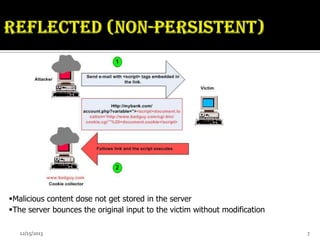
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a vulnerability that allows malicious code to be injected into web applications. There are two types of XSS attacks - reflected XSS occurs through links on other sites that pass malicious scripts, while stored XSS stores scripts in databases to be displayed for other users. XSS attacks can steal users' cookies and private information, redirect users to malicious sites, and perform actions as the victim. Developers can prevent XSS by validating all input data from users before displaying it and encoding output.