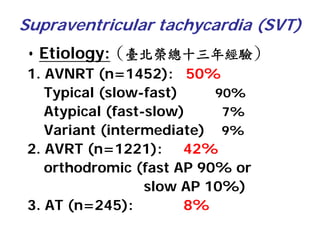
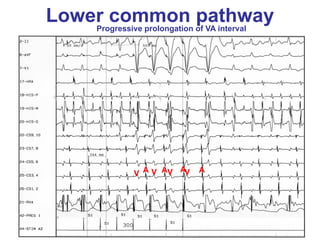
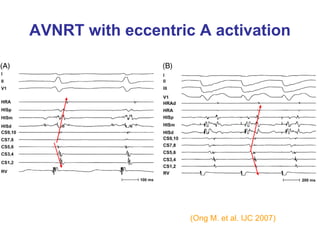
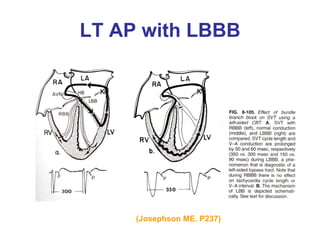
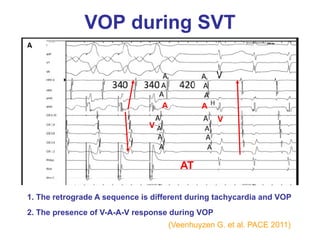
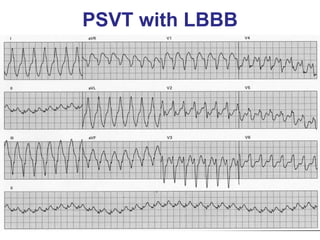
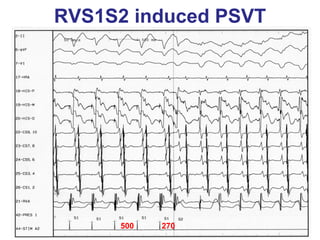
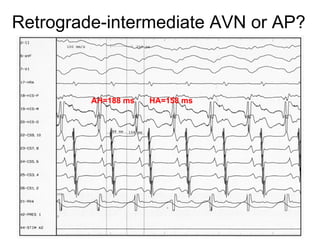
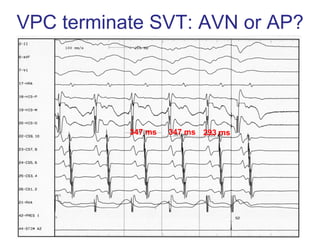
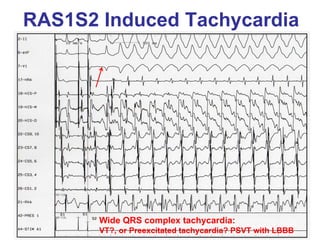
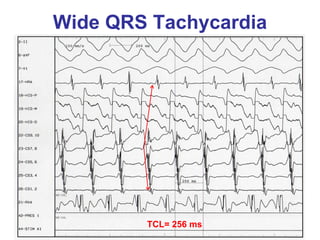
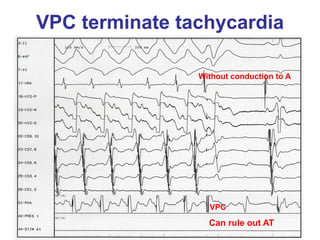
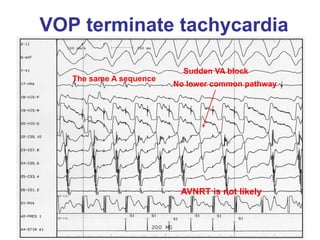
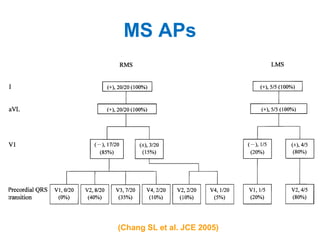
1. The document discusses different types of supraventricular tachycardia including AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), and atrial tachycardia (AT).
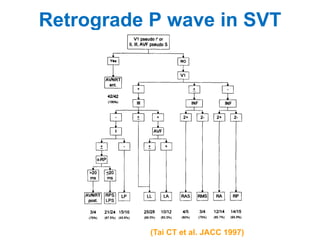
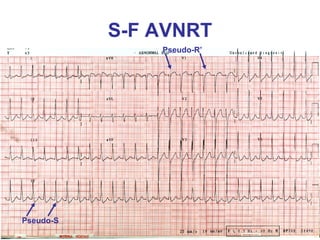
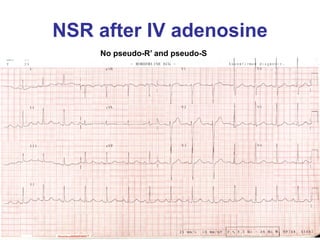
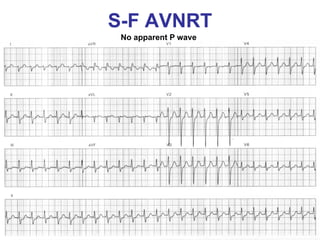
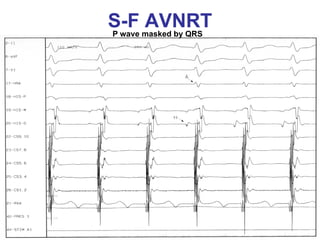
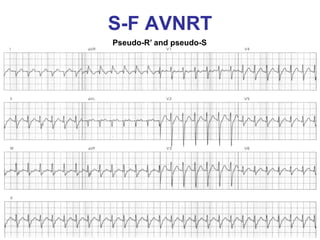
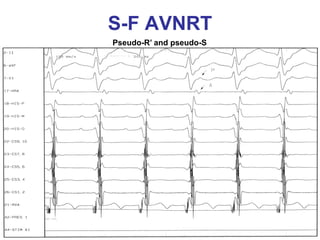
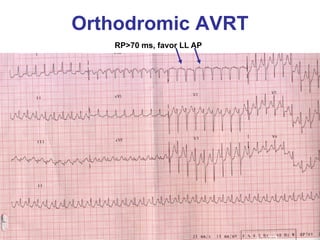
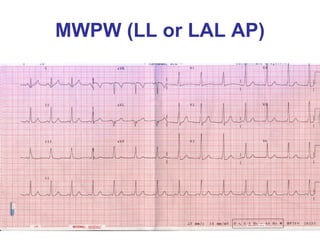
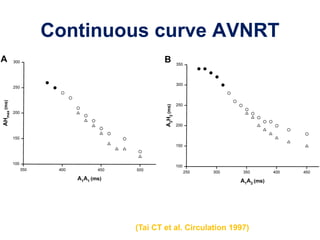
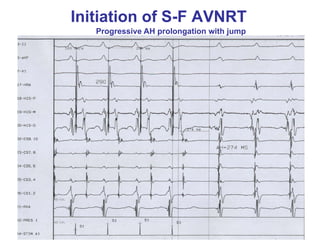
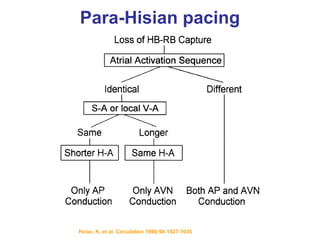
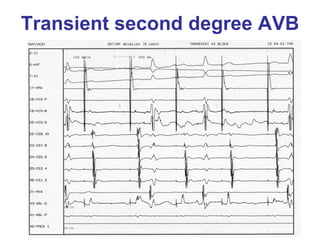
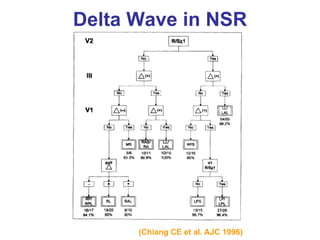
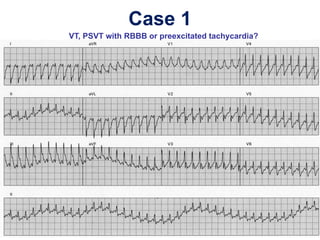
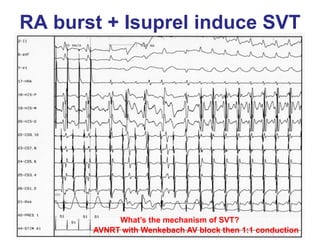
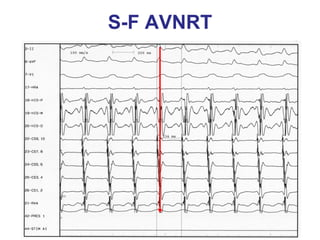
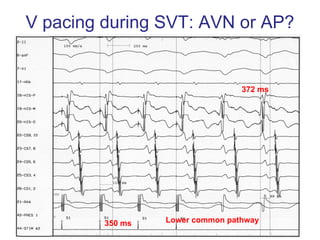
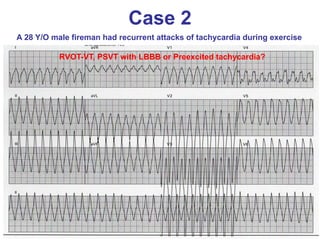
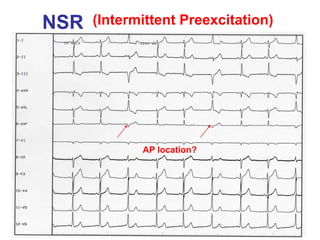
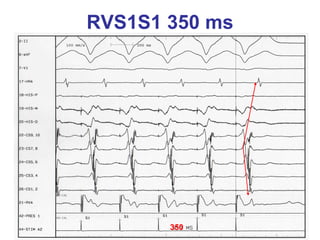
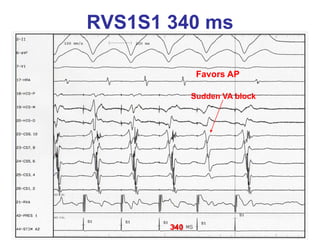
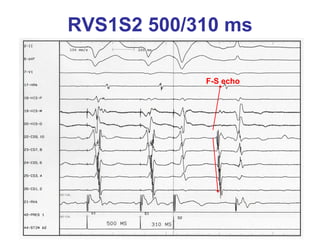
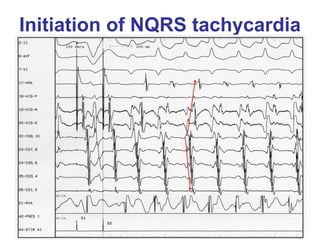
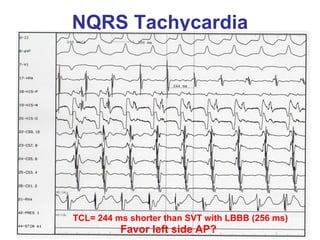
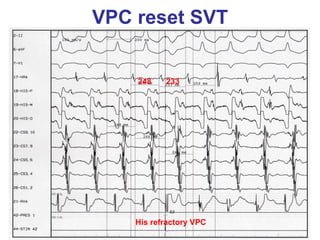
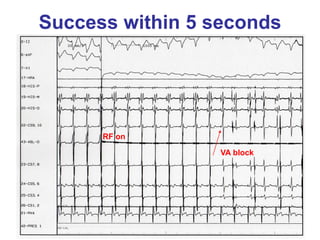
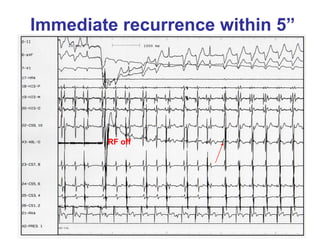
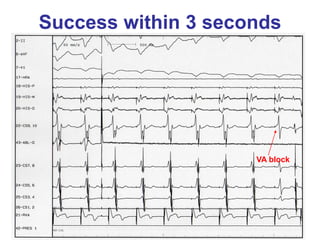
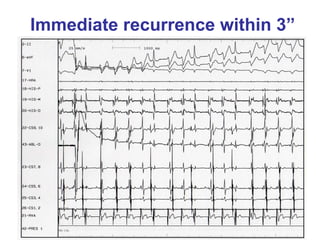
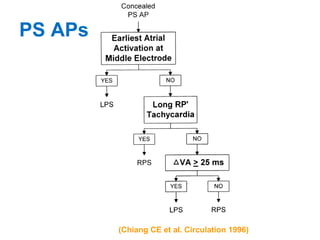
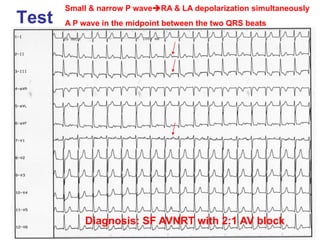
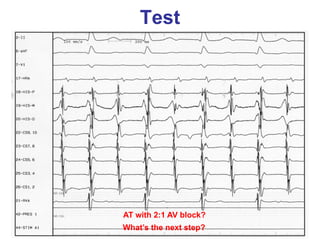
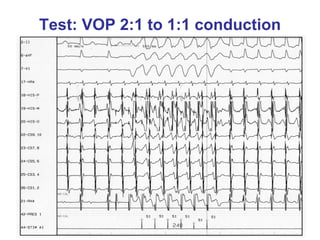
2. It provides details on electrocardiogram patterns that can help differentiate the different types of SVT. Features like retrograde P waves, RP intervals, and the effect of ventricular pacing are discussed.
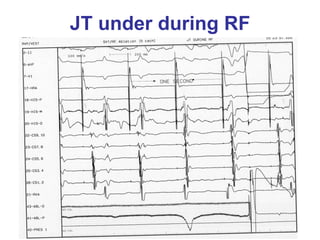
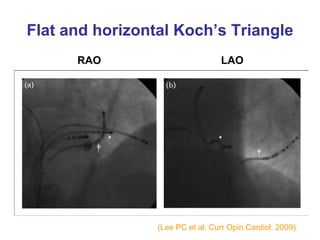
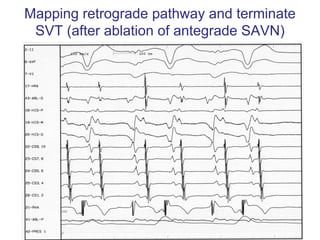
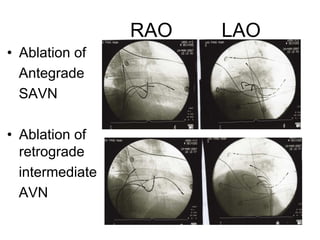
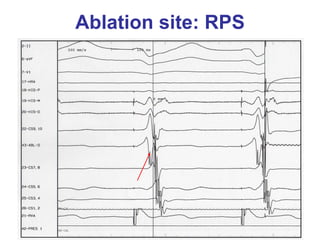
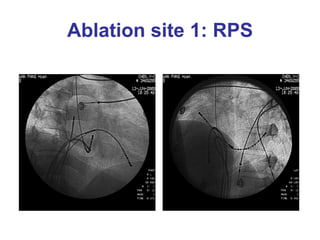
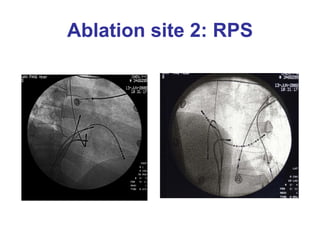
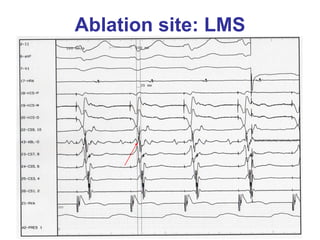
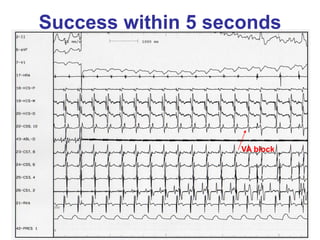
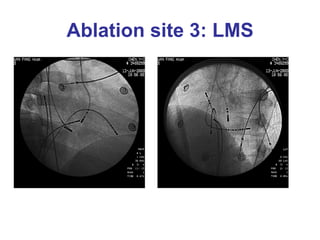
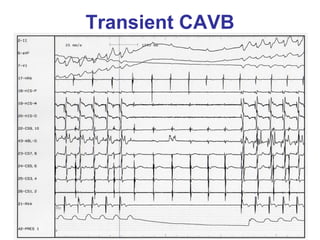
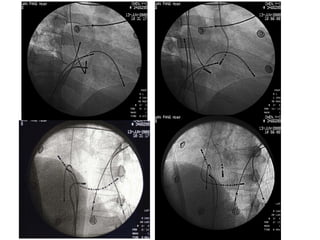
3. Ablation techniques for AVNRT and AVRT are covered, including approaches for mapping the circuits and terminating arrhythmias. The importance of making an accurate diagnosis is emphasized.