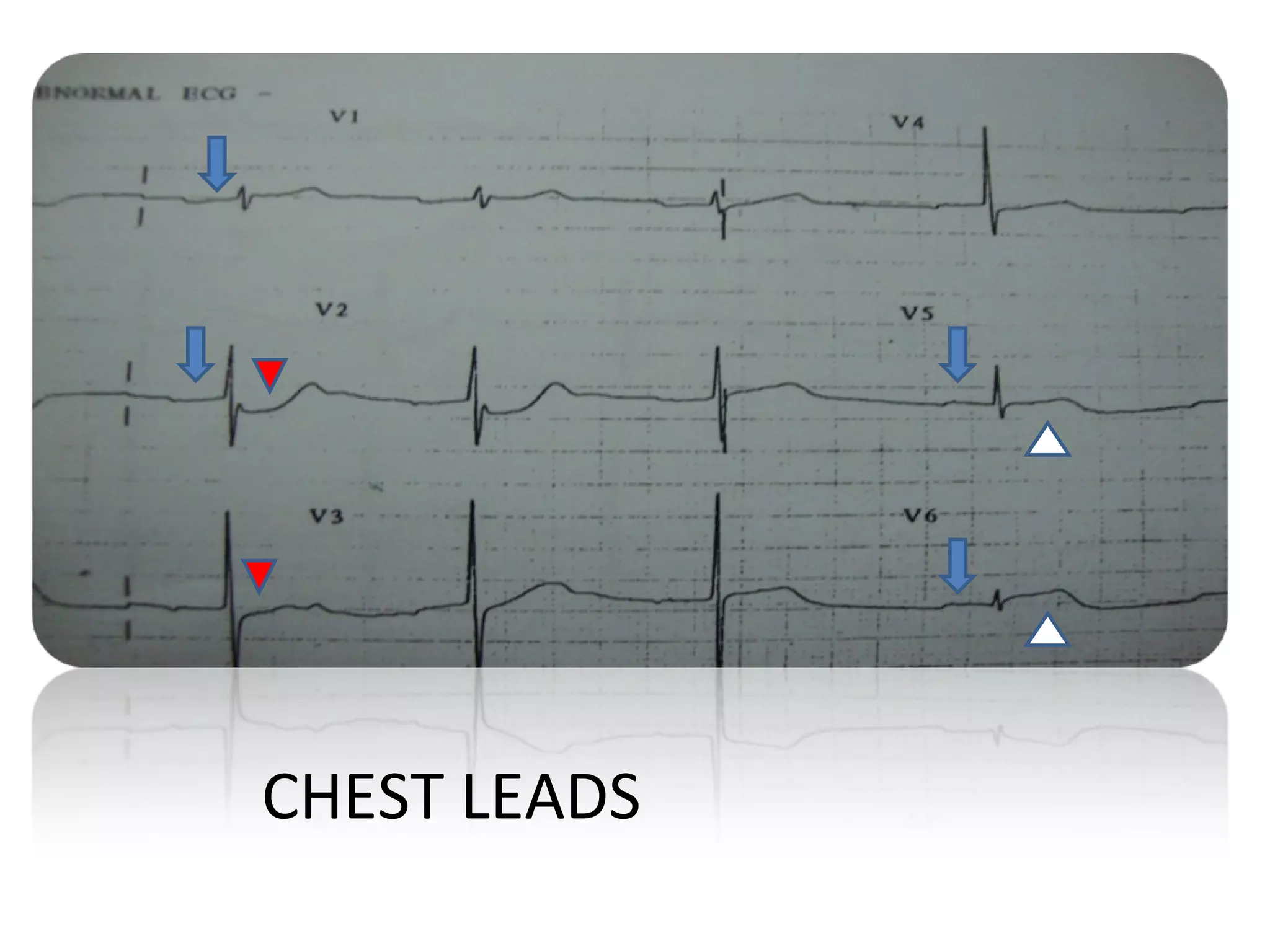
A 65-year-old man presented with chest discomfort and other symptoms. His ECG showed sinus rhythm with ST elevations and PR interval prolongation. The findings were consistent with an inferoposterior wall myocardial infarction as well as right atrial infarction, likely due to proximal right coronary artery occlusion. Atrial infarction can occur in up to 25% of STEMI cases but is often clinically unrecognized due to its subtle ECG changes such as P-Ta segment elevations. Complications of atrial infarction include arrhythmias and thromboembolism.