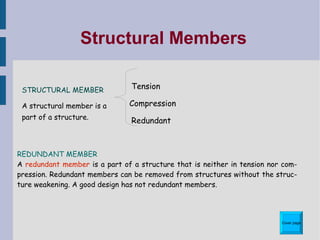
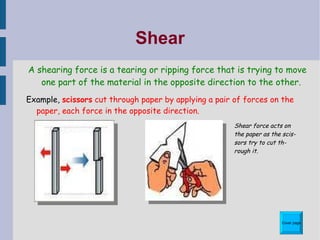
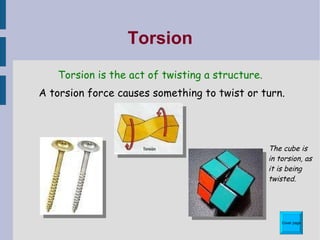
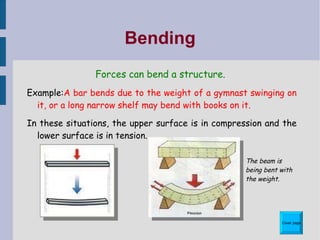
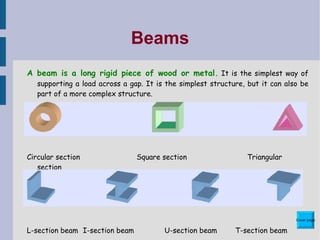
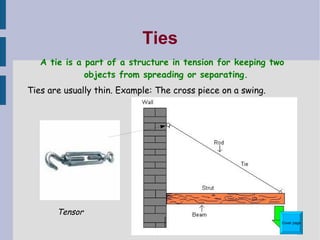
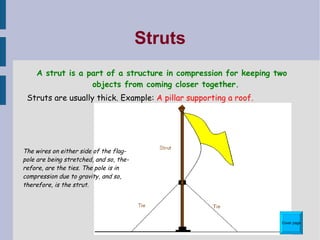
This document discusses different types of structures and structural elements. It describes frame structures which have a skeleton framework and shell structures which rely on their molded shape for strength. It defines structural members, loads, and different types of forces including tension, compression, shear, torsion, and bending. It also outlines common structural elements such as beams, bridges, cantilevers, columns, ties, struts, and triangulation and provides examples of each. Finally, it notes some ways structures can impact the environment, both positively and negatively.