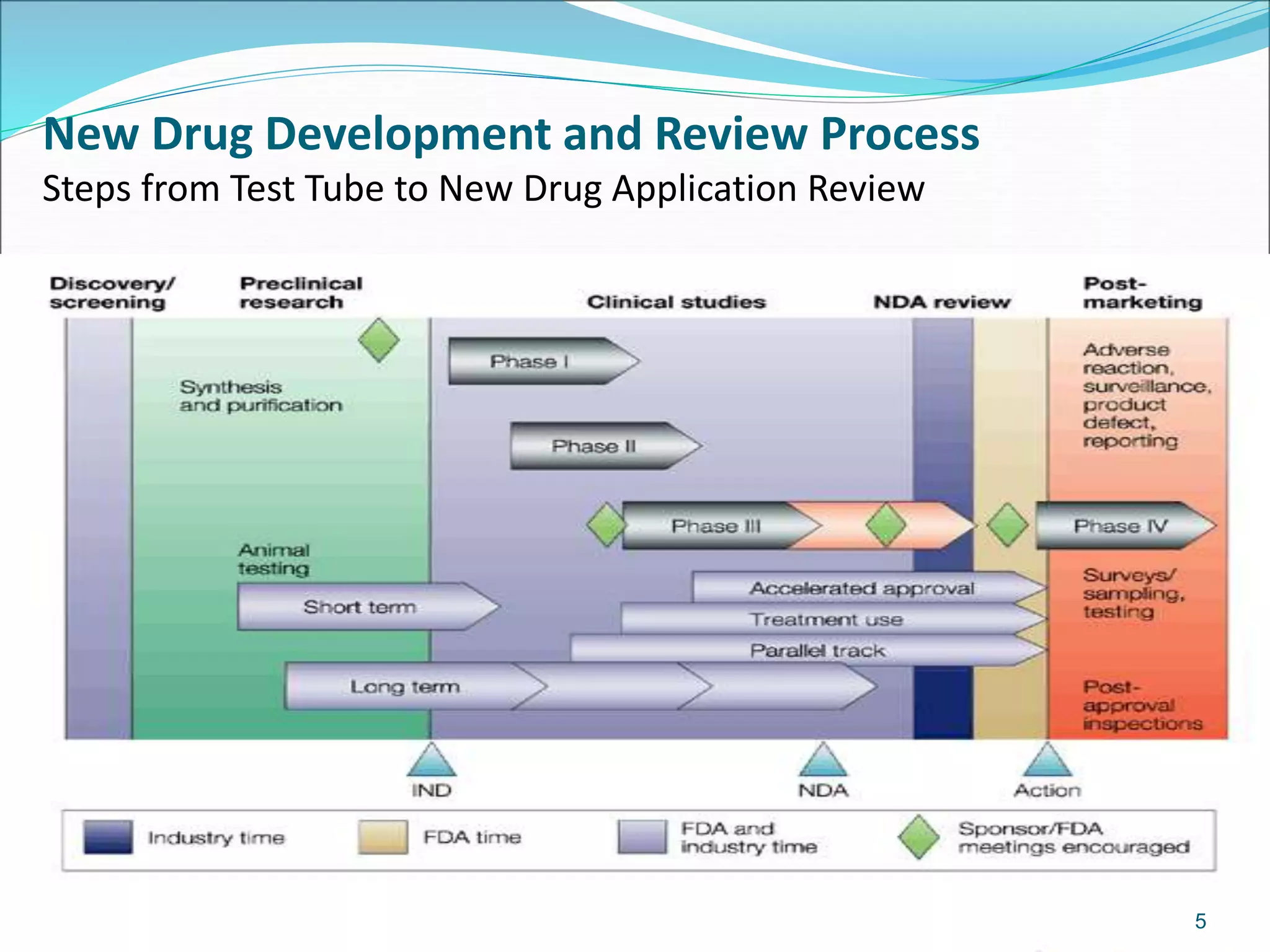
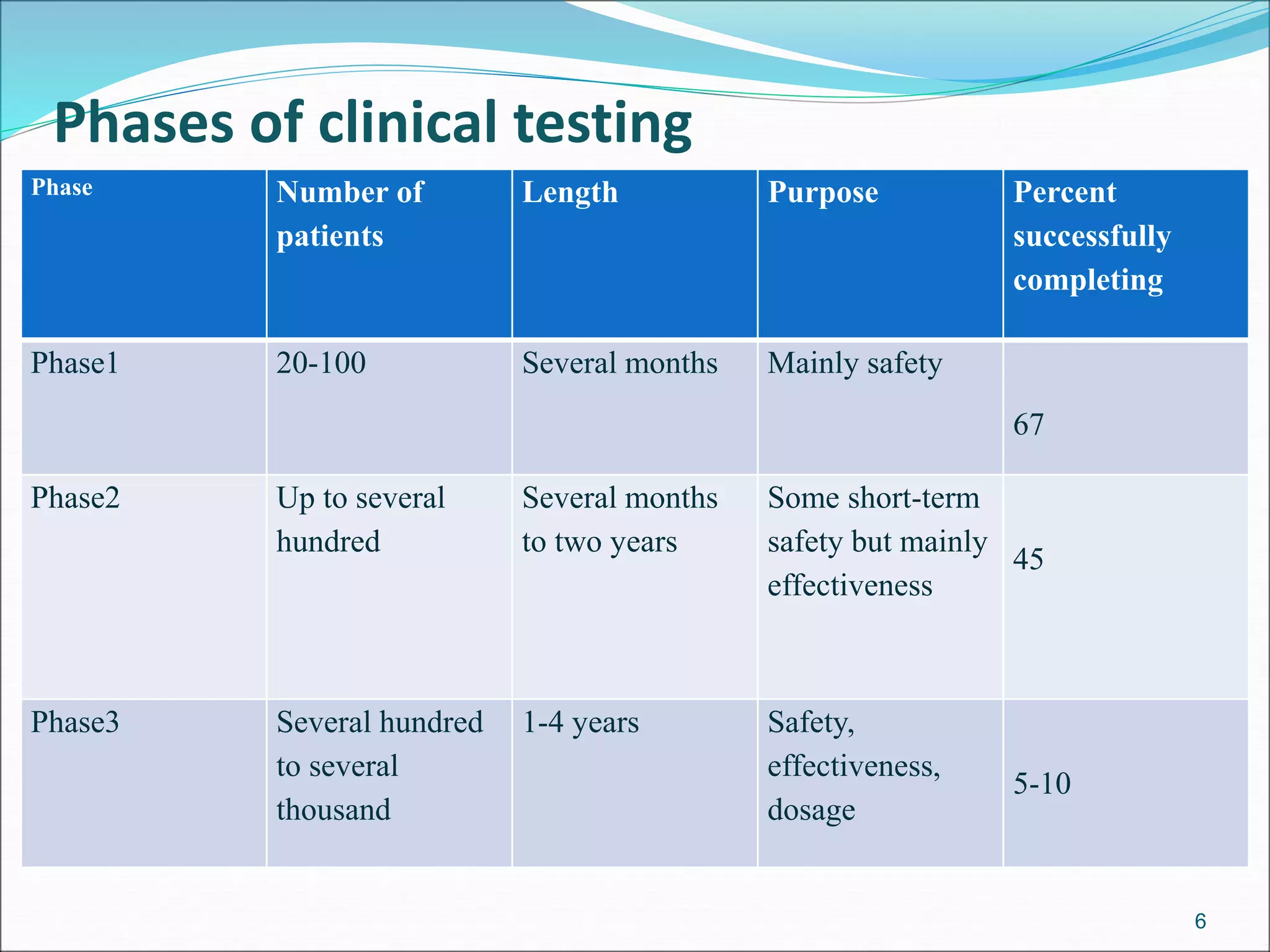
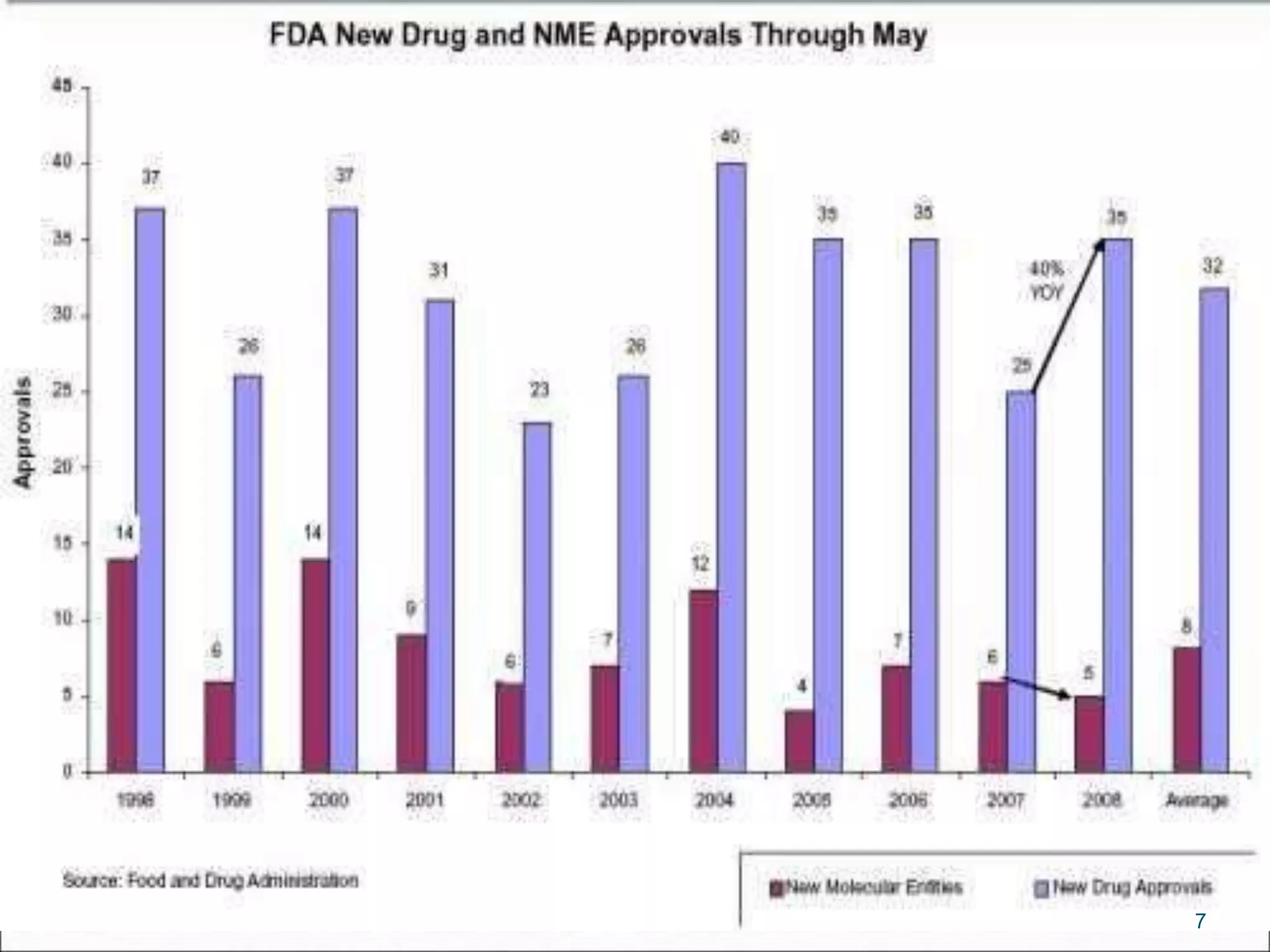
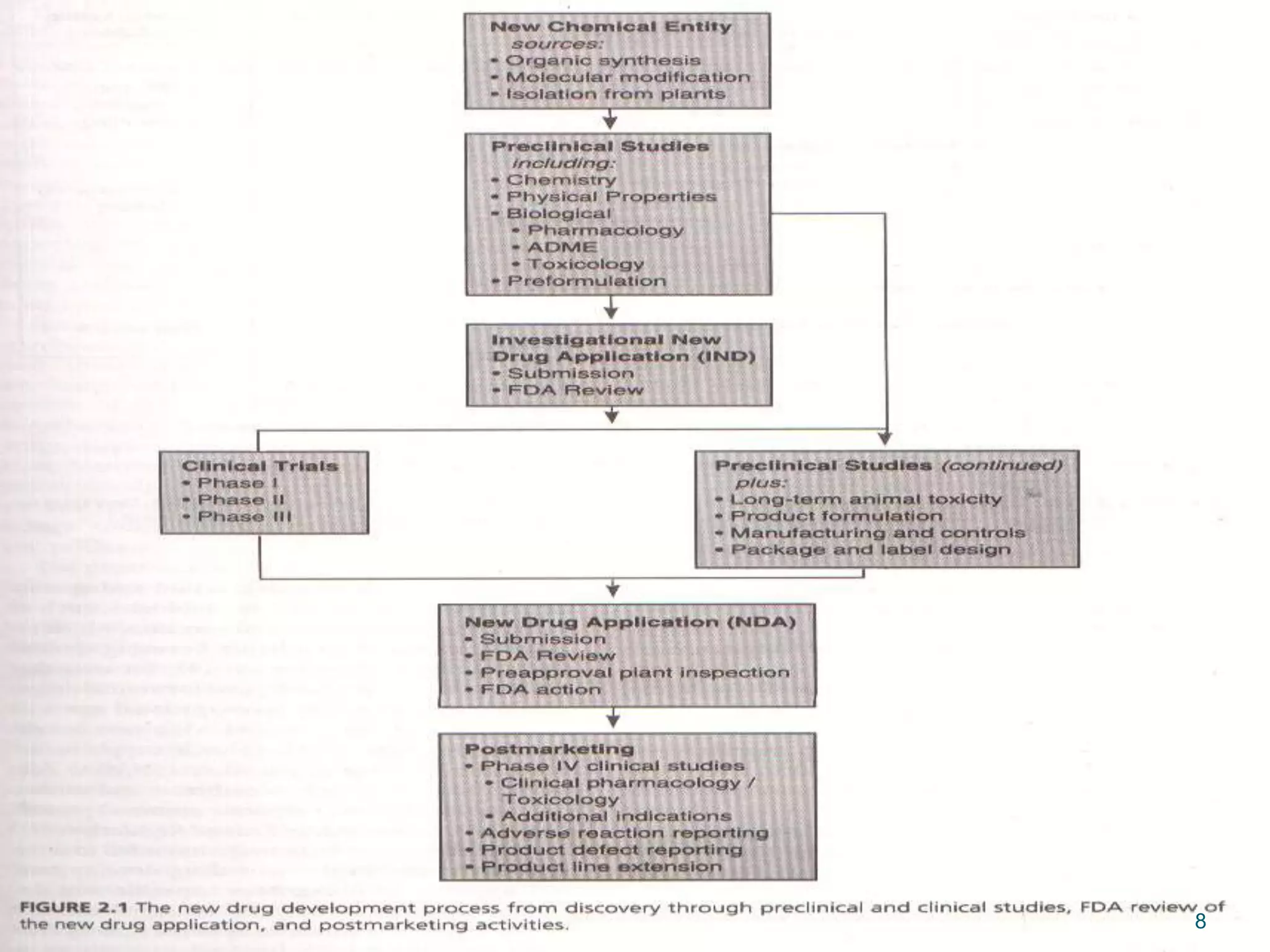
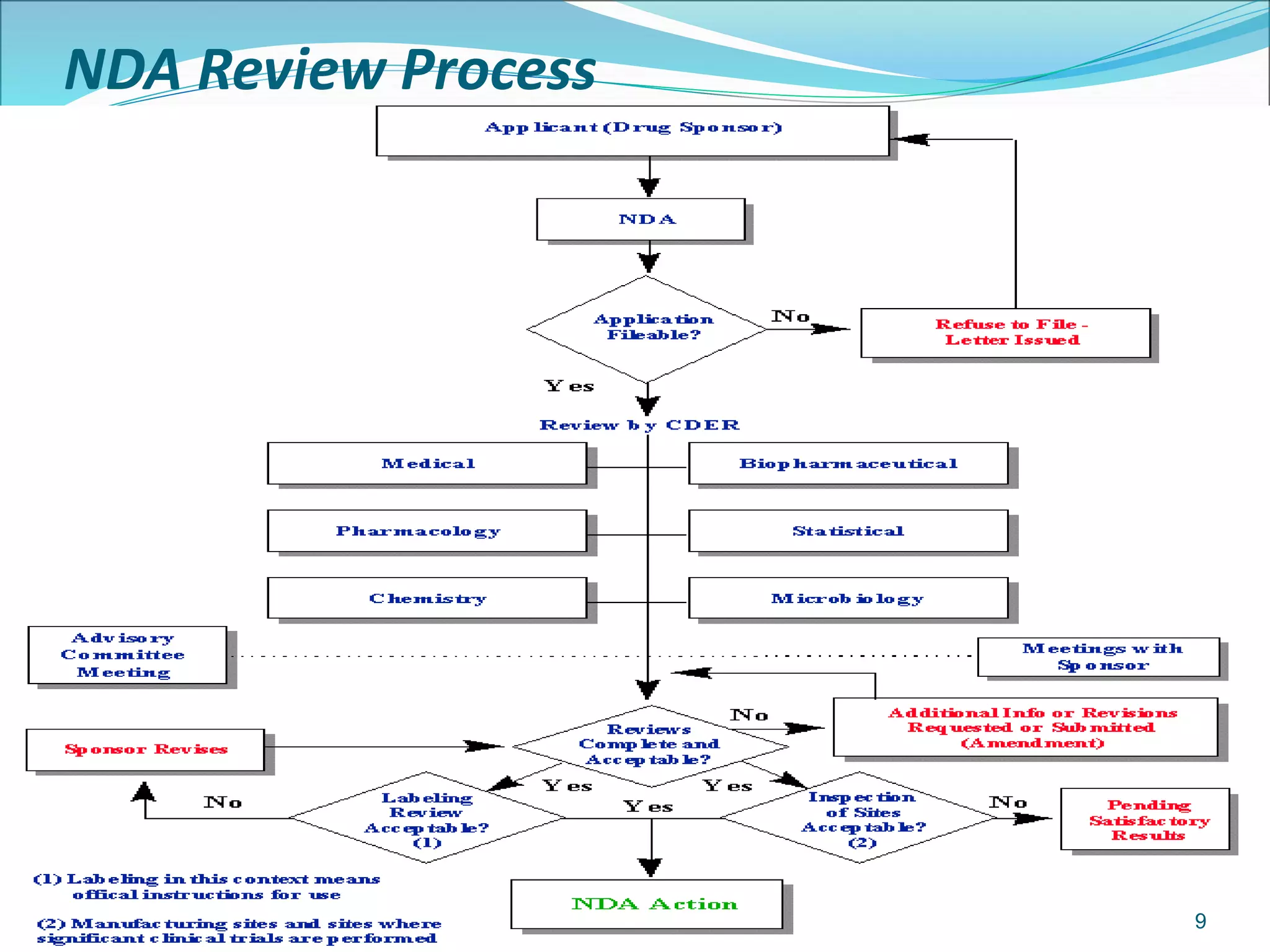
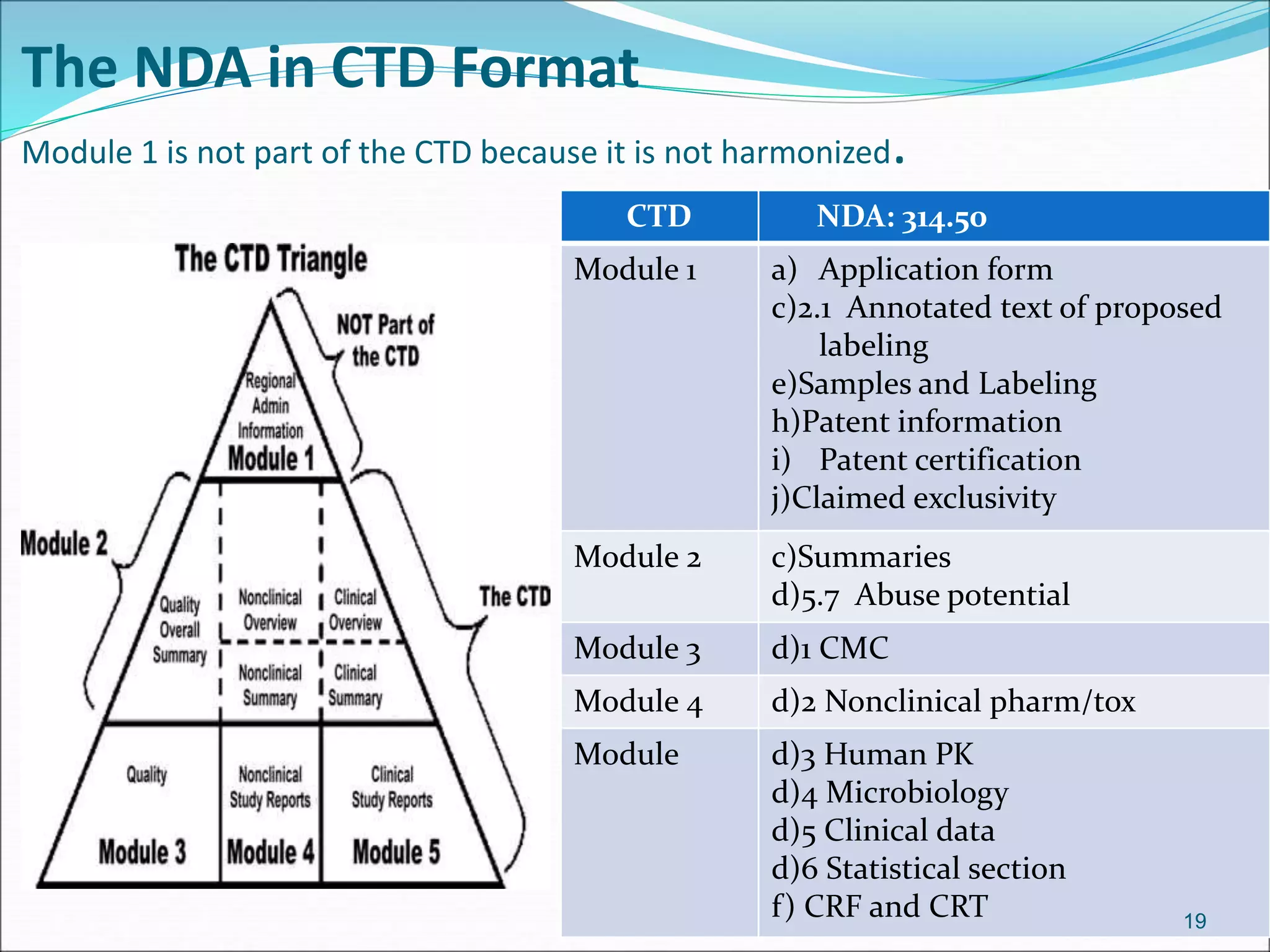
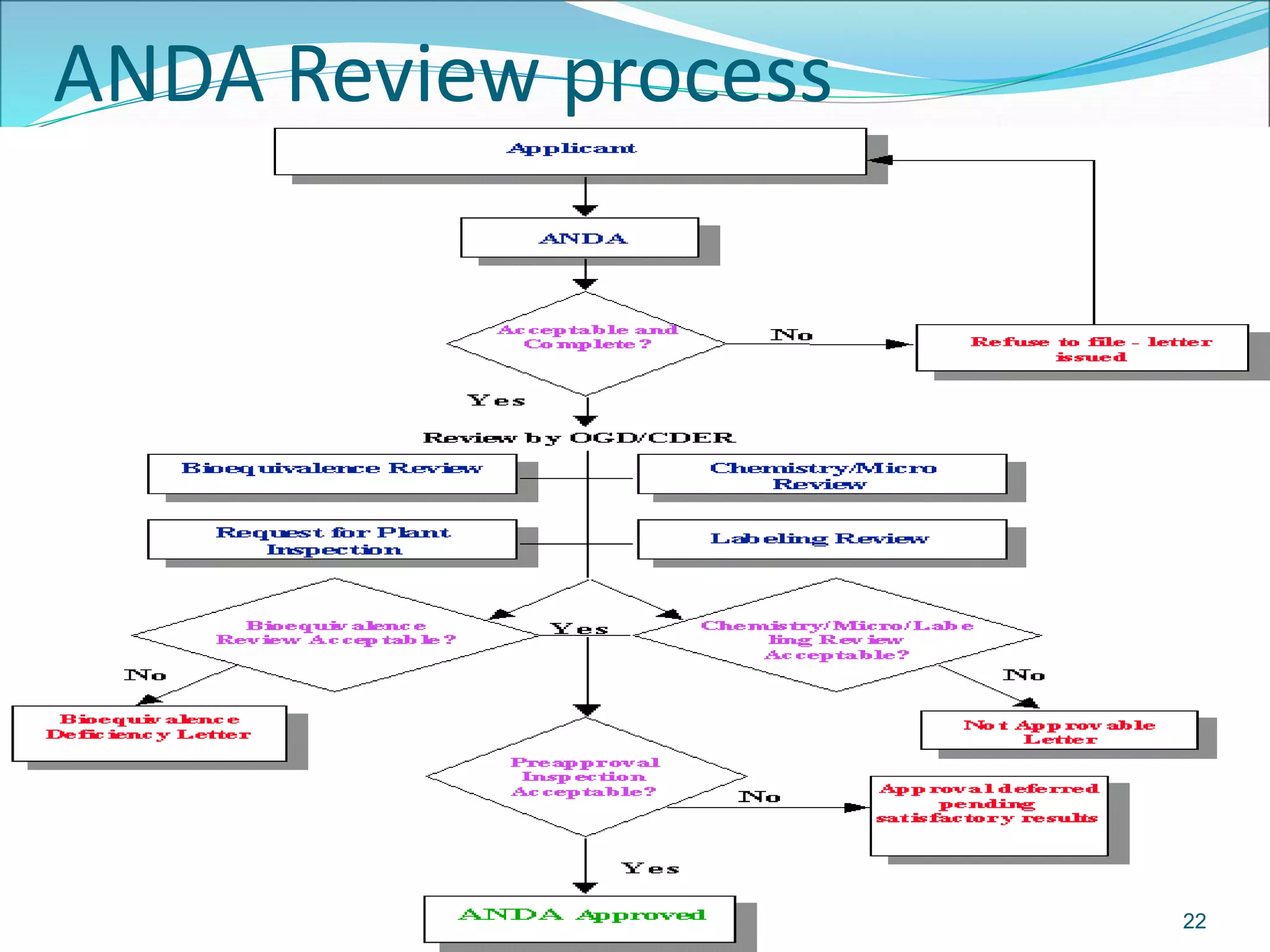
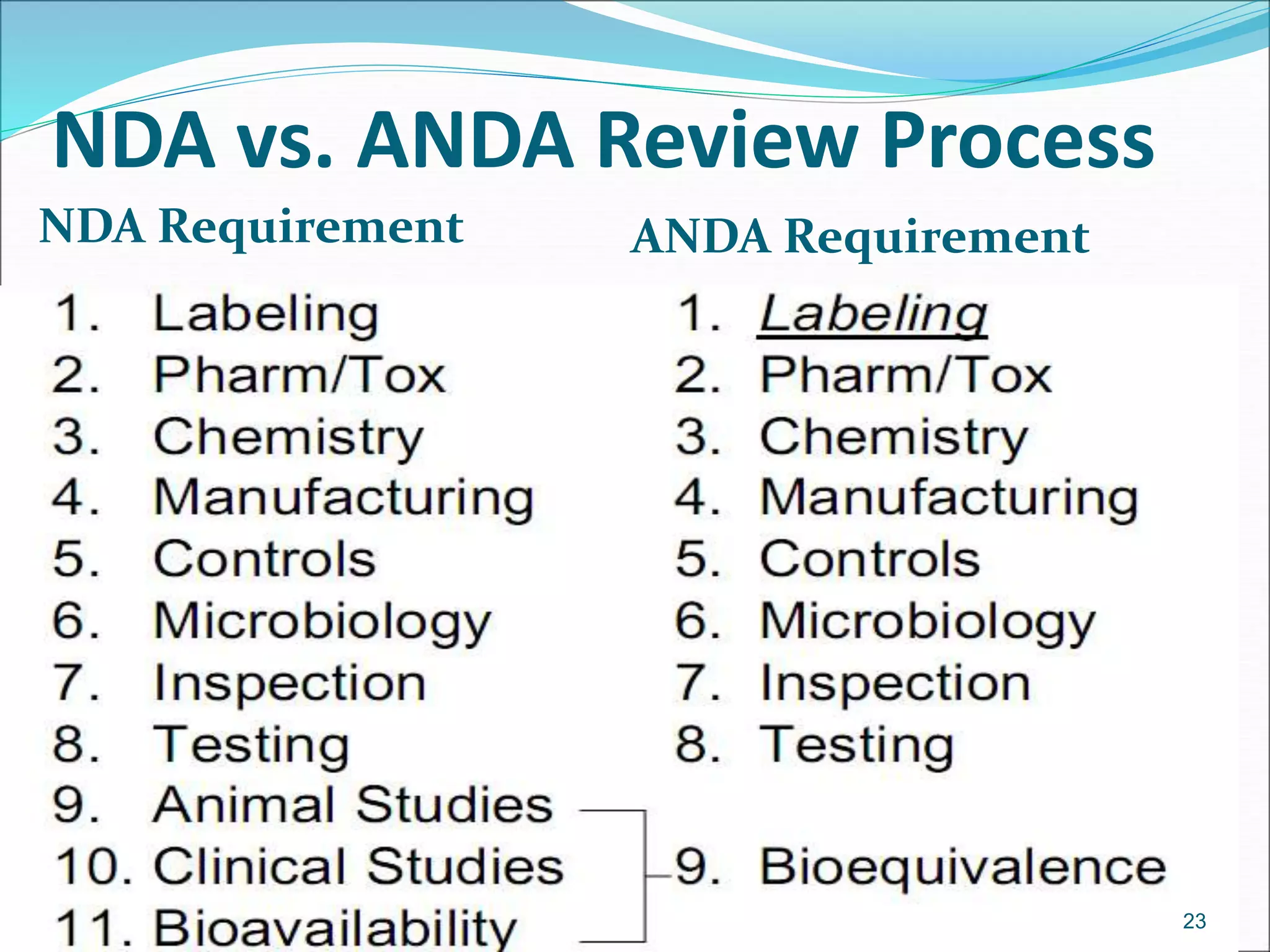
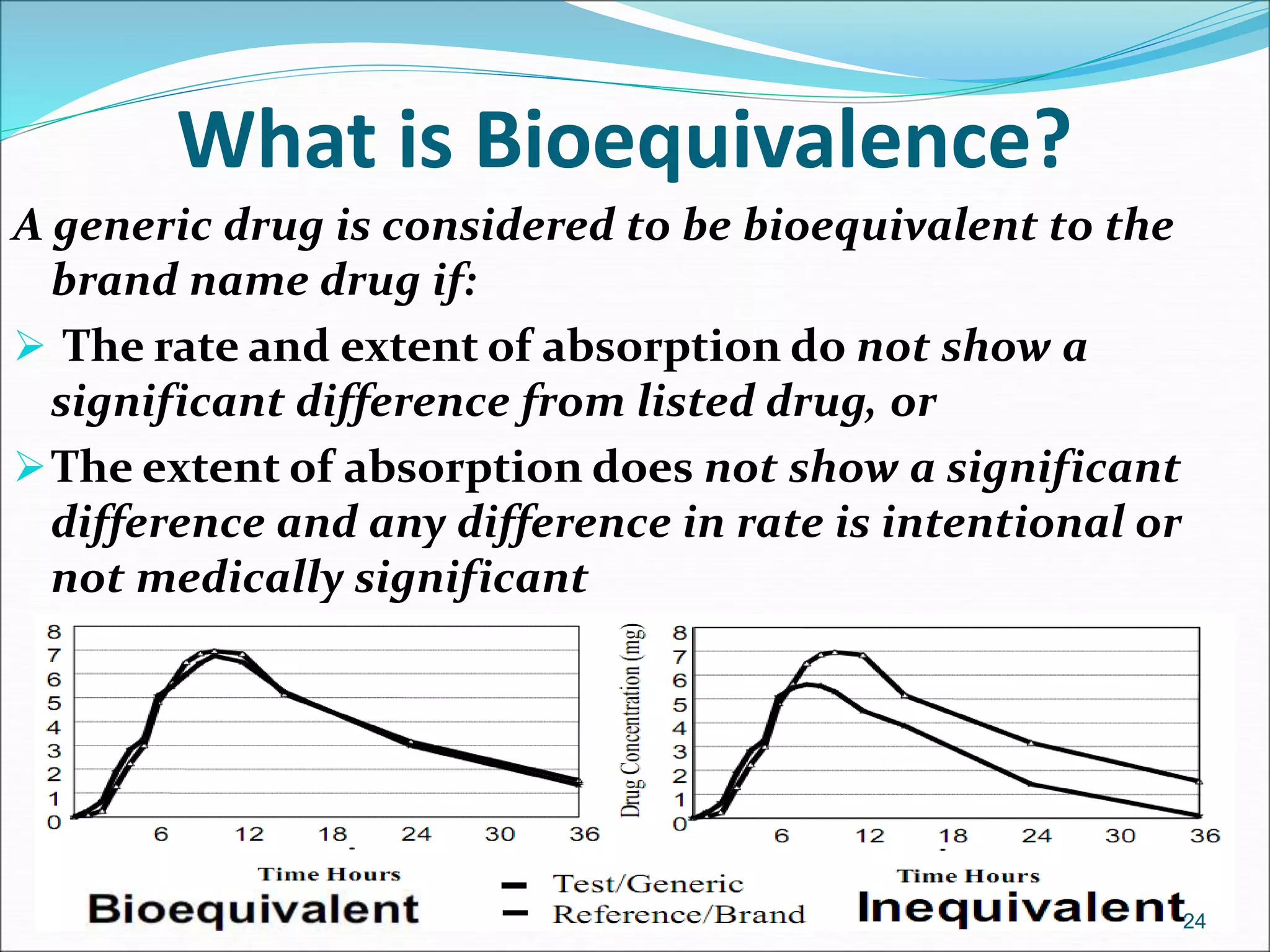
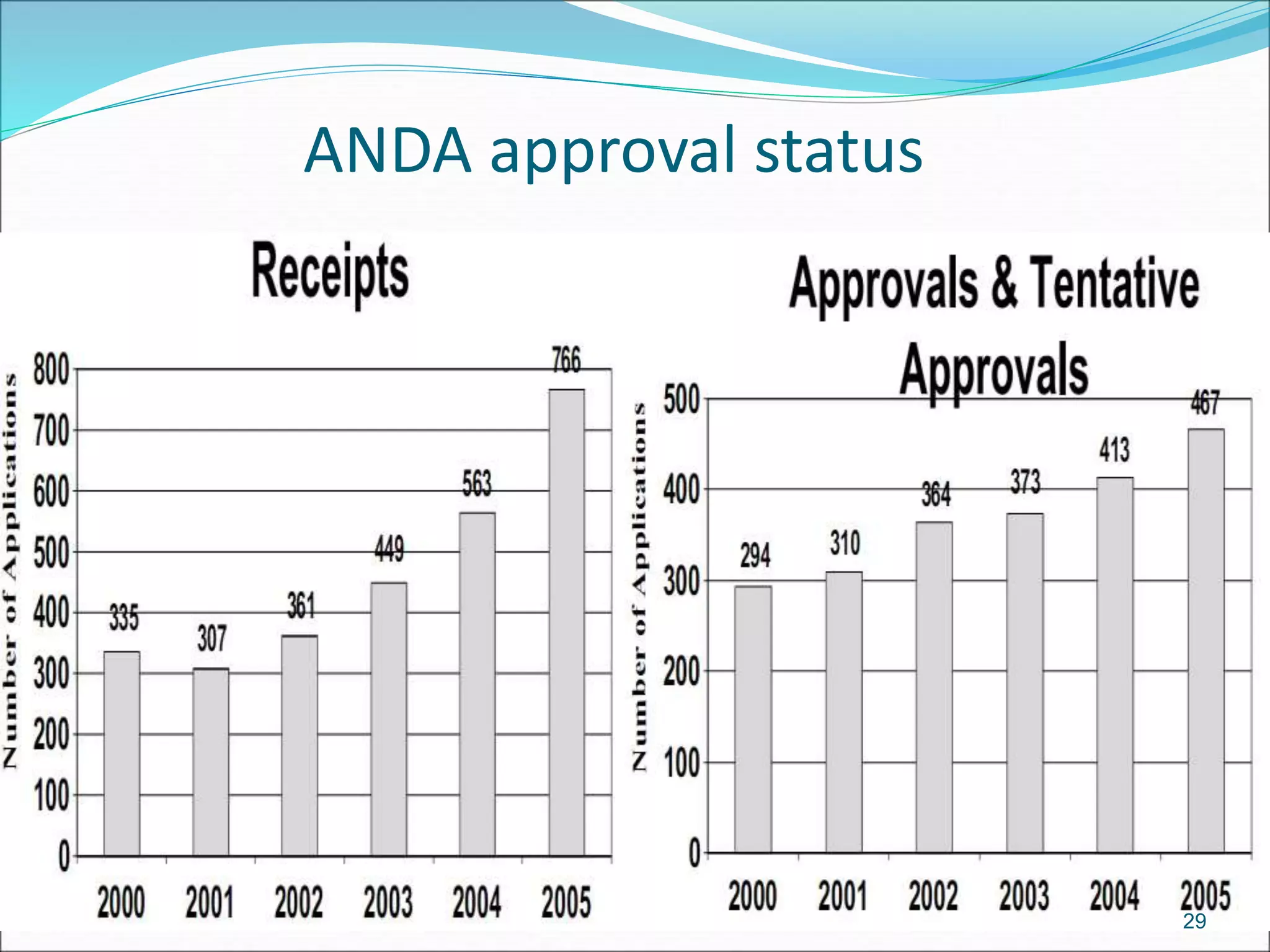
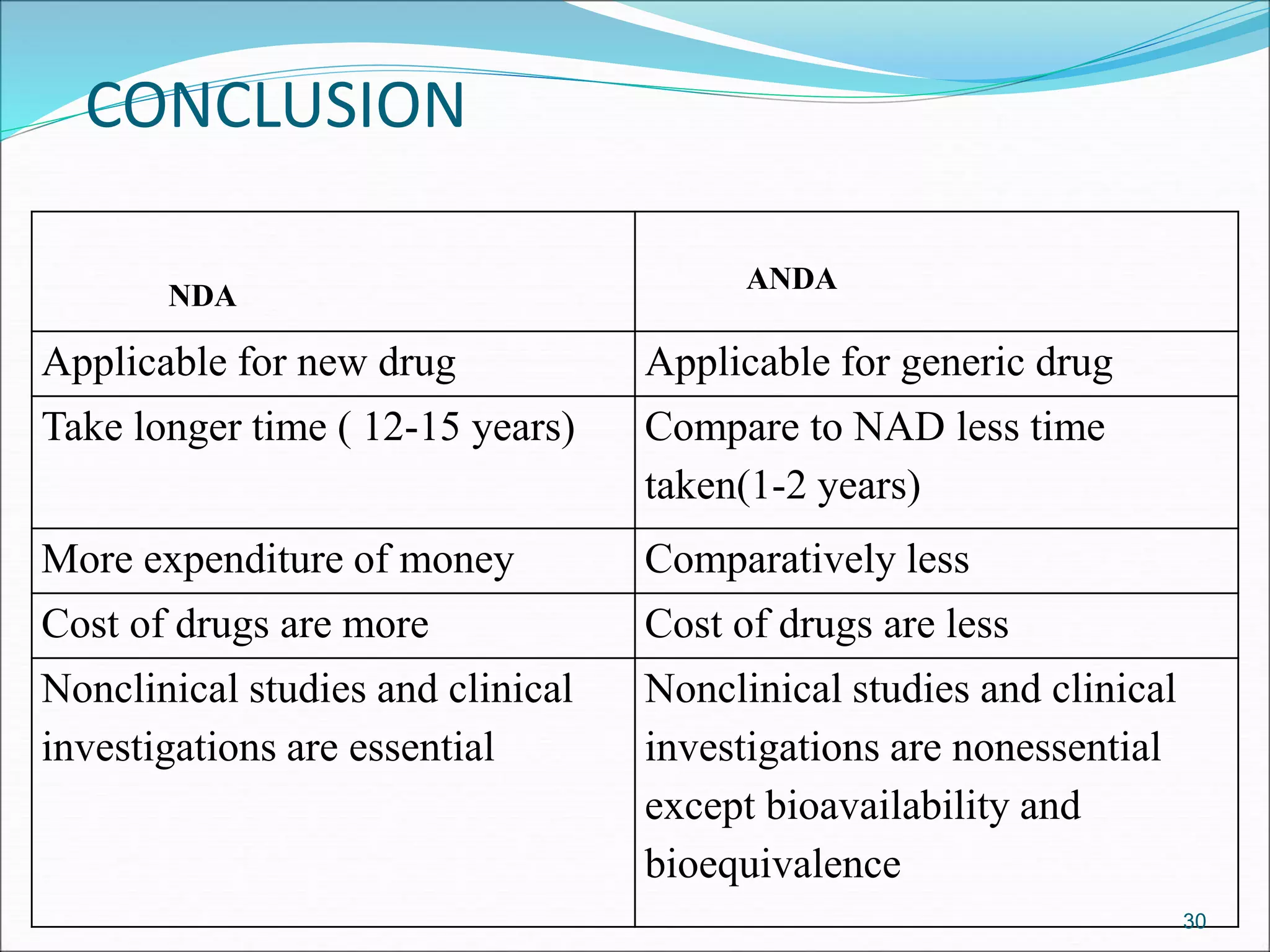
This document discusses new drug applications (NDAs) and abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) submitted to the FDA for drug approval. It describes the goals and contents of an NDA, including clinical trial data and manufacturing information, as well as the multi-step review process. For ANDAs, the goals are to reduce drug costs and development time by allowing generics if they are equivalent to branded drugs. ANDAs must demonstrate bioequivalence but do not require new clinical trials. The document provides details on patent certification and approval processes for both NDA and ANDA submissions.