Embed presentation
Download to read offline



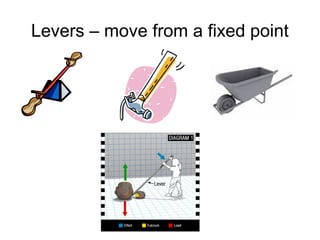
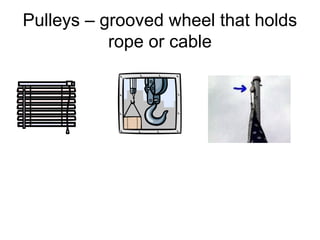
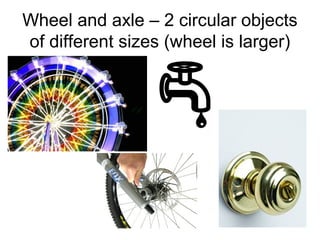
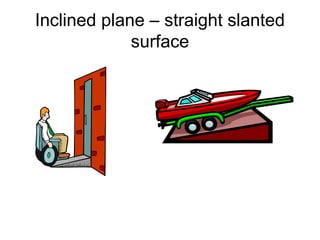



The document defines work as energy transferred by a force that causes an object to move, provides the formula for work (W=Fxd), and defines the units of measurement. It then defines power as the rate at which work is done, providing the formula (P=W/t) and units. Finally, it describes different types of simple machines - lever, pulley, wheel and axle, inclined plane, wedge, screw - that make work easier by changing the amount of force or distance required. A compound machine uses more than one simple machine.









