This document provides an overview of Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW) and catheter ablation of accessory pathways. Some key points:
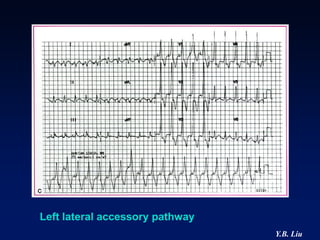
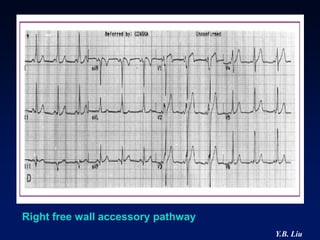
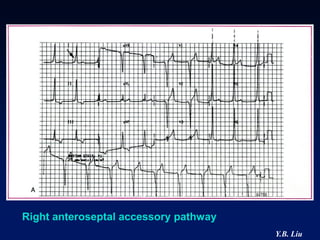
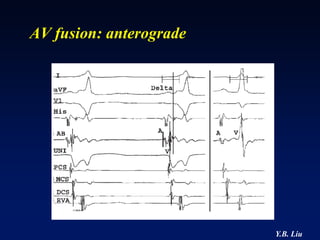
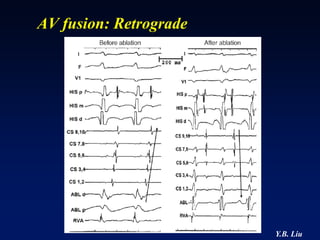
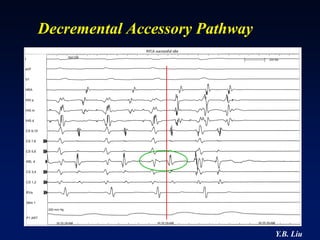
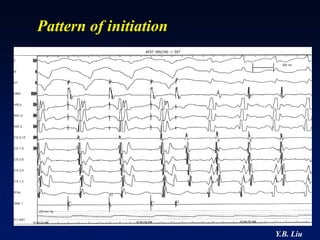
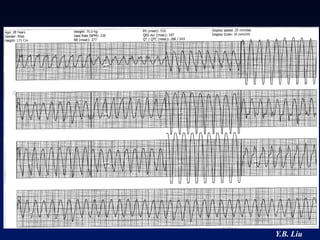
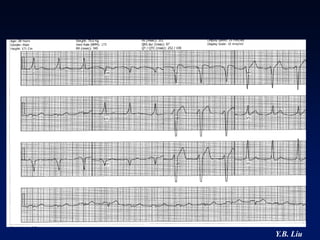
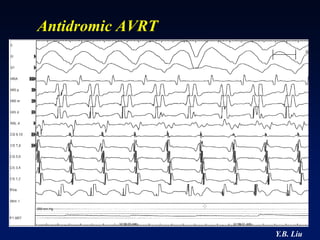
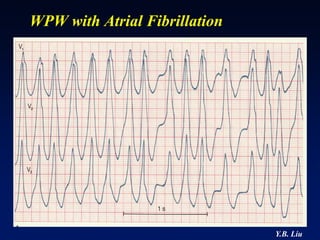
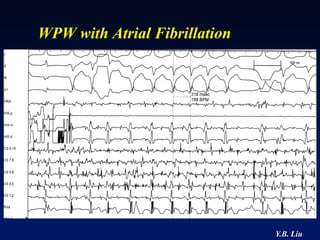
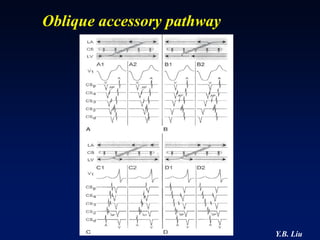
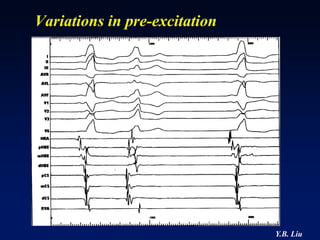
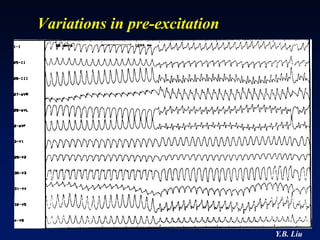
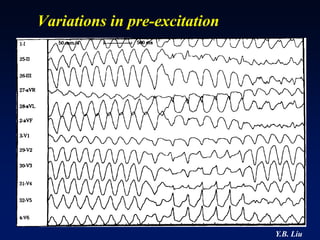
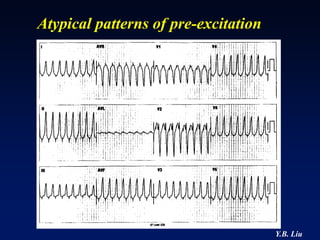
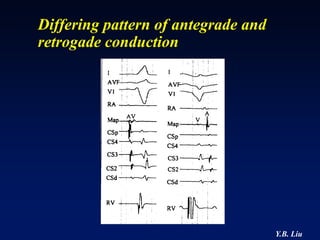
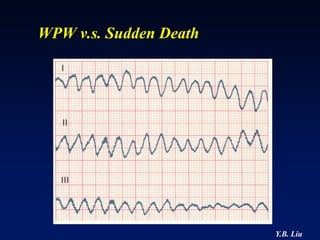
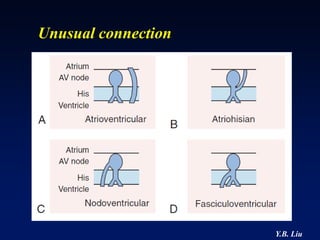
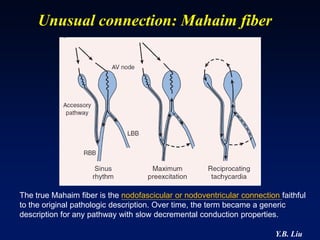
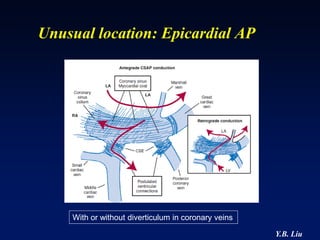
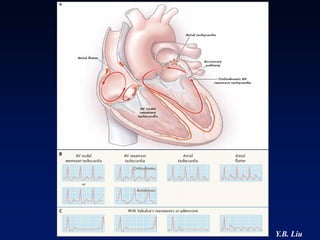
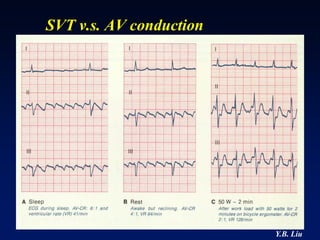
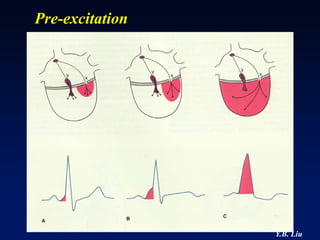
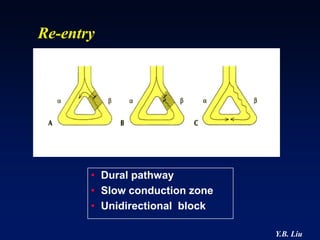
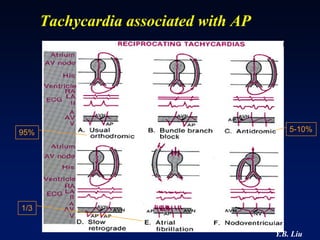
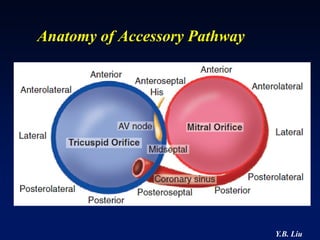
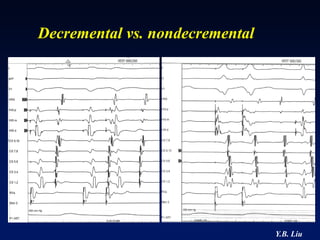
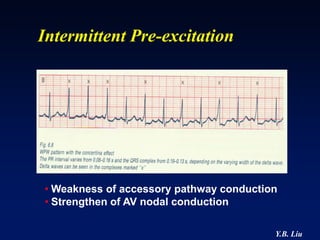
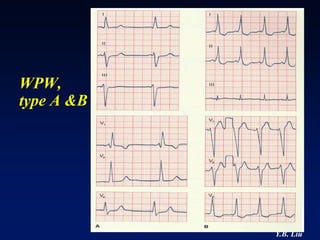
1) WPW is characterized by the presence of an accessory pathway that allows for pre-excitation and reentrant tachycardias. Accessory pathways can be located on the left or right side and have varying conduction properties.
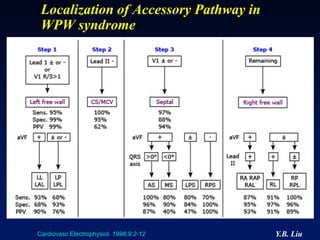
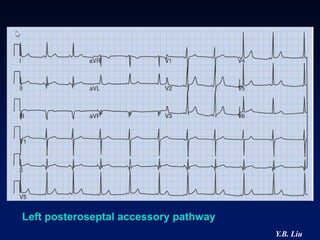
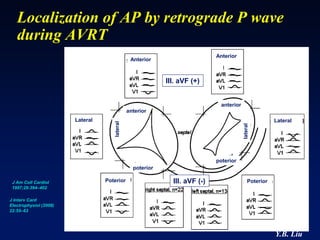
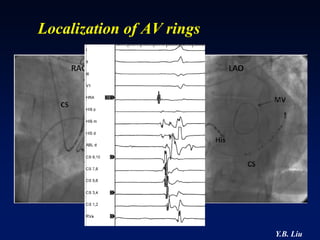
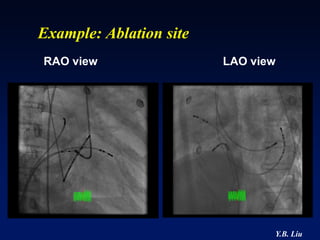
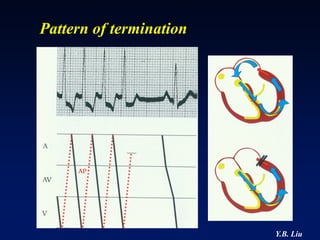
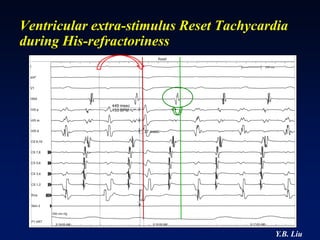
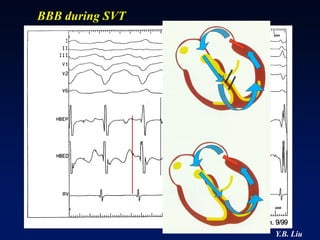
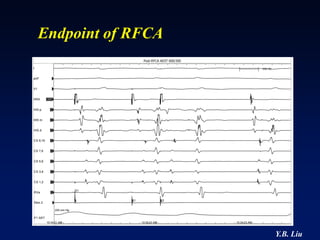
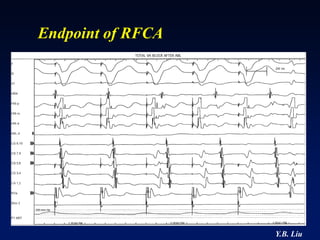
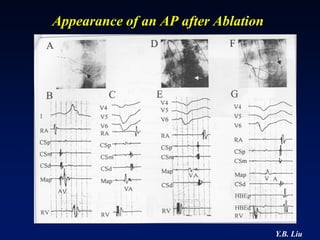
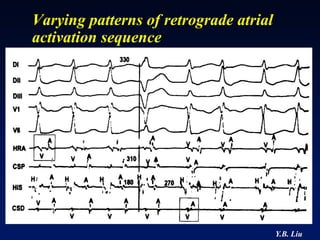
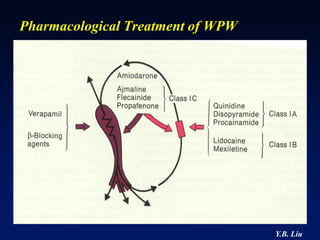
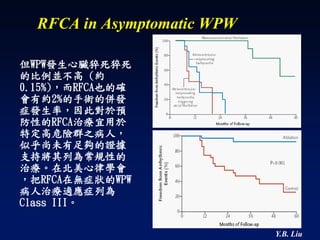
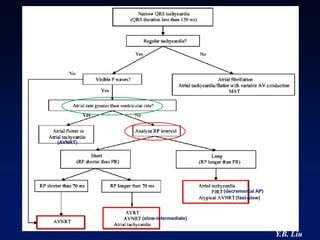
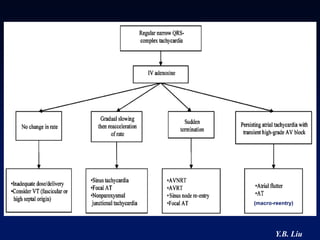
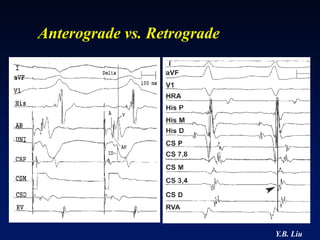
2) Catheter ablation is successful in eliminating the accessory pathway in 93-95% of cases. Localization of the pathway involves analyzing electrocardiogram patterns and effective sites are identified using techniques like accessory pathway conduction block.
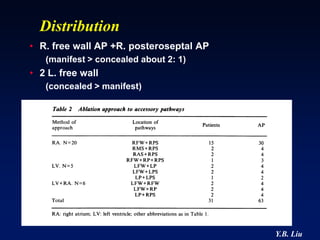
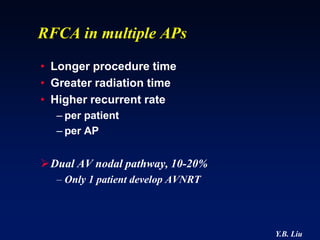
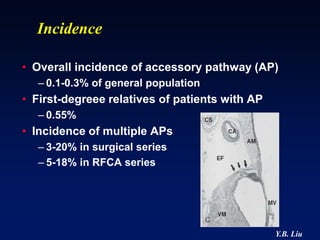
3) Multiple accessory pathways occur in 3-20% of cases and present additional challenges for localization



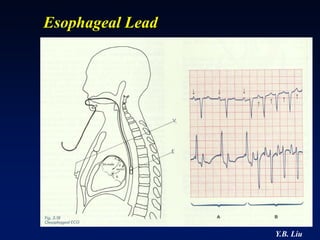




![Localization of Accessory
Pathway in WPW syndrome
• Transition zone
• R in lead I
• Positive or
Negative vector
of delta wave in
II, III, aVF
[PACE 1995; 18: 1469-1473]
Y.B. Liu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-wpw2013-130411023519-phpapp02/85/Wolff-Parkinson-White-Syndrome-22-320.jpg)