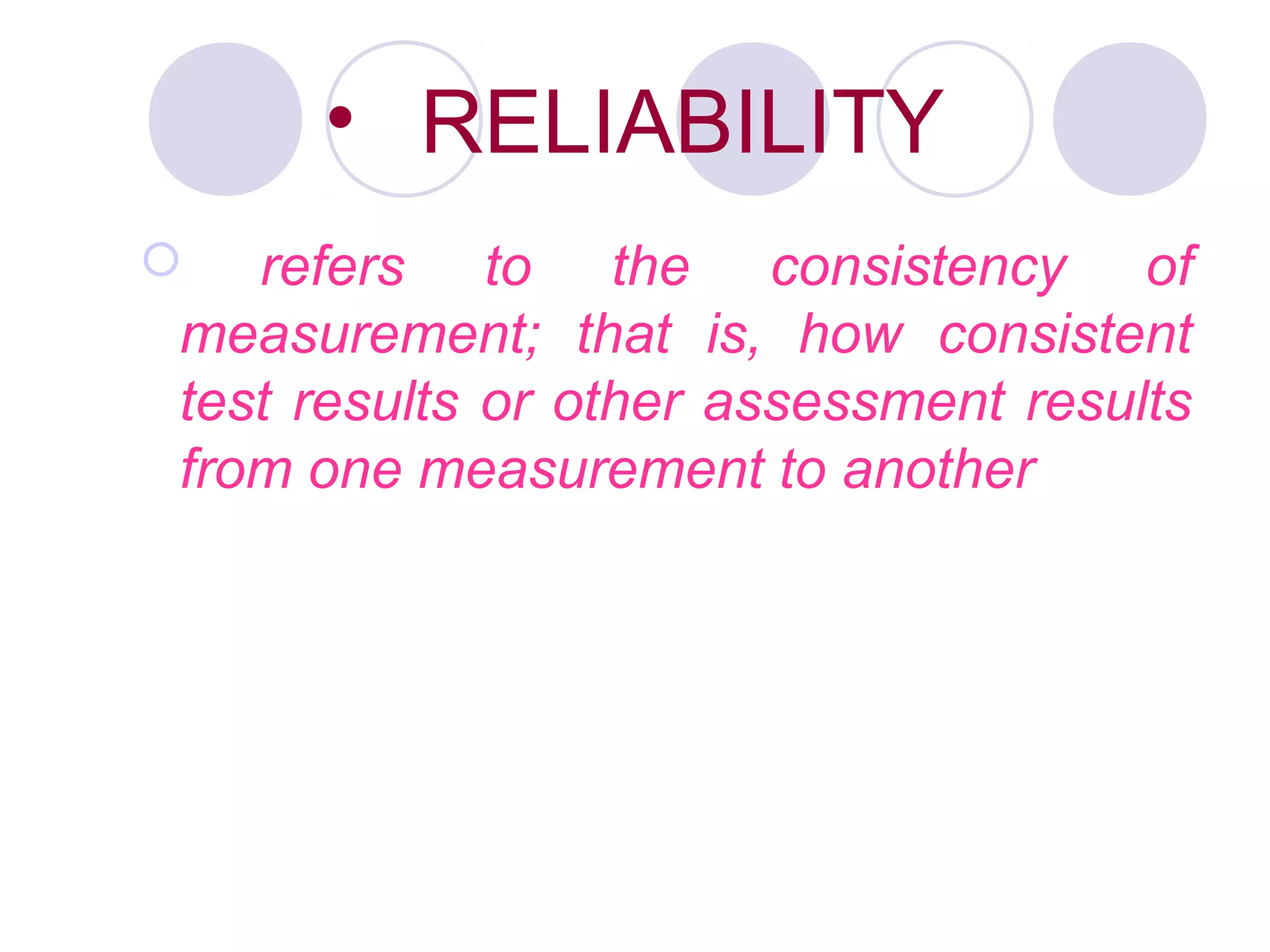
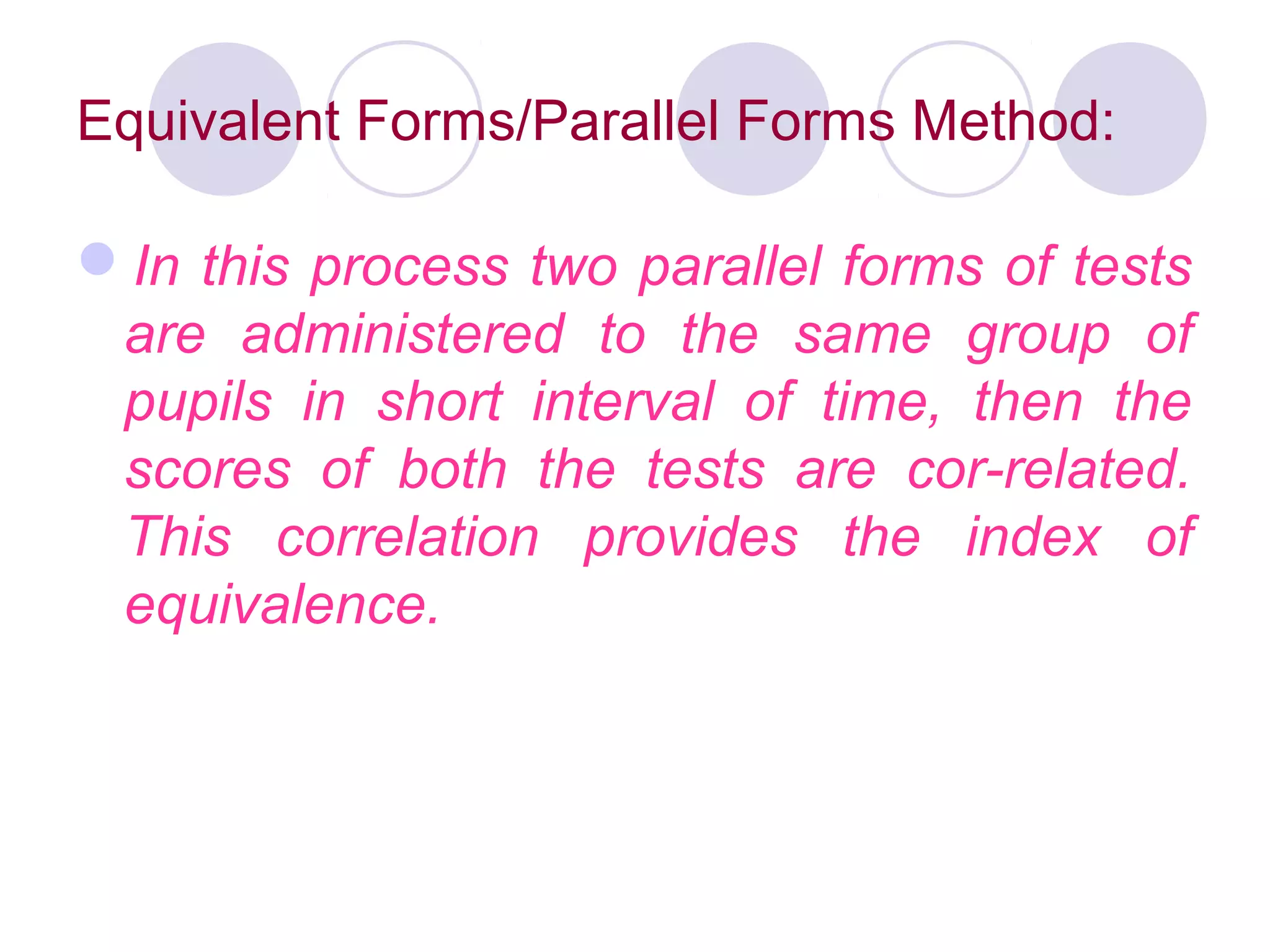
2. It should be a reliable instrument that consistently measures constructs and yields similar results over time as determined through methods like test-retest reliability.
3. It should be objective by eliminating personal bias and opinions of scorers so that different scorers arrive at the same score.