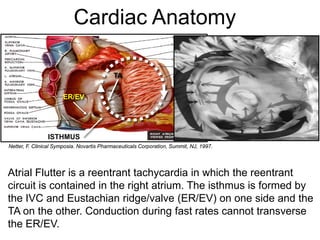
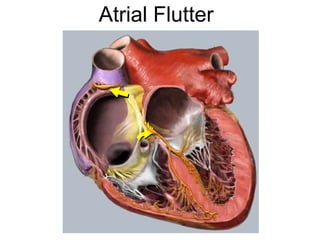
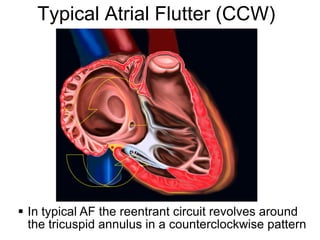
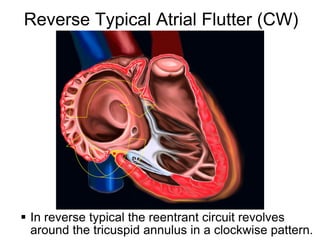
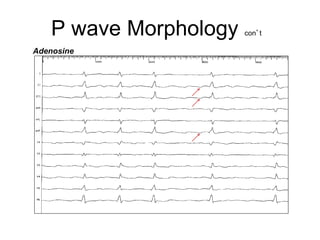
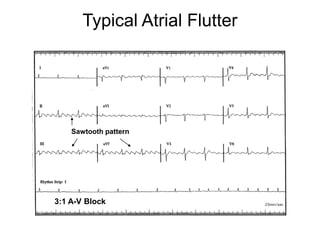
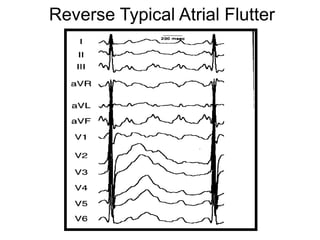
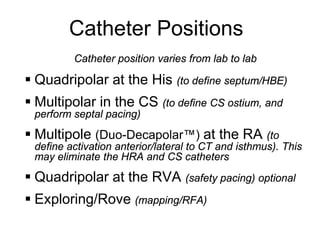
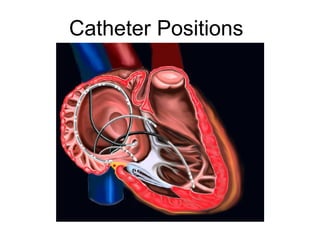
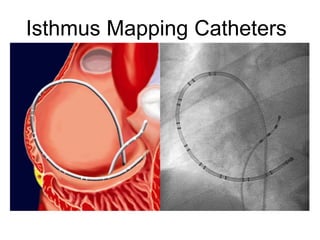
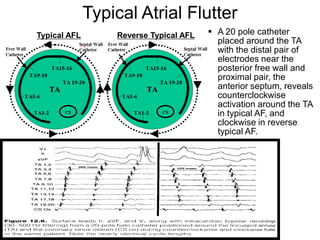
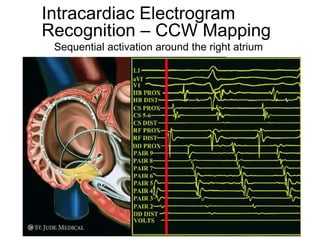
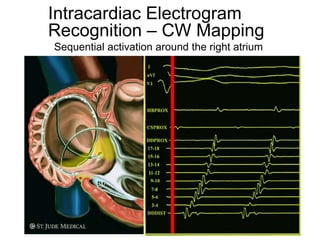
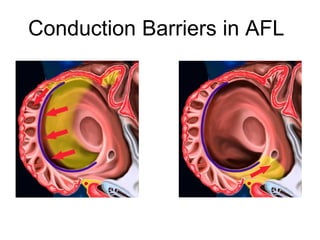
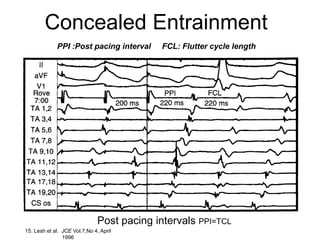
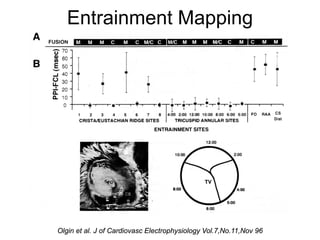
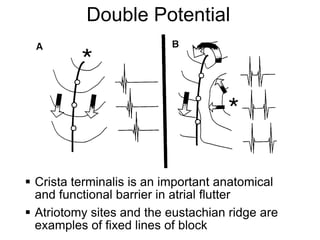
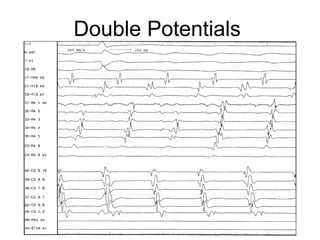
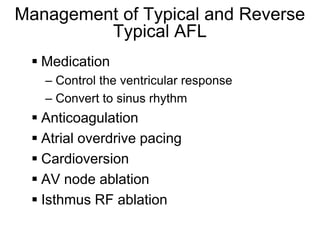
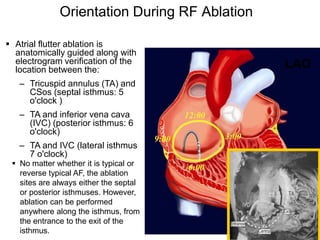
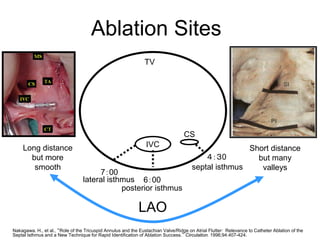
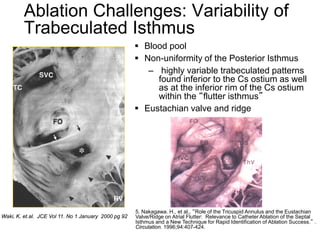
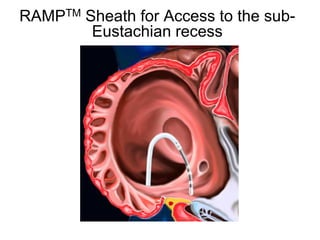
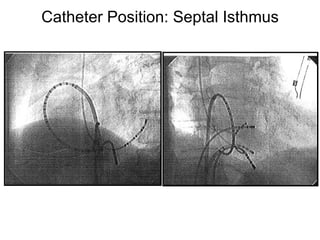
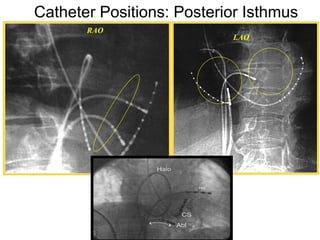
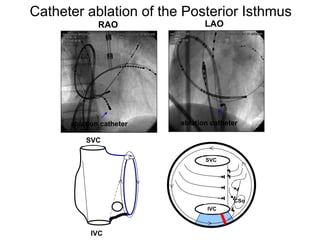
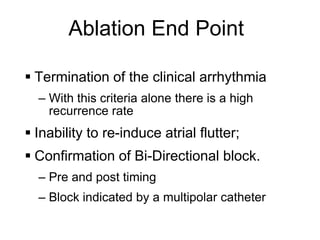
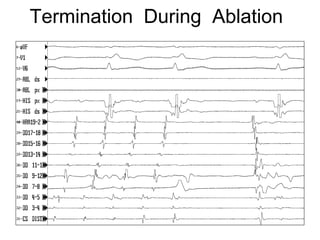
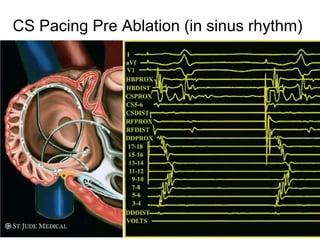
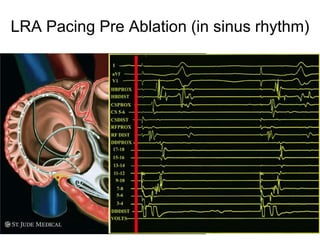
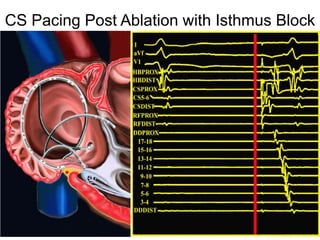
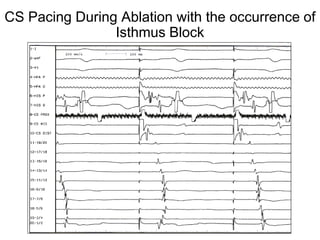
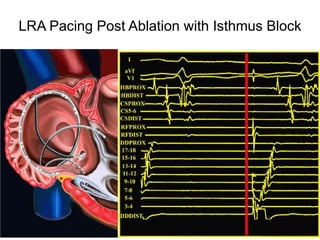
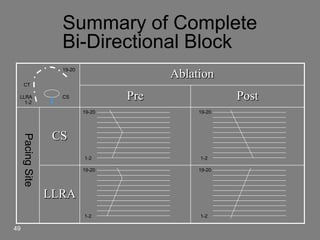
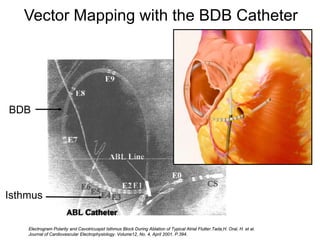
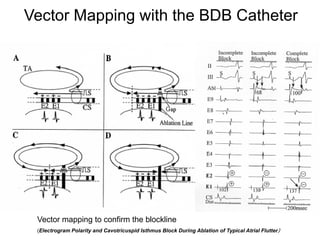
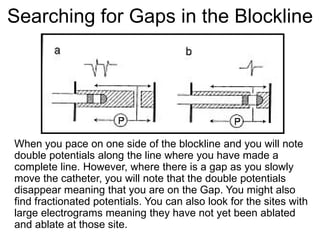
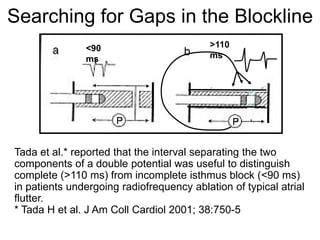
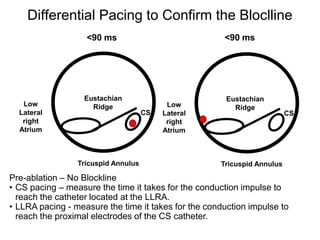
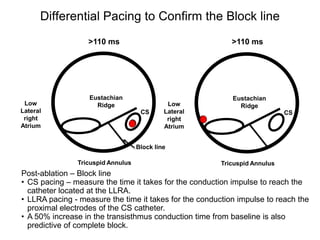
Atrial flutter is a reentrant tachycardia involving the right atrium. There are two main types - typical atrial flutter which revolves counterclockwise around the tricuspid annulus, and reverse typical atrial flutter which revolves clockwise. Catheter ablation aims to create a continuous linear lesion across the cavotricuspid isthmus to block conduction and terminate the arrhythmia. Successful ablation is confirmed by the inability to induce flutter and demonstration of bidirectional conduction block across the ablation line.