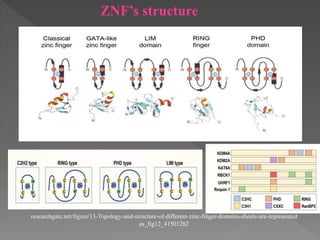
Zinc-finger proteins (ZnFs) are a versatile group of proteins involved in various cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation and disease progression, particularly in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. They interact with DNA and other cellular components due to their diverse structural motifs, with significant roles in development, tissue homeostasis, and gene expression regulation. Recent advances highlight their potential in drug discovery and therapeutic applications through engineered zinc finger technologies.