The document outlines the regulatory framework for the pharmaceutical industry in the European Union (EU), which consists of 28 member states and a population of around 500 million. It details the approval process for drugs, the role of the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the various authorization routes available. Additionally, it highlights the importance of safety monitoring, clinical trials oversight, and the cooperation between national competent authorities and the EMA.

![The Europe union
A political union also called as Europe union formed in 1993 for
purpose of achieving political and economic integration.
The EU includes 28 members states located in Europe .
The EU total population is about 500 millions people
The EU operates through a system of
1. Supranational independent institution
2. Intergovernmental negotiated decisions by its member of the
states .
It is legal entity and can negotiate international agreement on behalf
of its member states
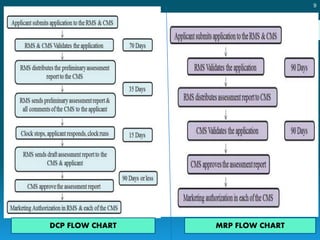
In EU there are two regulatory steps by which a drug is approved in
the market
1. Clinical trials application [ approved at member state level]
2. Marketing authorization [approved by both member state and
centralized level]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryrequirementforeuropeunion-copy-190924035947/85/Regulatory-requirement-for-europe-union-2-320.jpg)