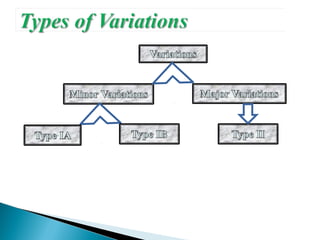
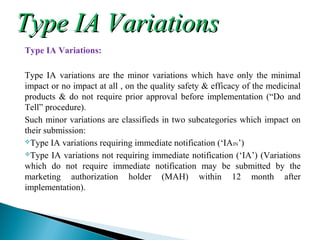
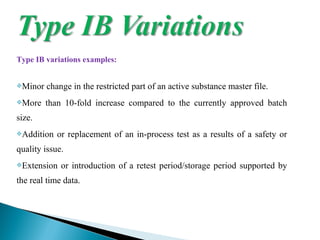
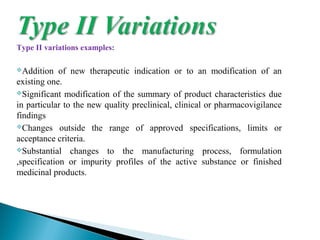
The document discusses different types of variations to marketing authorizations for medicinal products in the EU. Variations are classified as minor (Type I) or major (Type II), with Type I divided into IA and IB categories based on the approval process required. The presentation covers definitions of variations, examples of different variation types, procedures for filing variations, and grouping of variations in a single application.