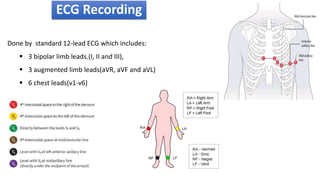
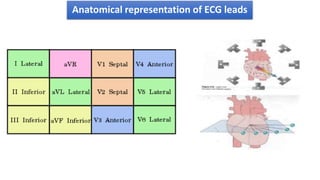
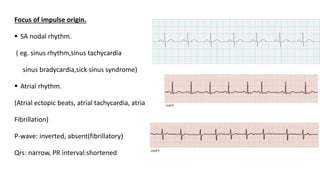
The document provides information about electrocardiograms (ECGs). It discusses the basics of ECGs including what they measure, how they are recorded, and interpretations of normal and abnormal ECG readings. Key points include that ECGs graphically represent the electrical activity of the heart and involve detecting electrical signals from electrode pairs on the body. Standard 12-lead ECGs are used to evaluate patients for conditions like arrhythmias, electrolyte imbalances, or to monitor implanted devices. The document outlines how to interpret various ECG waves, intervals, and other features.